CH16: ALDEHYDES & KETONES
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
The _____ is characterized by a carbon atom forming a double bond with an oxygen atom, accompanied by two single bonds.
carbonyl group
name of C on carbonyl group
carbonyl group
name of O on carbonyl group
carbonyl oxygen
carbonyl group adopts a ____ shape, with all 3 bond angles around the atoms measuring approximately ____degrees.
planar triangular
120°
double bond (C=O) is polar (covalent bond) in nature, resulting from the ______
electronegativity disparity — carbonyl oxygen holds higher electron density (δ-) while the carbonyl carbon is relatively electron-deficient (δ+)
The C=C is more polar than the single bond C-C due to there being _____.
more e- w/in the double bond (4) vs. the single bond (2). The e- are pulled towards the O atom and the C becomes less negative!
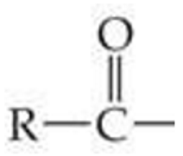
ID this structure
acyl group
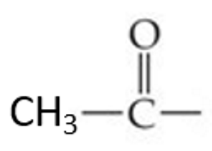
ID this structure
acetyl group
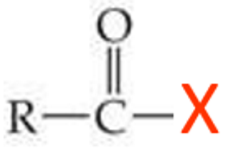
ID this structure
carbonyl compound
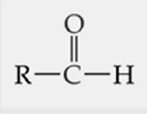
ID this structure
aldehyde
An acyl group consists of _____
an R group bonding to the carbonyl group. R may represent hydrogen, alkyl or aryl.
An essential acyl group in the realm of biochemistry is _____
the acetyl group, where R specifically represents a methyl group.
5 families of carbonyl compounds
aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, amide
The smallest ketone is _____
acetone - very good solvent; used in nail care routines
what are the two distinct groups of carbonyl compounds?
aldehydes and ketones
carboxylic acid, ester, amide
aldehyde and ketones have these similar properties:
X is either a H or C atom
C—X is a non-polar covalent bond
carboxylic acid, ester, amide have these similar properties
X is an EN element and either an O or N atom
C—X is a polar covalent bond
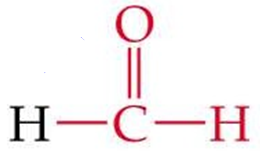
ID this structure by its common name
formaldehyde
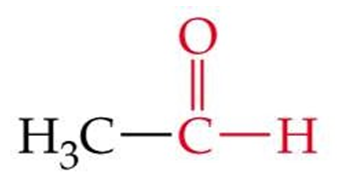
ID this structure by its common name
acetaldehyde
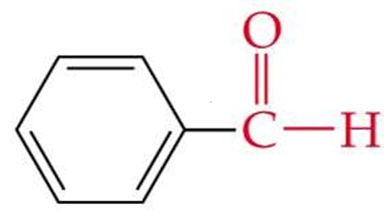
ID this structure by its common name
benzaldehyde
An aldehyde contains a carbonyl group (C=O) with the carbonyl carbon bonded to a _____
hydrogen atom and either another hydrogen, an alkyl group, or an aryl group.
The molecular formula of aldehyde is _____
R-CHO (not R-COH, that is Alcohol!).
common and IUPAC name of the smallest aldehyde
formaldehyde
methanal
common name of the second smallest aldehyde
acetaldehyde
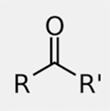
ID this structure
ketone
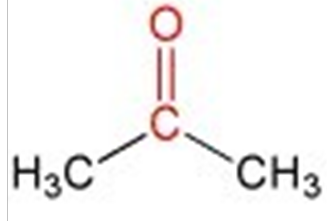
ID this structure
acetone
In a ketone, the carbonyl group is attached to two organic groups, which can be _____
alkyl, aryl, or their combinations but not a hydrogen atom — these two groups can be the same or different.
The general formula of ketones is _____.
RCOR’
Small aldehydes are often known by their common names, which end in_____.
-aldehyde.
IUPAC naming of simple aldehydes: the final -e of the name of the alkane is replaced by___,
-al
IUPAC naming of simple aldehydes: The aldehyde functional group is always at _____
the end of a carbon chain. Therefore, we do not use 1 to indicate its position is on carbon number 1.
Common Names of Simple Ketones: Consider the smaller alkyl as the ____ and the larger alkyl as the ____.
substituent
parent
IUPAC Names of Simple Ketones: Number the alkane chain begins at the _____
end nearest to the carbonyl group.
IUPAC Names of Simple Ketones: Replacing the final -e of the corresponding alkane name with _____
-one (pronounced own).
IUPAC Names of Simple Ketones: Number to indicate the location of the _____.
ketone group
Naming Aldehydes and Ketones in the Same Molecule: Molecules, which contain both aldehyde and ketone groups, are named as _____.
aldehydes (due to higher ranking) with the prefix of a ketone substituent being "oxo".
Naming Aldehydes and Ketones in the Same Molecule: the aldehyde gets ___ and the ketone gets ___.
no number to indicate location — since it is always at the end and therefore “1”.
does get a location number!
The root names of aldehydes and ketones are derived from the _____
longest continuous chain of carbon atoms that bonds the functional groups.
The carbonyl group is _____, resulting in ____. Consequently, the boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are ____.
polar
dipole-dipole interactions within aldehydes and ketones.
higher than alkanes of similar size
H must bond with an ____ in order to h-bond
EN atom
Given that aldehydes and ketones do not establish hydrogen bonds within their own kind, their boiling points typically ____.
fall below those of similarly sized alcohols.
boiling points ranked amongst ketones, aldehydes, alkanes, and alcohols, plus h-bonding ability
[highest BP]…Alcohol (h-bonding ability) > Aldehyde/Ketone (nope) > Alkane (nada)…[lowest BP]
Boiling points of ketones are _____ than aldehydes
higher
ketones are more or less polar than aldehydes? why?
more polar — two electron-donating alkyl groups in ketones increase the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon, strengthening dipole–dipole interactions.
which has the stronger dipole-dipole and LDFs, aldehydes or ketones?
ketones! = higher BPs!
recite which intermolecular forces are contained in alkanes, aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols
Intermolecular forces | Alkane | Aldehyde / Ketone | Alcohol |
London forces | + | + | + |
Dipole-dipole |
| + | + |
Hydrogen bonding |
|
| + |
The polar carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones allows their oxygen to form ____.
hydrogen bonds with water.
Ketones are more polar and water soluble than aldehydes due to _____.
their electron-rich R groups.
Small aldehydes and ketones are soluble in water, but solubility decreases with ____
increasing carbon chain length (increasing nonpolar parts), becoming insoluble for compounds with more than 5-6 carbons.