Chemistry Remove Summer Exam
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Metal Extraction Method Table
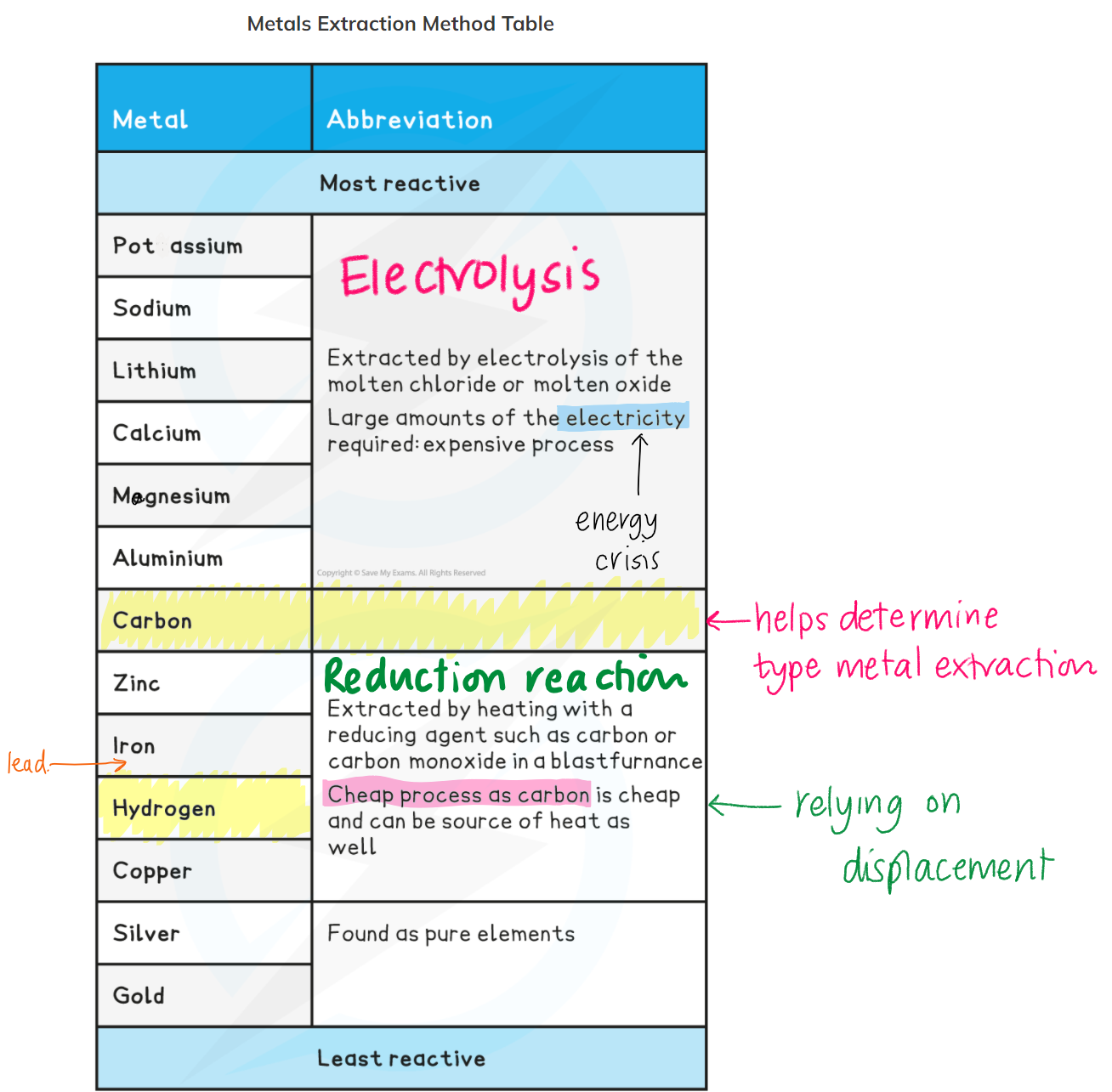
What is an ore?
A rock/mineral containing enough metal compounds to make it economical to extract.
What is electrolysis?
Extraction of a metal ore using electricity.
What is extracting by using carbon called?
Smelting
What is an electrolyte?
