Electromagnetism
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What causes electromagnetism to occur?
This could either be a wire carrying currents , or it could be electrons whizzing around the nuclei. When this interference with a magnetic field, electromagnetic force is experienced
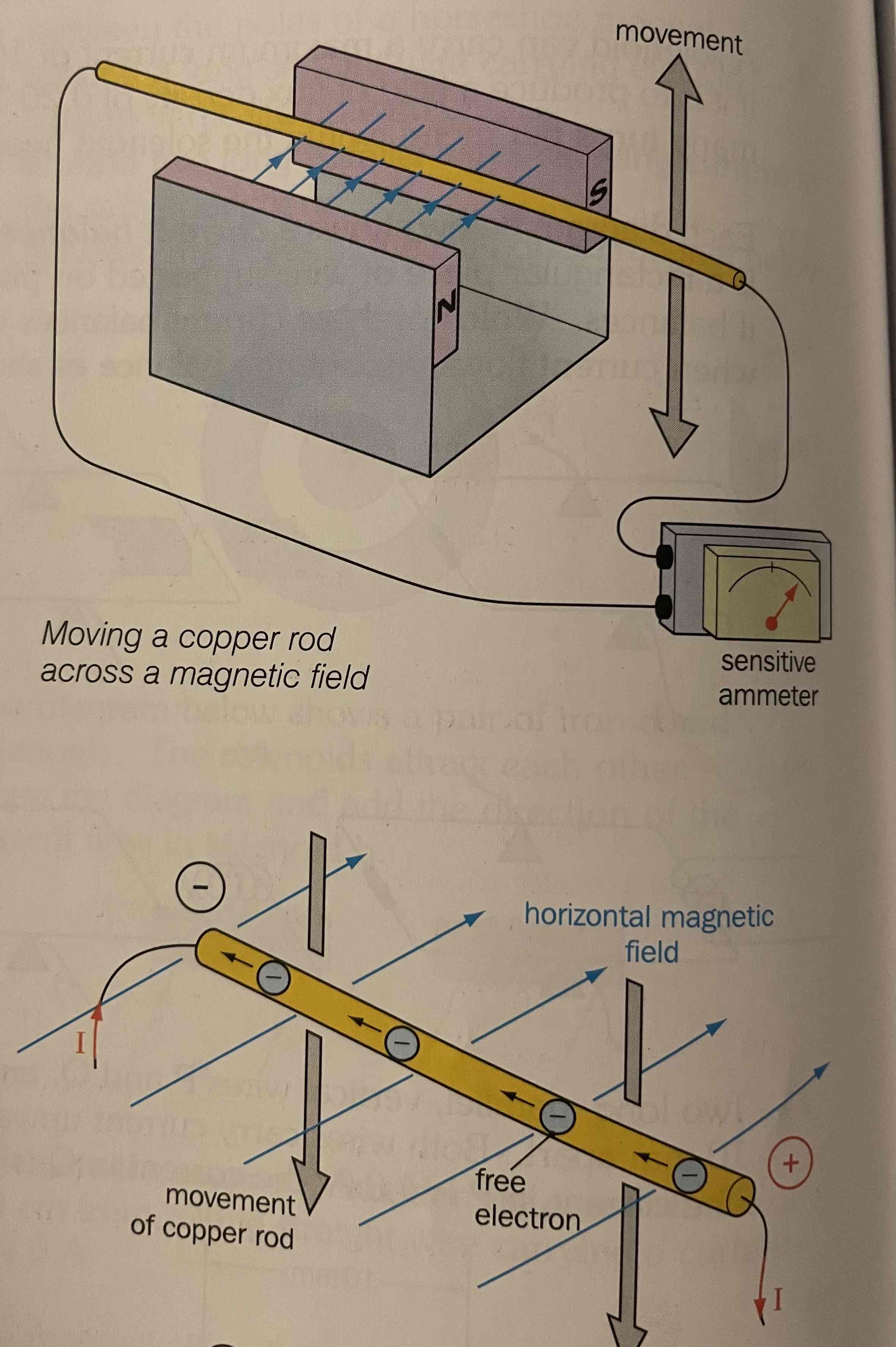
What happens if you move a conductive material through a magnetic field?
