3 Lipids and transport across membranes
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
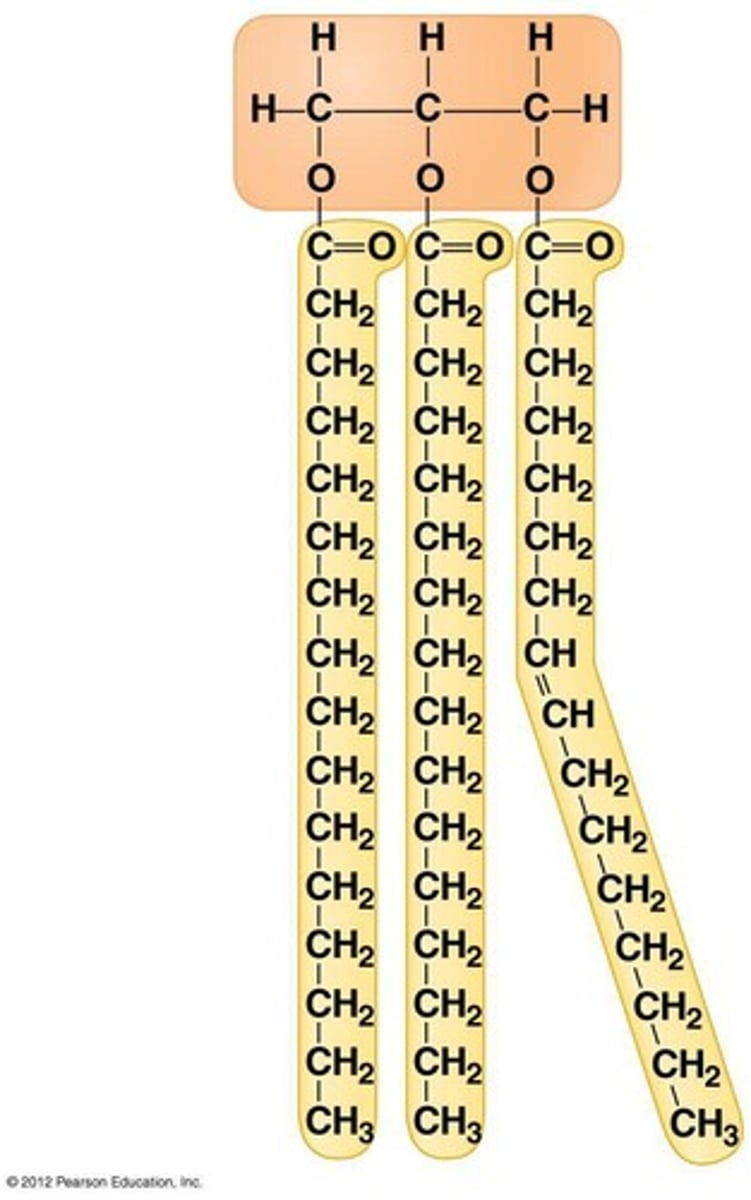
Triglyceride
· 3 fatty acids combined with 1 molecule of glycerol.
· Joined with ester bonds
