French Revolution
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

20 Terms
Third Estate (France)
By far the largest social group in France. Making up nearly 97% of the population. Members of this estate had few rights, and little political power.
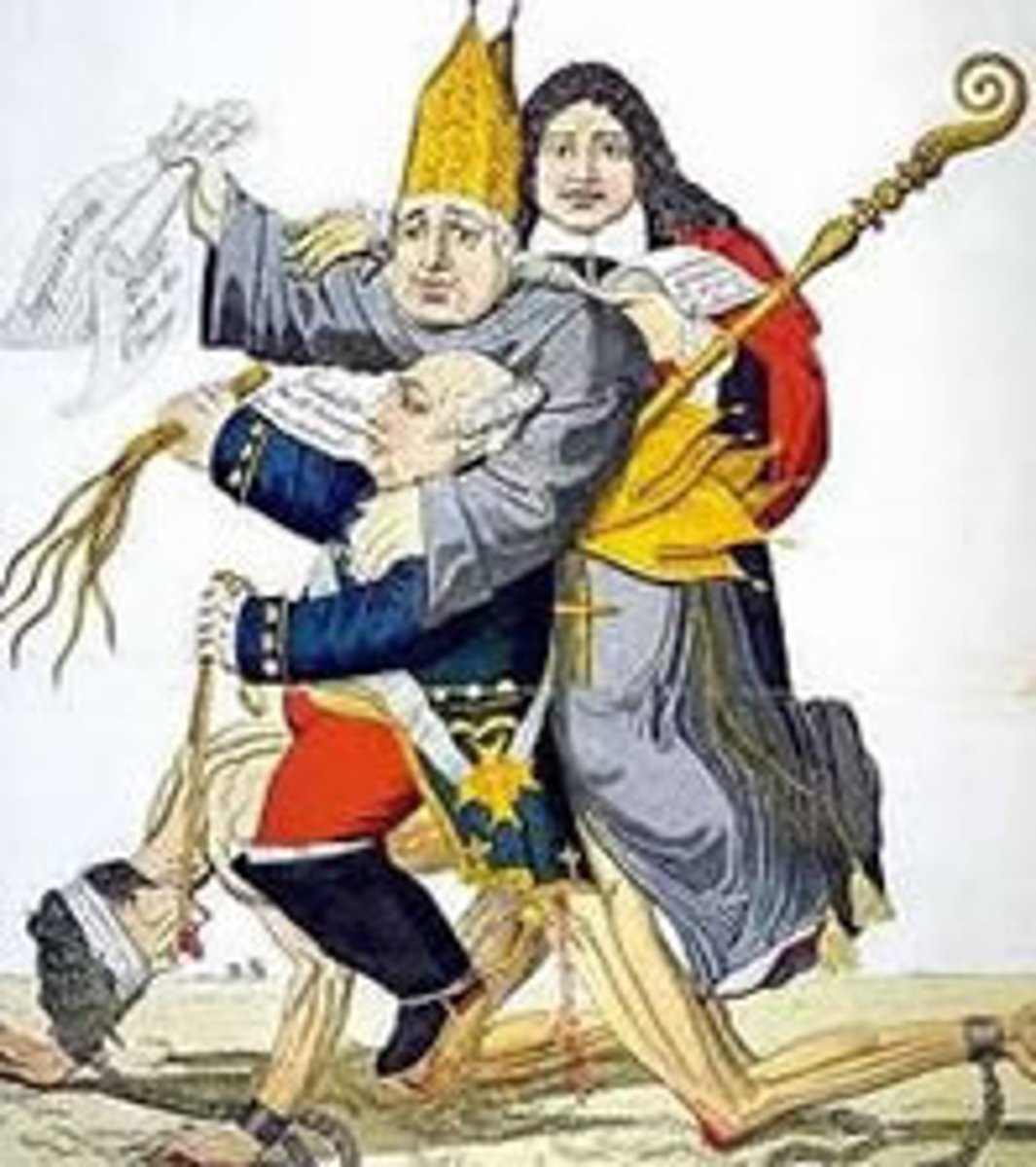

Bourgeoisie