A compound capable of conducting electricity when melted (ionic substance)
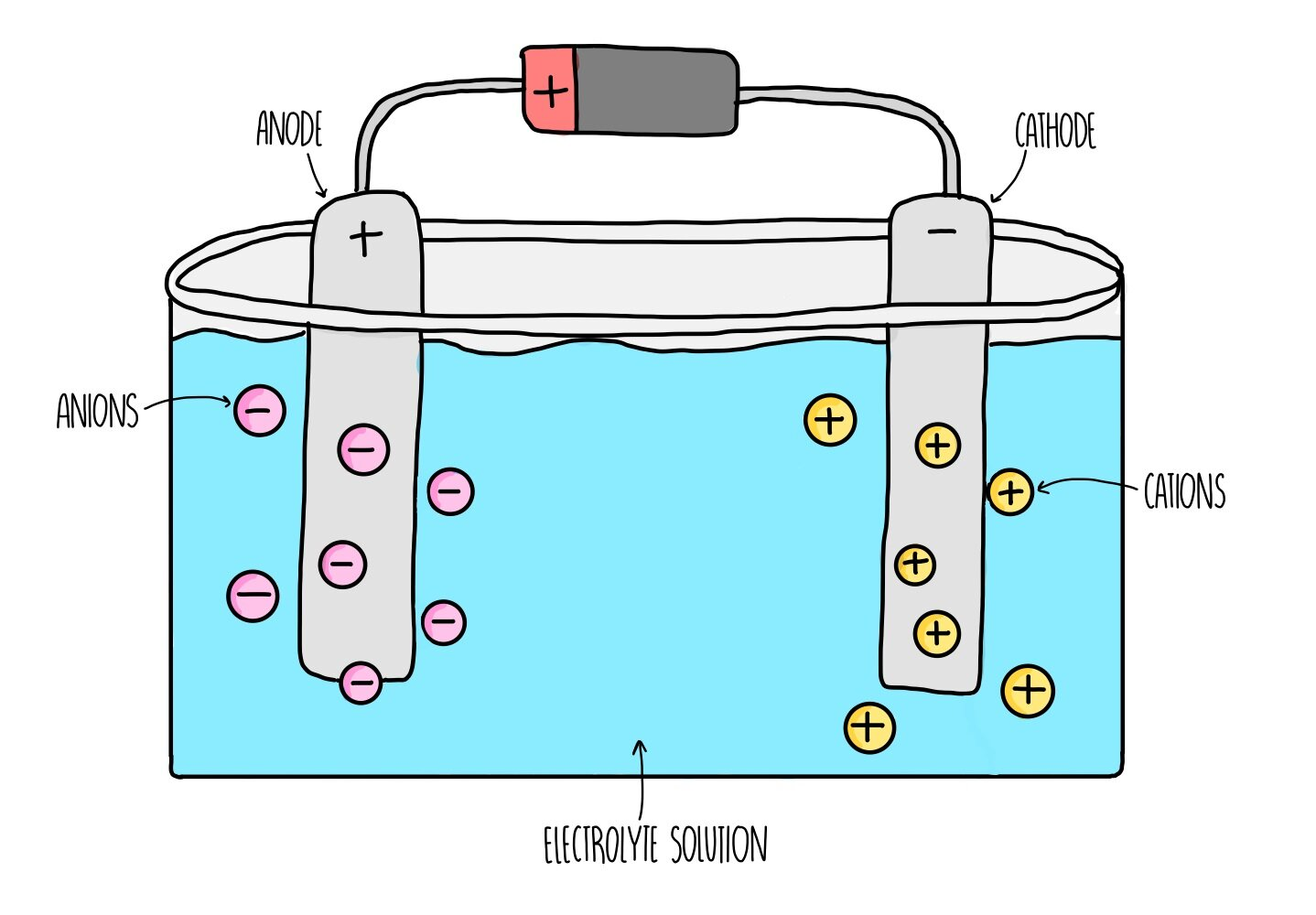
Electrolysis of aluminium oxide
Extract your ore (bauxite) - impure Al2O3
Purify the ore to give pure Al2O3
Melt the Al2O3 to form an electrolyte
Pass electrcity through the liquid Al2O3
What happens next in the electrolysis of aluminium oxide?
Anode (+) attracts anions (-) (oxide ions).
2O2- → O2 + 4e-
Cathode (-) attracts cations (+) (aluminium ions)
Al3++3e- → Al
Aluminium ions are reduced by electrons to form aluminium metal
What is corrosion?
