All of 3.1 Motion
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Define stopping distance
Total distance travelled from when the driver spots the hazard until the driver completely stops the vehicle
What is the equation for stopping distance?
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
Define thinking distance
Distance travelled between the moment the hazard is spotted until the moment the driver applied the brakes
What is the equation for thinking distance?
s = ut
s = thinking distance, m
u = initial velocity, ms^-1
t = reaction time, s
What factors affect thinking distance?
Alcohol/drugs
Tiredness
Vision/visibility
Music/distractions
Caffeine
Initial speed
Define braking distance?
Distance travelled between the moment the brakes are applied until the moment the vehicle stops
How do you workout braking distance?
u² / 2a
u = initial velocity, ms^-1
a = deceleration, ms^-2
What affects braking distance?
Weather conditions
Road conditions
Heavy load
Tyre traction/bald tyres
Damaged brakes
Initial speed
Define a projectile
An object thrown at an angle to the horizontal
Describe everything you know about projectile motion
The projectile travels in 2 planes, vertical and horizontal which means we needs 2 SUVATs.
Time is the same in both planes since we assume air resistance is negligible.
Describe everything you know about vertical motion
Acceleration is due to gravity, a = g = 9.81^-s
Max height is reached when v = 0
Negative acceleration = deceleration
Time to reach maximum height = time of flight / 2
From/to rest = u/v = 0
Describe everything you know about horizontal motion
No horizontal acceleration, a = 0
Velocity remains constant since there’s no resultant force, u = v
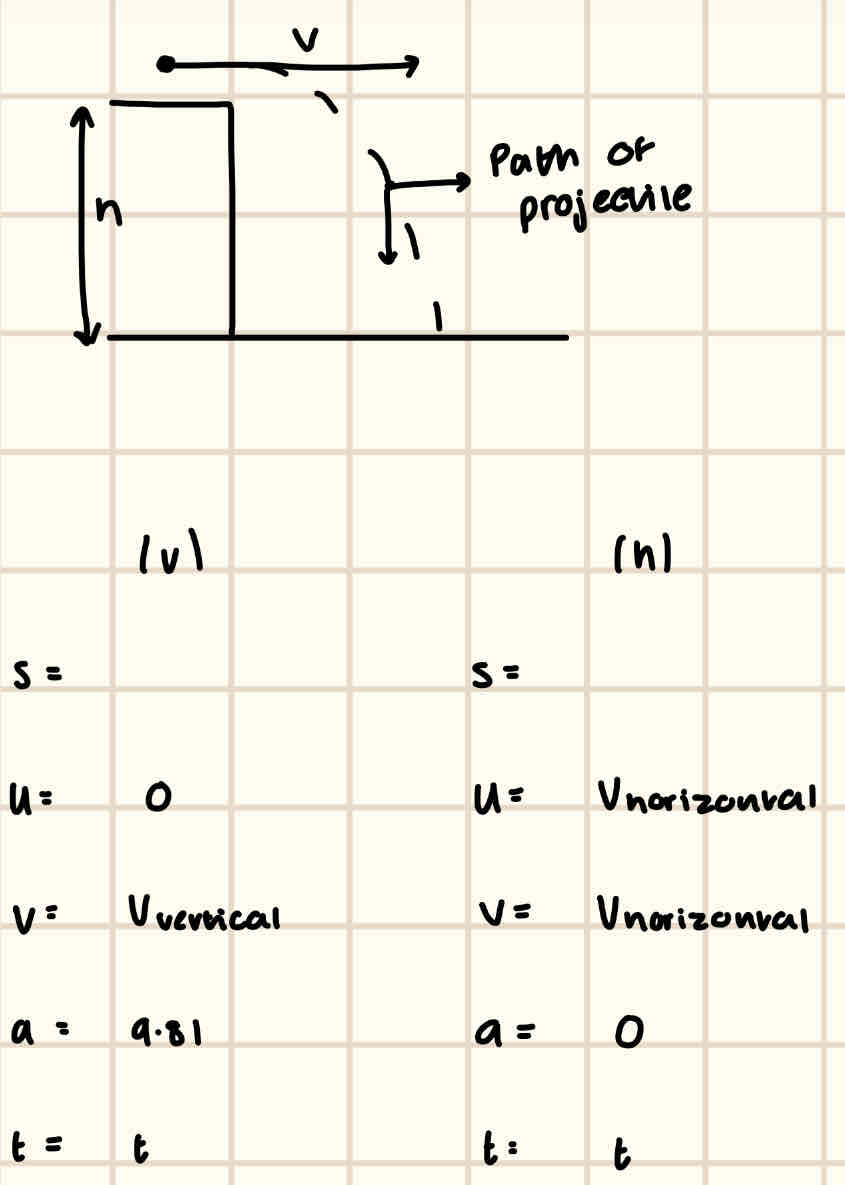
Sketch the 1st model of projectile motion and describe what we need to do to find all missing variables
1) Find the time of flight, t
2a) Find the maximum vertical height, when v = 0
2b) Find the horizontal displacement/range, ONLY after t is found
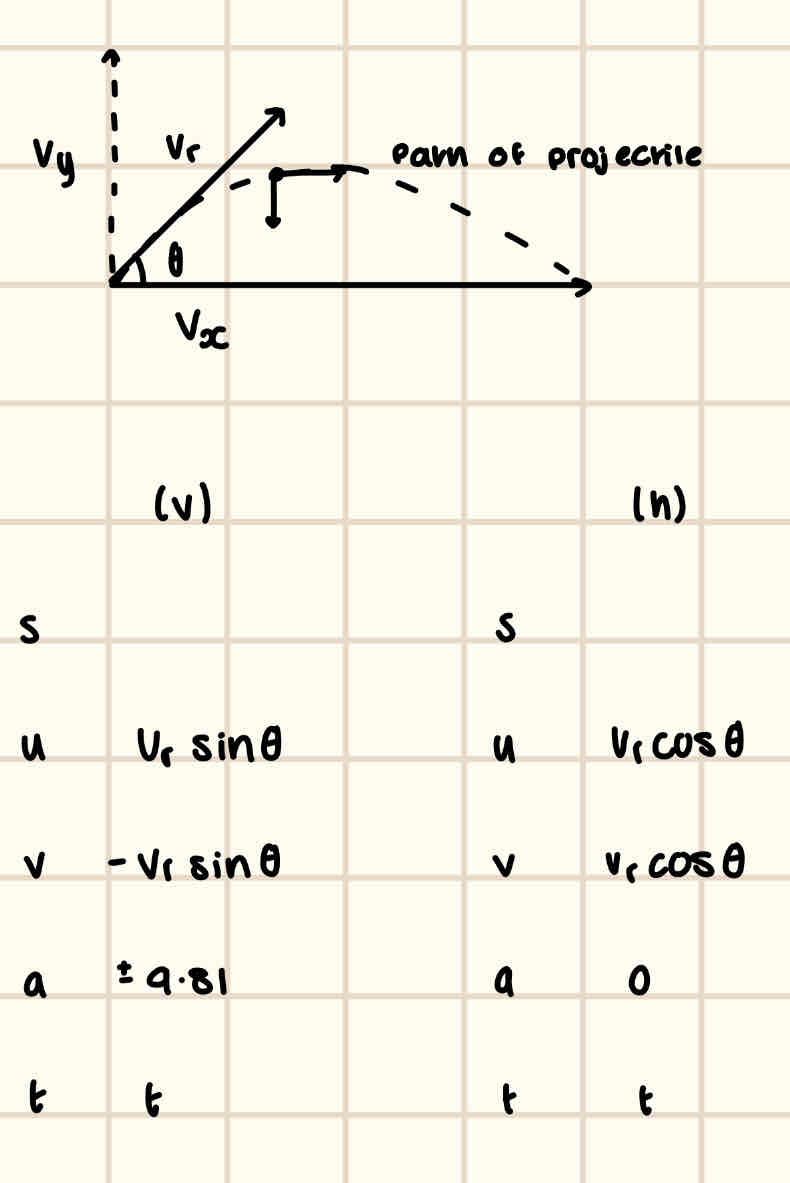
Sketch the 2nd model of projectile motion and describe what we need to do to find all missing variables
1) Find the time of flight, t
2) Find the horizontal displacement/range, ONLY after t is found
3) Find V(v)
What are all the suvat equations?