the middle class, including merchants, industrialists, and professional people; wanted greater rights; gain more rights as a result of the French Revolution
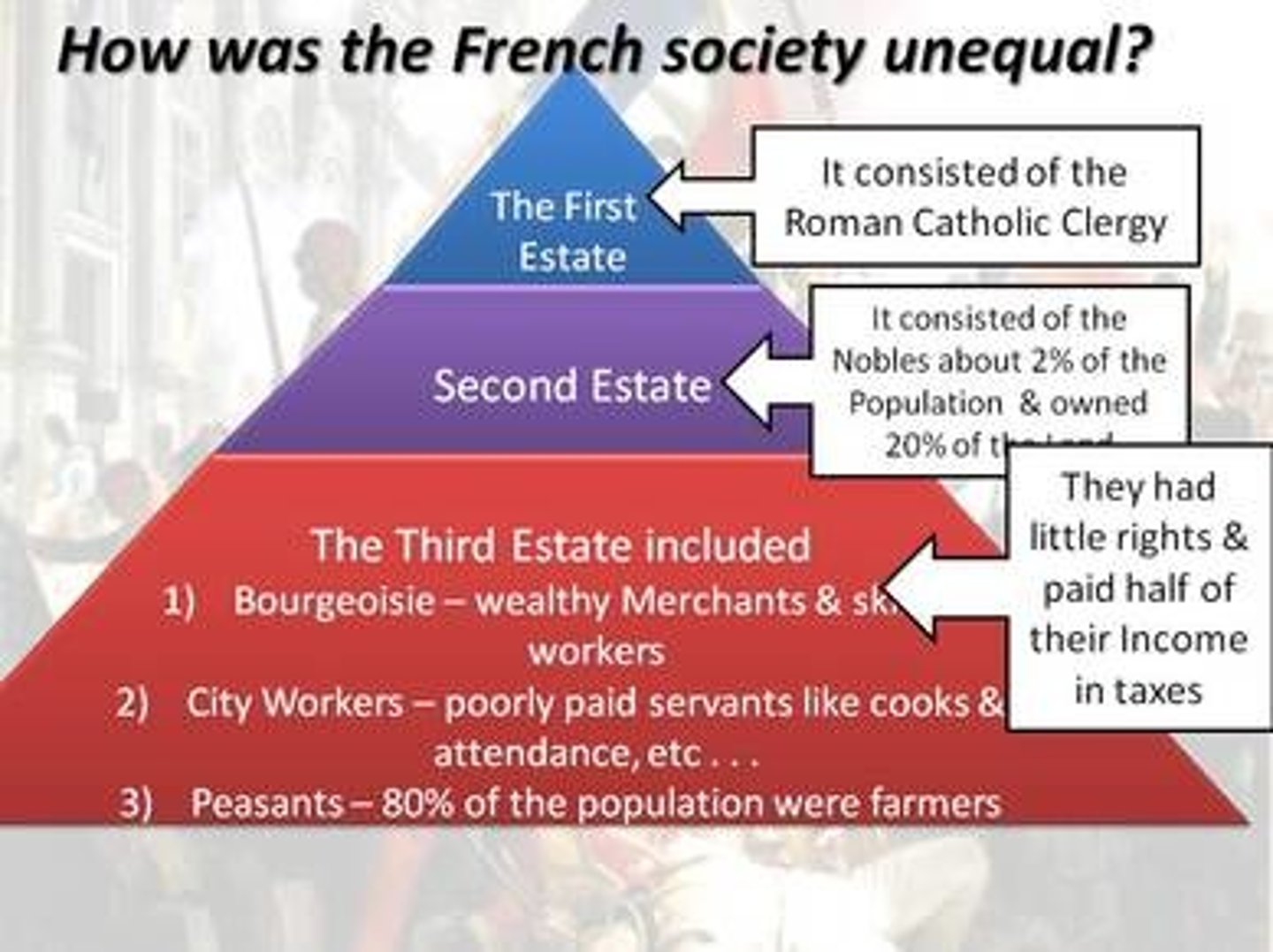
Old Regime (Ancien Regime)
the period of time in France under the rule of the monarchy when society was sharply divided into three estates and the majority of the people lived with few rights in poverty.
