Allocation/Translocation L7 Part 2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Define Companion Cell
Present in sieve tube members, provides metabolic support. Angiosperms
Define Transfer Cell
Has folded walls for sucrose loading. Apoplastic movement
Define Intermediary Cells
Smooth walls with many plasmodesmata to collect solutes. Symplastic movement
What do P-proteins and callose do?
Form callus plugs in injured phloem
Define Reducing Sugars
Not translocated within phloem and have a free aldehyde/ketone group
Glucose, mannose, fructose
Non-reducing Sugars
Can be translocated
Sucrose
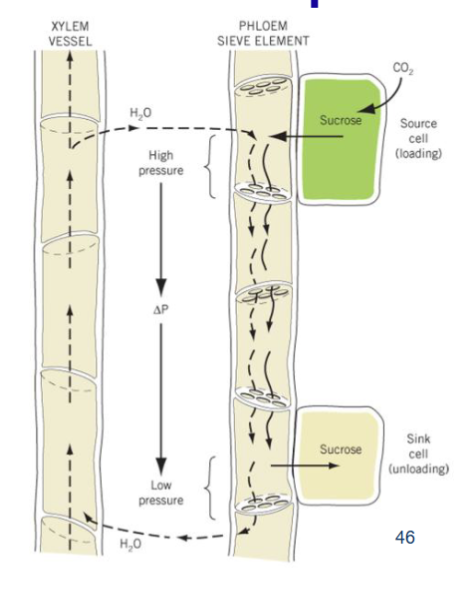
Describe the Pressure Flow Model
Phloem loading at source cell. Companion cell loads sugar into sieve tube
Water flows from xylem due to decreased water pressure in the seive tube
Pressure pushes fluid through sieve tubes to areas with lower water pressure potential, until arriving where the phloem occurs near the sink
Water flows back into the xylem due to change in seive tube pressure
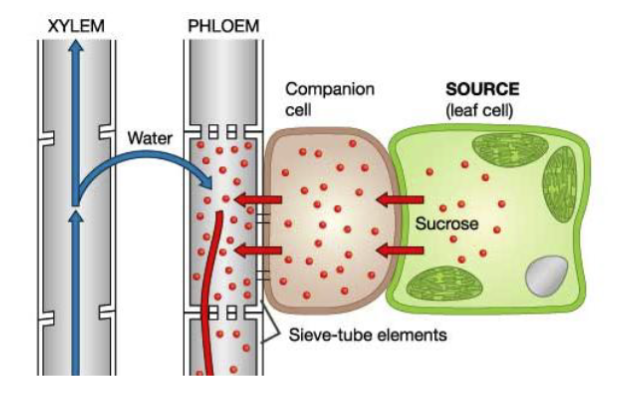
Define Phloem Loading
Occurs at the source. Photosynthates are transported into sieve tube members
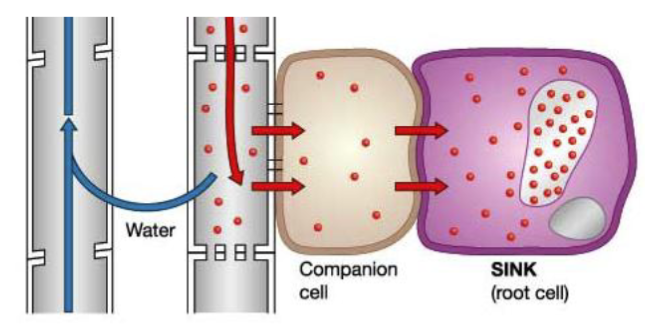
Define Phloem Unloading
Occurs at the sink. Photosynthates are transported out of sieve tube members
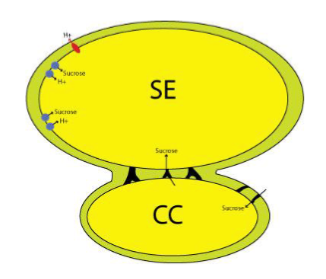
Define Sieve Element-Companion Cell Complex
Holds source cells
What are the two loading and unloading pathways?
Symplastic: passive or assisted
Apoplastic: Requires metabolic energy (active transport)
Sucrose H+ Symporter
Transports sucrose into the se-cc complex
Requires active transport (apoplastic)
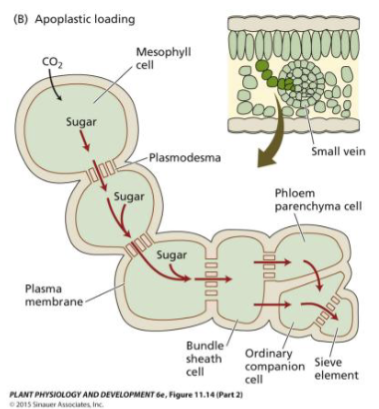
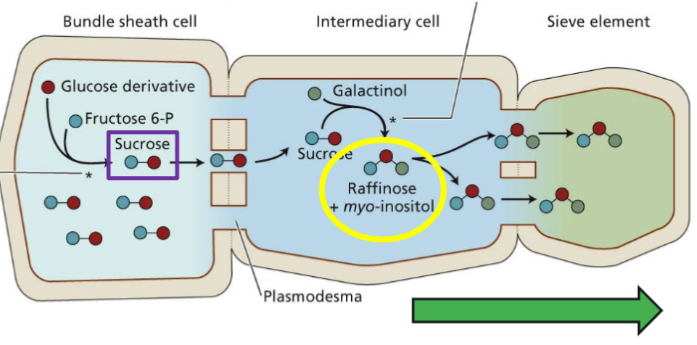
What is the Polymer-Trapping Model?
Sucrose moved into the se-cc is converted in oligosaccharides
Prevents back-diffusion of sucrose into source cells and maintains the se-cc concentration gradient
Bundle sheath cell → Intermediary cell → Sieve element
What are three uses for photosynthates?
Leaf metabolism and biomass maintenance
Short-term storage
Export to other plant parts
Define Partitioning
Distribution of photosynthates between sinks; determined by competition between sink tissues
Define Sink Strength
Decides which sink obtains more of the photosynthate pool
Define Sink Size
Dry weight biomass of sink tissue
Define Sink Activity
Rate of uptake per unit biomass per unit time
What is sink strength influenced by?
Sink proximity to source
Environmental factors (drought)
Cell turgor
Phytohormones