v = u + at
s = ut + 1/2at²
s = 1/2(u+v)t
v²=u²+2as
s = displacement, m
u = initial velocity, ms^-1
v = final velocity, ms^-1
a = acceleration, ms^-2
t = time, s
What graph are all suvat equations derived from?
This velocity time graph
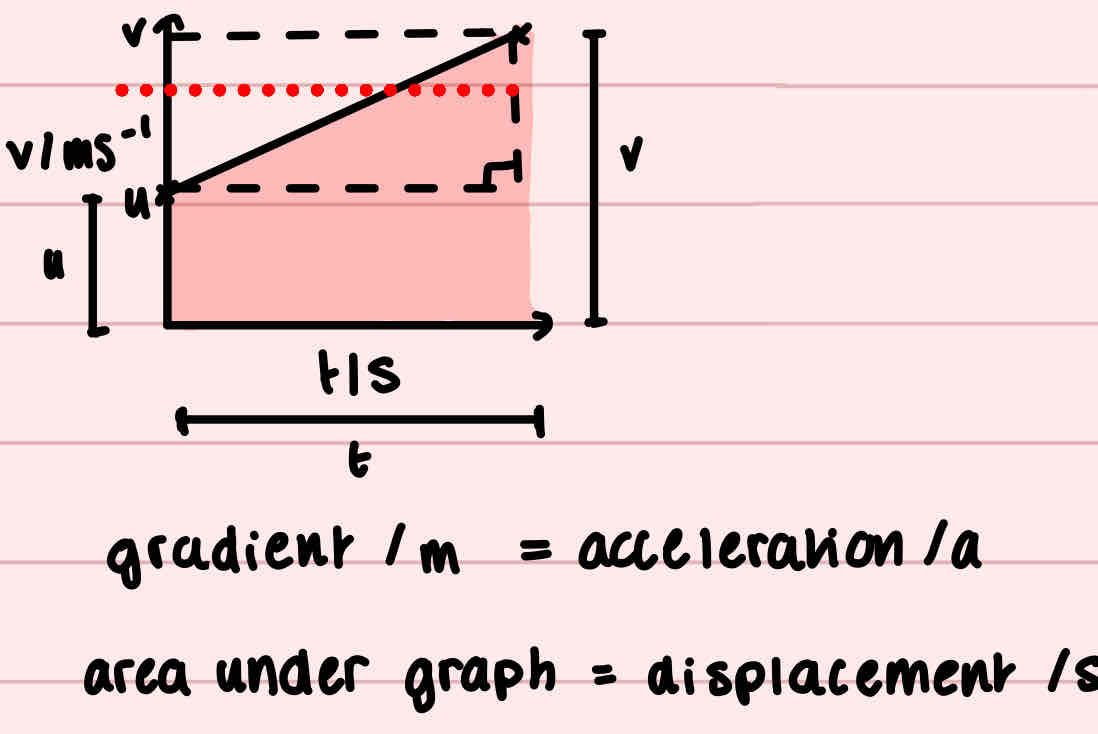
How is the equation without s derived?
Gradient
a = Δv / Δt = v - u / t, xt, +u
v = u + at
How is the equation without v derived?
Area under graph (rectangle and triangle)
Rectangle area = ut
Triangle area = ½ (v-u)t
v = u + at
s = ut + ½ at²
How is the equation without a derived?
Area under graph (trapezium)
½ (a+b)h
½ (u+v)t
How is the equation without t derived?
t = (v - u) / a
s = ½ (v+u) x (v - u) / a x2a
2as = (v+u)(v-u)
v² = u² +2as
What is the acceleration of freefall when an object is falling?