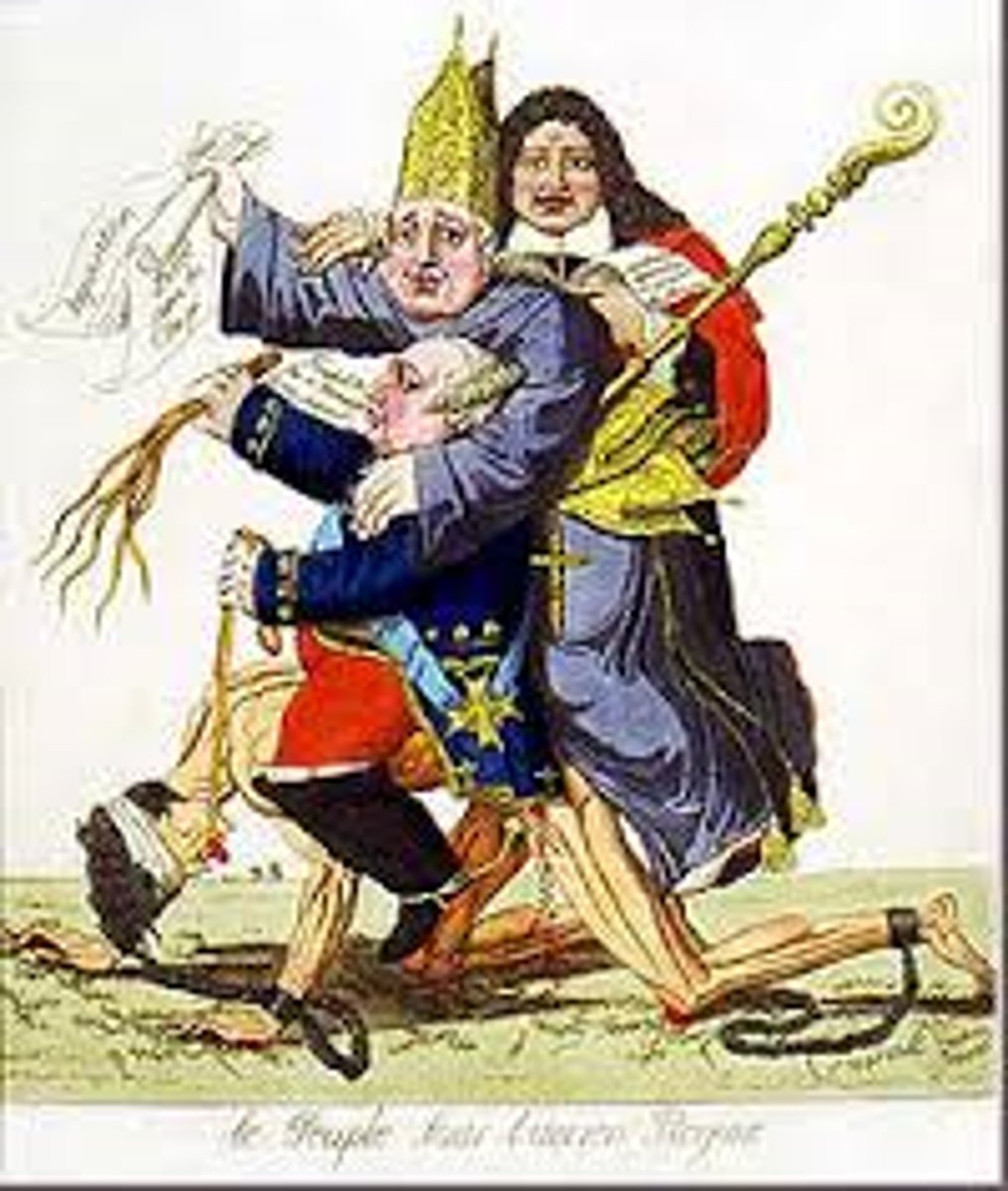

Estates General
An assembly of representatives from all three of the estates, or social classes, in France; voting system, can only meet when called upon by the king.
