Lec 2: Overview of the Cranial Nerves
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
The __ are 12 paired nerves that emerge directly from the brain rather than the spinal cord.
They carry sensory (afferent), motor (efferent), or both (mixed) information between the brain and various regions of the head, neck, and body.
cranial nerves
carry sensory information to the CNS
afferent fibers
carry motor commands from the CNS.
efferent fibers
contain both motor and sensory information
mixed nerves

Mnemonics
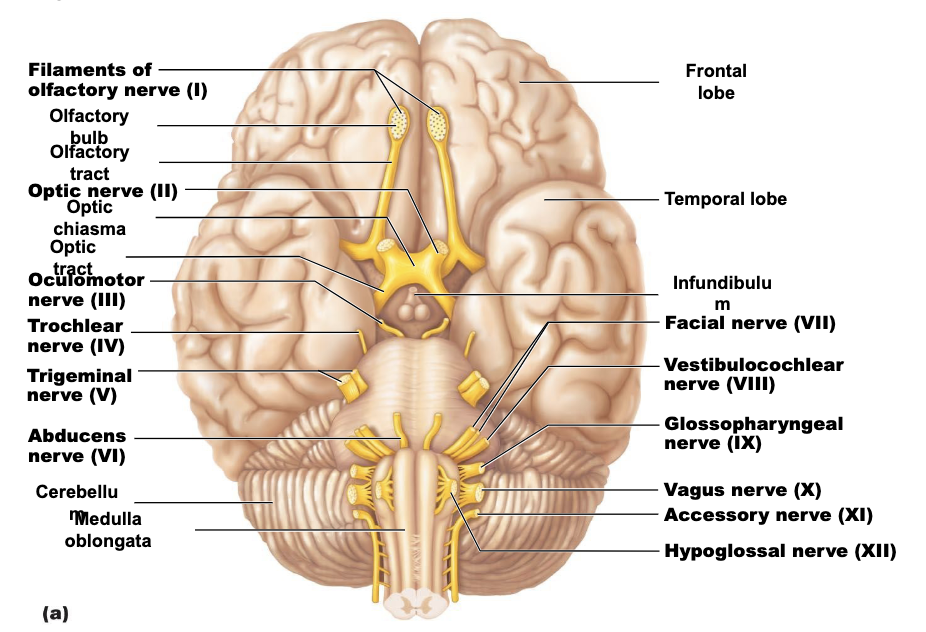
Look at BOLDED names
Figure 13.6a Location and function of cranial nerves.
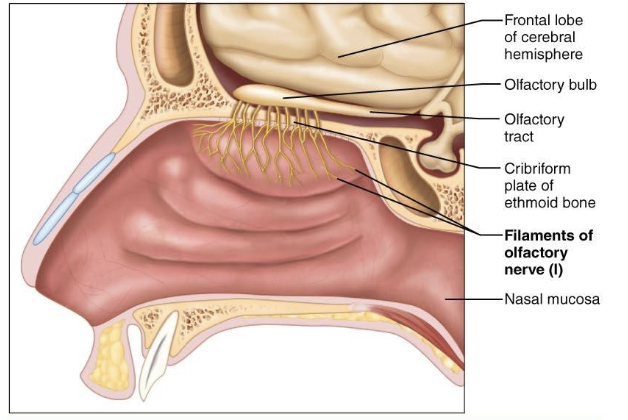
what is component of Cranial Nerve I – Olfactory Nerve?
afferent
what is function of Cranial Nerve I – Olfactory Nerve?
Sense of smell (olfaction)
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve I – Olfactory Nerve?
Damage causes anosmia—loss of smell, which also impacts taste perception.
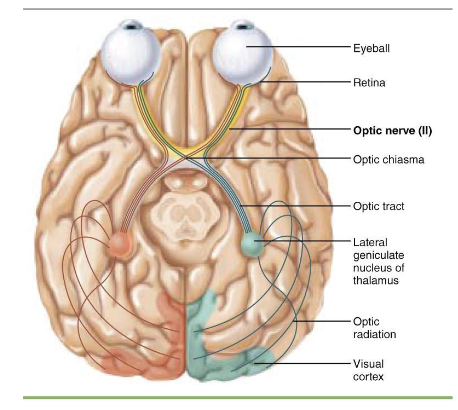
what is component of Cranial Nerve II – Optic Nerve?
afferent
what is function of Cranial Nerve II – Optic Nerve?
vision
what is pathway of Cranial Nerve II – Optic Nerve?
Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve II – Optic Nerve?
Lesion results in partial or complete blindness depending on the location of damage
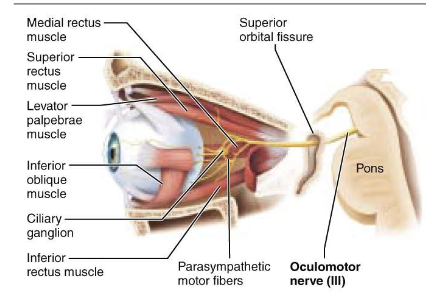
what is the component of Cranial Nerve III – Oculomotor Nerve?
efferent (somatic and visceral)
what is the somatic function of Cranial Nerve III – Oculomotor Nerve?
• Elevates the eyelid (levator palpebrae superioris)
• Moves the eye up, down, and inward
what is the visceral function (parasympathetic) of Cranial Nerve III – Oculomotor Nerve?
contricts the pupil (pupillary sphincter muscle)
accommodates the lens for near vision (ciliary muscle)
what is the clinical note of Cranial Nerve III – Oculomotor Nerve?
Oculomotor palsy causes ptosis (drooping eyelid) and dilated pupil.
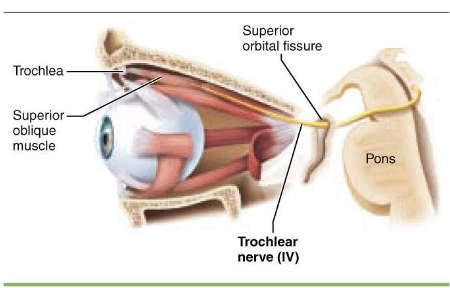
what is component of Cranial Nerve IV – Trochlear Nerve?
efferent (somatic)
what is function of Cranial Nerve IV – Trochlear Nerve?
Controls the superior oblique muscle, which turns the adducted eye downward and medially (intorsion).
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve IV – Trochlear Nerve?
Damage causes difficulty looking down when the eye is adducted (e.g., reading or descending stairs)
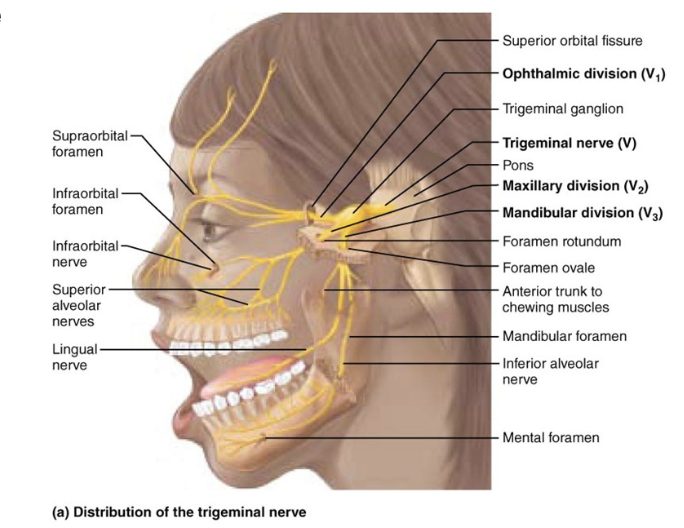
what is component of Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Nerve?
Mixed (Afferent and Efferent)
what is afferent functions of Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Nerve?
● Sensation from the face
● Sensation from the cornea
● Sensation from the anterior tongue
what is efferent functions of Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Nerve?
● Controls muscles of mastication (chewing)
● Dampens sound via the tensor tympani muscle
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Nerve?
