The Languague of medecine: Respirtory system/ exercises A-L
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
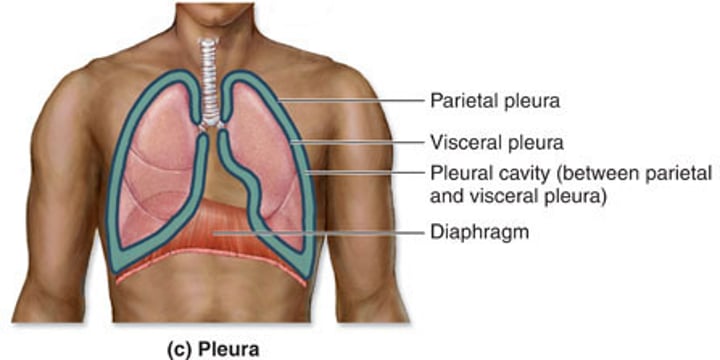
parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura laying closer to the ribs

hilum
midline region of the lungs where bronchi, blood vessels, and nerves enter and exit the lungs

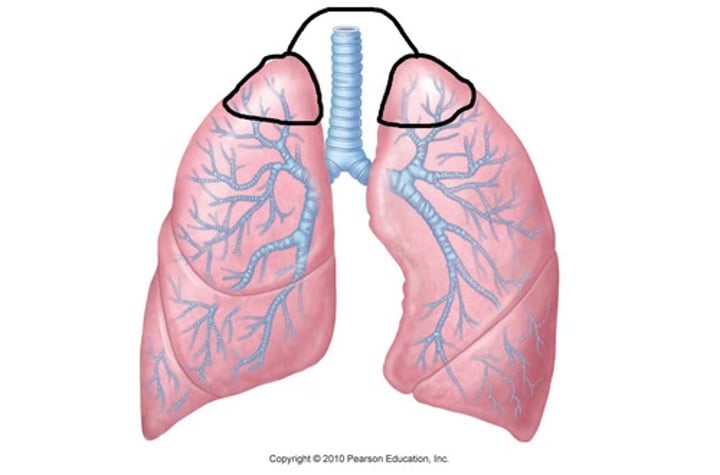
uppermost
the apical part of the lung is the...
oxygen
the gas that passes into the bloodstream at the lungs is...
inhalation/inspiration
Breathing in air is called...
lobes
Divisions of the lungs are known as...
carbon dioxide
the gas produced by cells and exhaled through the lungs is...
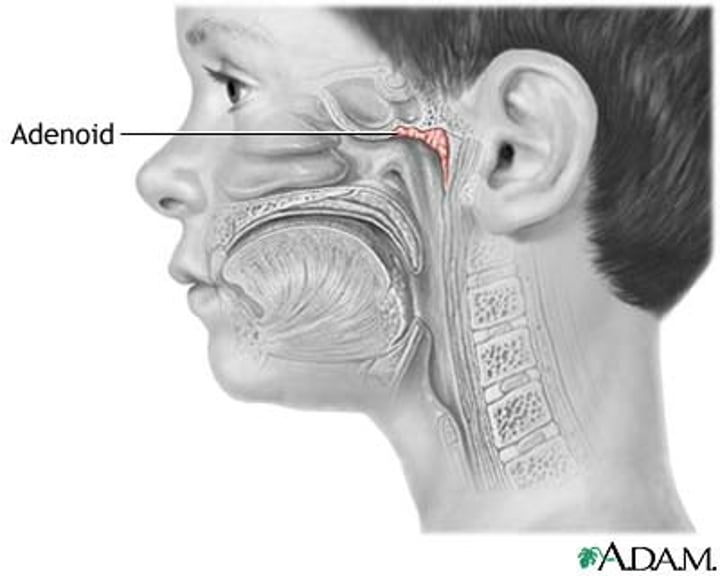
adenoids
collections of lymph tissue in the nasopharynx
trachea
windpipe
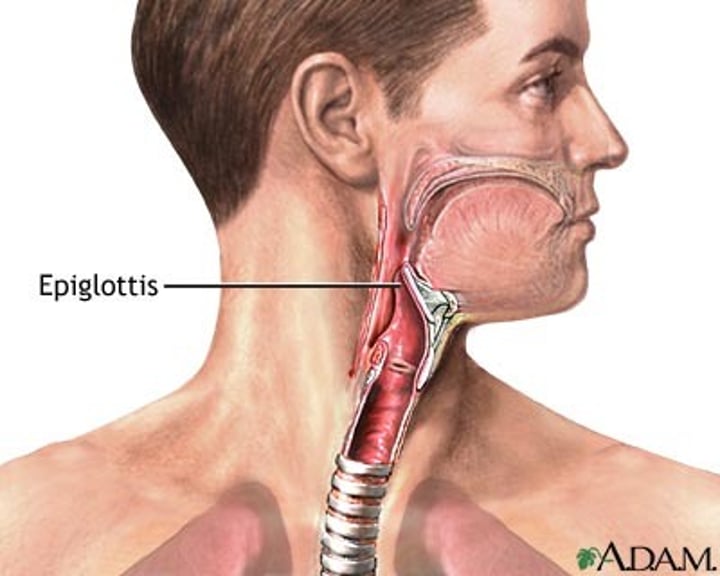
Epiglottis
lid-like piece of cartilage that covers the voice box
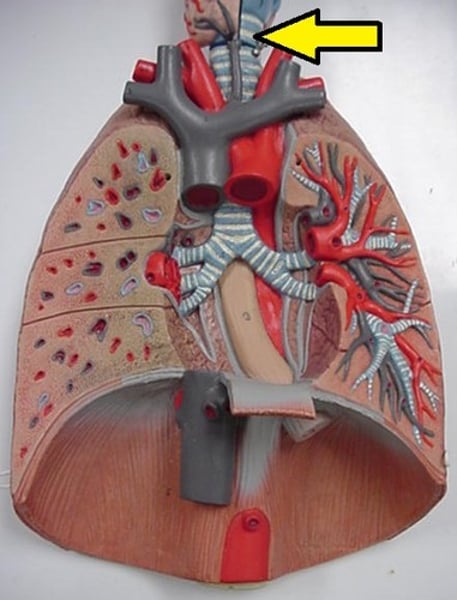
bronchi
branches of the windpipe that lead into the lungs
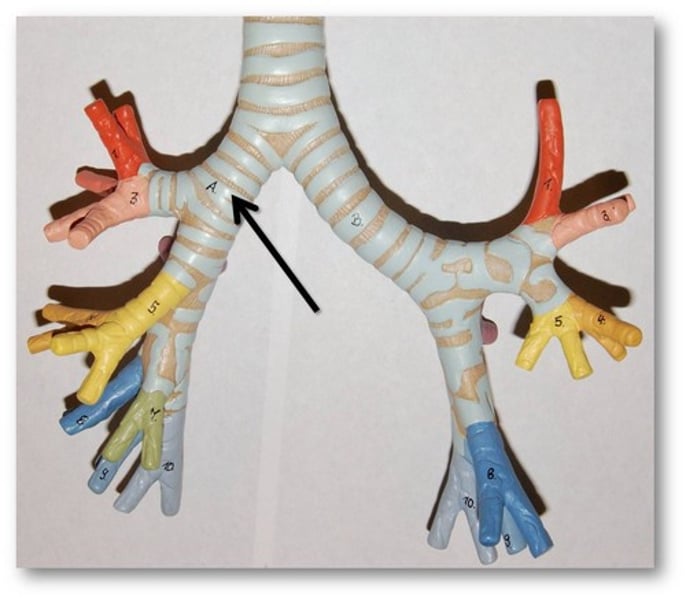
Mediastinum
region between the lungs in the chest cavity
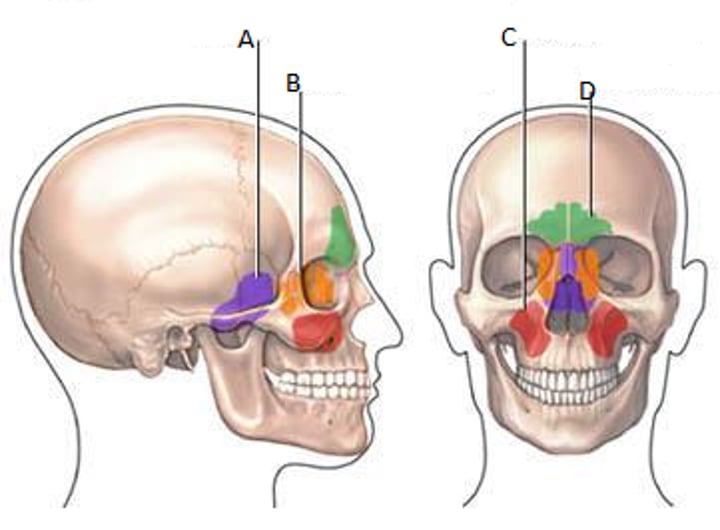
paranasal sinuses