Tennis Court Oath
A pledge made by the members of France's National Assembly in 1789, in which they vowed to continue meeting until they had drawn up a new constitution
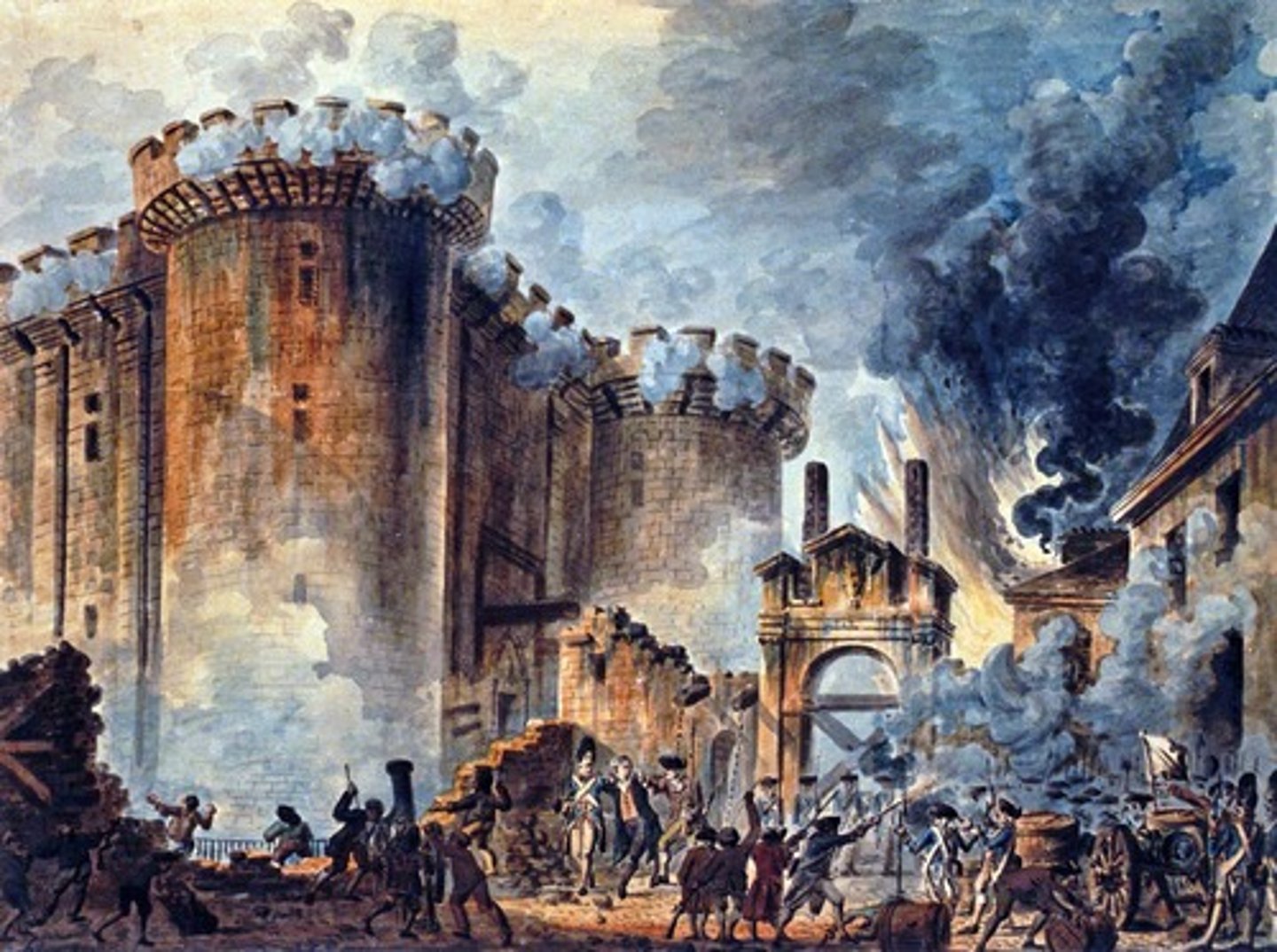
Bastille
Medieval fortress that was converted to a prison stormed by peasants for ammunition during the early stages of the French Revolution. Immediate cause of the French Revolution.

Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
Adopted August 26, 1789, created by the National Assembly to give rights to all (except women).