Lesion may cause loss of facial sensation or weakness in jaw movement; overactivity can lead to trigeminal neuralgia
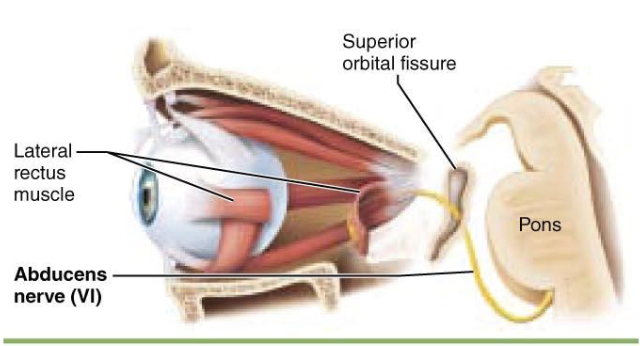
what is components of Cranial Nerve VI – Abducens Nerve?
Efferent (Somatic)
what is function of Cranial Nerve VI – Abducens Nerve?
Turns the eye outward (controls the lateral rectus muscle)
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve VI – Abducens Nerve?
Lesion causes medial strabismus—the affected eye cannot move laterally
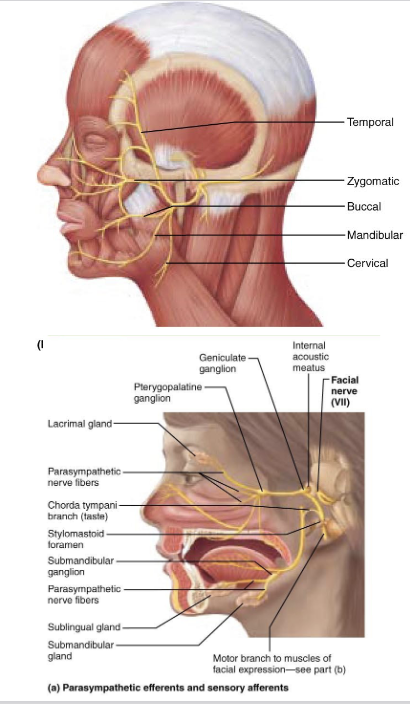
what is components of Cranial Nerve VII – Facial Nerve?
mixed
what is afferent function of Cranial Nerve VII – Facial Nerve?
Taste from anterior 2/3 of the tongue
what is efferent function (somatic) of Cranial Nerve VII – Facial Nerve?
Muscles of facial expression and stapedius (dampens sound)
what is efferent function (visceral) of Cranial Nerve VII – Facial Nerve?
● Tearing via lacrimal glands
● Salivation via submandibular and sublingual glands
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve VII – Facial Nerve?
Bell’s palsy involves paralysis of facial muscles on one side, loss of taste, and reduced tear/saliva production
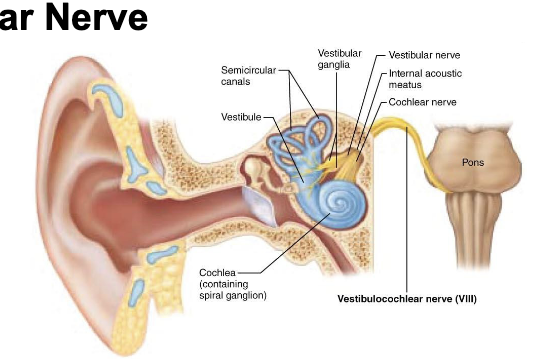
what is component of Cranial Nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear Nerve?
afferent
what is function of Cranial Nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear Nerve?
○ Vestibular branch: Balance and equilibrium (from semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule)
○ Cochlear branch: Hearing (from the organ of Corti)
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear Nerve?
Lesions cause vertigo, balance disturbances, or sensorineural hearing loss
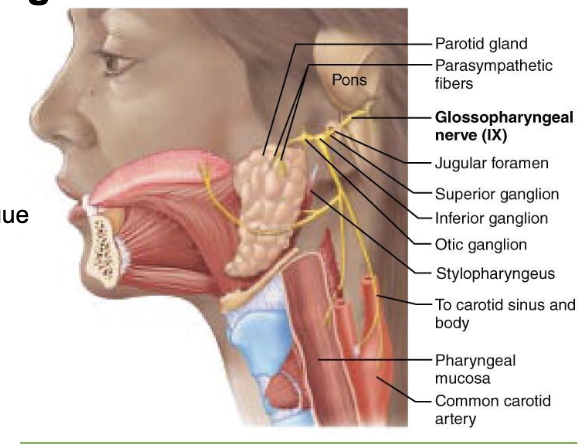
what is component of Cranial Nerve IX – Glossopharyngeal Nerve?
mixed
what is afferent functions of Cranial Nerve IX – Glossopharyngeal Nerve?
