Chemistry Paper 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:24 AM on 6/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
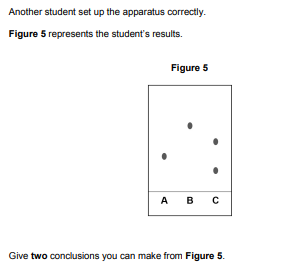
Give two conclusions you can make from Figure 5
• the flowers have no colours in common
• A / B contain one colour
• C contains two colours
• (the colour in) B is most soluble
• A / B contain one colour
• C contains two colours
• (the colour in) B is most soluble
2
New cards
Describe how oxides of nitrogen are produced when petrol is burned in car engines.
* nitrogen (from atmosphere) reacts with oxygen (from atmosphere)
* at high temperature (in engine)
* at high temperature (in engine)
3
New cards
HOW did the composition of the atomosphere change
• volcanic activity released water vapour
• the water vapour condensed to form oceans
• carbon dioxide dissolved in oceans
\---
• algae and plants evolved / appeared
• algae / plants absorbed carbon dioxide
• by photosynthesis
• which also released oxygen
\---
• carbon locked up in fossil fuels
• the water vapour condensed to form oceans
• carbon dioxide dissolved in oceans
\---
• algae and plants evolved / appeared
• algae / plants absorbed carbon dioxide
• by photosynthesis
• which also released oxygen
\---
• carbon locked up in fossil fuels
4
New cards
Why are scientists not certain about the percentage of each gas in the Earth’s early atmosphere?
limited or no evidence as it was billions of years ago
5
New cards
6
New cards
7
New cards
what ion is to be present by the cream precipitate (when silver nitrate is added)
bromIDE (ignore bromine)b
8
New cards
describe the combustion of alkenes
they burn with smoky flames due to incomplete combustion
9
New cards
oxidation of the alcohols leads to ----
carboxilic acids
10
New cards
characteristsics of carboxilic acids
disolve in water to form an acidic solution
react with metal carbonates to form CO2
react with metals to give off hydrogen gas
react with alcohols to make esters, but onlu in the presence of an acid catalyst
react with metal carbonates to form CO2
react with metals to give off hydrogen gas
react with alcohols to make esters, but onlu in the presence of an acid catalyst
11
New cards
amide bond
(C=O)NH2
12
New cards
what is an amino acid
(COOH)-NH2
13
New cards
reaction for the combustion of ethane in oxygen
2C2H6+7O2→4CO2+6H2O+Energy
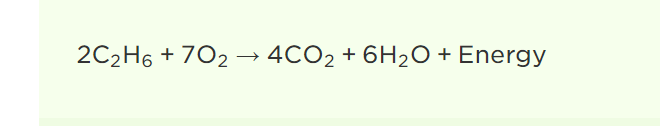
14
New cards
describe how ethene forms polyethen
1. double bond breaks
2. many (ethene) molecules
3. bond together (join to form a long hydrocarbon)
15
New cards
Glucose is produced when algae photosynthesise.
Name two naturally occurring polymers produced from glucose
Name two naturally occurring polymers produced from glucose
starch and cellulose
16
New cards
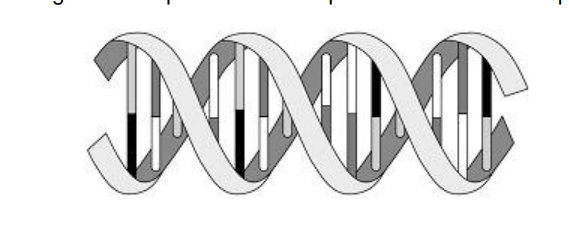
describe the shape and structure of this polymer
2 polymers wound together to form a double helix, with 4 nucleotides
17
New cards
Particles of soot in the atmosphere cause
global dimming
18
New cards
Titan is warmer than the other moons of Saturn because its atmosphere contains the greenhouse gas methane.
Explain how this greenhouse gas keeps Titan warmer than the other moons of Saturn
Explain how this greenhouse gas keeps Titan warmer than the other moons of Saturn
1. (methane) allows short(er) wavelength radiation to pass through (from the sun)
2. (which is) re-emitted from the surface as long(er) wavelength radiation
3. (which is) absorbed (by methane in the atmosphere)
19
New cards
Glass is made by heating sand with two other materials. Which two other materials are used to make glass?
limestone
sodium carbonate
sodium carbonate
20
New cards
Chlorine gas is used to produce poly(chloroethene). Describe a test to identify chlorine gas. Give the result of the test
(add damp) litmus paper
(litmus paper) is bleached or (litmus paper) turns white
(litmus paper) is bleached or (litmus paper) turns white
21
New cards
what is a thermosetting polymer
is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer
22
New cards
what is a thermosoftening polymer
Thermosoftening (also called thermoplastics) are plastics which will soften when heated and can be reshaped.
23
New cards
Poly(ethene) is a thermosoftening polymer. Suggest why poly(ethene) is easier to recycle than thermosetting polymers.