9.81ms^-2
What is the acceleration of freefall/g when an object is rising?
-9.81ms^-2
Define speed, its equation and SI base unit
The rate of change of distance
v = d / t
v = speed, ms^-1
d = distance, m
t = time, s
How is average speed measured?
Work out the speed over a specific time interval
Define distance
The total length covered
Define velocity, its equation and its SI base unit
The rate of change of displacement
v = s / t
v = velocity, ms^-1
s = displacement, m
t = time, s
Define displacement
The distance covered in a given direction
Define acceleration, its equation and SI base unit
The rate of change of velocity
a = v / t
a = acceleration, ms^-2
v = velocity, ms^-1
t = time, s
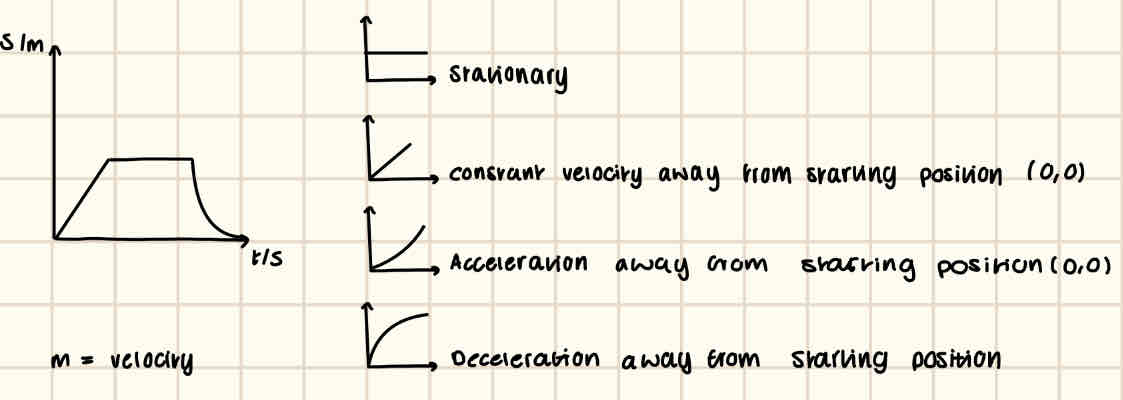
Describe a distance time graph with notes
x axis = time/s
y axis = distance/m
m = speed, ms^-1
The gradient cannot be negative because direction isn’t accounted for.
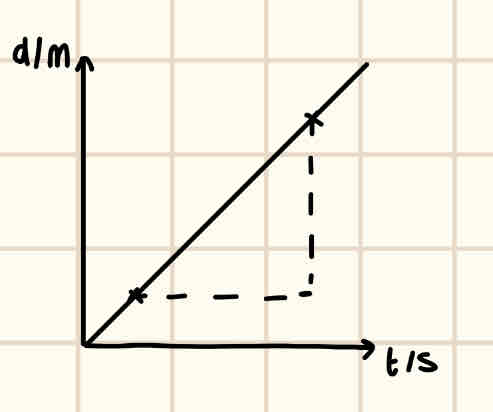
Describe a displacement time graph with notes
x axis = time/s
y axis = displacement/m
m = velocity, ms^-1
The y intercept determines the starting position.
When the gradient becomes positive or negative, it determines whether the object is moving away from/towards the starting position. NOT whether its accelerating or decelerating.
When the gradient increases rapidly then slows down the object is decelerating, when the gradient increases slowly but speeds up rapidly , the object is accelerating.