The oxidation of metals.
What is iron said to do instead of corrode?
Rust
What reaction is rusting?
An oxidation reaction.
Iron becomes hydrated iron(III) Oxide.
Rust redox reaction:
4Fe + 3O2 → 2FeO3
The arrow is water
What is needed for rusting?
Iron, water and oxygen
What is a good catalyst for rusting?
Sodium chloride
Barrier Methods of preventing rusting
Barrier Methods prevent water and oxygen from reaching the iron:
Painting
Oil
Grease
Plastic Coating
Sacrificial methods of preventing rusting:
Sacrificial Methods involve allowing a more reactive metal to corrode instead of the iron:
Galvanising - Coating iron with Zn
Sacrificial Protection - Zn/Mg
Zinc acts as both a…
sacrificial method and a barrier method
Why will iron not rust even if the zinc coating is broken?
The electrons produced by zinc are given to the iron which reduces back to normal iron (stops rusting).
Uses of aluminium:
aircraft, drinks cans, electrical power lines
Uses of copper:
wires, pans, water pipes
Uses of iron:
converted to steel (mostly turned into alloys)
Uses of steel:
building and cutlery
What is group 7 called?
The halogens
The halogens are…
A group of reactive, non-metallic elements which are all diatomic molecules.
Colours and physical states of chlorine, bromine and iodine at room temperature:
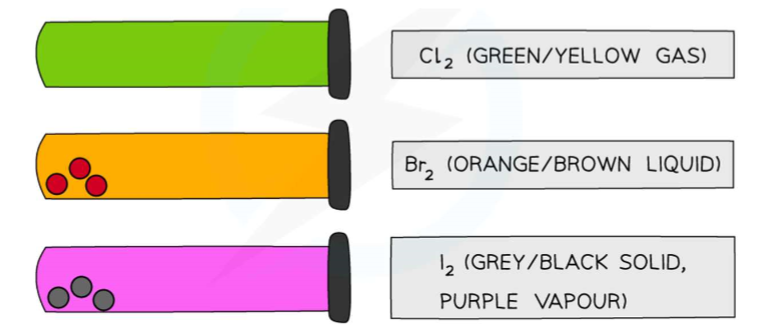
The melting points and boiling points _______ as you go down the group.
increase
Why do the melting and boiling points increase as you go down the group?
This is due to increasing molecular forces as the atoms become larger, so more energy is required to overcome these forces.
Fluorine (F2) colour,state and reactivity:
A pale yellow gas - highly reactive
Astatine (At2) colour,state and reactivity:
A black solid - very unreactive
The reactivity _______ as you go down the group.
decreases
Explain the reactivity in group 7 in terms of electronic configuration:
All group 7 elements can gain one electron to obtain a full outer shell.
The easier it is for a halogen to attract an electron, the more reactive the halogen will be.
As you go down group 7, the extra electron becomes further away from the nucleus which makes it harder to attract.
This causes them to get less reactive as you go down the group.
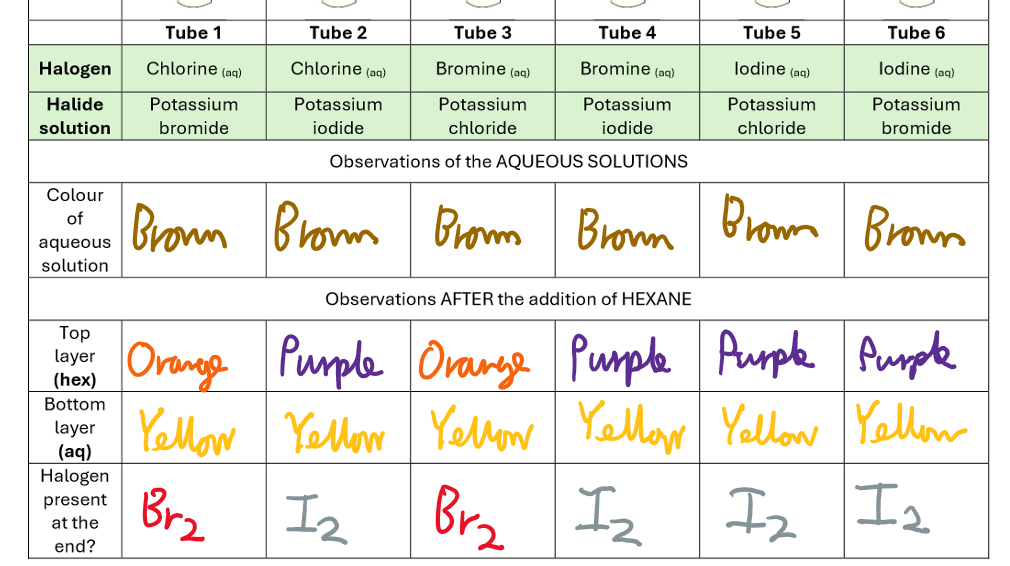
Describe a test for chlorine:
It bleaches damp litmus paper white.