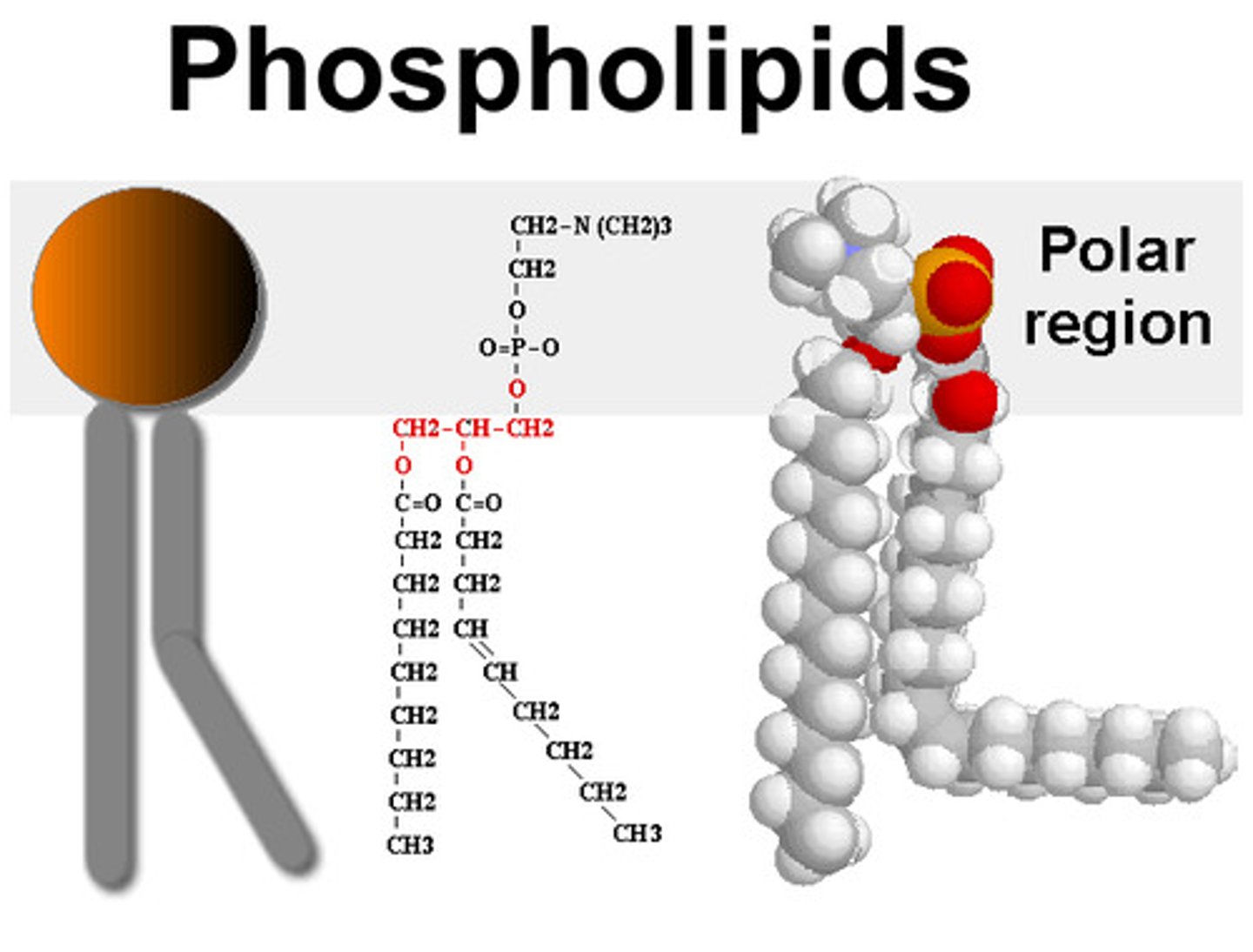
Phospholipid
Contains two fatty acids joined to a glycerol and a phosphate group instead of one fatty acid
Polar /hydrophilic (attracts water) head (glycerol and phosphate)
Non-polar /hydrophobic (repels water) tails (fatty acids ).
