chem midterm study guide
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
number of naturally occurring elements
90
number of lab-created elements
28
most abundant element in earth’s crust
oxygen
AMU is a unit of measurement equal to
the mass of one proton
metals are
good conductors, shiny, malleable, ductile, corrosive
metalloids are
shiny or dull, semi-good conductors, ductile, malleable
the metalloids include
B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, [Po, At]
![<p>B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, [Po, At]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/292aa24f-a716-44e6-9683-c6c8a4b73fd6.jpeg)
nonmetals are
poor conductors, not ductile/malleable, brittle, dull, gases
families/groups are
columns of elements w similar but not identical properties w same number of valence electrons
periods are
rows of elements w different properties (first is extremely active solid; last is inactive gas)
hydrogen
has no family, sits above alkali family
alkali metals
are the first column, all have 1 valence electron, shiny, clay consistency, easily cut w knife, most reactive (violent w water), always naturally bonded w another element
reactive elements
bond easily w other elements to form compounds, are reactive if they do not have a complete valence electron level (rule of octet)
alkaline earth metals
are group 2, always combined w other elements in nature (typically salt)
transition metals
groups 3-12, all elements in B families, good conductors, brightly colored, 1-2 valence electrons (more often 2), in d block (up to 10 electrons) so cannot lose enough to attain noble gas configuration, combine w oxygen to form oxides, properties do not fit w any other families
boron/earth metals