A more reactive halogen will displace a…
less reactive halogen.
What is a redox reaction?
Reduction/oxidation (gain or loss of oxygen)
However, it can sometimes refer to reactions involving the movement of electrons.
OIL RIG
Oxidation Is Loss of electrons.
Reduction Is Gain of electrons.
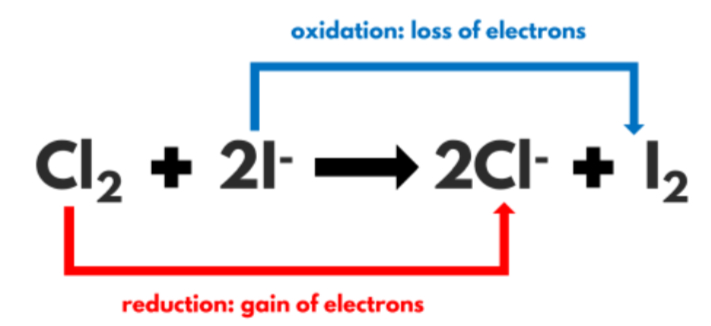
What is a halogen called when it becomes an ion?
A halide ion (Halogen-)
Halogens Reactivity: Most Reactive to least reactive
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Halogens In Solution Results
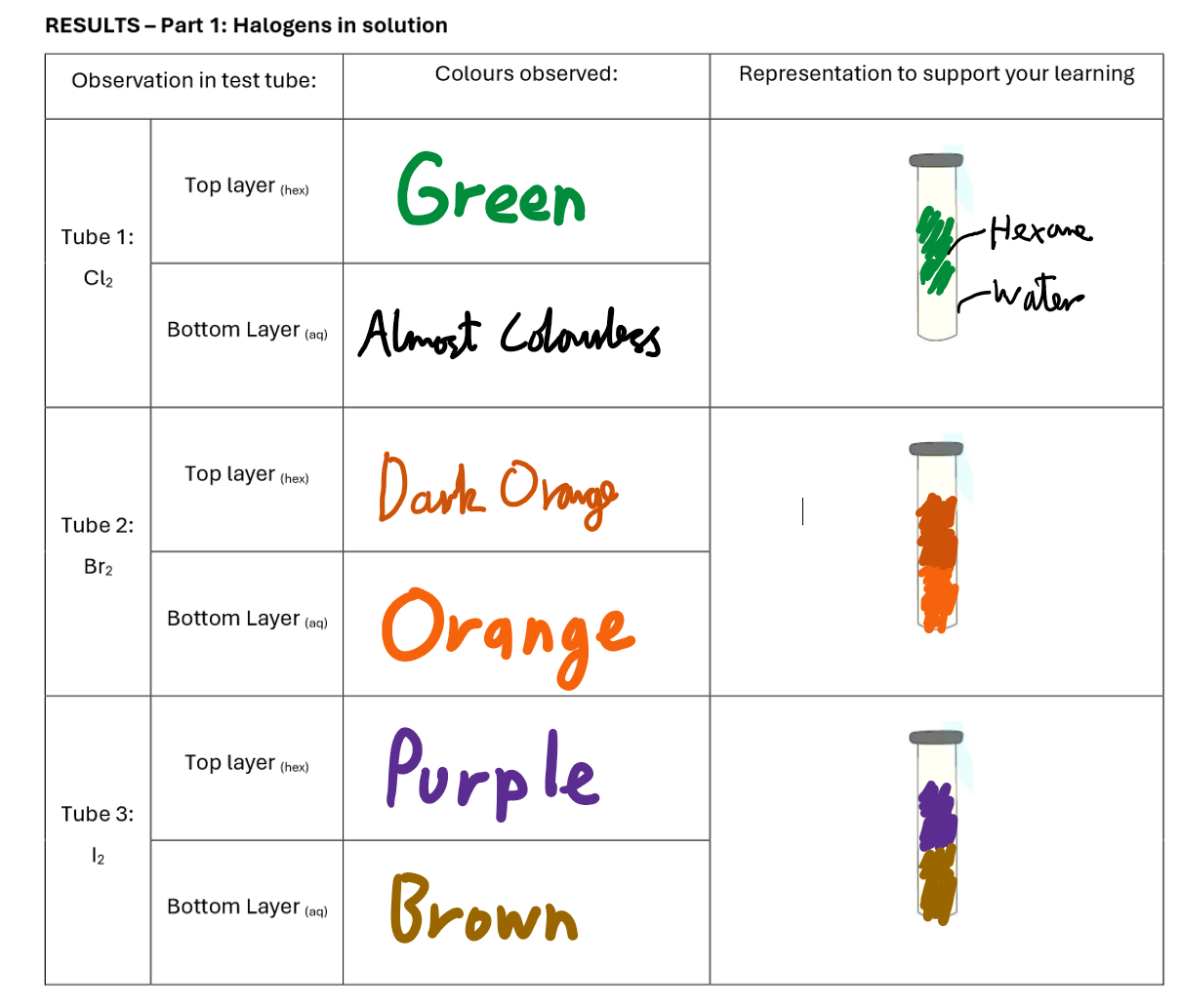
Halogen Displacement Reactions Results
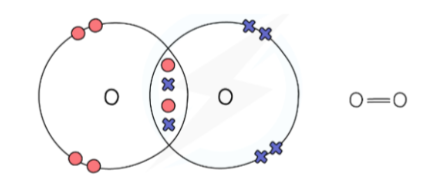
What is a covalent bond?
A shared pair of electrons between two neighbouring nuclei.
Are covalent bonds strong?
Yes
Covalent Bond Dot and Cross Diagram
What is the structure of covalent bonds called?
