Science Reproduction Flashcards, Mr. Meier
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mr Meier, Physical Science, Human Sexuality quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
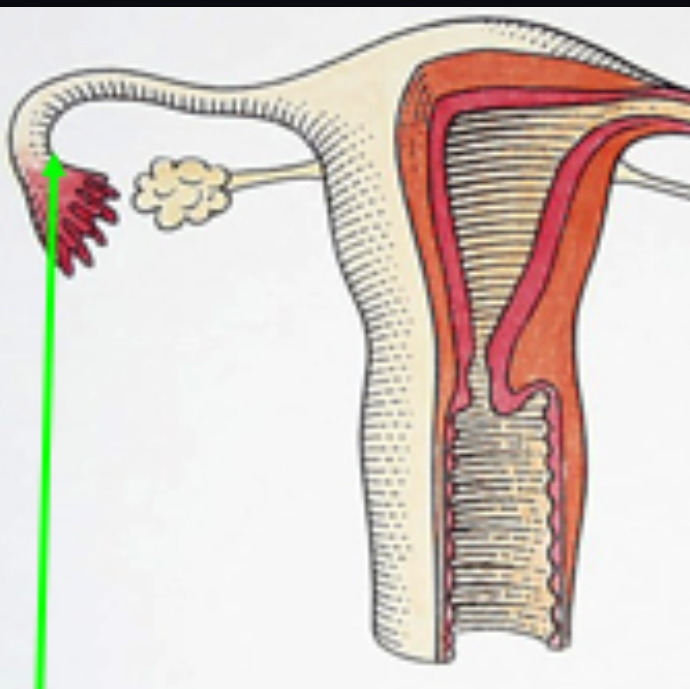
Fallipian Tube
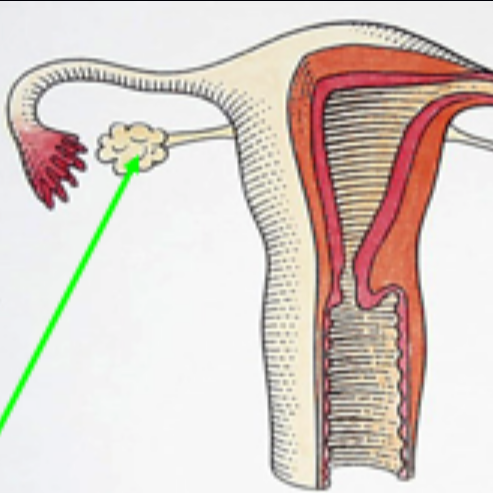
