2.4 Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
What experiences a force in a magnetic field?
Magnets, magnetic material, moving charges and current carrying conductors
2
New cards
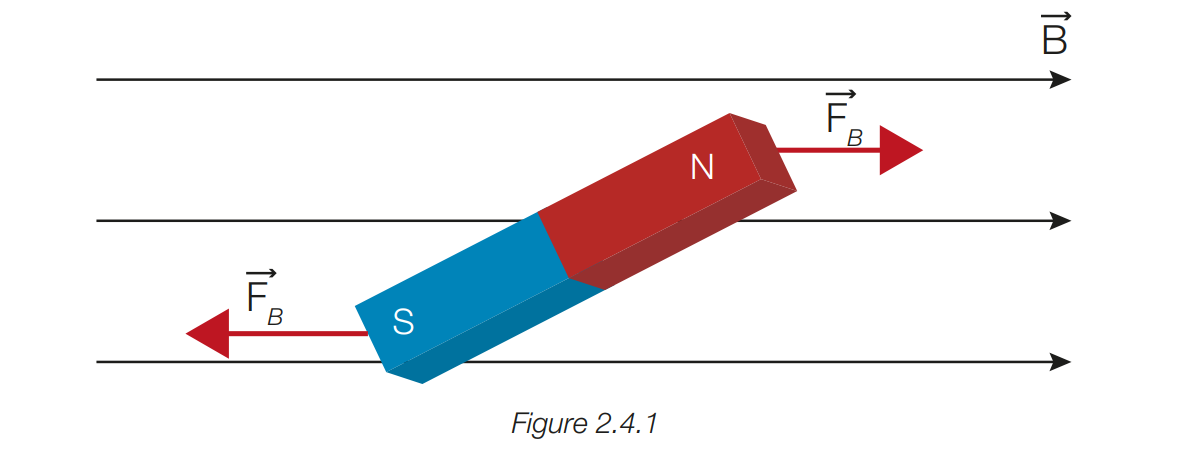
describe the forces experienced by each end of a bar magnet while in a magnetic field
the north pole experiences a force parrallel to the magnetic field while the south pole experiences a force which is antiparrallel to the magnetic field.
3
New cards
What is the force experienced by a straight current carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field dependant on?
the current flowing through the conductor, the strength of the magnetic field, the length of the straight current carrying conductor, and the angle the straight current carrying conductor makes with the magnetic field.
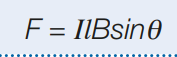
4
New cards
At what angle must a current element be placed at with the magnetic field to experience 0 force due to the magnetic field and why?
when the angle is 0 or 180, and therefore the current element is parrallel or anti-parrallel to the magnetic field. This is because the sin of 0 and 180 is 0.

5
New cards
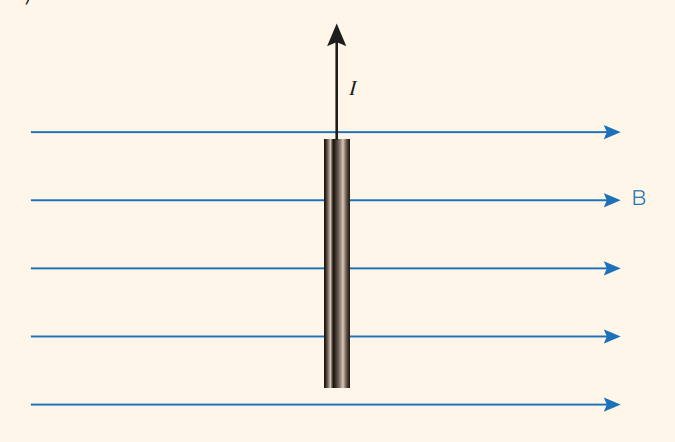
At what angle is a maximum force due to the magnetic field experienced by a current element and why?
When the current element is perpendicular to the magnetic field, and therefore makes an angle of 90 or 270. This is because sin of 90 is 1 and 270 is -1.