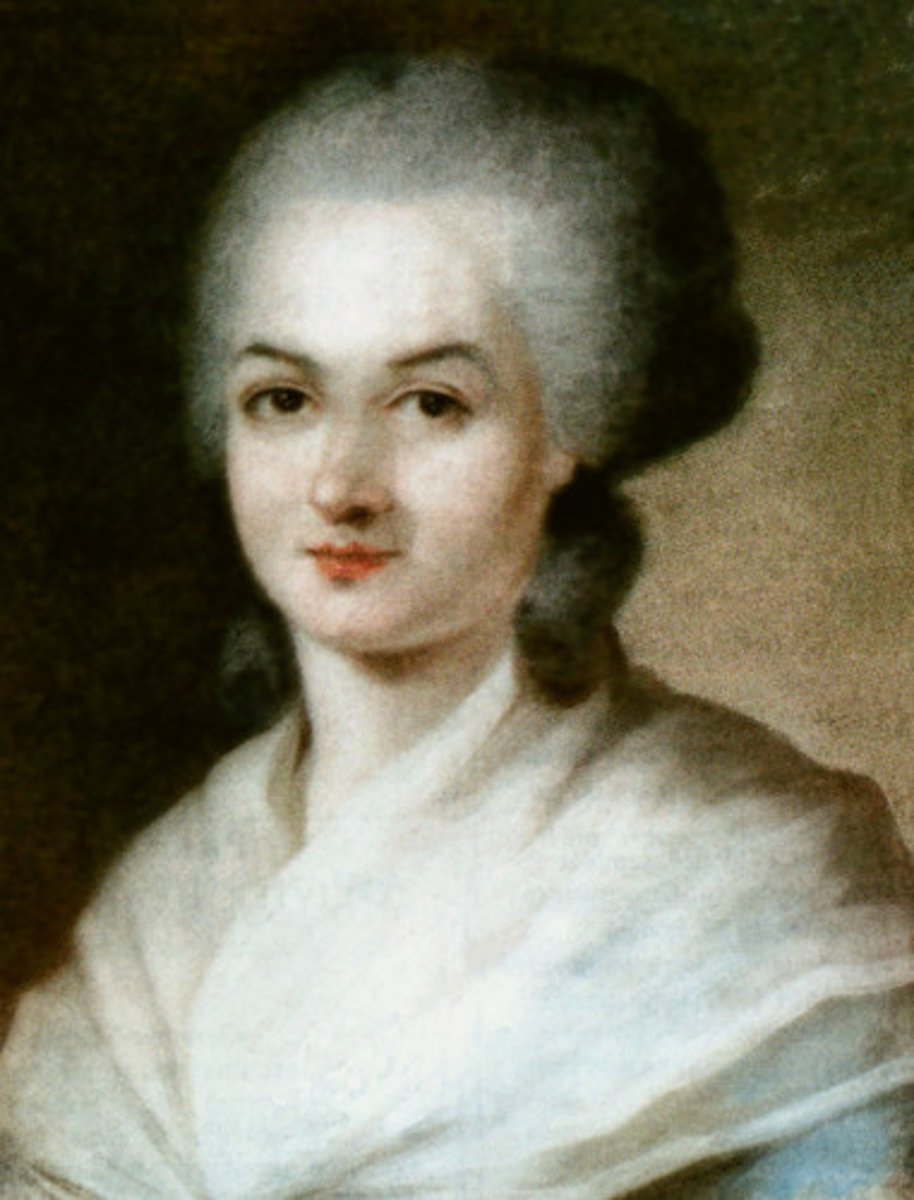
Olympe de Gouges
French journalist who demanded equal rights for women.

Constitution of 1791
Constitution created by the French Revolution that had a limited monarchy. Defined the role & purpose of the new government (set up a limited monarchy, natural rights, church under gov control).
Annexation
the formal act of acquiring something (especially territory) by conquest or occupation
Continental System
Napoleon's policy of preventing trade between Great Britain and continental Europe, intended to destroy Great Britain's economy. Led to the fall of Napoleon. Hurt people because there was a scarcity of goods.