Ovary
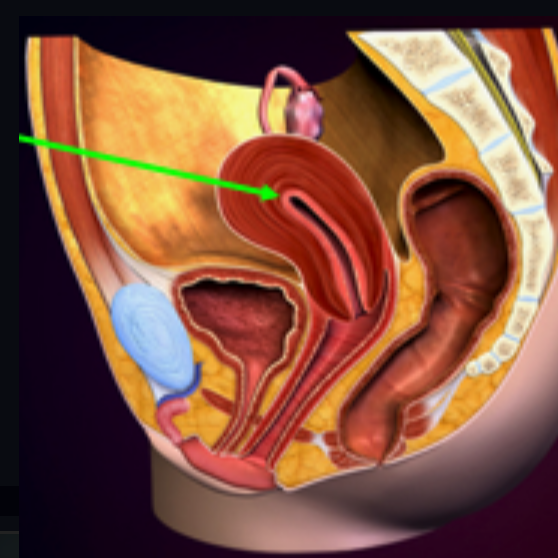
Uterus
Vagina
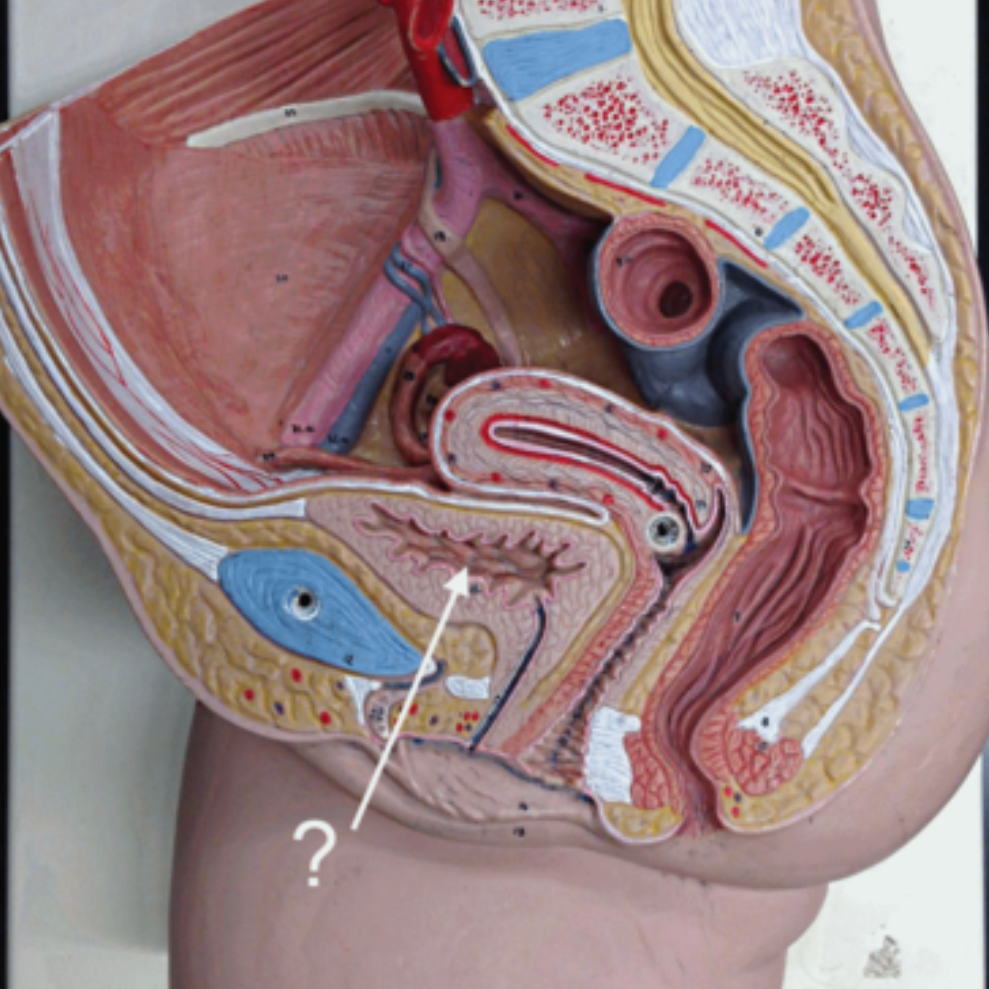
Urinary Bladder
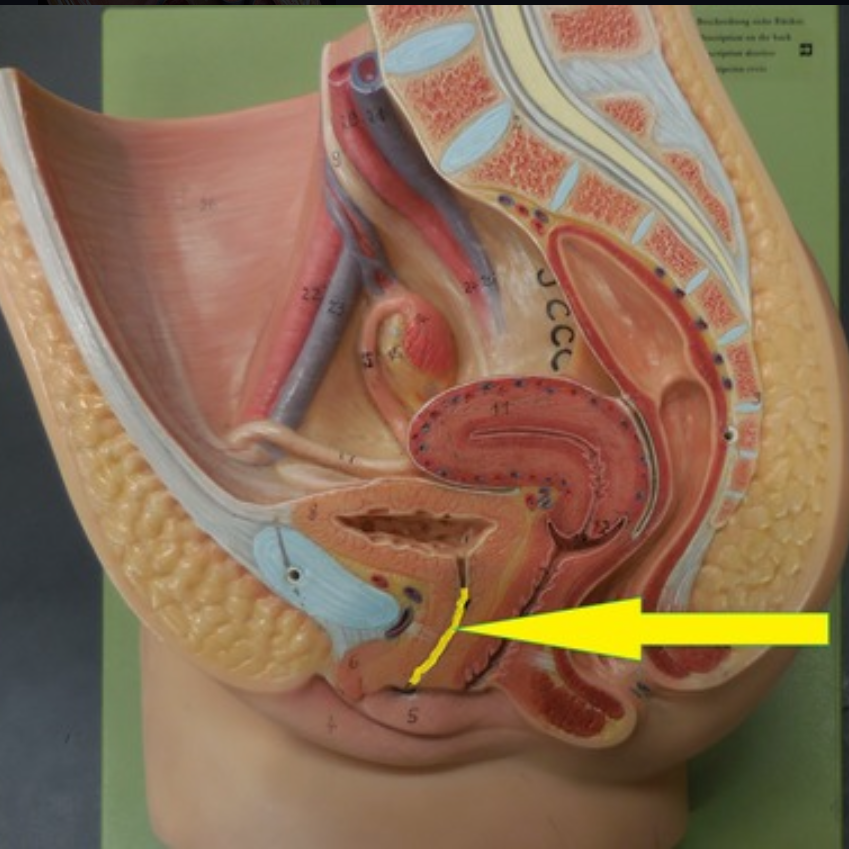
Urethra
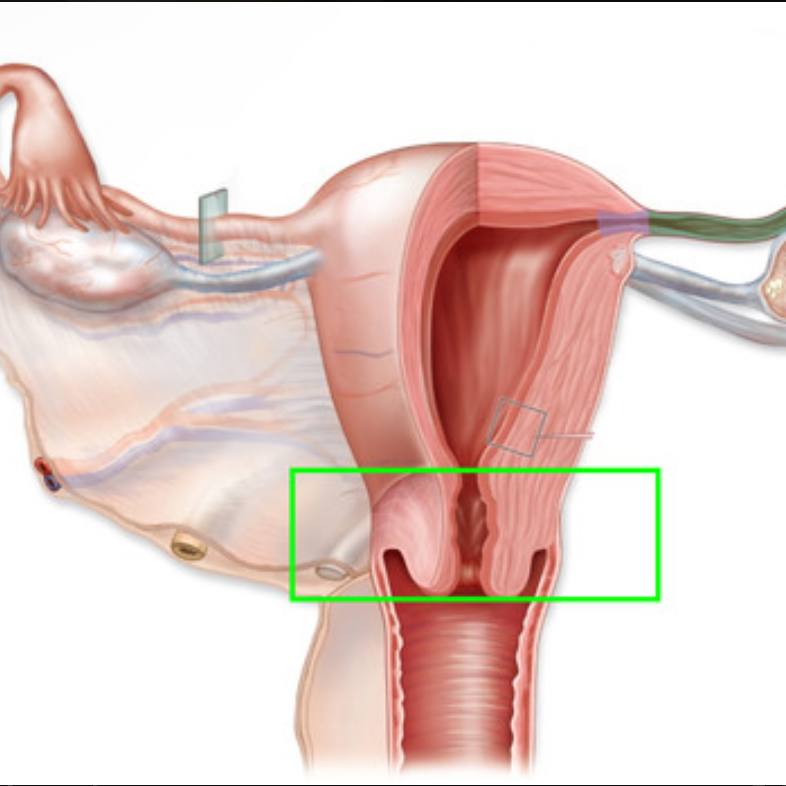
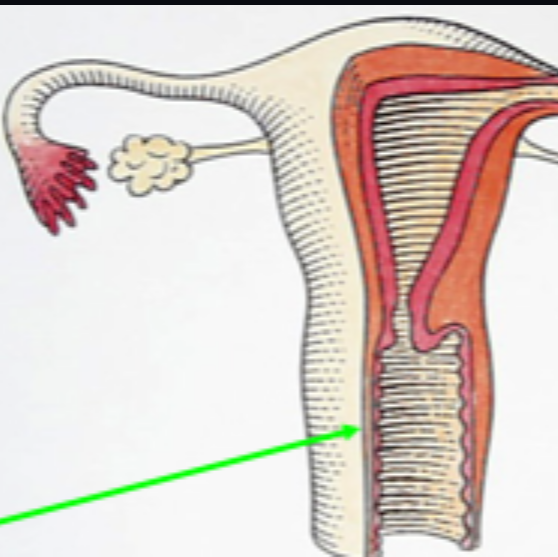
Cervix