Air-containing cavities in the bones around the nose
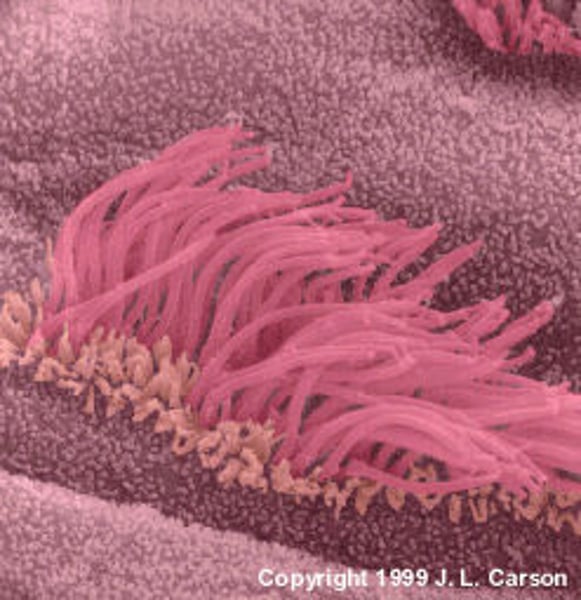
cilia
thin hairs attached to the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract
visceral pleura
inner fold of pleura closer to lung tissue
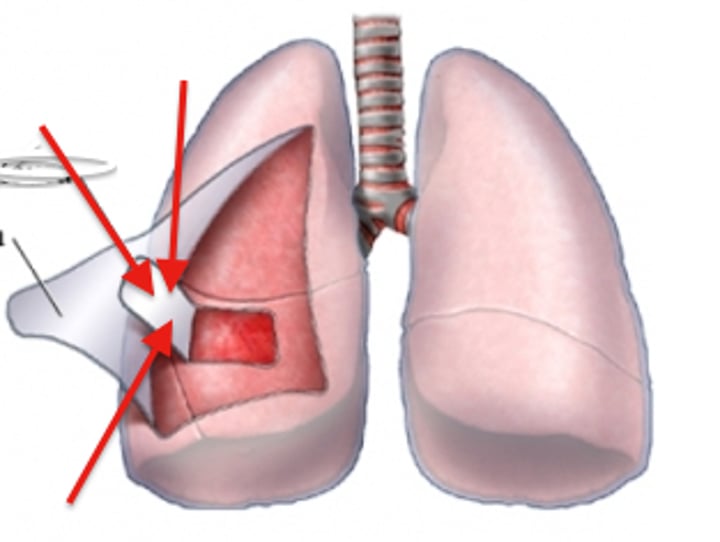
pharynx
throat
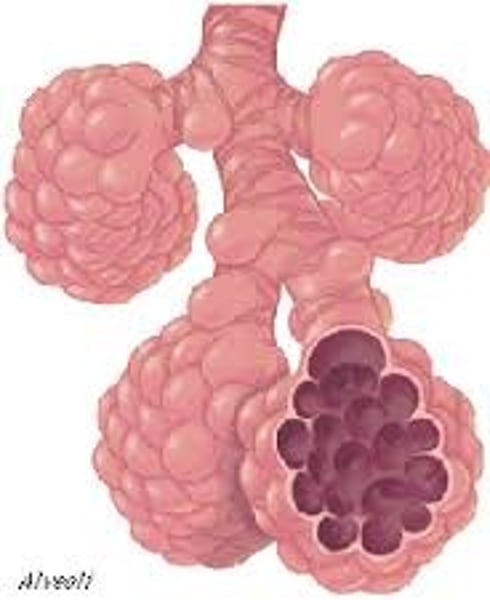
alveoli
air sacs of the lung
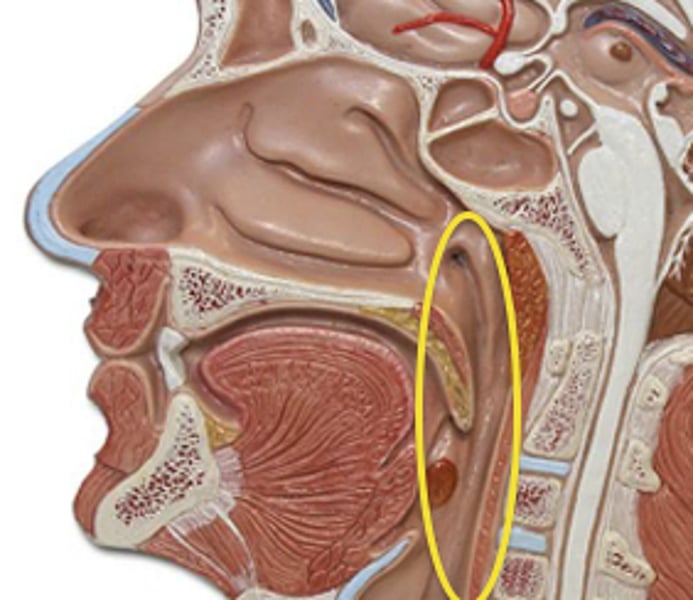
larynx
voice box
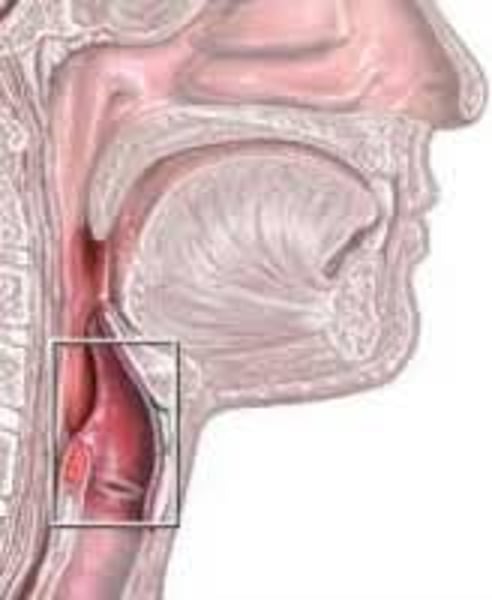
bronchioles
smallest branches of bronchi
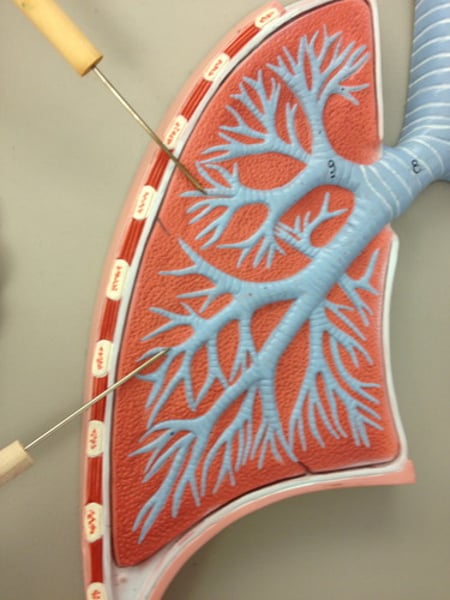
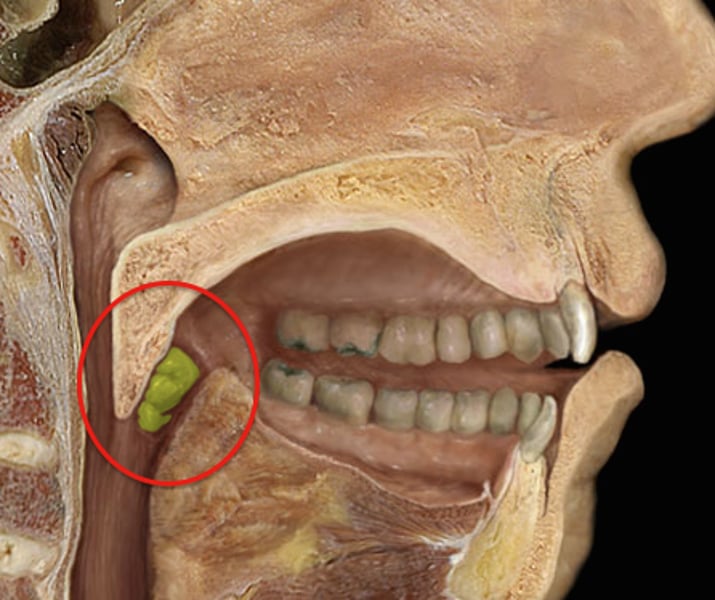
palatine tonsils
collections of lymph tissue in the oropharynx
pleural cavity
the space between the visceral and the parietal pleura is the...
exhalation/expiration
breathing out air is called...
parenchyma
the essential tissues of the lung that perform its main function are pulmonary...
external
The exchange of gases in the lung is _________________ respiration
internal
the exchange of gases at the tissue cells is _______________ respiration
bronchiectasis
chronic dilation of a bronchus
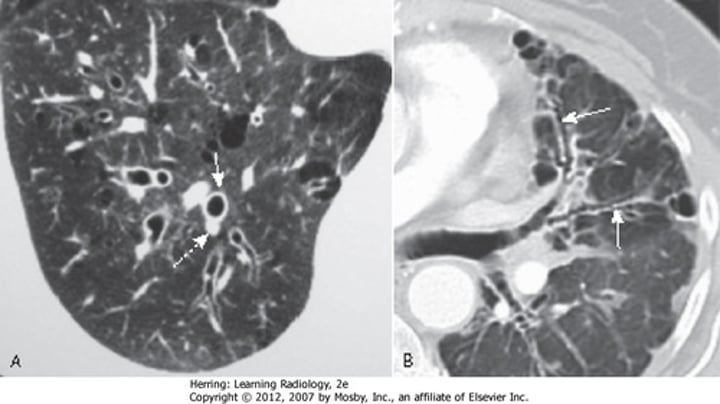
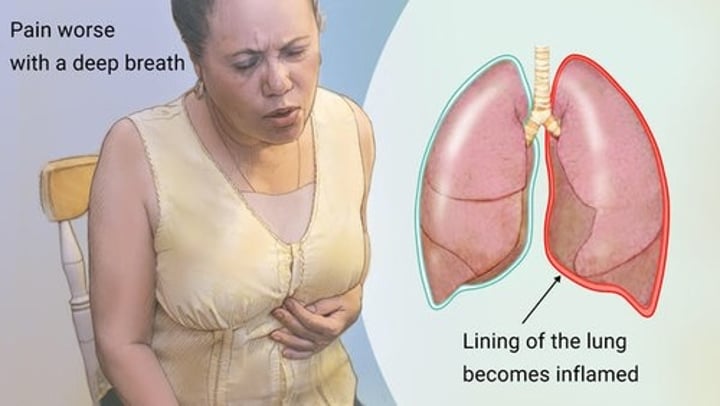