Simple molecular
Simple molecular structures have…
LOW melting and boiling points.
Weak intermolecular forces.
Why do they have low melting and boiling points?
There are only weak intermolecular forces which do not need much energy to overcome.
Allotropes of carbon
Diamond, Graphite and C60 Fullerene
Which of these have giant covalent structures?
Diamond and graphite
Giant covalent structures have…
High melting points.
Why do Giant Covalent Structures have high melting points?
Because lots of energy is requires to break the many strong covalent bonds.
Do covalent compounds usually conduct elctricity?
No, as they have no delocalised electrons.
Graphite is an exception.
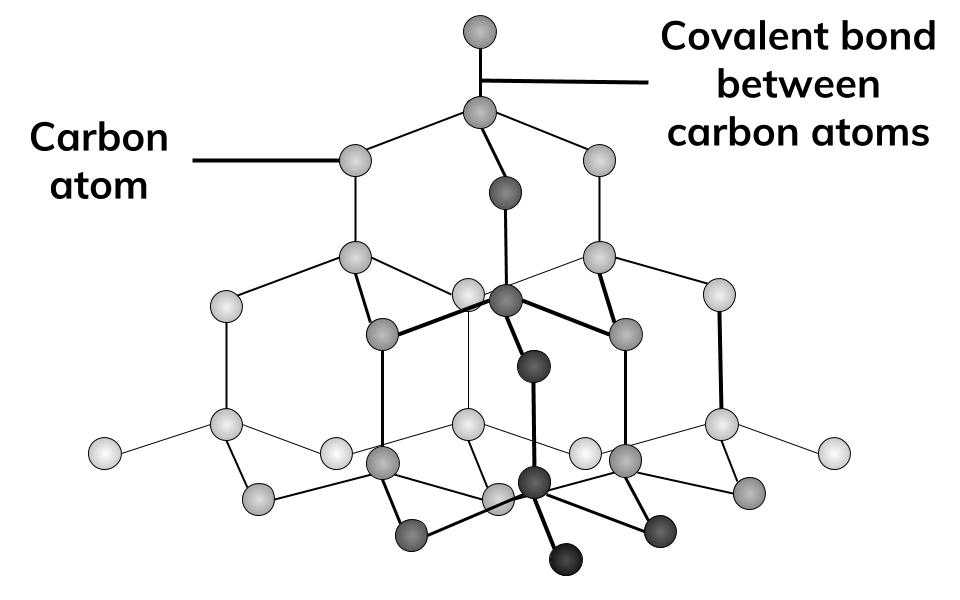
Structure of Diamond
Giant Lattice
Diamond is very hard because:
Each carbon atom is contently bonded to four other carbon atoms.