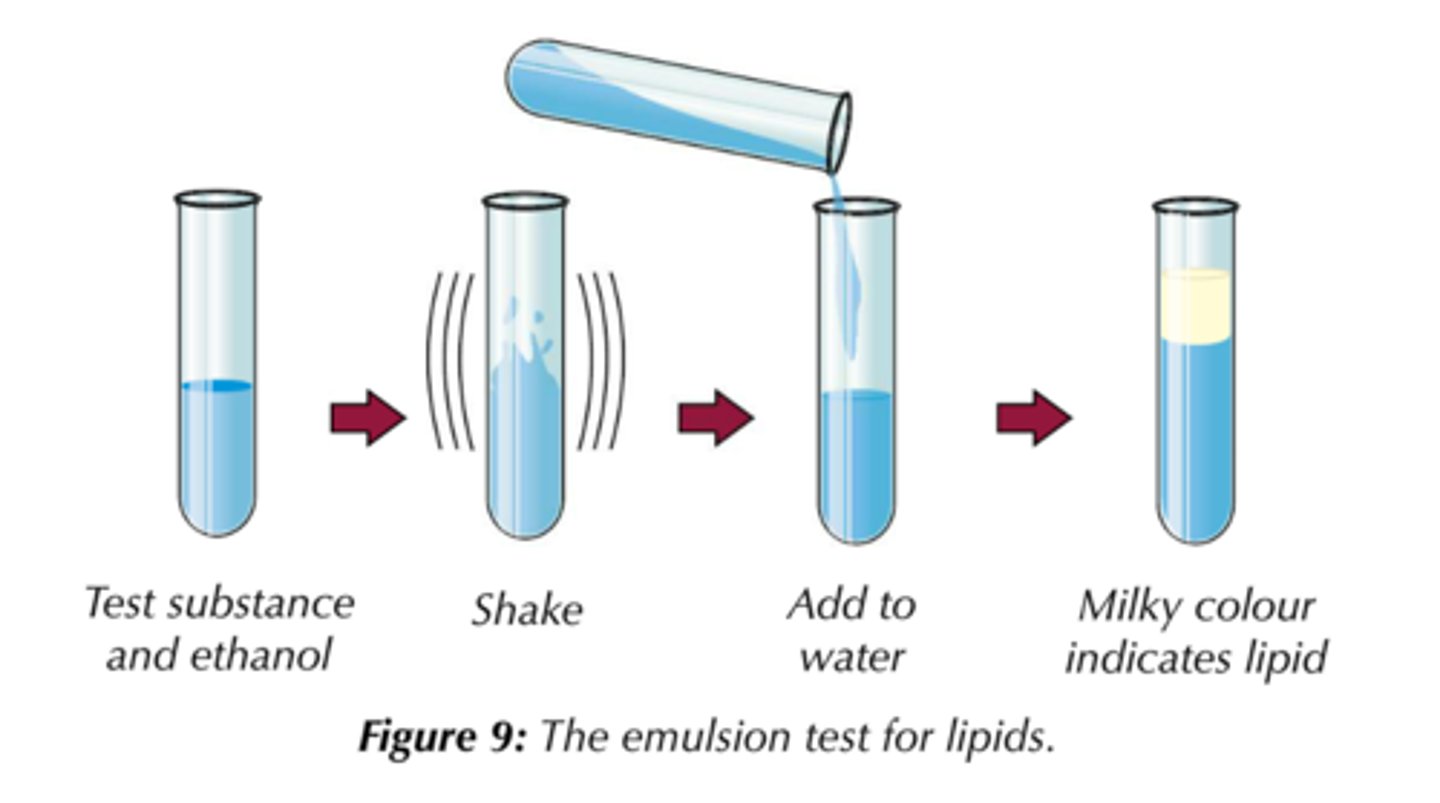
Test for Lipids
Add ethanol to the sample.
Shake thoroughly to dissolve any lipid
Then add water to the sample and shake gently.
A milky white emulsion indicates the presence of lipid (NB: not a precipitate).