● Taste and sensation from posterior 1/3 of the tongue
● Sensation from the oropharynx
what is efferent functions of Cranial Nerve IX – Glossopharyngeal Nerve?
Stimulates salivation via the parotid gland
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve IX – Glossopharyngeal Nerve?
Damage can cause loss of gag reflex and impaired swallowing.
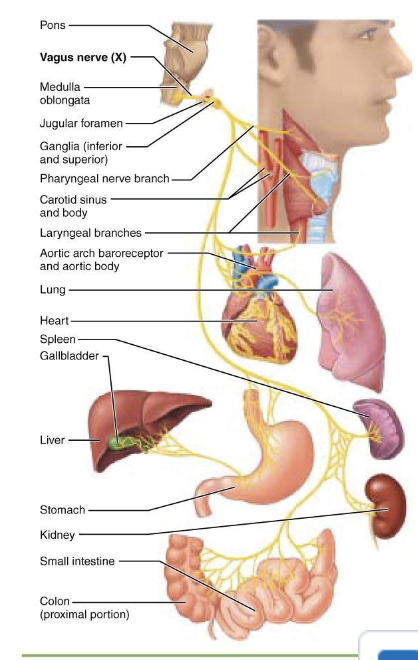
what is component of Cranial Nerve X – Vagus Nerve?
mixed
what is afferent function of Cranial Nerve X – Vagus Nerve?
Sensory input from thoracic and abdominal viscera
what is efferent function of Cranial Nerve X – Vagus Nerve?
● Controls muscles of the larynx and pharynx (speech and swallowing)
● Decreases heart rate
● Increases gastrointestinal motility
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve X – Vagus Nerve?
Lesions may cause hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, and autonomic dysfunction
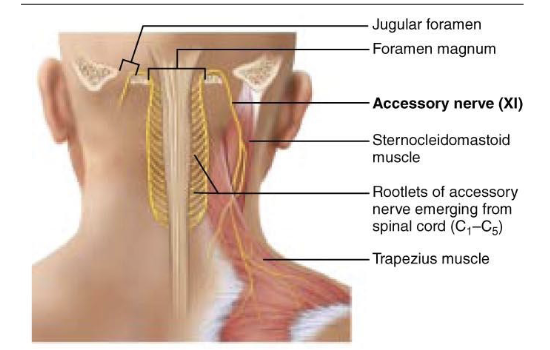
what is component of Cranial Nerve XI – Accessory Nerve?
efferent
what is function of Cranial Nerve XI – Accessory Nerve?
Controls head movements through the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve XI – Accessory Nerve?
Damage causes weakness in shoulder elevation and head rotation.
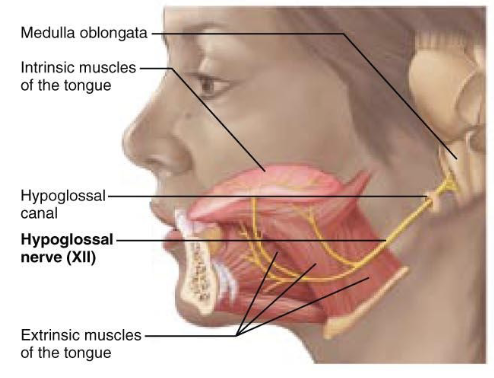
what is component of Cranial Nerve XII – Hypoglossal Nerve?
efferent
what is function of Cranial Nerve XII – Hypoglossal Nerve?
Controls tongue movements and shape
what is clinical note of Cranial Nerve XII – Hypoglossal Nerve?
Lesion causes tongue deviation toward the side of the lesion upon protrusion