The Covalent bonds are very strong.
Diamond does not conduct electricity because…
Each atom is using all of its electrons to form four covalent bonds, so there are no delocalised electrons.
Graphite is…
Soft and slippery.
What is the structure of graphite?
Giant Lattice
Graphite forms in layers that are free to slide over each other because there are only weak forces between the layers.
Graphite can…
Conduct electricity and heat.
Graphite can conduct electricity and heat because…
Each carbon atom only forms three bonds. This leaves some delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry charge.
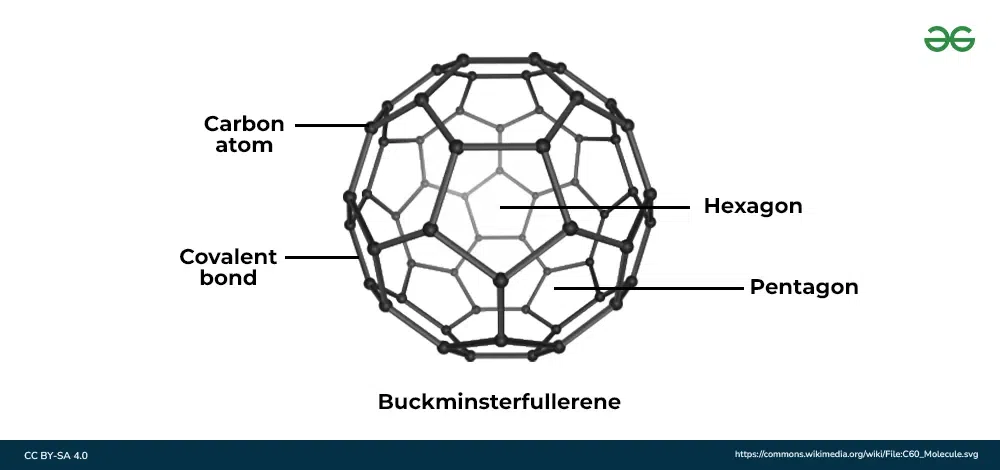
C60 Fullerne Structure
Simple molecular structure.
C60 Fullerne has…
A low melting and boiling point because there are only weak intermolecular forces which require little energy to overcome.
C60 Fullerene is also…
Soft and slippery
Use of C60 Fullerne:
Drug delivery due to its hollow structure.
Graphite information
Giant Lattice Structure (layers)
3 covalent bonds formed by each carbon atom plus 1 weak attraction between the layers of carbon atoms
Soft, shiny, grey
Conducts electricity
High melting and boiling point
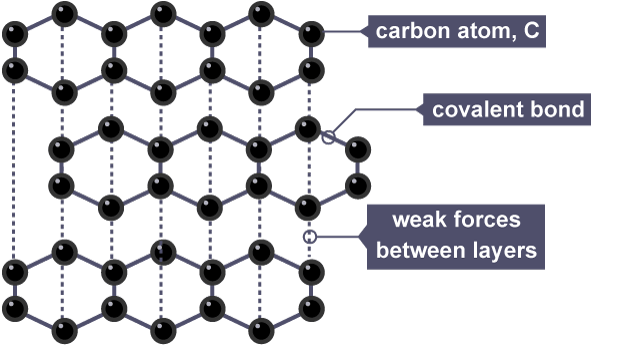
Diamond Information:
Giant Lattice Structure
4 covalent bonds per carbon atom
Very high boiling and melting point
Hard, transparent
Can not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)
Each carbon atom bonds in a tetrahedral shape
C60 Fullerene Information:
Simple molecular structure
Each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
High melting and boiling point
Bonds between molecules are weak
Can not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)
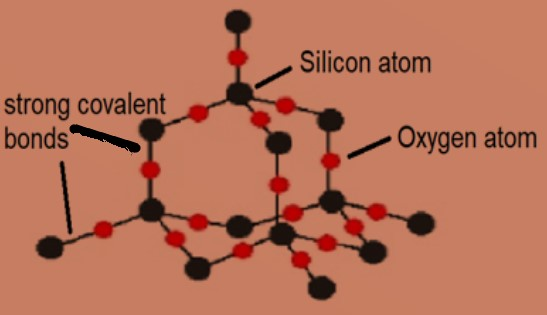
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon forms 4 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds
Giant Structure
High melting and boiling point
Can not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)
Atoms which lose electrons become
Positive Ions (Cations)
Atoms which gain electrons become
Negative Ions (Anions)
Pb
Cu
Fe
Ag
Zn
2+
2+
2/3+
+
2+
Ionic bonding is the
Strong electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions.