As it cuts the field, it gets a brief current reading on the ammeter. Since the field is going left to right and the force applied to the material goes down, the velocity of the electrons goes into the paper, so conventional currents comes out of the paper.Electrons make a separation of charge (a pd has been induced)
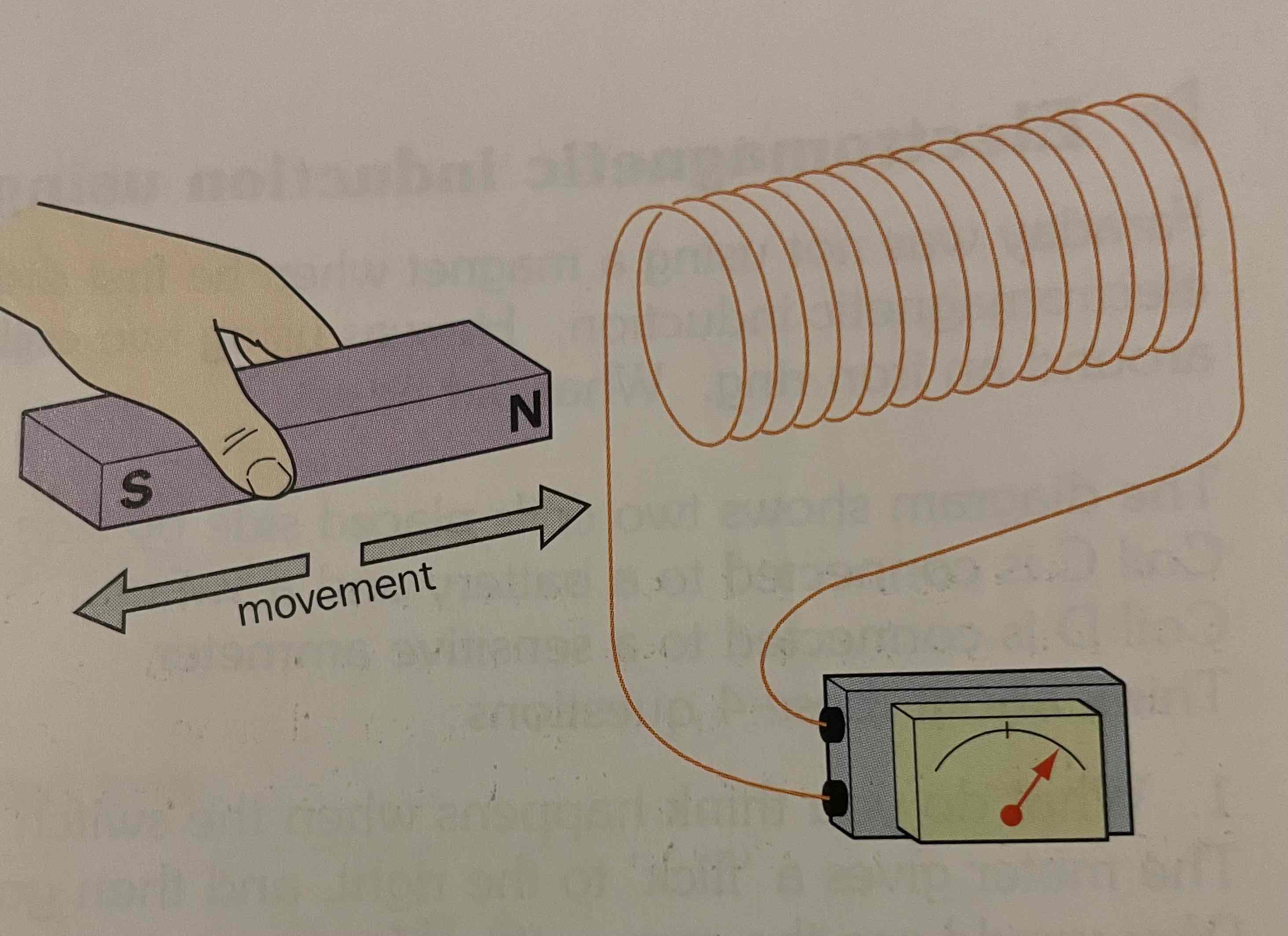
Faraday model for electromagnetic induction
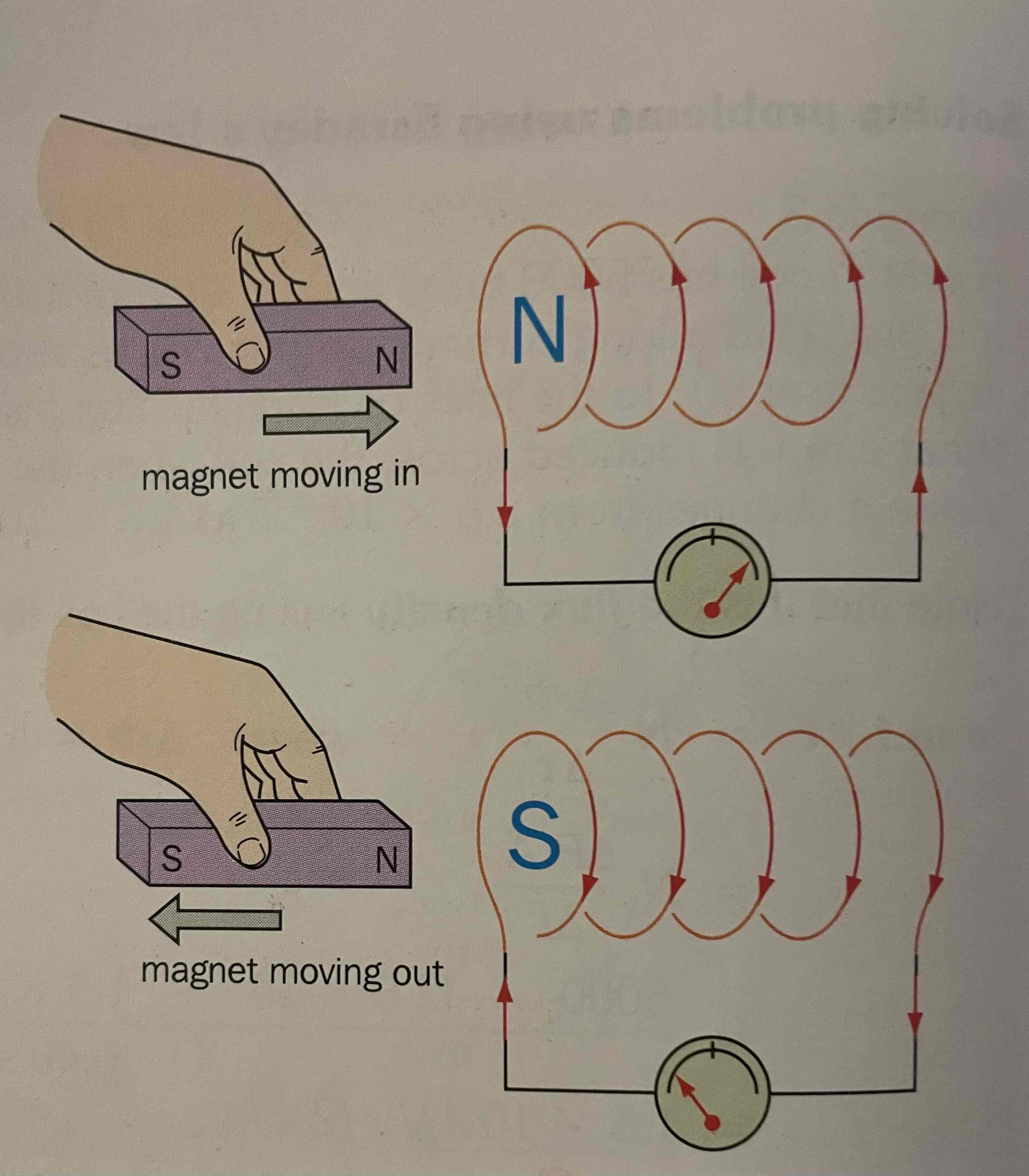