pleuritis
inflammation of pleura
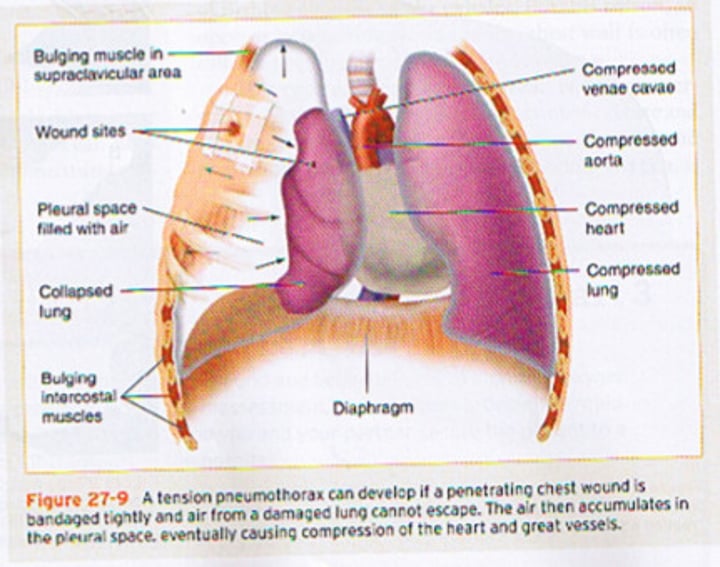
pneumothorax
air in the chest (pleural cavity)
anosmia
lack of sense of smell
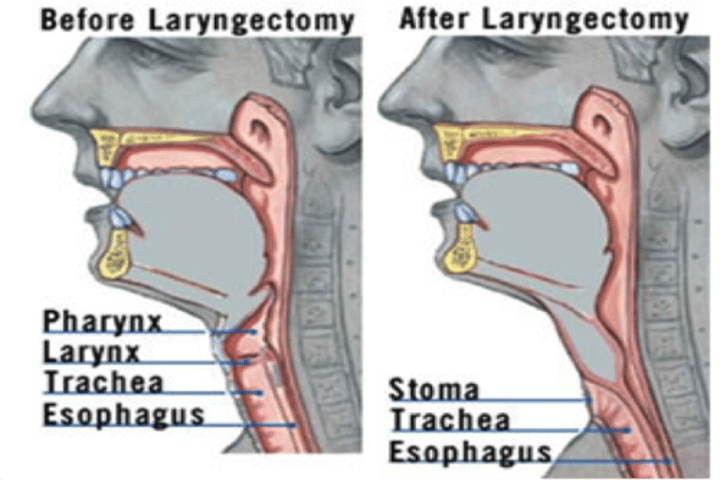
laryngectomy
removal of the voice box
nasopharyngitis
inflammation of the nose and throat
phrenic
pertaining to the diaphragm
alveolar
pertaining to an air sac
glottis
opening to the larynx
tracheal stenosis
narrowing of the windpipe
-capnia
excessive carbon dioxide in the blood: hyper_______
Ortho-
breathing is easiest or possible only in an upright position: _____-pnea
dys-
difficult breathing: _____-pnea
cyan-
condition of blueness of skin: ____-osis
-ptysis
spitting up blood: hemo-______
-oxia
deficiency of oxygen: hyp-________
-thorax/-pyema
condition of pus in the pleural cavity: pyo-_________ or em-___________
-phonia
hoarseness; voice impairment: dys-_________
-thorax
blood in the pleural cavity: hemo-__________
-staxis
nosebleed: epi-___________
rales (crackles)
fine crackling sounds heard during inhalation when there is fluid in the alveoli
auscultation
listening to sounds within the body
sputum