Ions compounds have a
Giant Ionic Lattice Structure
Dot and Cross Diagram
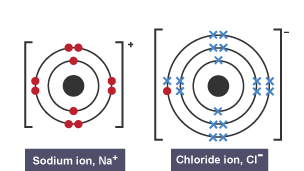
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
This is due to their strong electrostatic forces of attraction, which take a lot of energy to overcome.
Ionic compounds can not
Conduct electricity as solids because the ions are fixed and not free to move around.
Ionic compounds can
Conduct electricity when molten (melted) or dissolved in water because the ions are free to move around.
Test for Hydrogen
Hold a burning splint to mouth of test tube containing gas. Listen for squeaky pop.
Test for Oxygen
Relights a glowing splint
Test for Carbon Dioxide
Bubble through lime water (Calcium Hydroxide). Turns cloudy.
Test for Ammonia - ONLY ALKALI GAS
Turns Damp RED litmus BLUE.
Test for Chlorine
Bleaches damp litmus paper.
Test for Water
Boils at exactly 100 degrees.
What Flame is needed for a flame test?
A roaring blue flame as safety flame already has a colour.
Result for these Cations:
L²+
Na+
K+
Ca²+
Cu²+
Red
Yellow
Lilac
Orange/Red
Blue/Green
NH⁴+ Test
Add sodium hydroxide solution and warm. Turns damp red litmus paper blue.
Test for
Cu²+
Fe²+
Fe³+
Add sodium hydroxide.
Colour of metal hydroxide precipitate formed:
Blue
Green
Brown
Test for
Cl-
Br-
I-
Add dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate solution.
Colour of silver halide precipitate:
White
Cream
Yellow
Test for SO4²-
Add dilute hydrochloric acid and barium chloride solution:
White barium sulphate precipitate formed.
Test for CO3²-
Add dilute hydrochloric acid:
Bubble the gas given off through limewater. It should turn cloudy.
Acid is used to
destroy CO3²- ions
Why are alkali metals stored under oil?
Because they react very vigorously with oxygen and water, including moisture in the air
General equation for the reaction of Alkali Metals with oxygen
Metal + Oxygen --> Metal oxide
What is the balanced equation for the reaction of sodium with oxygen? (Include state symbols)
4Na(s) + O2(g) --> 2Na2O(s)
General equation for the reaction of alkali metals with water
Metal + Water --> Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
What is the balanced equation for the reaction of potassium with water? (Include state symbols)
2K(s) + 2H20(l) --> 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
Why do all the Alkali Metals react in a similar way with water?
They all have 1 electron in their outer shell
What would you observe when lithium metal reacts with water containing universal indicator solution? (4 points)
Lithium moves slowly on the surface of the water
Fizzing
The metal gets smaller and eventually disappears
Universal indicator turns purple
What would you observe when sodium metal reacts with water containing universal indicator solution? (5 points)
Sodium moves quickly on the surface of the water
Fizzing
Sodium melts to form a ball
The metal gets smaller and eventually disappears
Universal indicator turns purple
What would you observe when potassium metal reacts with water containing universal indicator solution? (6 points)
Potassium moves very quickly on the surface
Fizzing
Potassium melts to form a ball
A lilac flame
The metal gets smaller and eventually disappears
Universal indicator turns purple
Why does the universal indicator turn purple?
An alkaline solution of the metal hydroxide is formed
Which ion causes the solution to become alkaline?
The hydroxide ion (OH-)
What is the trend in reactivity down Group 1
Reactivity increases as you go down the group
Why does reactivity increase down Group 1?
Down the group, the number of electron shells increases.
The outer electron is therefore further away from the nucleus and is lost more easily. There is more shielding as you go further down the group.