This moves a bar magnet into a coil, connected to an ammeter, we experience a flicker in current, but when it is still, or fully inside coil, there’s no current detected.An emf is induced due to the repulsion of the separation of charge- it’s trying to minimise the effect of the change in B
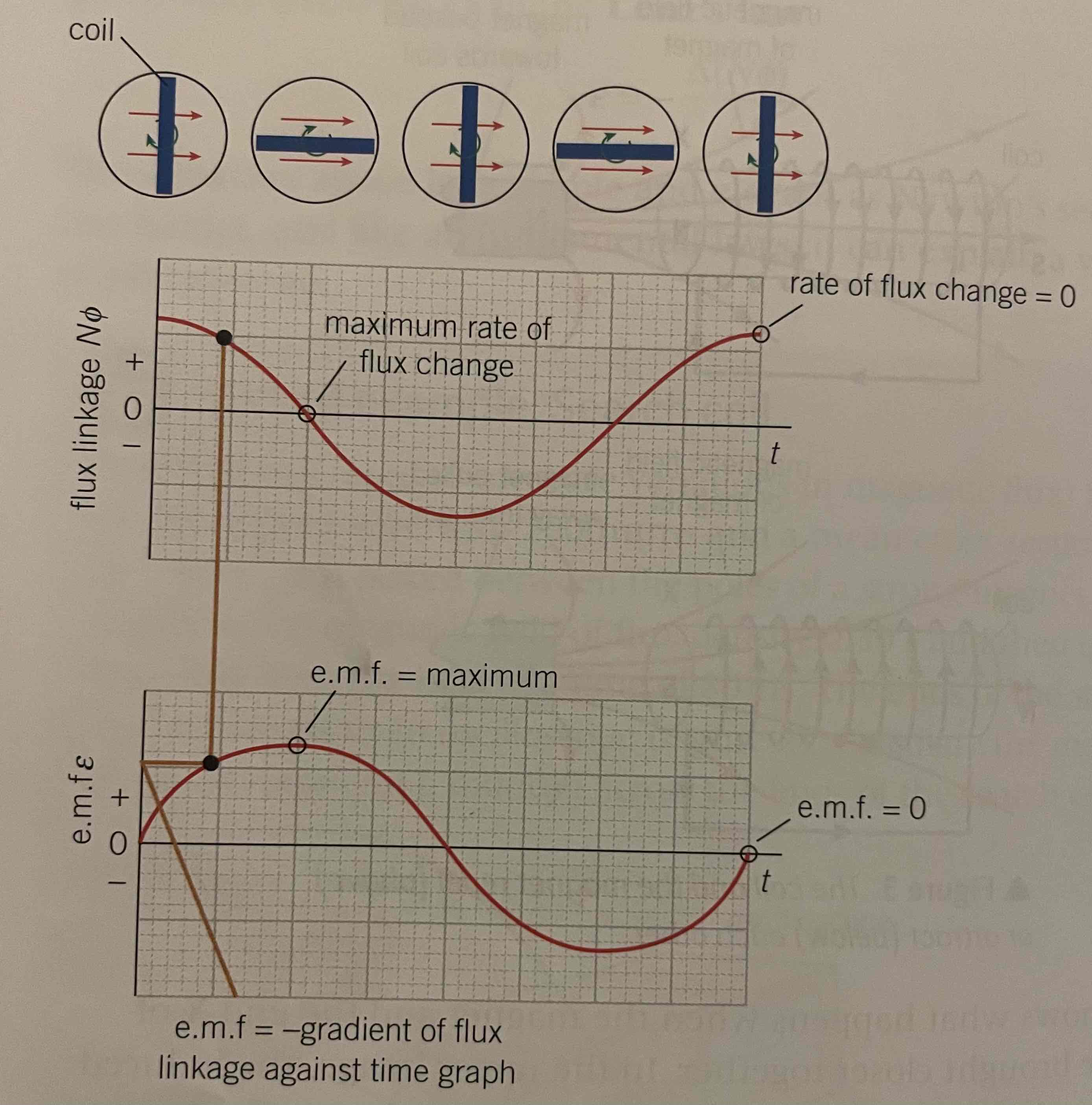
When is emf induced?
1: a conductor cutting through lines of flux
2: a change in flux linkage of a coil
How to increase the size of the emf
Stronger magnet, more turns on coil, greater cross section area, move magnet faster
What us magnetic flux vs flux linkage
Flux is the number of lines of flux in a given area and linkage is the same when it passes a coil. They are measured in weber Wb. Resolve by timesing by cos(theta) to get parallel lines
(N)phi= (N)BA
What causes a change in flux linkage?