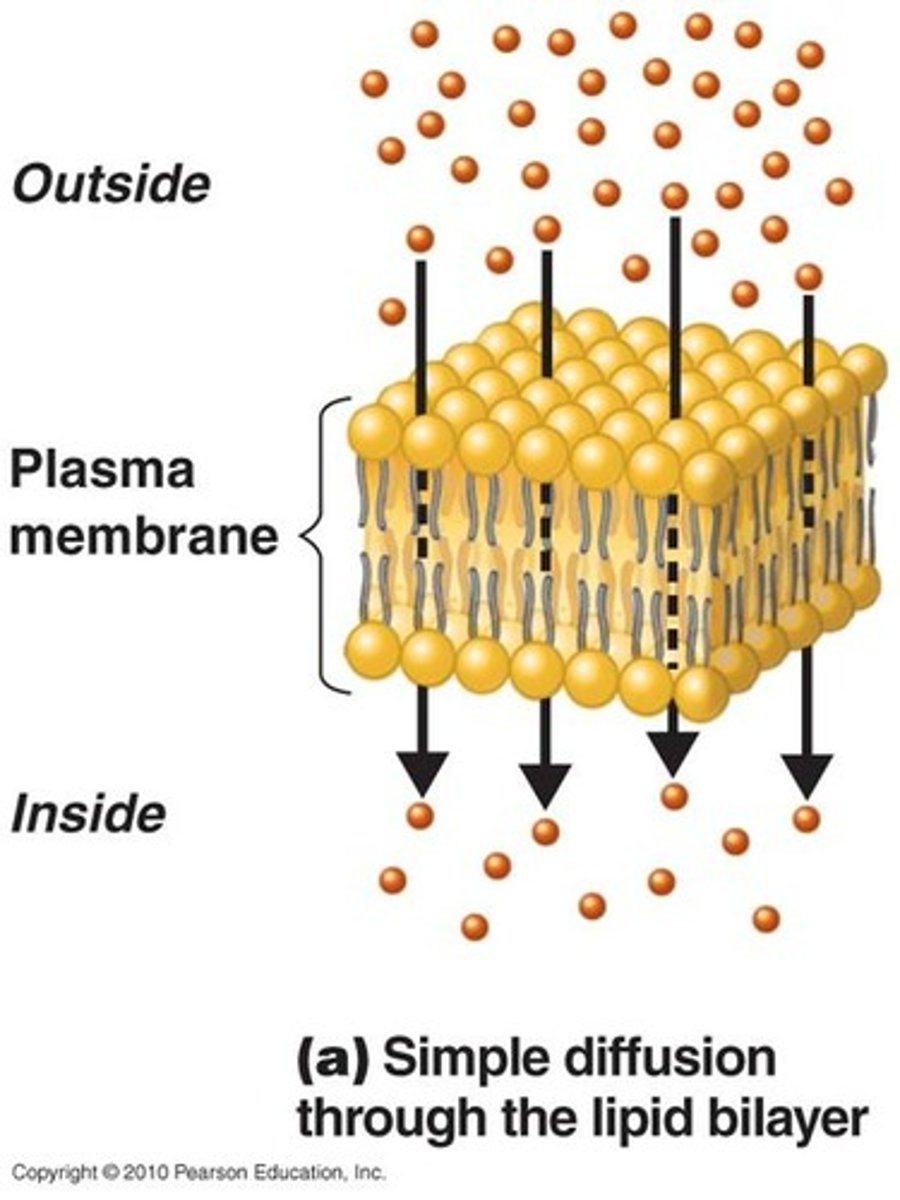
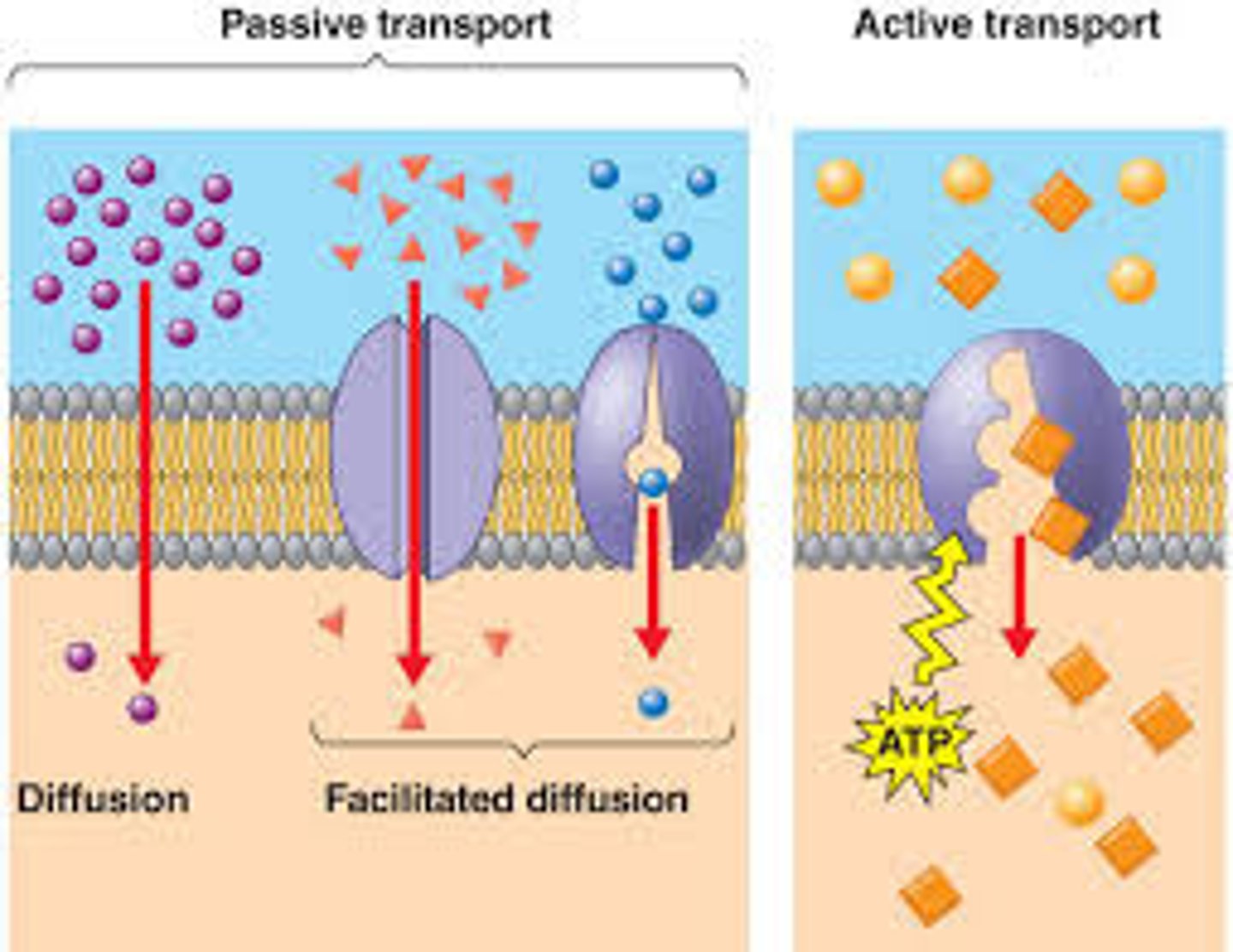
Simple diffusion
· The movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
· The difference is called a concentration gradient.