group 13, boron is metalloid, all others are metals, includes aluminum (most abundant metal in earth’s crust)
carbon/tetrel
group 14, carbon is nonmetal, all others metals/metalloids, carbon is “basis of life”—organic chemistry
nitrogen/pnictogen
group 15, nitrogen makes up 78% of earth’s atmosphere, contains metals/metalloids/nonmetals, tend to share valence electrons when bonding
oxygen/chalcogen
group 16, mostly shares electrons when bonding, oxygen is extremely active and combines w nearly all elements
halogen
group 17, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, astatine, iodine, most active nonmetals, never found free in nature, form salts w alkali metals
noble gases
group 18, colorless, unreactive gases, inactive bc outermost energy level is full, called inert, all found in small amounts in atmosphere
rare earth elements/inner transition metals
30, lanthanides & actinides, one in lanthanides and most in actinides are trans-uranium (synthetic)
liquid metals:
bromine & mercury
gases are all
nonmetals
all actinides are
radioactive
molecules of one substance are called
pure
representative elements are
groups 1, 2, 13-18
si base unit for mass
kilogram
precision
how close multiple measurements are to each other
accuracy
how close a measurement is to the accepted/correct value
percent error
|experimental value - accepted value|/accepted value*100
Law of Definite Proportion
a given compound has a fixed ratio of elements
Law of Conservation of Mass
matter is neither created nor destroyed (Lavoisier)
deposition
gas to solid
sublimation
solid to gas
Periodic Law
elements organized by atomic number fall into recurring groups and are a function of their atomic number
second most abundant gas in the atmosphere