Napoleonic Code
A comprehensive and uniform system of laws established for France by Napoleon. Included Enlightenment ideas - legal equality of citizens (not women) & religious toleration
Social Causes of the French Revolution
1. Split up into 3 estates
2. 1st and 2nd estates had all of the power
3. Bourgeoisie were unhappy that they did not have political representation
Political Causes of the French Revolution
1. Absolute Monarchy
2. Voting System of the Estates General
3. Enlightenment ideas & other revolutions
Economic Causes of the French Revolution
1. unfair tax system & land distribution between estates
2. France = bankrupt, debt & overspending
3. Deficit spending
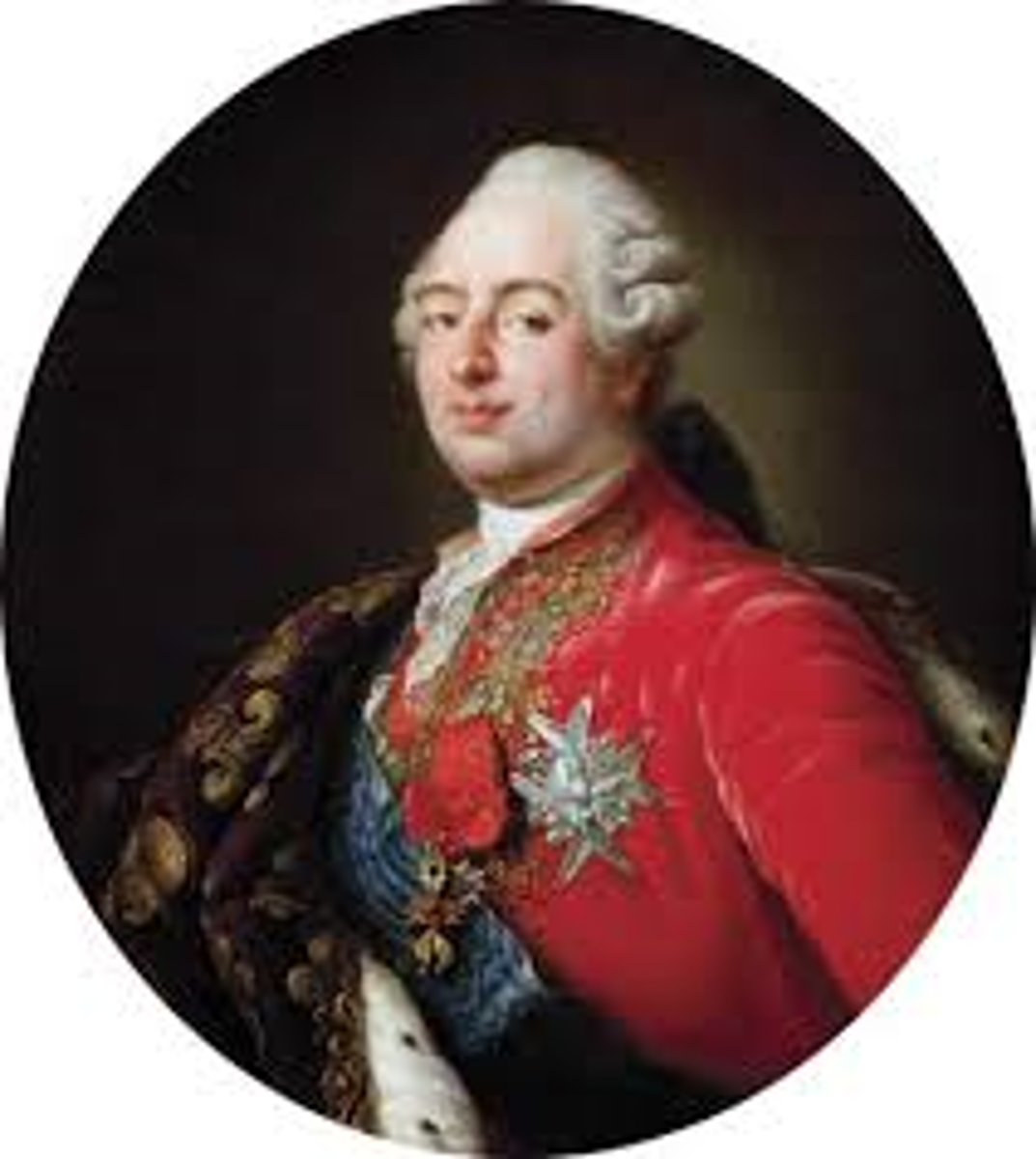
King Louis XVI