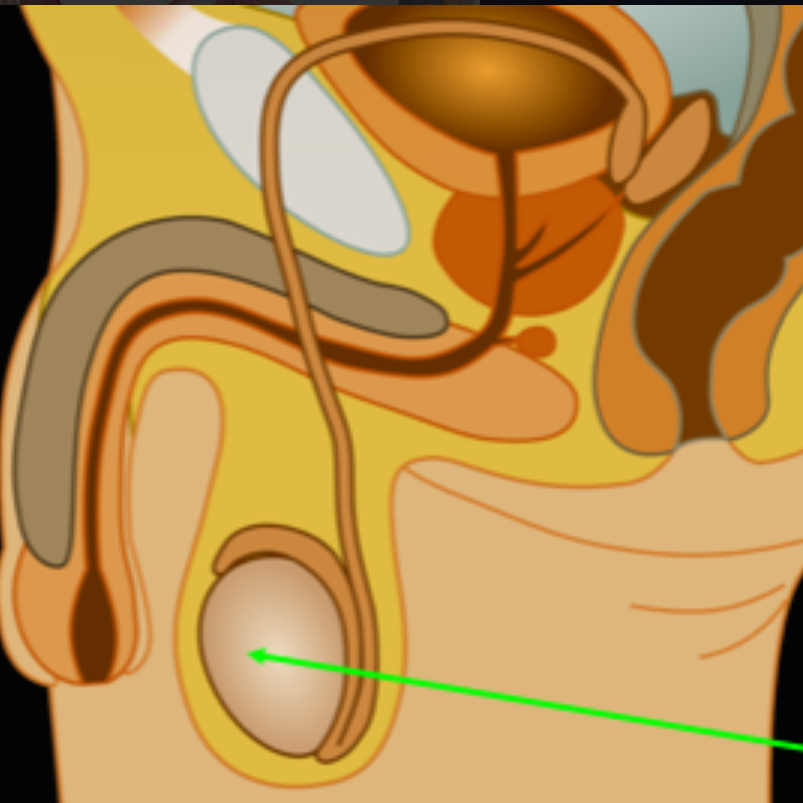
Testes
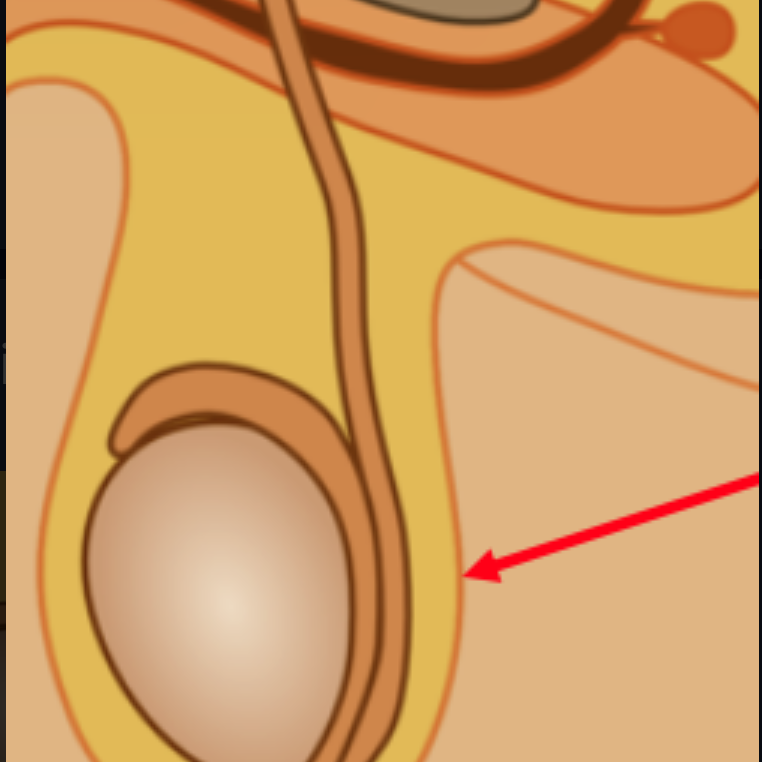
Scrotum
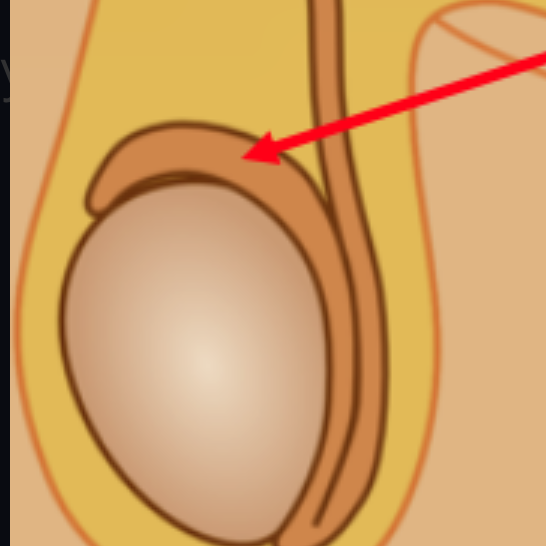
Epididymis
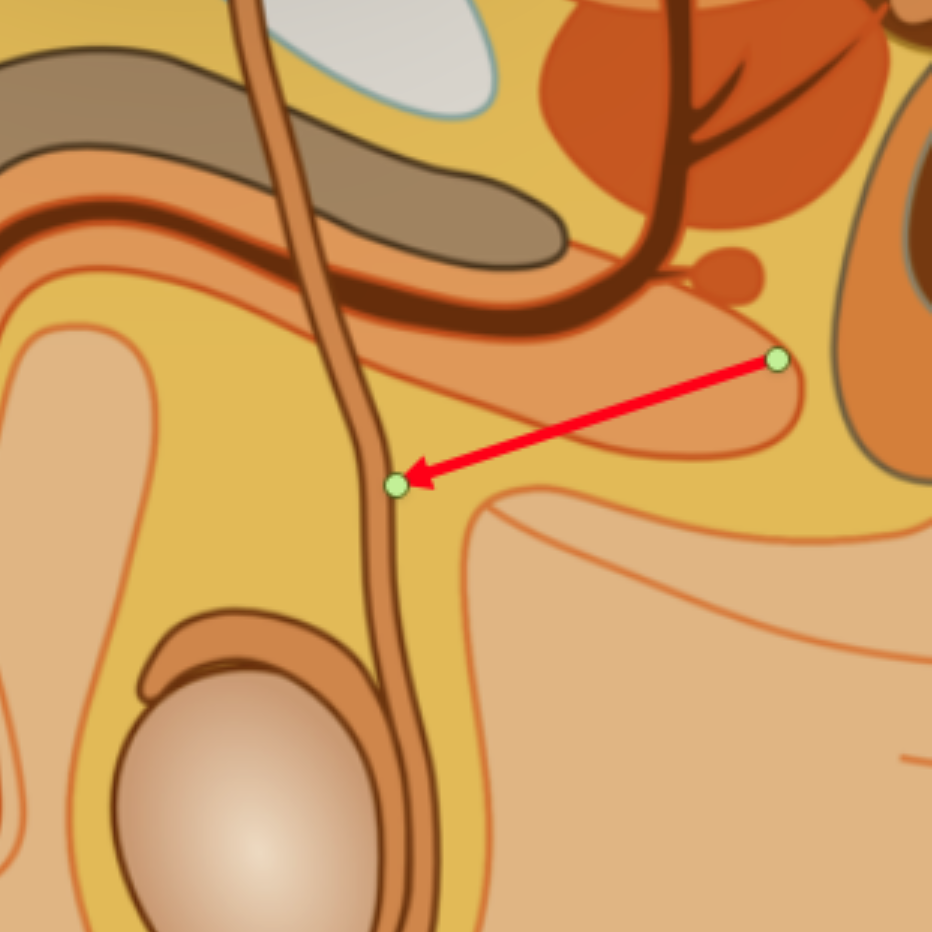
vas deferens
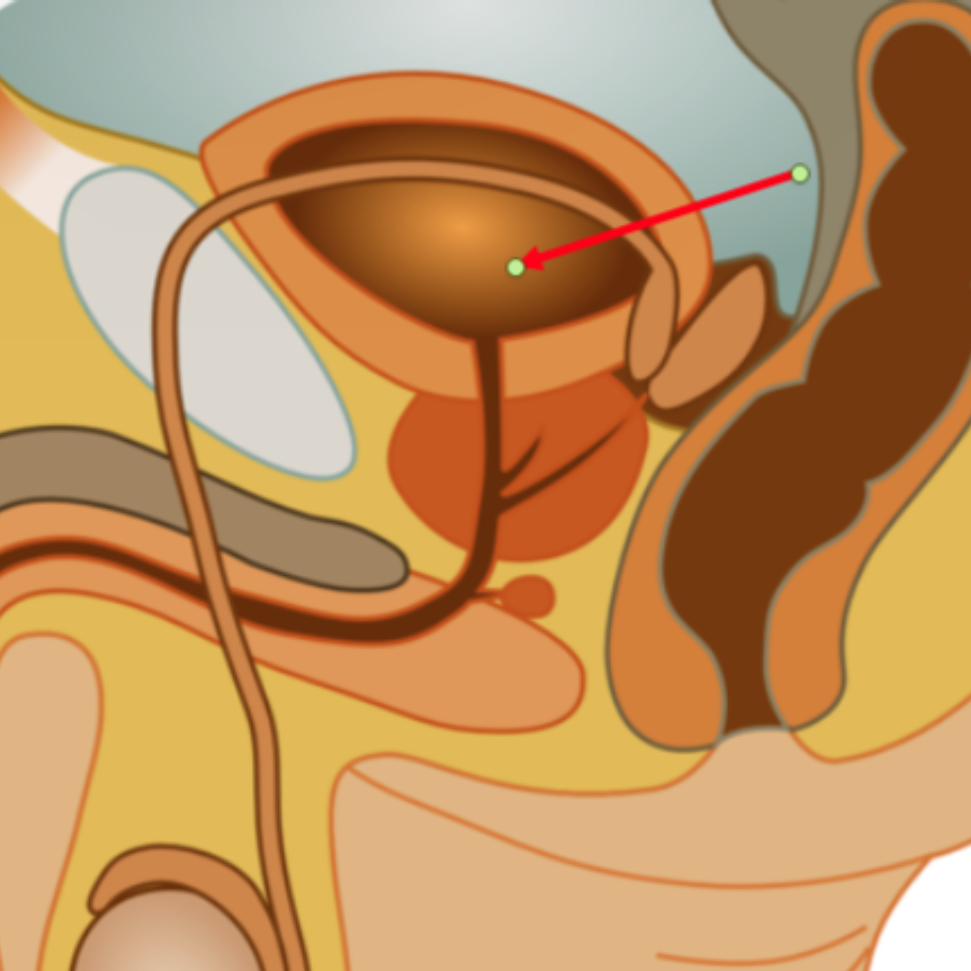
Urinary bladder