6
New cards
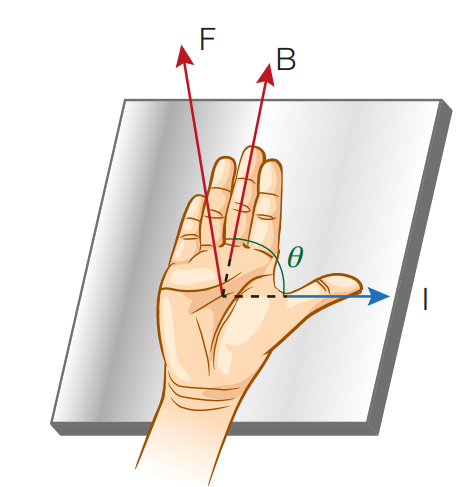
Describe how the right hand rule can be used to determine the direction of the force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field, or the magnetic field or the conventional current given two of three are known.
* the thumb points in the direction of the conventional current
* the outstretched fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field
* the force acting on the conductor is perpendicularly away from the palm of the hand
* the outstretched fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field
* the force acting on the conductor is perpendicularly away from the palm of the hand
7
New cards
does a stationary charge in a magnetic field experience a force?
no
8
New cards
decribe the force experienced by a charged particle moving parrallel or anti parrallel to a magnetic field?
no force as sin of 0 is 0
9
New cards
decribe the force experienced by a charged particle moving perpendicular to a magnetic field?
maximum force as sin of 90 is 1
10
New cards
describe use of right hand rule to determine the direction of the force acting on a charged particle moving through a magnetic field
is the same as with a current carrying conductor except the thumb points in the direction of the charge movement not conventional current.
11
New cards
Descibe how a magnetic force can provide the centripetal accelleration necessary for a charged particle to experience uniform circular motion?
* a moving charged particle whose direction is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field it moves through will experience a force of constant magnitude at right angles to its velocity * therefore the charge changes direction without a change in speed * the magnetic force provides the centripetal accelleration required for uniform circular motion
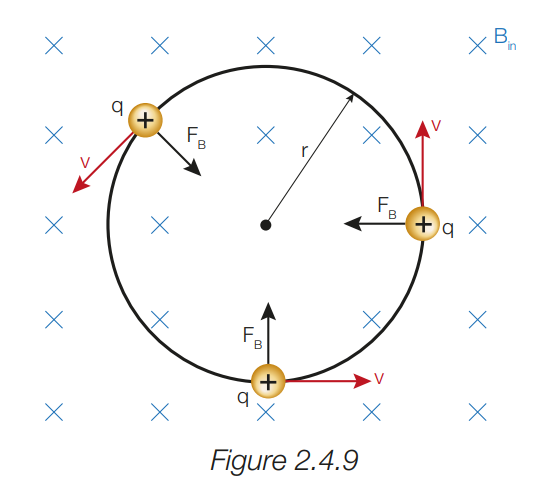
12
New cards
Derive the formula for the radius of the circular path of a charged particle moving at right angles to a uniform magnetic field.
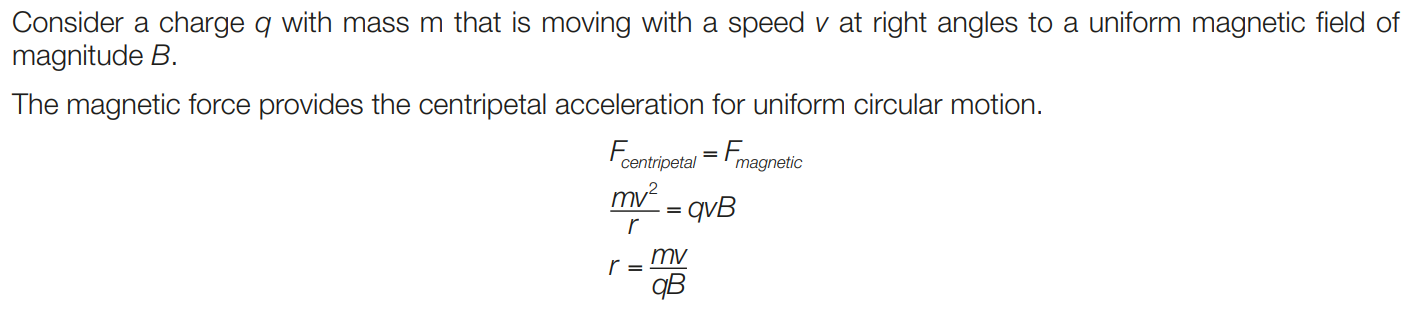
13
New cards
What is a cyclotron?
