Lecture Notes on Waves
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to waves, wavelengths, frequency, and the Doppler effect.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Which waves carries the most
energy?
Gamma rays
Radio Waves
Waves with the least energy.
Waves used in food preparation
Microwaves
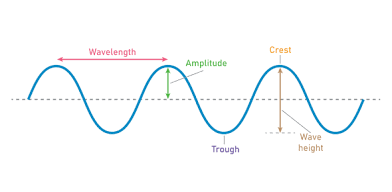
Crest
Highest point of a wave. ( Transverse wave)
Trough
Lowest point of a wave. (Transverse wave)
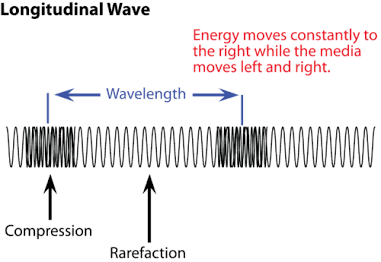
Compression
Regions of increased density in a longitudinal wave.
Rarefaction
Regions of decreased density in a longitudinal wave.
Formula to calculate wave speed
V = fλ
Effect of decreasing wavelength on speed
Speed decreases
Effect of increasing frequency on speed
Speed Increases
Effect of increasing wavelength on speed
Speed increases
V
speed, Measured in Meters per seconds (m/s)
Unit for Frequency (f)
Hertz (Hz)
Unit for Wavelength (λ)
Meters (m)
Doppler Effect
An increase or decrease in the frequency of sound, light, or other waves as the source and observer move towards/or away from each other.
Transverse Waves
Waves that travel perpendicular to the direction of energy transport.
Relationship between frequency and energy in a wave
Directly related
A wave with a low frequency had a
Low energy
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
List two items that can convert chemical energy into mechanical energy.
car engine and human body
List two items that can convert electrical energy into heat energy.
Electric heater and a toaster
Displacement
Change in an oblect's position specifically the straght -line distance/ direction Between it's inital and anal positions
Provide the formula for calculating the heat of an object, list the units that accompany each part.
Q= MC🔺T
Q=heat /unit = JOUles(5)
C=specitic heat Capicity
Unit=J/gx•c
M: Mass
unit=GraMs |Kg
🔺T=Change in TeMPerature
Unit=•C or oK
Which is the highest PE or KE when the car on a roller coaster is at the top of a hill?
Potential energy
*Kinetic onergy is lowest point when top because it slows down
PE= Potential Energy Formula
PE= M G H
KE=Kinetic Energy
KE= (1/2) MV²
Define a conductor
Material or substances which allow
electricity to flow through them
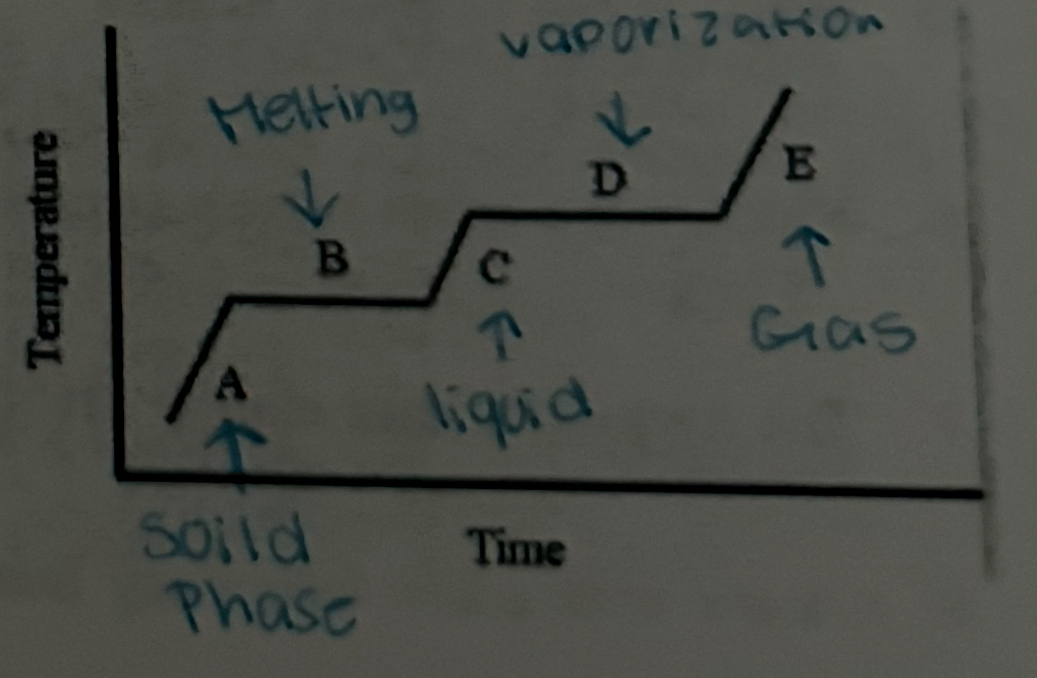
List the Phase changes matter can experience.