material expelled from the respiratory tract by deep coughing and spitting
percussion
tapping on the surface to determine the underlying structure
Rhonchi (description)
loud rumbling sounds on auscultation of chest; bronchi obstructed by sputum
pleural rub
scratching sound produced by pleural surfaces rubbing against each other
purulent
pus-filled
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
sudden attack of different breathing associated with lying down at night
hydrothorax
fluid in the pleural cavity
pulmonary infarction
area of dead tissue in the lung
stridor
strained, high-pitched inspirational sound
wheeze
continuous high-pitched whistling sound produced during breathing when air is forced through a narrow space; heard in asthma
Diptheria
acute infectious disease of the throat caused by Corynebacterium
croup
acute respiratory syndrome in children and infants that is marked by obstruction of the larynx and stridor
emphysema
hyperinflation of air sacs with destruction of alveolar walls
chronic bronchitis
inflammation of tubes that lead from the trachea, over a long period of time
asthma
chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by airway obstruction
atelectasis
lung or a portion of a lung is collapsed
lung cancer
malignant neoplasm originating in a lung or bronchus
pertussis
whooping cough
infiltrate
a collection of fluid or other material within the lung as seen on chest film, CT scan, or other radiologic study
cystic fibrosis
inherited disease of exocrine glands; mucous secretions lead to airway obstruction
asbestosis
type of pneumoconiosis; dust particles are inhaled
sarcoidosis
inflammatory disease in which small nodules form in lungs and lymph nodes.
FEV1 (Forced Expiratory volume in first second)
Sarah had a pulmonary function test in which she inhaled as much air as she could and the air that she expelled in the first second was measured. The result of this PFT is a/an...
rhonchi (case scenario)
Dr. Smith heard loud __________ when he auscultated Kate's chest. Her bronchial tubes were obstructed with thick mucous secretions .
DLco (Diffusion Capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide)
Karl was asked to breath in a small amount of carbon monoxide and then blood samples were taken to detect the gas in his bloodstream. This PFT assesses how well gases can diffuse across the alveolar membrane, and the result of the test is called....