Devices used to accellerated charged particles (usually protons) or ions to high speeds. These are then used to collide with other nuclei and experience nuclear reactions to form radioisotopes. These have many applications in medicine and industry and therefore cyclotrons are kept in hospitals. This allows for radioactive materials, such as fluorine-18 which is used in PET scans, to be produced when needed.
14
New cards
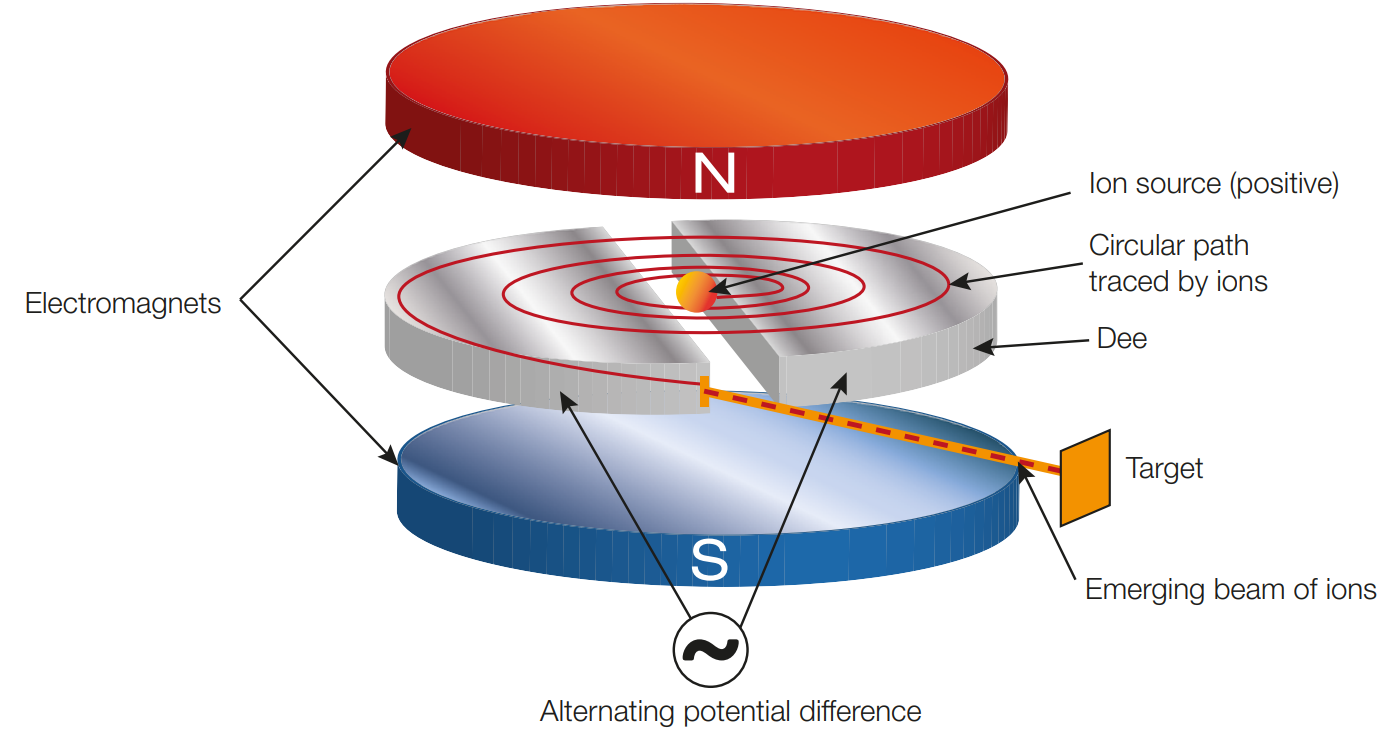
Explain how cyclotrons utilise electric fields and magnetic fields
* Consists of an electromagnet placed above and below two dees (hollow D-shaped copper conductors)
* Due to the elecromagnet, a uniform magnetic field is produced perpendicular to the the plane of the dees
* The Dees are seperated by a gap, and charged particles are accellerated across this gap by a uniform electric field created by the potential difference between the dees which performs worl on them
* once the particles move across the gap between the dees the magnetic field supplies magnetic force and thus centripetal accelleration, causing them to turn and return to the electric field.