Change in magnetic flux density or a change in area or more coils
How can we link Faradays Law and Len’s law?
F: Magnitude of induced emf is equal to the rate of change of flux (linkage)
L: direction of induced EMF will oppose the change in flux that made it.
emf= -(N) change in phi/ change in time
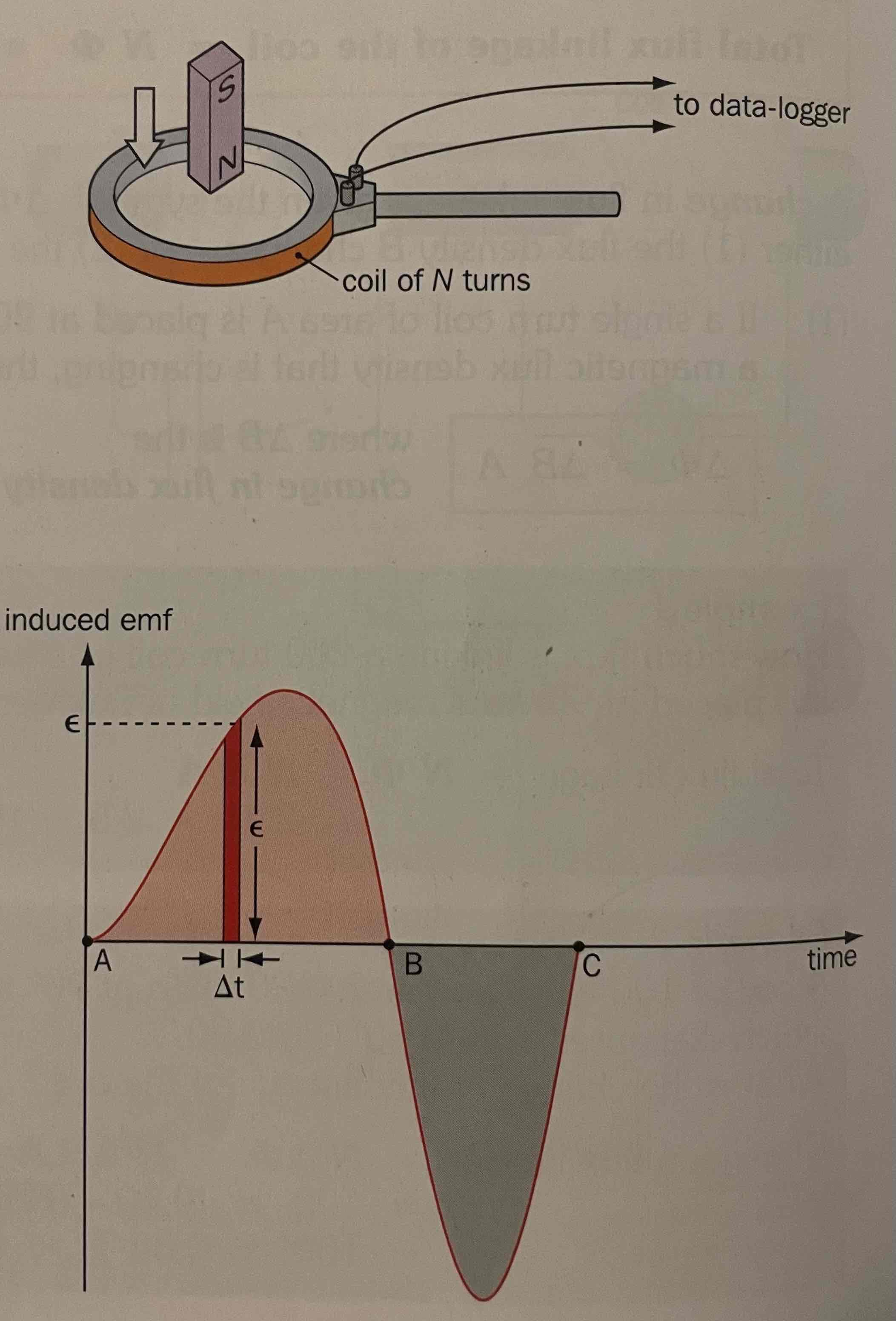
Explain the graph of emf-time when we drop a bar magnet through a coil with N turns
sinusoidal curve. areas in each curve are equal: it shows magnitude of emf induced .second half of the curve is slim and thin since the rate of change increases as it is at a higher velocity at the bottom of the coil (gravity) max emf induced is greater.