· Diffusion is movement of molecules down a concentration gradient.
• Small, non polar molecules through the bilayer
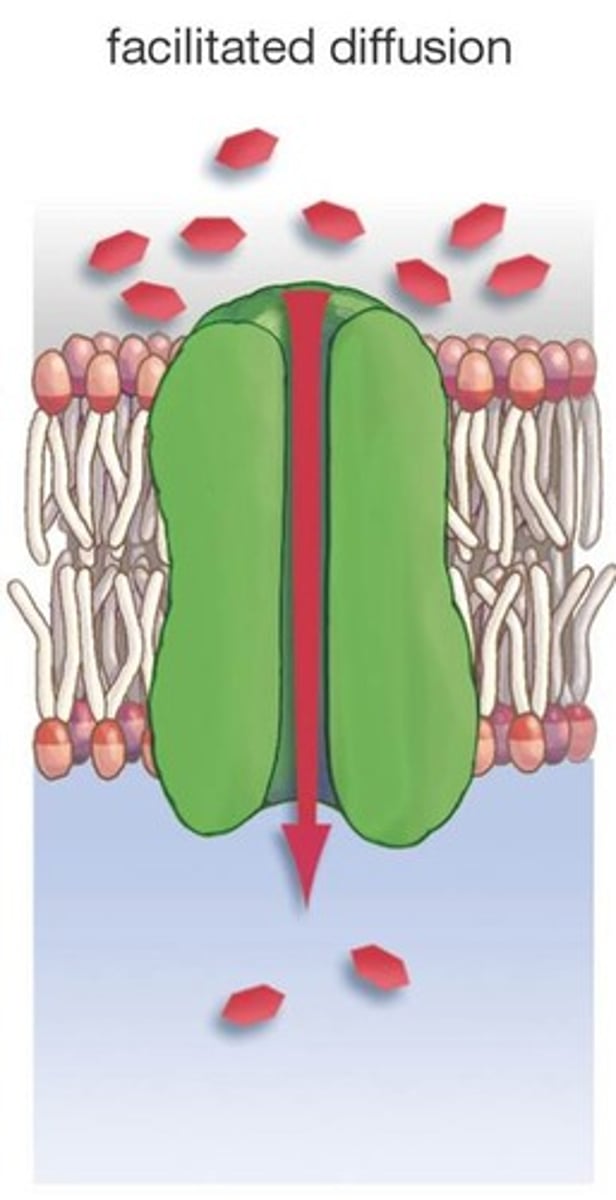
Facilitated diffusion
· The movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
· Uses a channel or carrier protein
• Large, charged, polar molecules
Osmosis
· The movement of water across a partially permeable membrane down a water potential gradient i.e. from higher (less negative) to lower (more negative) water potential
Active Transport
· The movement of substances against their concentration gradient
· Uses a carrier protein and ATP
• Large, charged, polar molecules
Fick's Law
Rate of Diffusion is proportional to surface area x difference in concentration/
thickness of exchange surface
To increase diffusion rate we need to...
· maximise the surface area
· maximise the concentration difference
· minimise the thickness of the exchange surface.
Which molecules will be able to move through the phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion and why?
Molecules that are non-polar can diffuse rapidly across the phospholipid bilayer, as they are lipid-soluble and are not repelled by the fatty acids in the hydrophobic tails.
Smaller molecules can also diffuse through more easily. Oxygen molecules are non-polar and small and so diffuse rapidly through the bilayer.
Lipid-soluble, small, non-polar e.g oxygen and carbon dioxide
Which type of molecule moves via facilitated diffusion and why?
It is more difficult for polar molecules to pass through the bilayer as the fatty acid tails are a barrier to these molecules.
Charged, polar, large, water-soluble molecules e.g. ions, glucose, amino acids
Triglycerides have many biological roles such as:
storage of energy
insulation- electrical and heat
protection
The structure and properties of triglycerides related to their function
· high ratio of energy storing carbon-hydrogen bonds to carbon atoms - so excellent source of energy
- Low mass to energy ratio - so lots of energy can be stored in a small volume.
· Large, non-polar molecules, insoluble in water so do not affect the water potential in cells.