oxygen
all are diatomic
halogens
members include all states of matter
halogens
cations are
smaller than neutral atoms
anions are
larger than neutral atoms
electronegativity
indicates the ability of an atom to attract electrons when chemically bonded
photoelectric effect
emission of electrons from a metallic surface when light of a certain frequency shines on it
quantum
a particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy
aufbau principle
electrons fill lower energy orbitals before higher energy levels
pauli exclusion principle
two electrons in an orbital must have opposite spins
hund’s rule
electrons in a subshell must occupy different orbitals before being paired
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired and atom slightly repels magnets
paramagnetic
not all electrons are paired and atom slightly attracts magnets
extensive properties
vary with the amount of substance (mass, volume, weight)
intensive properties
do not vary with amount of substance
taste and odor are
chemical properties
air, bronze, milk, gas, ink, and concrete are
mixtures
distillation
boiling, going through a sill, and condensation
chromatography
separation and purification of a mixture
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
if you know position of a particle, you can’t know its velocity and vice versa
Democritus
all things are composed of minute, invisible, indestructible particles of matter which move about eternally in infinite empty
Aristotle
against atomic theory, believed the four elements were water, fire, earth, and air
John Dalton
chemical properties unique to elements, atoms cannot be destroyed/broken down (false!), atoms of dif elements combine in whole number ratios, solid sphere model, father of modern atomic theory