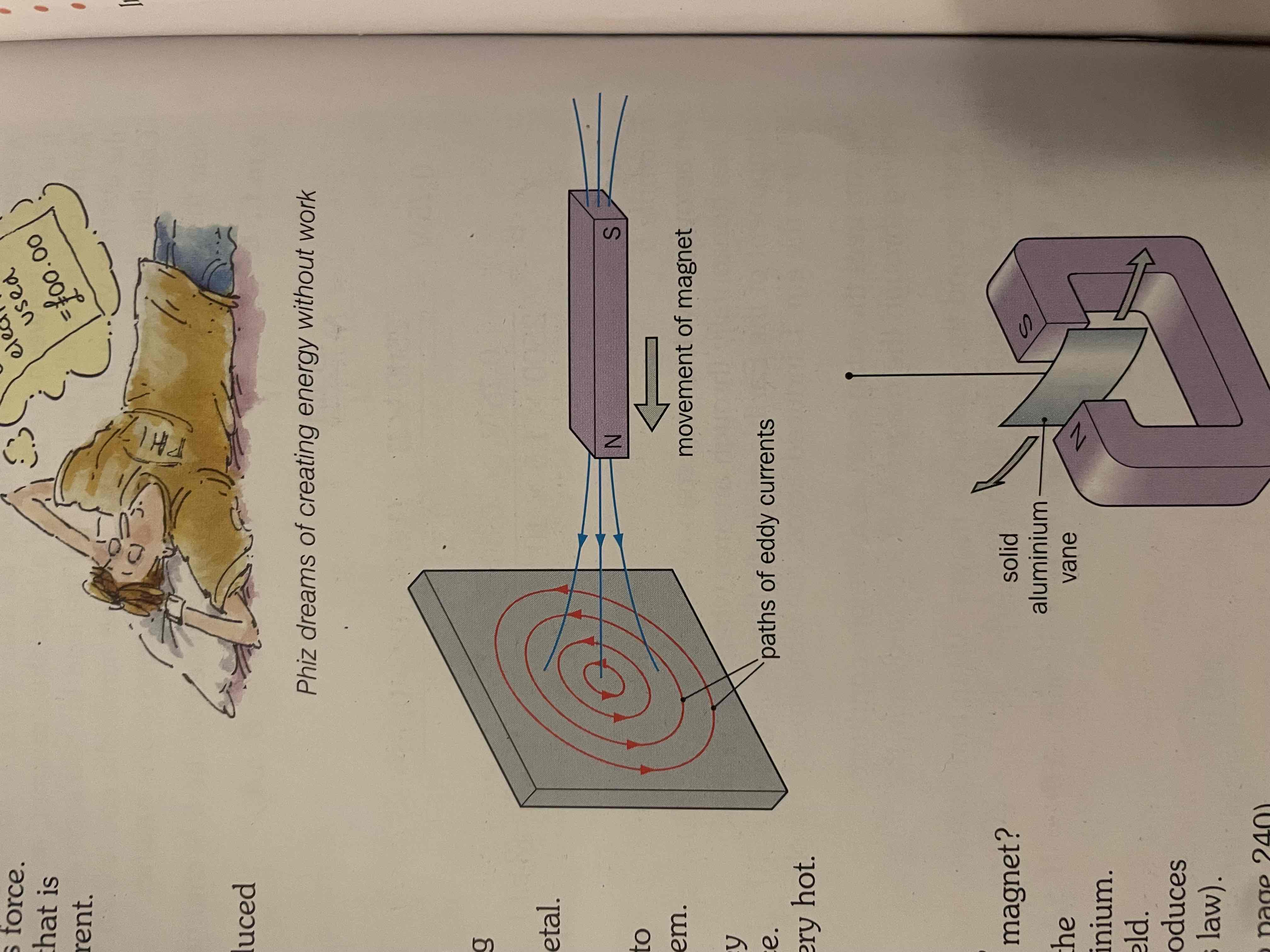
what are eddy currents ?