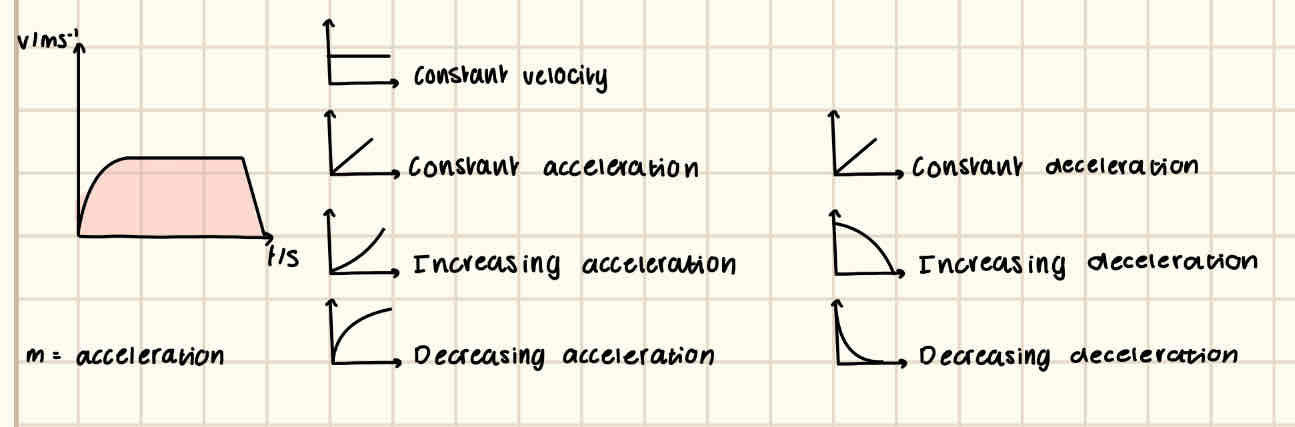
Describe a velocity time graph with notes
x axis = time/s
y axis = velocity/ms^-1
m = acceleration, ms^-2
area under graph = displacement, m
The y intercept determines the stating velocity.
When the gradient becomes positive or negative, it determines whether the object is accelerating or decelerating.
Define instantaneous speed/velocity/acceleration
The speed/velocity/acceleration measured over a very short period of time
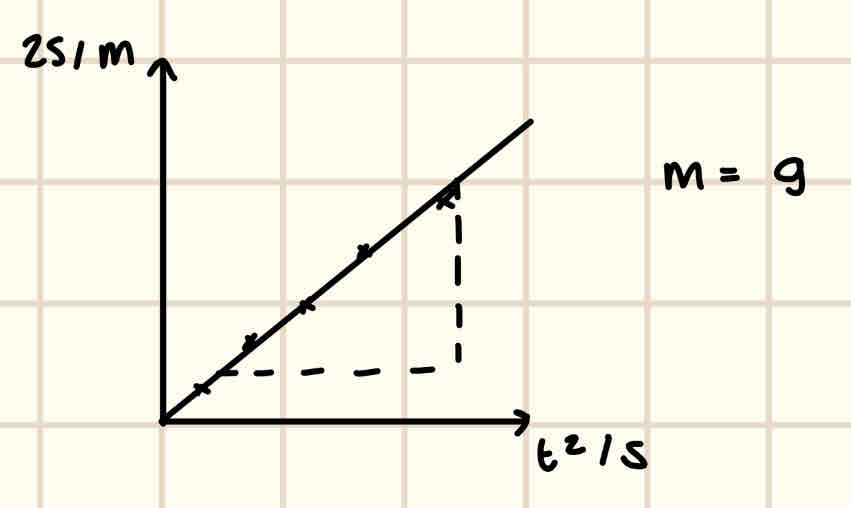
Describe how to determine the acceleration of freefall
We use a trapdoor and electromagnet/light gates, a steel ball bearing and a data logger.
1) A displacement between the trapdoor and electromagnet/light gates is measured with a metre ruler.
2) The steel ball bearing is dropped from rest. We record the time taken for the ball to travel the entire displacement measured on the data logger. This is repeated 3 times to calculate a mean time for this displacement. We repeat the entire process at regular decreasing displacement intervals.
3) We rearrange s = ut + ½ at² to have it in the form y = mx + c where a = g since there’s no external forces acting on the bearing and u = 0 since it’s dropped from rest. We get, 2s = gt².
4) This is the graph:
We draw a line of best fit and the gradient of this line will equal g, m =g