J. J. Thomson
discovered electrons, plum pudding model, showed that cathode rays were made of electrons
Ernest Rutherford
alpha particles (stripped hydrogen atoms) through gold sheet showed positively charged nucleus, discovered protons, nuclear model
Niels Bohr
Danish, measured line spectrum of hydrogen, proposed electron shells (dif. energy levels) in planetary model
Erwin Schrodinger
Austrian physicist who explained electron’s movement w/ wave equation, no set orbits, created quantum model
James Chadwick
student of Rutherford who discovered neutrons, bombarded beryllium nuclei w/ alpha particles to discover new radiation
Antoine Lavoisier
“father of modern chemistry,” list of 33 elements (“simple substances”),
Mendeleev
left gaps for “eka-” elements in periodic table organized by atomic mass, predicted “eka-aluminum” (gallium)
Henry Moseley
ordered elements by atomic number, indicating how many natural elements were to be discovered
Robert Millikan
American physicist who determined the magnitude of an electron’s charge (oil-drop experiment), photoelectric effect
Billiard ball model
Dalton
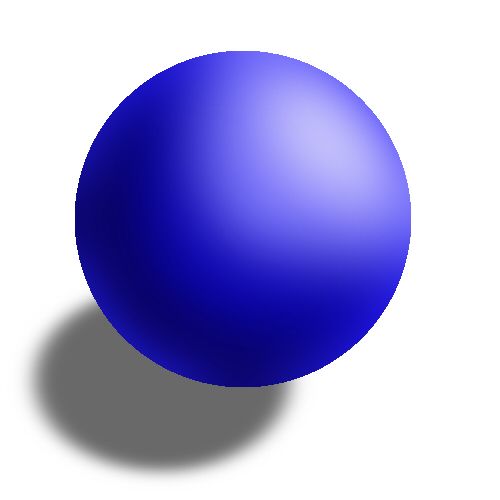

Plum Pudding Model
JJ Thomson
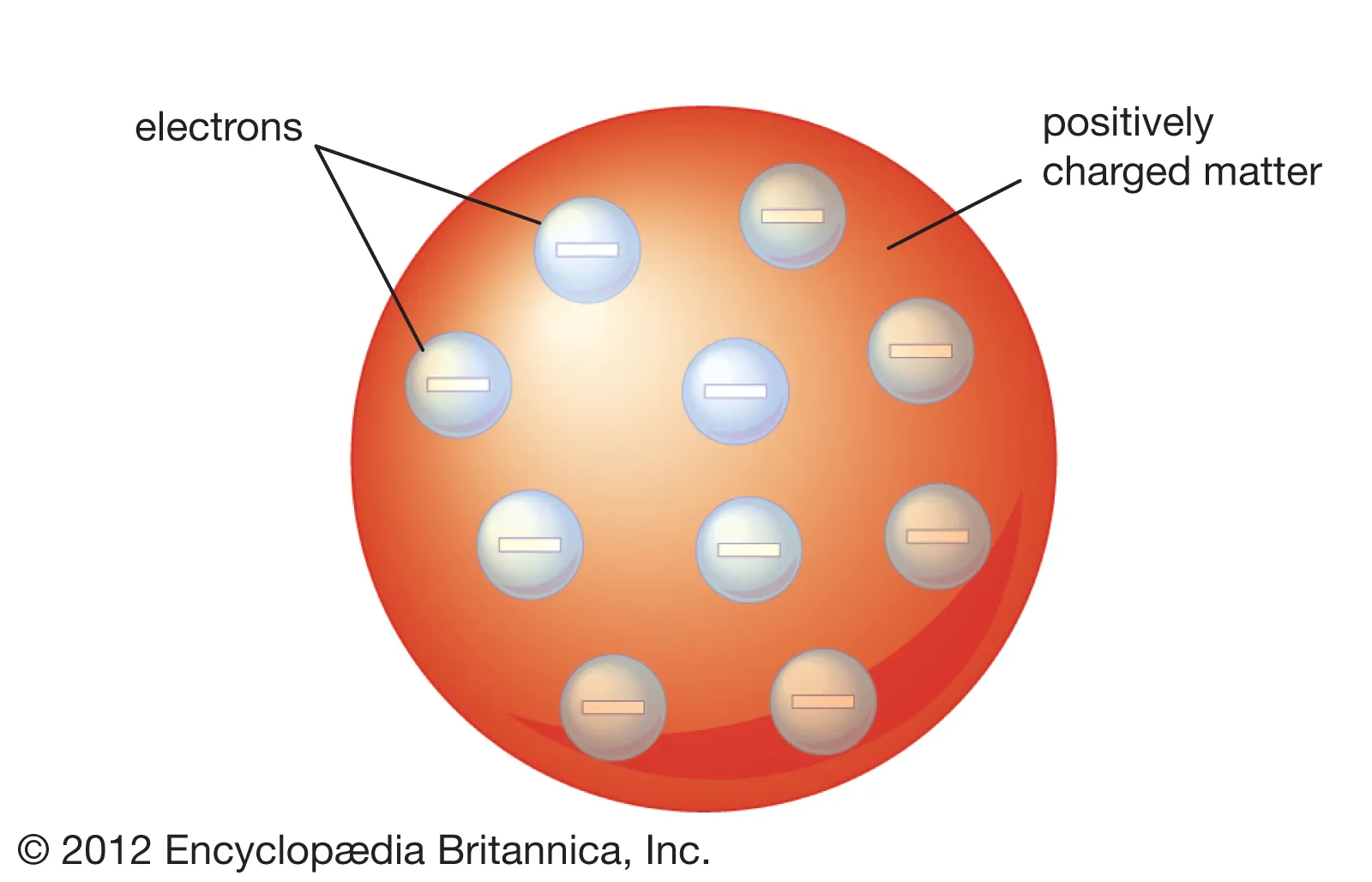
Nuclear Model
Rutherford

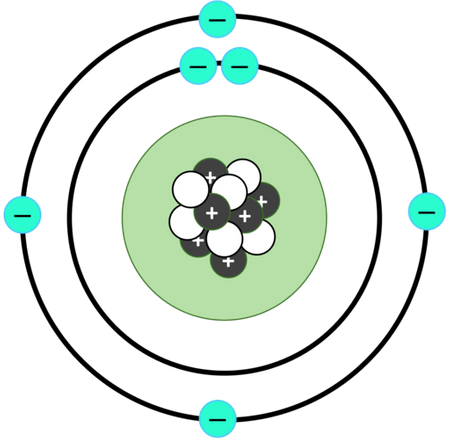
Planetary Model
Bohr
Quantum Mechanical Model
Schrodinger
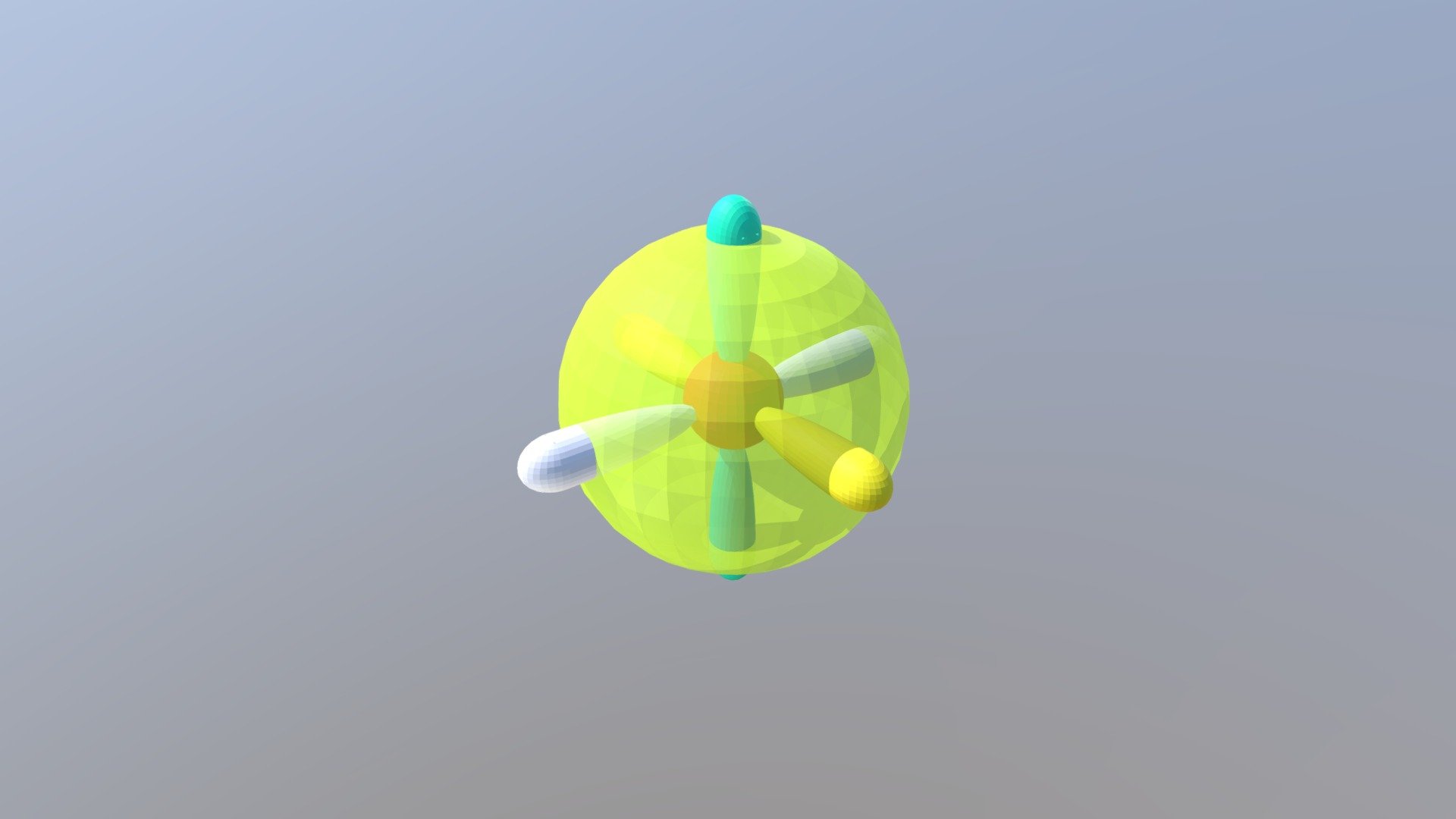

Electron Cloud Model
Schrodinger
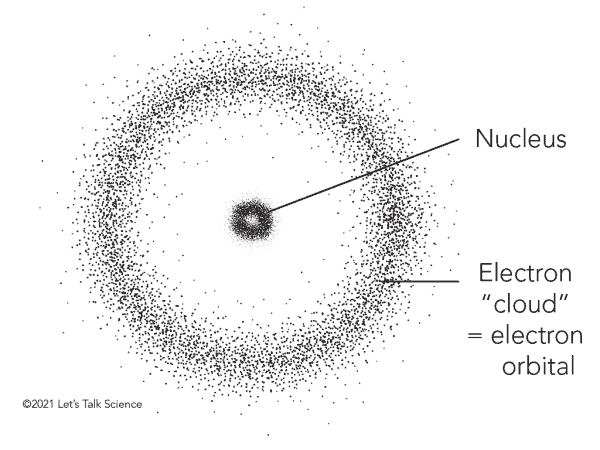
cathode ray tube
used by JJ Thomson to discover electrons,
gold foil experiment
alpha particles through gold foil showed atoms are mostly empty space and had nuclei
oil drop experiment
Milikan discovered the exact charge of an electron of drops in an oil mist