fibrosis
formation of scar tissue in the connective tissue of the lungs is pulmonary...
exudate
a purulent ___________ consist of white blood cells, microorganisms (dead and alive) and other debris
restrictive lung disease
myasthenia gravis and muscular dystrophy are examples of neuromuscular conditions that produce....
obstuctive lung disease
chronic bronchitis and asthma are examples of........
OSA; obstructive sleep apnea
patients with a small pharyngeal airway that closes during sleep may experience....
CPAP
with nasal __________ , positive pressure (air coming from a compressor ) opens the oropharynx, preventing obstructive sleep apnea
palliative
doctors realized that they could not cure Jean's adenocarcinoma of the lung. They used _______________ measures to relieve her uncomfortable symptoms
PaO2 / PaCO2
During an apneic period, a patient experiences severe hypoxemia, (decreased __________________) and hypercapnia (increased ________________ )
PFT
pulmonary function test
pulmonary abscess
collection of pus in the lungs
pulmonary edema
swelling, fluid collection in the air sacs and bronchioles
pneumoconiosis
abnormal condition of dust in the lungs
pneumonia
acute inflammation and infection of alveoli; they become filled with fluid and blood cells
pulmonary embolism
floating clot or other material blocking the blood vessels of the lung
tuberculosis
infections disease caused by rod-shaped bacilli
pleural effusion
collection of fluid in the pleural cavity
pleurisy
inflammation of pleura
anthracosis
abnormal condition of coal dust (black lung)
mesothelioma
malignant tumor arising in the pleura
adenoid hypertrophy
excessive growth of cells in the adenoids
pleurodynia
pain of the the pleura
expectoration
coughing up of material from the chest
tachypnea
rapid breathing; hyperventilation
endotracheal intubation
placement of a that mouth into the trachea to establish an airway
V/Q scan
injection or inhalation of radioactive material and recording images of its distribution in the lungs
tuberculin tests
tine and Mantoux tests
thoracentesis
puncture of the chest wall to obtain fluid from the pleural cavity
Pulmonary function test
tests that measure the ventilation mechanics of the lung