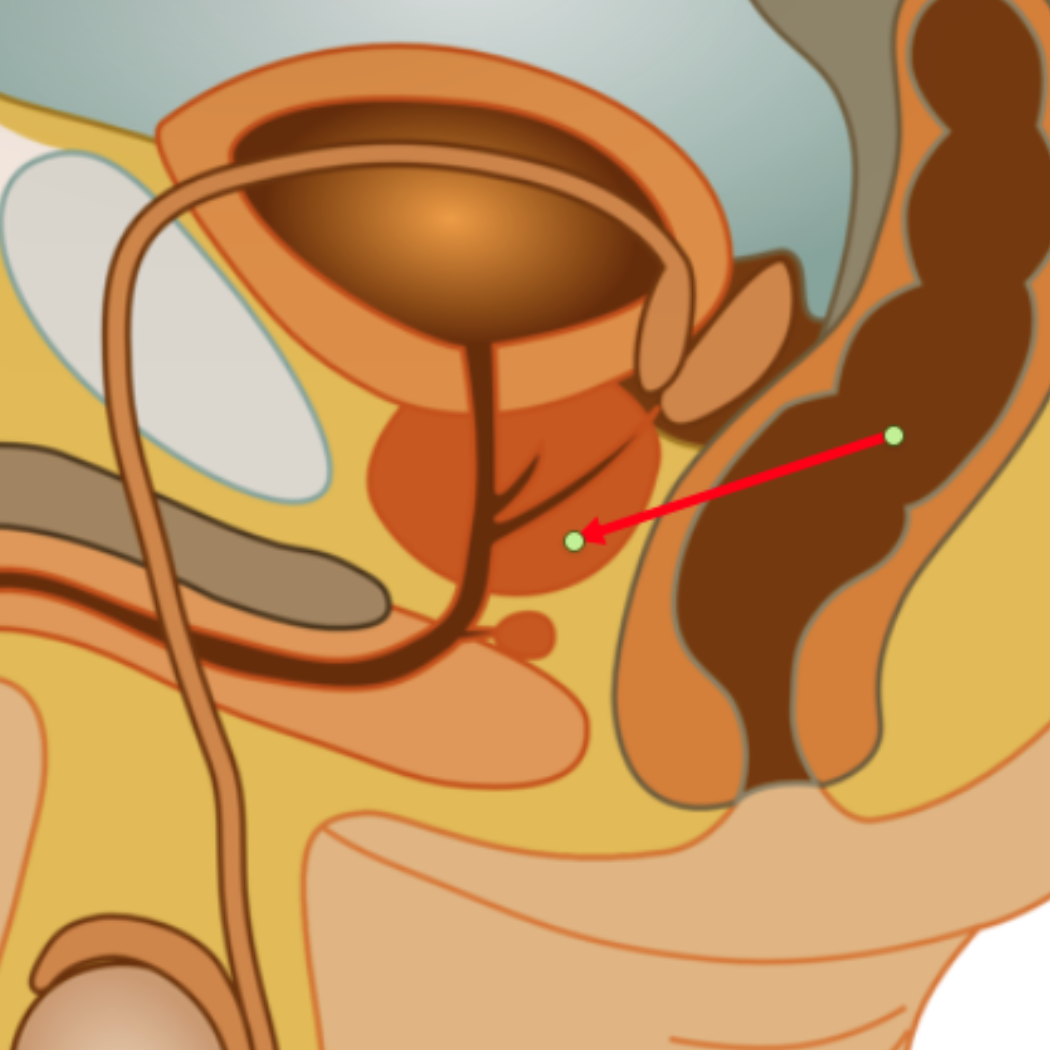
Prostate gland
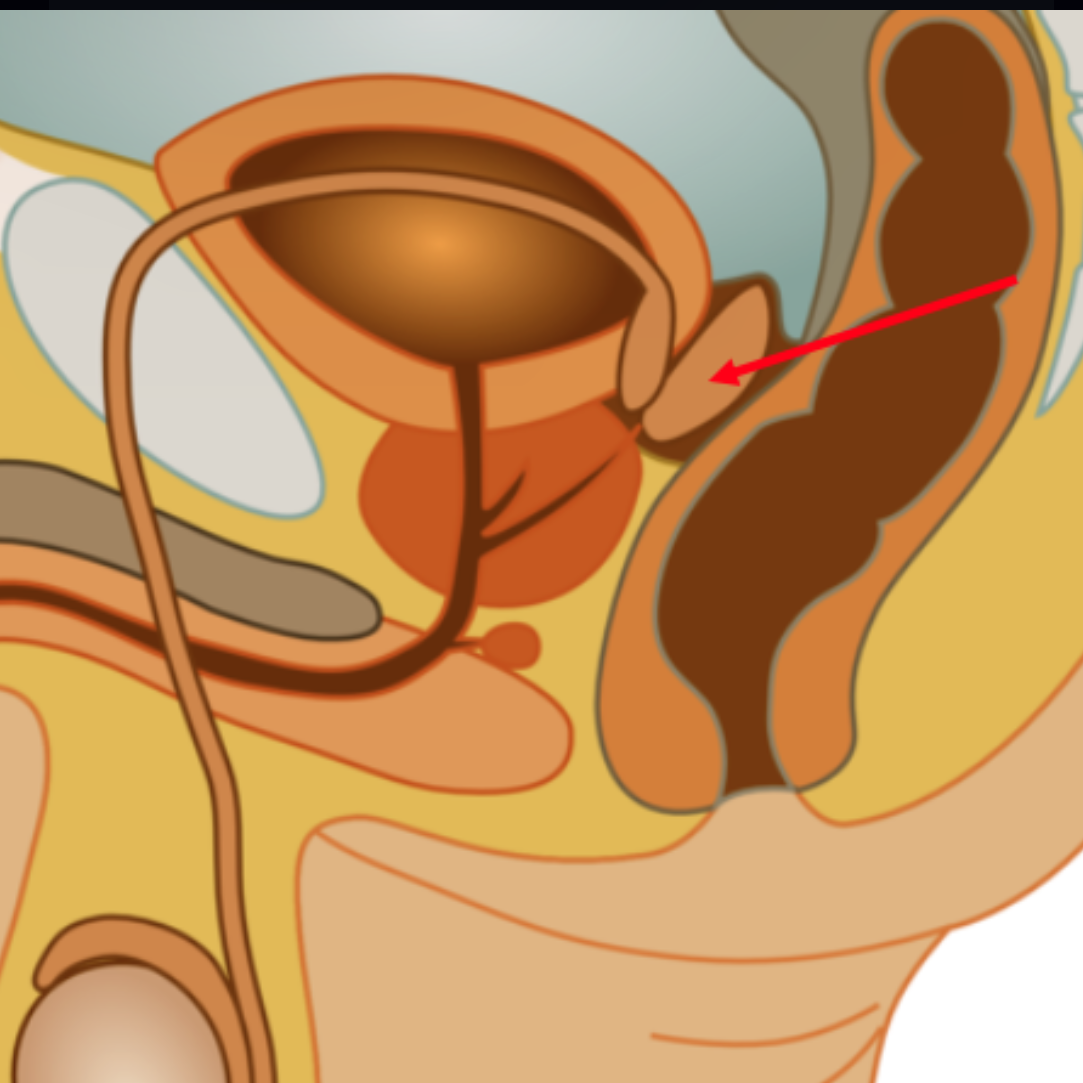
Seminal vesicle
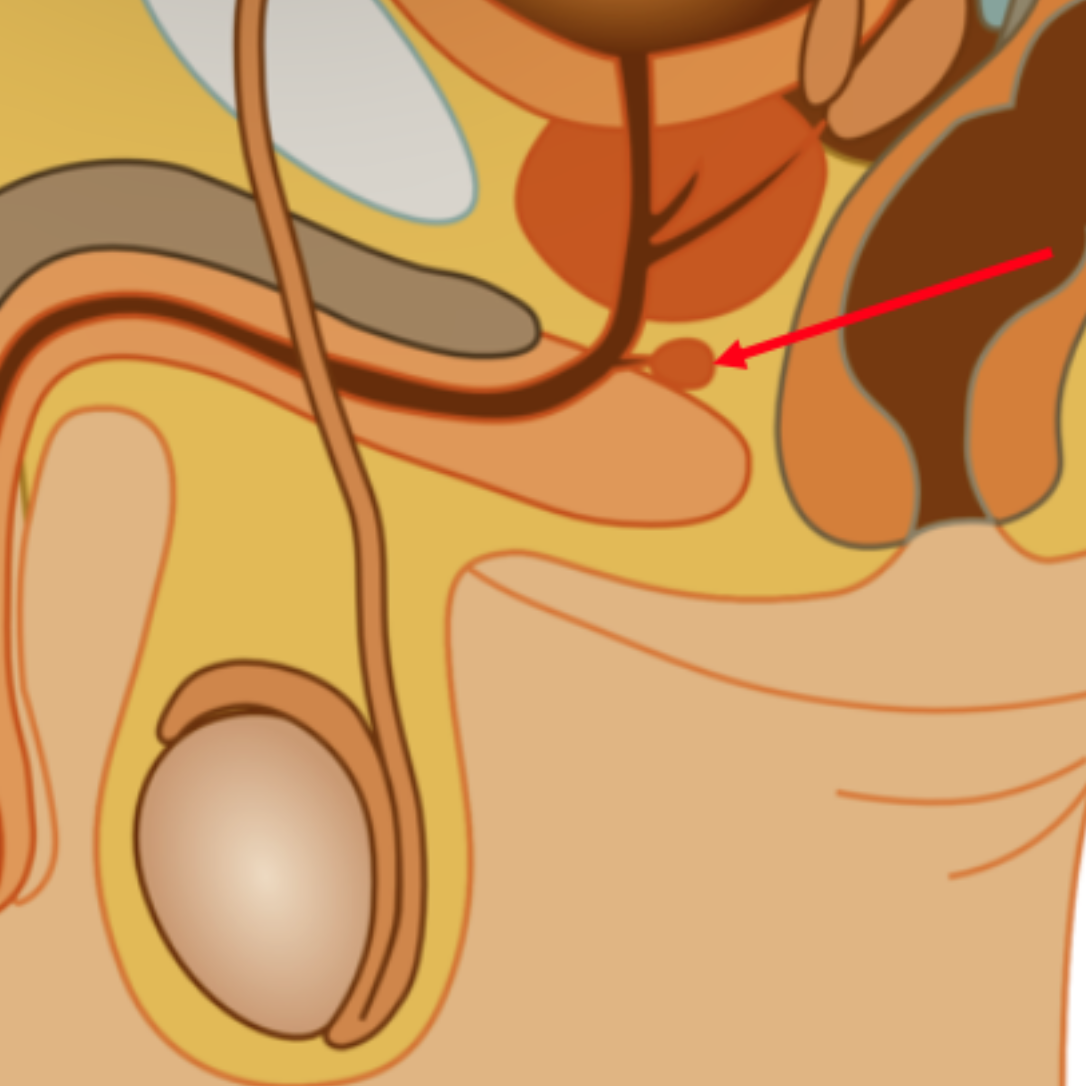
Cowper’s gland
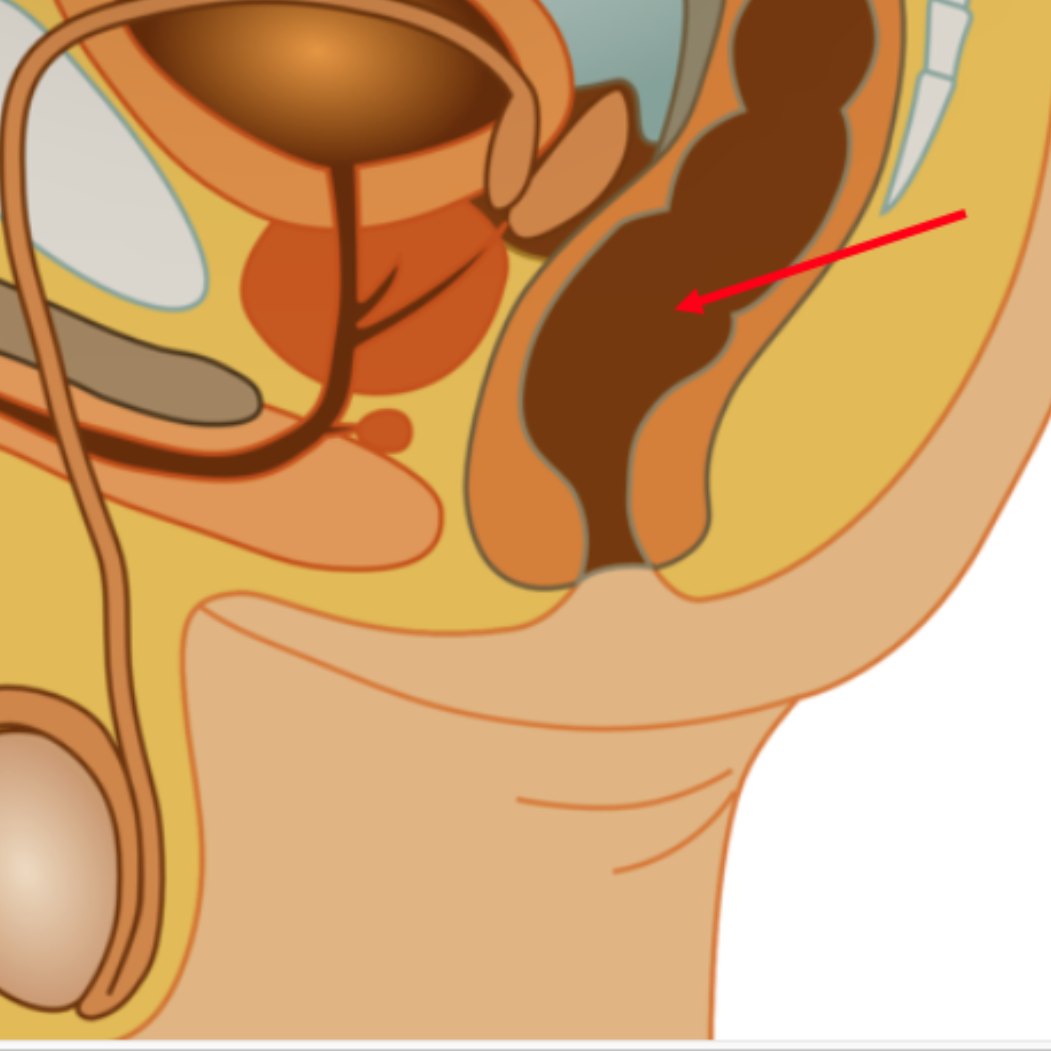
Rectum
Ovary
produces eggs, estrogen, and progesterone
Fallopian tubes
tubes which captures and carries eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and which provides the place where fertilization occurs
Uterus
A hollow muscular organ in the pelvic cavity of the female, in which the embryo is nourished and develops before birth
Cilia
Moves egg in the fallopian tubes
Cervix
The opening of the uterus that dilates at birth.
Vagina
A muscular, elastic passageway that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body and is the birth canal
Epididymis
A long, coiled duct on the outside of the testis in which sperm mature and are stored
Follicle
the sac in the ovary in which the egg develops
Nutrient lining
the wall of the uterus
Testosterone
A male sex hormone produced by the testes
Scrotum
Regulates temperature of the testes by moving closer and further from the body cavity
Seminal vesicles
two small glands that secrete a fluid rich in sugar that nourishes and helps sperm move
Prostate gland
Adds an alkaline (basic) fluid to the sperm in the acidic vagina
Cowper’s gland
2 small pea sized glands located on each side of the urethra that secretes a lubrication fluid