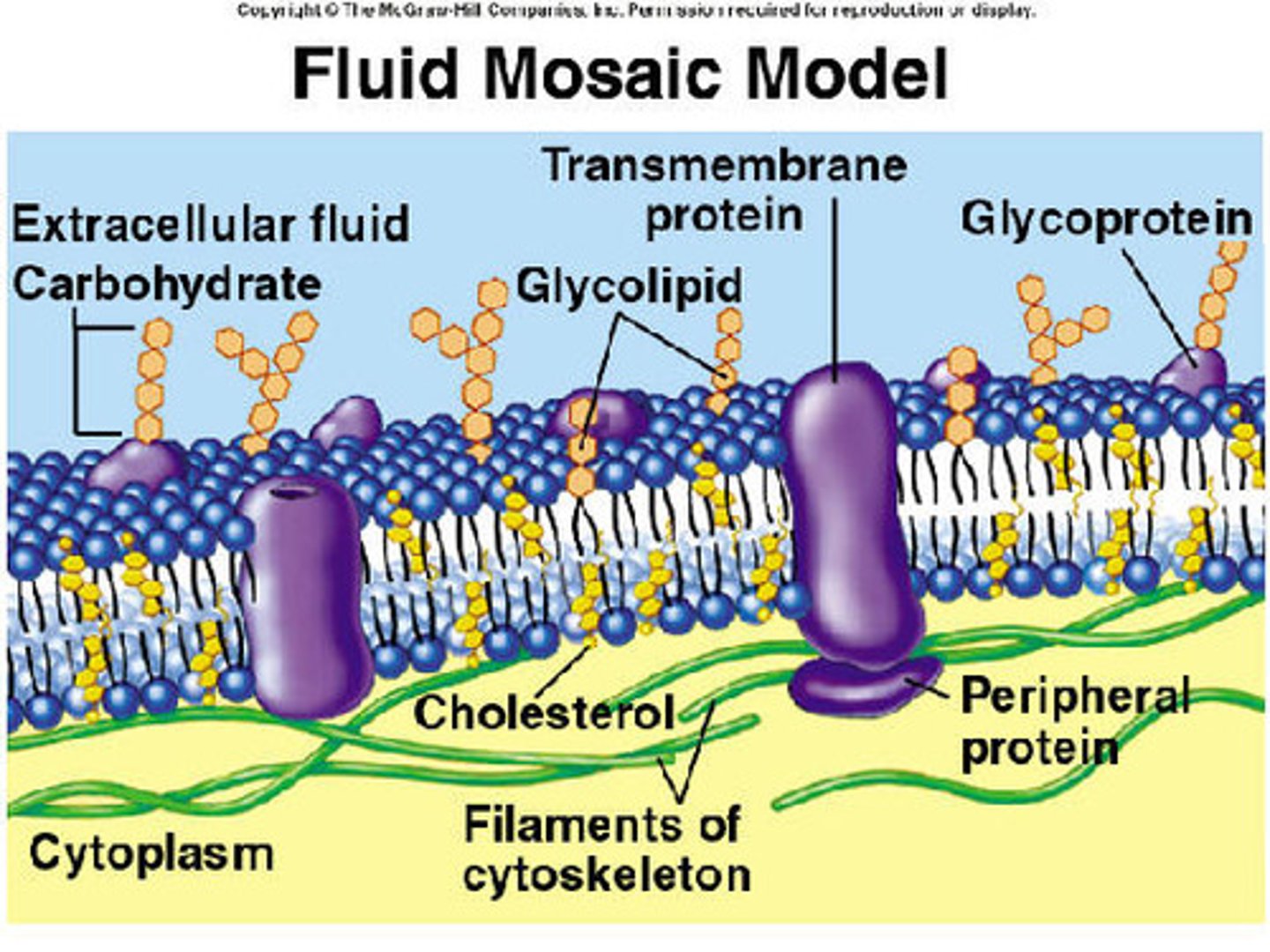
Why is the model described as fluid mosaic?
Fluid refers to the fact that all the different molecules can move around.
Mosaic because there are different types of molecule - the proteins and carbohydrates 'float around' within the phospholipid bilayer.
Why are triglycerides not polymers?
They are not made of monomers- they are made of two different types of molecule
Describe the formation of a triglyceride
A condensation reaction- producing 3 molecules of water. Ester bond formed between the hydroxyl group of the glycerol and the carboxyl group of the fatty acids
What is surrounded by a plasma membrane?
All cells and some organelles (some organelles have double e.g. chloroplast and nucleus)
What are cell membranes made from?