when a metal is moved in magnetic field, eddy currents oppose direction to cancel out change in flux. these are massive since resistance is low
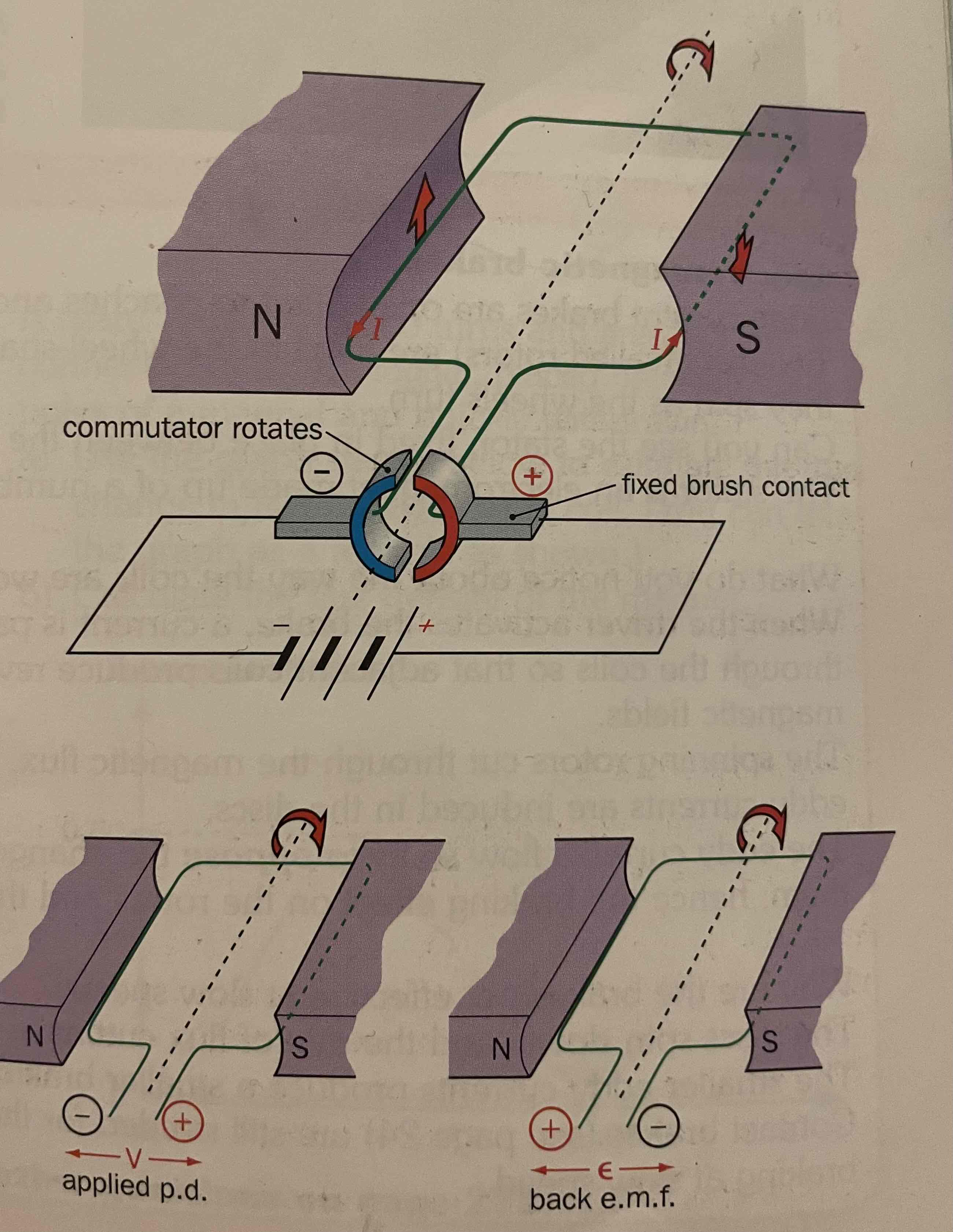
How do DC Electric Motors work?