King of France, weak leader, executed during the French Revolution

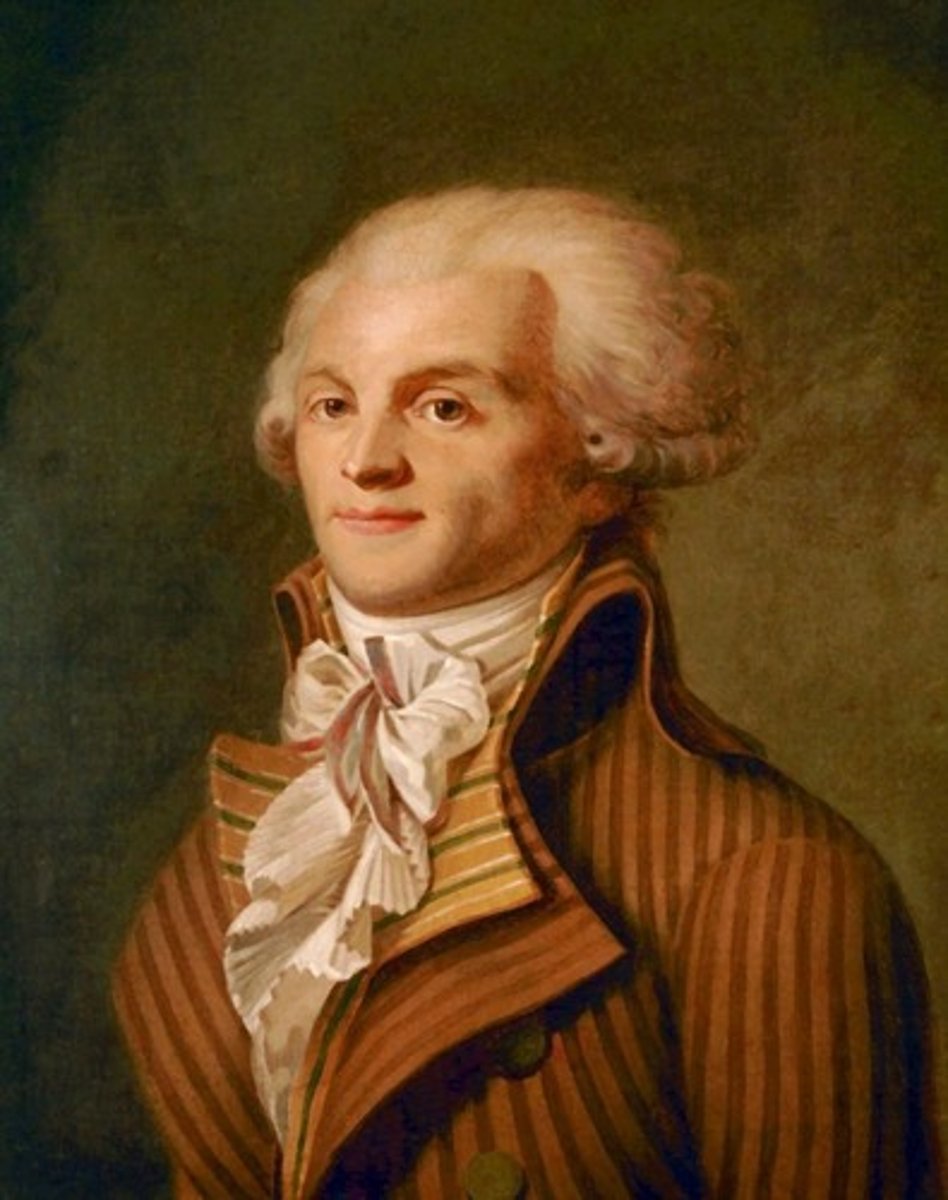
Maximillian Robespierre (1758-1794)
-One of the best-known and most influential figures of the French Revolution
-Largely dominated the Committee of Public Safety and was the leader of the National Assembly
-Instrumental during the Reign of Terror, which ended with his arrest and execution in 1794.

Reign of Terror
(1793-94) during the French Revolution when thousands were executed for "disloyalty"
Major results of the French Revolution
1. Ends Absolute Monarchy
2. Ends Old Regime & Rigid Class structure
3. Bourgeoisie gain role in government
4. Rights increased for the people
5. Spread of revolution & nationalism
How was the French Revolution a turning point in history?