A phospholipid bilayer
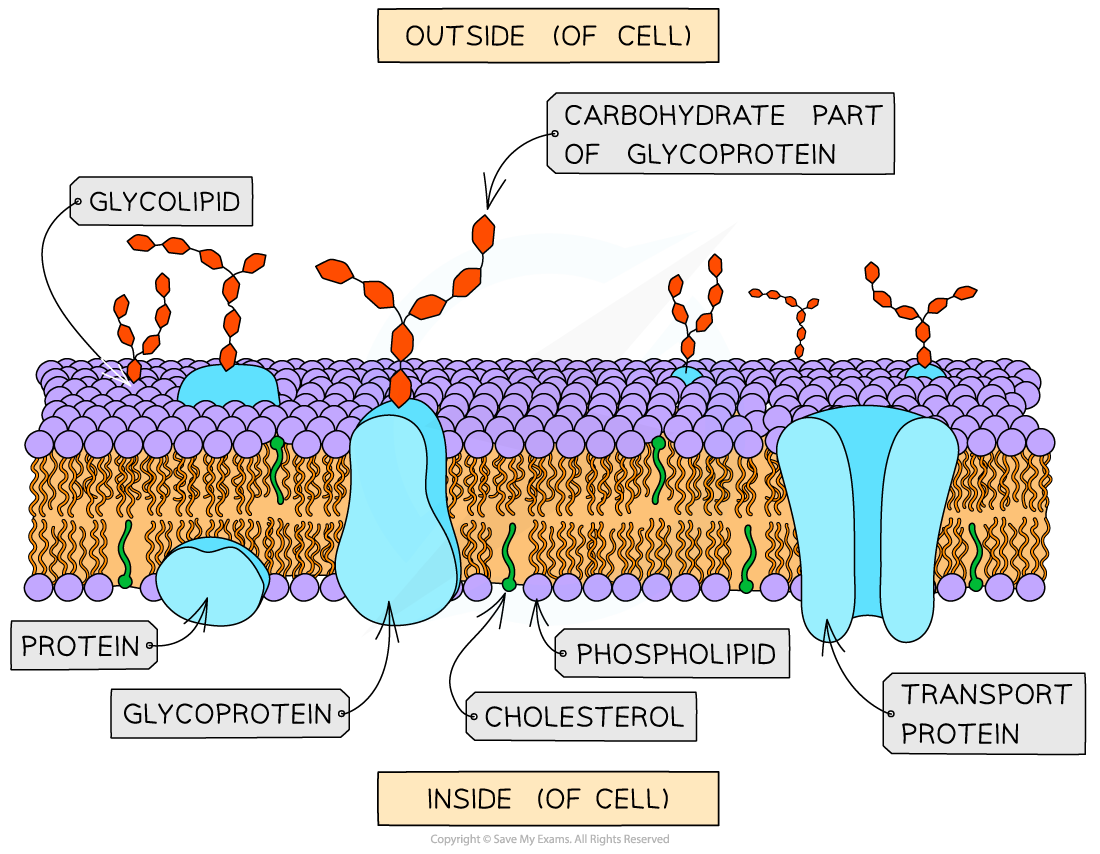
Label and describe a plasma membrane
Why does the rate of facilitated diffusion become limited?
Limited by the number of carriers/channels above a certain concentration as all proteins are occupied/saturated
What limits the rate of active transport?