Freezing: Liquid to solid.
Melting: Solid to liquid.
Evaporation (also called vaporization): Liquid to gas.
Condensation: Gas to liquid.
Sublimation: Solid directly to gas.
Deposition: Gas directly to solid.
Ionization: Gas to plasma.
Recombination: Plasma to gas.
Evaluate the diagram, then for each letter identify what is occurring at those points.
A. Temperature increases Solid phase B. teMperature constant soild to liquid (Melting) C. temperture increase liqua phase D. temperature constant Liquid to gas E. temperature increase gas Phase |
Distance
Is a Measure of the space between two points object, or location, quantified linearly along a straight line or specific path
Define velocity
rate at which an object changes its position
Define speed
rate at which an object covers distance
Provide the formula to calculate speed

Provide the formula to calculate velocity

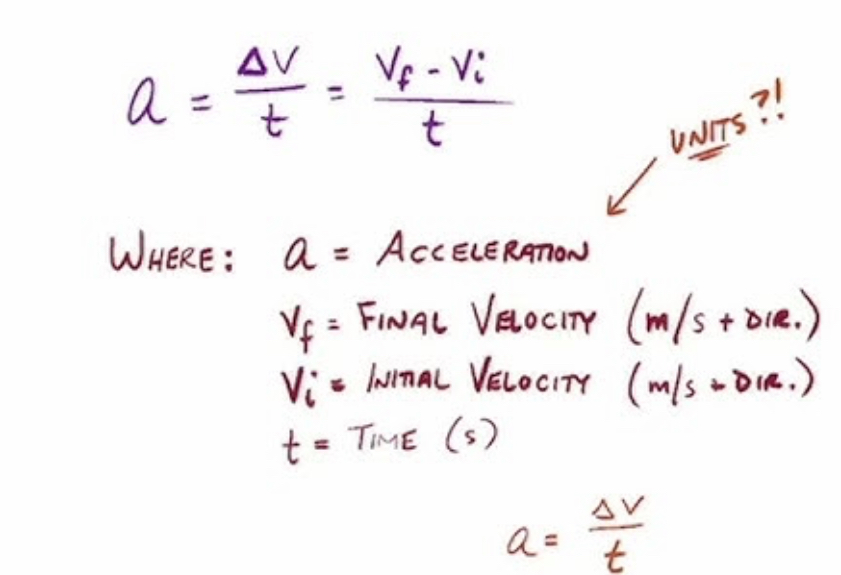
Provide the formula for calculating acceleration:
What is force?
is a push or pull that can cause an object to accelerate
State the 3 newton’s law
First law law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object multiplied by its acceleration. Mathematically, this is represented as F = ma
Newton's third law of motion
Law of Action and Reaction", states that when two objects interact, they apply equal and opposite forces on each other.
What is the speed of gravity?
299,792,458 metors per second (roughly 300,000 Kilometers per second or 180,000 miles per second)