WJEC AS Physics Unit 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Unit of charge
Coulomb (C)
The net charge in a system remains constant (provided charges can’t enter or leave)
Electron’s charge
Charge of one electron is a very small fraction of a Coulomb
1.6×10-19C
Efficiency of a system
% efficiency = useful work (or energy) out/work (or energy) out in
X 100
Conductors
Materials through which a charge can flow
Electricity
The flow of electric charges through a conductor in one direction
Electric current

Base units of current
Cs^-1
Where C = coulombs and s = seconds
Units of current
Amperes (A)
Units of Charge
Coulombs (C)
Charge of electrons
1.6 × 10^-19 C
Number of electrons in 1 amp
Divide by the charge of electrons
Conduction
The result of free electrons which shift towards the higher potential when a voltage is placed across the ends of the wire
n in I=nAve
Number of electrons per unit volume (charge density)
V in I=nAve
Drift velocity
e in I=nAve
Charge of electrons
What current is equal to
Q/t where Q=charge in coulombs and t=time in seconds
Derivation of I=nAve

Potential difference
The pd between two points is the energy converted from electrical potential energy to some other form per coulomb of charge flowing from one point to the other. Unit; V (JC^-1)
What potential difference is also known as
Voltage
How to measure the potential difference in a circuit
Use a voltmeter in parallel
The Volt
Electric resistance
The resistance of a conductor of a conduction is the pd (V) across it divided by the resulting current (I) through it.
R=V/I
Unit; Ω (ohms) = VA^-1
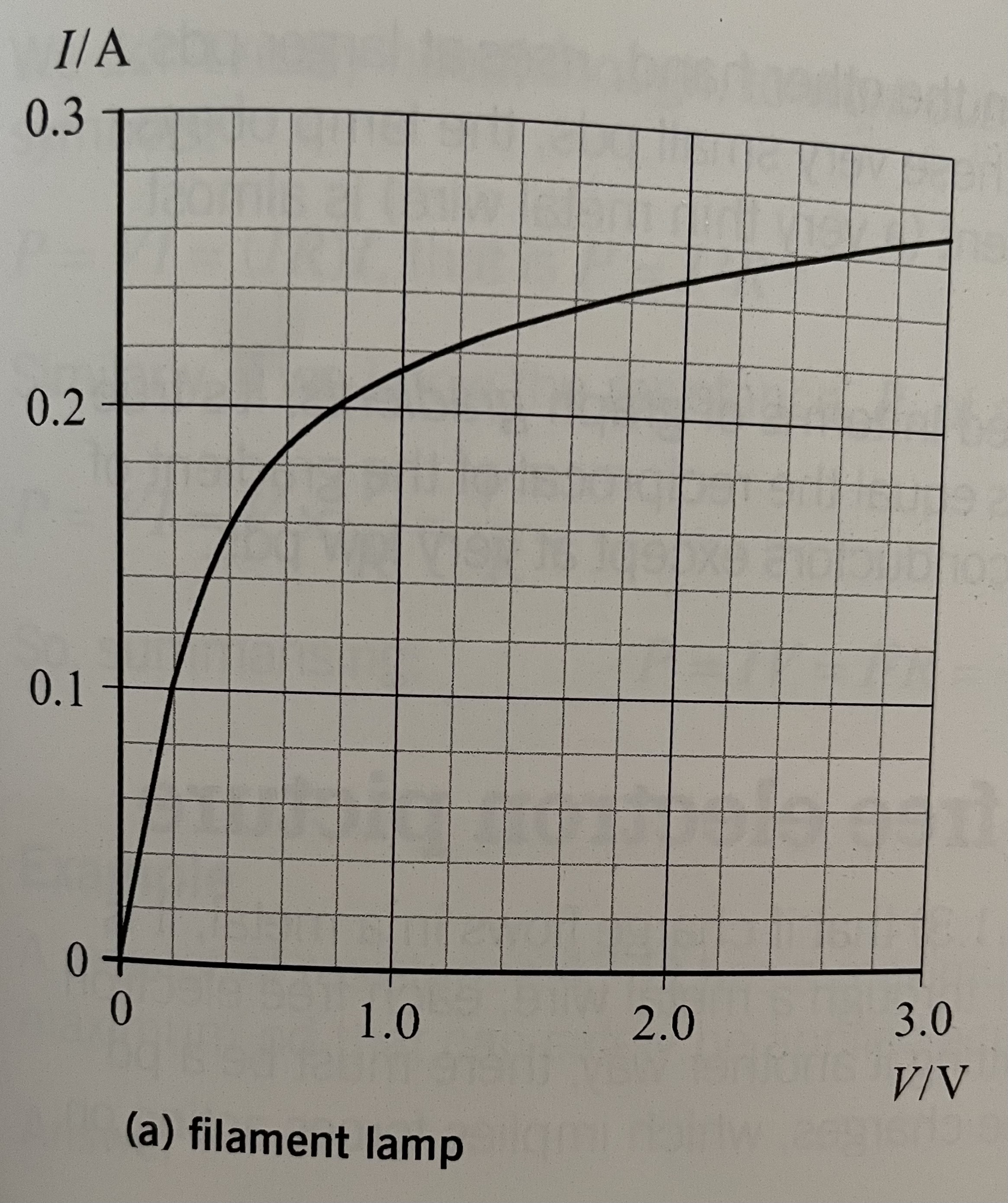
I-V graphs for the filament of a lamp at constant temperature
I-V graphs for a metal wire at constant temperature
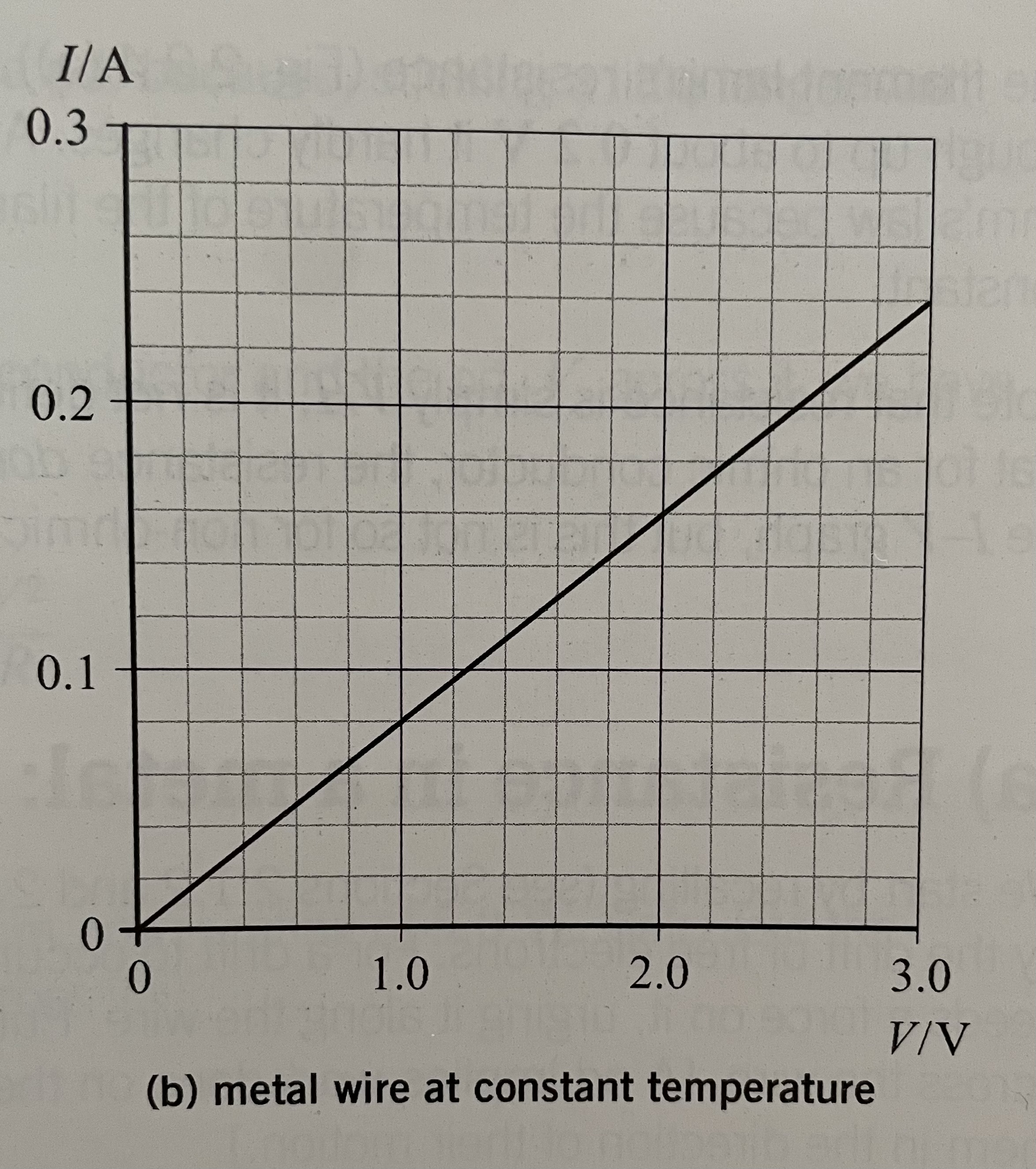
Ohms Law
The current in a metal wire at a constant temperature is proportional to the pd across it
Resistance is equal to
R=V/I
Where; V=voltage and I=current
Units of resistance
Ω (ohms) = VA^-1
Ohmic components
Components that obey Ohm’s law
Non-Ohmic components
Components that don’t obey Ohm’s law
Resistivity, ρ