* the potential difference of the dees is alternated to reverse the electric field and the ion travels back to the other dee, entering it with a greater speed
* the process repeats with each time the ions pass through the dees their radius increases
* by the time they exit they have accumulated a large amount of kinetic energy and thus speed
* Due to the elecromagnet, a uniform magnetic field is produced perpendicular to the the plane of the dees
* The Dees are seperated by a gap, and charged particles are accellerated across this gap by a uniform electric field created by the potential difference between the dees which performs worl on them
* once the particles move across the gap between the dees the magnetic field supplies magnetic force and thus centripetal accelleration, causing them to turn and return to the electric field.
* the potential difference of the dees is alternated to reverse the electric field and the ion travels back to the other dee, entering it with a greater speed
* the process repeats with each time the ions pass through the dees their radius increases
* by the time they exit they have accumulated a large amount of kinetic energy and thus speed
15
New cards
Derive the formula for the period of ions in a cyclotron
note speed of ions does not affect their period in the cyclotron
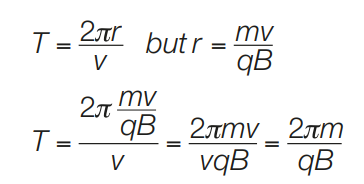
16
New cards
how often is the potential difference applied across the dees reversed?
every half revolution, therefore half the period.

17
New cards
Derive the formula for the kinetic energy of ions emerging from the cyclotron
* kinetic energy is indedependant ofthe potential difference across the dees
* larger potential difference transfers more kinetic energy to the ions, they travel faster, and in circular paths of greater radii
* therefore ions cross electric field fewer times before emerging from cyclotron than if the potential difference were lower
* therefore the ions gain the same amount of kinetic energy before exiting as if the dees had a smaller potential difference
* kinetic enegry is only dependant on the magnetic field strength, and the radius of the final circular path, the radius of the cyclotron
* larger potential difference transfers more kinetic energy to the ions, they travel faster, and in circular paths of greater radii
* therefore ions cross electric field fewer times before emerging from cyclotron than if the potential difference were lower
* therefore the ions gain the same amount of kinetic energy before exiting as if the dees had a smaller potential difference
* kinetic enegry is only dependant on the magnetic field strength, and the radius of the final circular path, the radius of the cyclotron
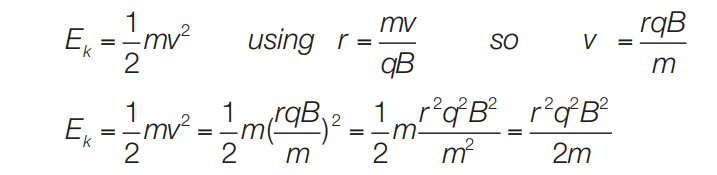
18
New cards