This converts electrical energy to kinetic energy. Split ring communicator reverses direction of current every half turn. Change in flux= emf (tries to stop turning motor; the ‘back emf’)
If we put a load onto the motor, it turns slower, giving lower emf and increases current
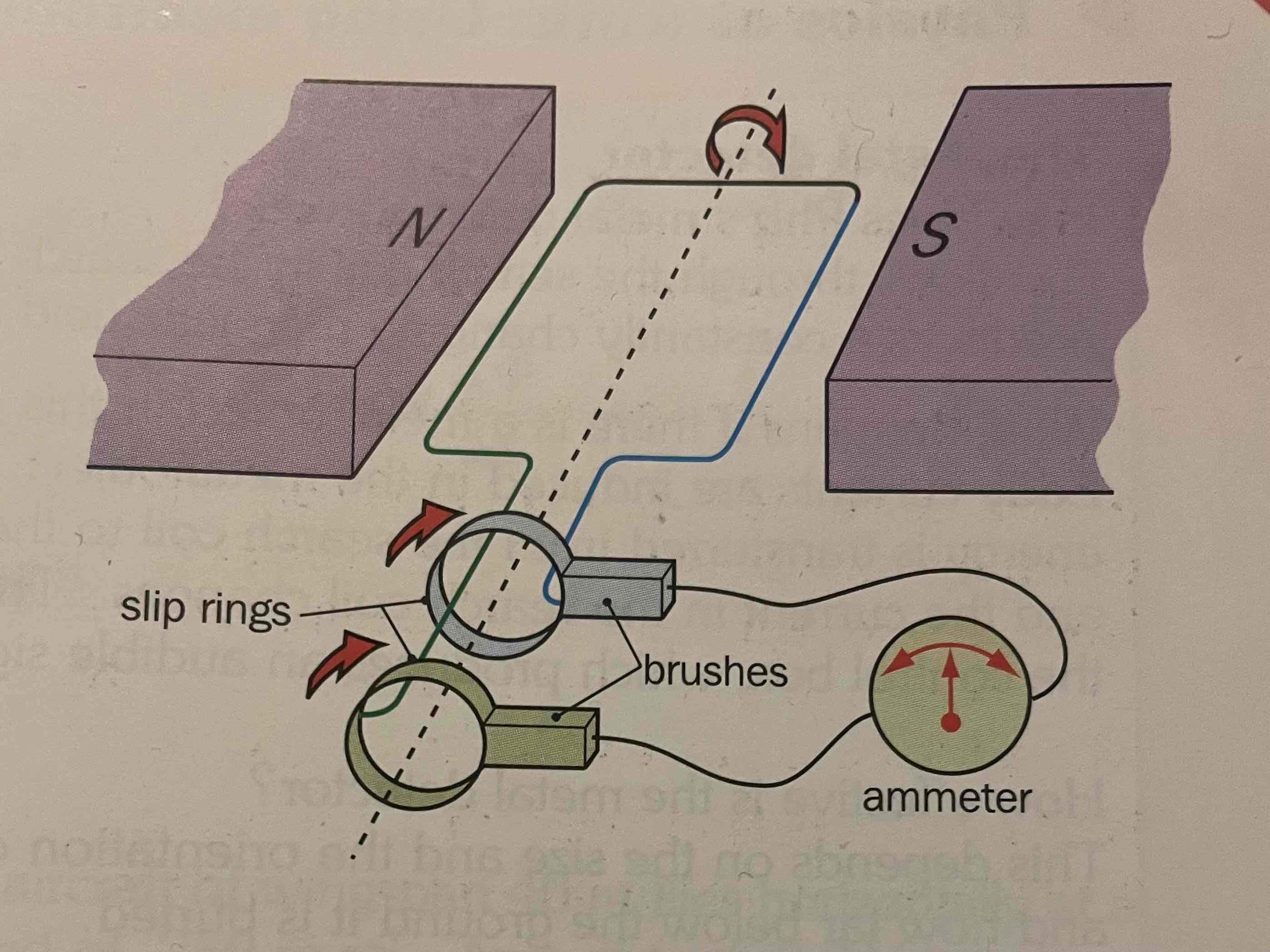
How to AC Generators work?
Only these can be transformers, turning kinetic energy to electrical energy. It rotates showing change in flux detected by the carson brushes. Ammeter keeps changing (AC). We can vary peak emf by having more turns, increasing field strength, increasing cross section area of coil