The resistance, R, of a metal wire of length L and cross-sectional area A is given by R=ρL/A, in which ρ is the resistivity is a constant (at constant temperature) for the material of the wire
Unit ; Ωm
Units of resistivity
Ωm
What reactivity is equal to
RA/L
Where; R=resistance, A=cross-sectional area and L=length of wire
Factors that effect the resistance of a wire
Length
Cross-sectional area
Material
How does cross-sectional area affect resistance of a wire
When the area is doubled, the resistance is halved
How length affect resistance of a wire
Double the length, the resistance doubles
How does material affect resistance of a wire
Resistance is affected by the type of material the wire is made from
Restivity
The resistance, R, of a metal wire of length L and cross-sectional area A is given by R=ρL/A, in which ρ the resistivity, is a constant at a constant temperature for the material of the wire.
Unit; Ωm
Electrical Power
The rate of transfer of electrical potential energy into some other form
The equations for power
P=IV
P=I²R
Where; P=Power, V=Voltage, I=Current and R=Resistance
Deriving the power equations

Superconductivity
Material loses all its electrical resistance below a certain temperature, the superconducting transition temperature. Observed in many metals.
Superconducting transition temperature
The temperature at which a metal, when cooled, loses all its electrical resistance, and becomes super-conducting. Some materials (e.g. copper) never become superconducting however low the temperature becomes
Uses of superconductors
superconducting wires will carry currents without dissipating any energy at all
Prototypes of electrical power transmission cables have been set up using ‘high temperature’ conductors. Energy savings
Electromagnets producing large magnetic fields over large volumes of space use superconducting writes to make coils. MRI
Law of conservation of charge
Electrical charge cannot be created or destroyed, though positive and negative charges can neutralise each other. Charge cannot pile up at a point in a circuit
Current in a parallel circuit
I=I1+I2+I3
Current in a series circuit
I=I1=I2=I3
Potential difference in series circuits
V=V1+V2+V3
Potential difference in parallel circuits
V=V1=V2=V3
Resistance in series circuits