Number of carrier proteins
Rate of respiration
Lack of oxygen, glucose, low temp
example of active transport is roots taking up ions

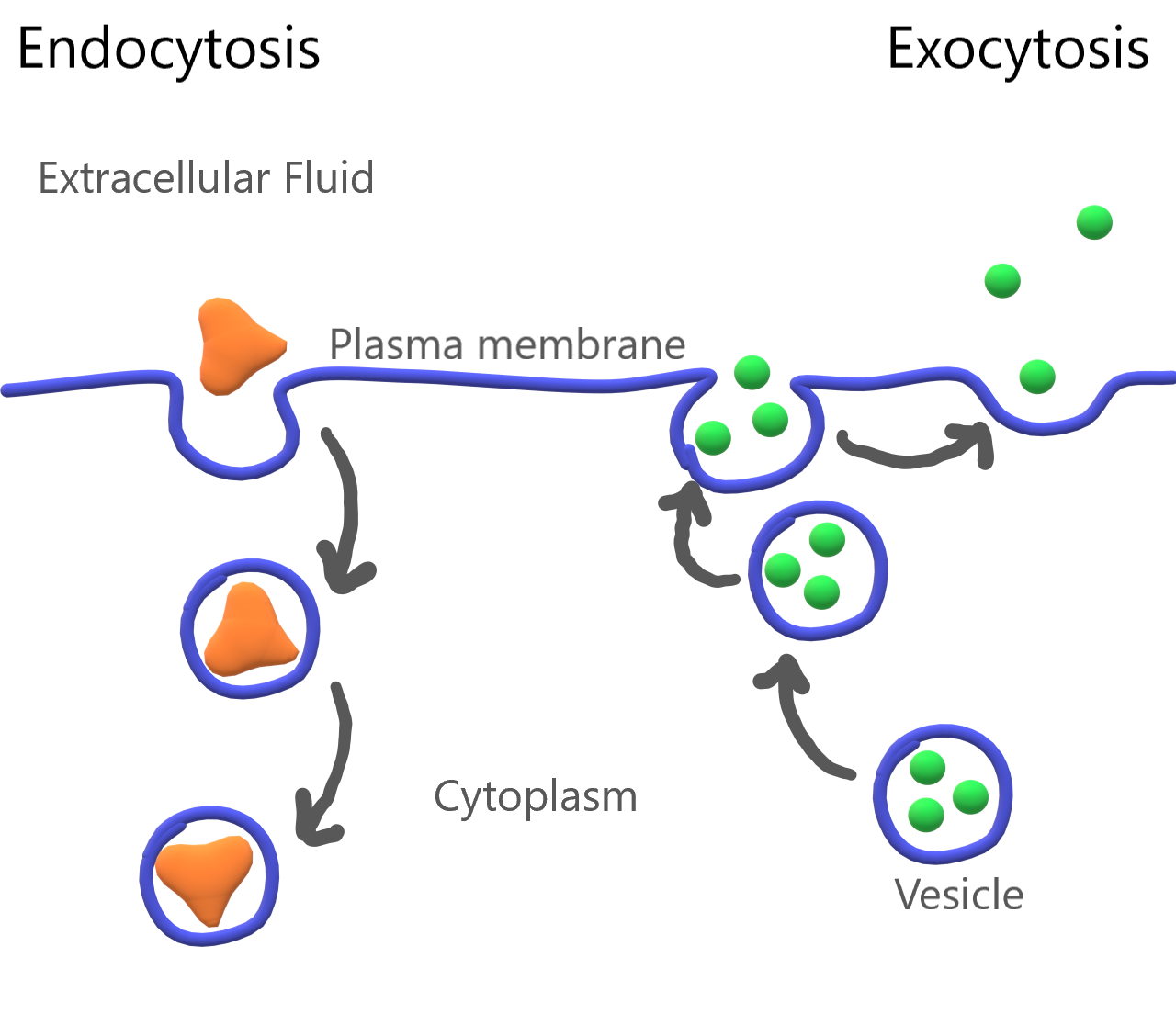
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
The process of importing material in vesicles
The process of exporting material in vesicles
Both require ATP
What is the process of endocytosis/exocytosis?
Cells need to transport large amounts of material
Cells make containers from the plasma membrane called vesicles to transport solids or liquids across the plasmas membrane, in or out a cell
Requires ATP
Functions of plasma membranes
To control the transport of substances into and out of the cell or organelles
To act as a receptor site
To compartmentalise, separate off the cell from the environment and forming organelles
Fatty acids
Saturated- contain no double bonds between carbon atoms
Unsaturated- one or more double bonds between carbon atoms
Function of glycoproteins and glycolipids
Glycoproteins- extrinsic proteins with carbohydrate chains attached
Glycolipids- phospholipids with carbohydrate chains attached
Act as recognition sites and receptors and antigens
Function of cholesterol
A lipid that sits with phospholipids in the core of the membrane and helps to make it less fluid/ more rigid
Examples of intrinsic proteins
Proteins which span the whole length of the phospholipid bilayer e.g. carrier (active transport) and channel
Hypertonic definition
The solute concentration in the solution is higher than in the cell- so water moves by osmosis into the solution
Isotonic definition
The solute concentration in the solution is the same as the solute concentration of the cell- therefore there is no net movement of water
Hypotonic definition
The solute concentration in the solution is lower than in the cell- so water moves by osmosis into the cell
How does surface area affect the rate of movement across a membrane
A larger surface area increases the rate of movement across a membrane, because there is more space for molecules to pass through simultaneously and more channel and carrier proteins available at once
How does the number of carrier or channel proteins affect the rate of movement across a membrane
increases the rate of facilitated diffusion and active transport, as more proteins means more active sites for molecules to bind and cross