Add the resistances
Resistance in parallel circuits
Add the reciprocals and then reciprocal the product
1/R=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3
Potential divider
A circuit used to pass on a fraction of the input voltage. Consists of a combination of resistors. Uses a series of resistors or variable resistors or components such as a light dependent resistor or thermistor to divide up the potential difference of the source
Uses of potential dividers in circuits
With LDR
With thermistor
Circuits containing an LDR and a fixed resistor to form a potential divider
As light level falls, the resistance of the LDR increases, and the voltage increases accordingly (V=IR)
Circuits containing a thermistor and a fixed resistor to form a potential divider
As the temperature level increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases and then voltage decreases accordingly (V=IR)
emf of a source, E
The emf of a source is the energy converted from some other form (e.g. chemical) to electrical potential energy per coulomb of charge flowing through the source. Unit; V
Internal resistance
The resistance to the flow of current within the source
Current in a circuit containing multiple cells in series
Constant throughout
Potential difference in a circuit containing multiple cells in series
Sum of individual values
Theory of Resistance
In a filament lamp, the resistance increases with temperature. This is because the lattice ions have a greater amplitude (size) of vibration. This causes a greater probability of collisions, causing the frequency of collisions to increase. The average drift velocity increases, hence the resistance increases
1st circuit law
The sum of currents entering a junction is equal to the currents leaving the junction
What the 1st circuit law is due to
The conservation of charge
2nd circuit law
The sum of the p.d.s across the components in a series circuit is equal to the p.d. across the supply
What the 2nd circuit law is due to
The conservation of energy
Constant in a series circuit
Current
Constant in a parallel circuit
Voltage
What a voltmeter reads in an open circuit
E volts (voltage of source)
What EMF can be thought of
The voltage of the source