1. (poly(ethene)) melts
2. (so) can be reshaped (into new products)
24
New cards
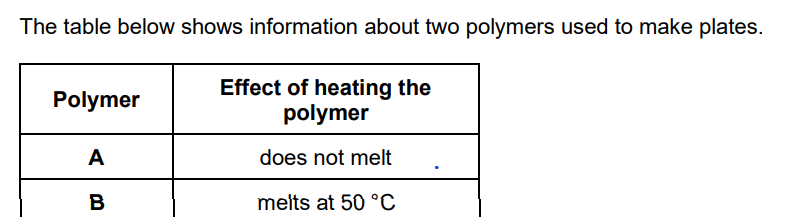
What type of polymer is polymer A?
thermosetting
25
New cards
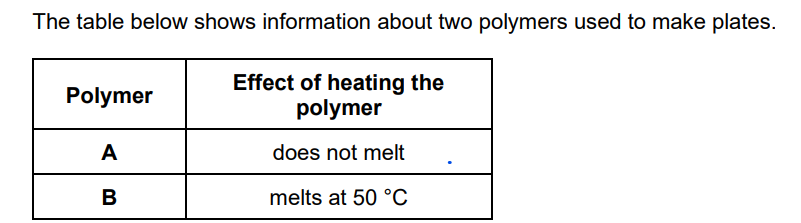
Why does polymer A behave differently to polymer B when heated?
polymer A has crosslinks (between polymer molecules) or polymer B has no crosslinks (between polymer molecules)
26
New cards
what does crosslinks mean
molecules r held in position
and unable to slide past eachother
and unable to slide past eachother
27
New cards
meaning of memory polymer
(can be deformed but) return to their original shape (when heated or cooled)
28
New cards
Name the monomers from which starch and proteins are produced.
starch - glucose
proteins - amino acids
proteins - amino acids
29
New cards
combustion of hydrocarbons is endothermic / exothermic
EXOTHERMIC
30
New cards
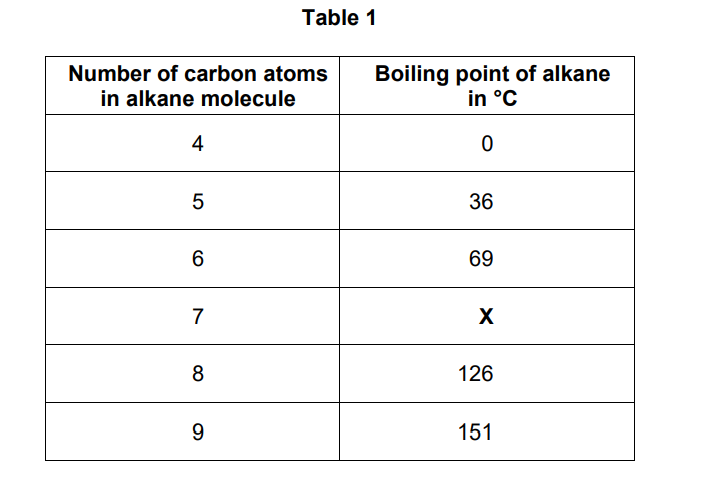
Nonane will condense lower in a fractionating column during fractional distillation than the other alkanes in Table 1.
Explain why.
You should refer to the temperature gradient in the fractionating column.
Explain why.
You should refer to the temperature gradient in the fractionating column.
(nonane) has a higher boiling point
(so nonane) condenses where the column has a higher temperature
(so nonane) condenses where the column has a higher temperature
31
New cards
Compare ethane with ethene. You should refer to their structure
__***Structure and bonding***__
%%both%% are hydrocarbons
%%both%% contain two carbon atoms (per molecule)
ethane contains six hydrogen atoms (per molecule) ==(but)== ethene contains four hydrogen atoms (per molecule)
%%both%% have covalent bonds
ethane contains a single C—C bond ==(but)== ethene contains a double bond
%%both%% contain C—H bonds • both small molecules
%%both%% are hydrocarbons
%%both%% contain two carbon atoms (per molecule)
ethane contains six hydrogen atoms (per molecule) ==(but)== ethene contains four hydrogen atoms (per molecule)
%%both%% have covalent bonds
ethane contains a single C—C bond ==(but)== ethene contains a double bond
%%both%% contain C—H bonds • both small molecules
32
New cards
Compare ethane with ethene. You should refer to reacting
1. both react with oxygen in complete combustion reactions
2. to produce water and carbon dioxide
3. both react with oxygen in incomplete combustion reactions to produce water, carbon monoxide and carbon
4. incomplete combustion is more likely with ethene
5. ethene decolourises bromine water (but) ethane does not decolourise bromine water
6. ethene is more reactive (than ethane)
7. ethene can react with hydrogen (to produce ethane)
8. ethene can react with water (to produce ethanol)
9. ethene can react with halogens (to produce halogenoalkanes)
10. ethene can undergo addition reactions
11. ethene can polymerise (to produce poly(ethene))
33
New cards
what type of reaction produces ethanoic acid from ethanol
oxidation reaction
34
New cards
Why do ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid have different pH?
Ethanoic acid is a weak acid, HCL is a strong acid. This is because Ethanoic acid doesn't fully dissociate in solution where as HCL does.
35
New cards
higher ph means
more alkaline
36
New cards
volatile meaning
Volatile substances have a tendency to vaporize whereas non volatile substances do not have a tendency to vaporize
37
New cards
thermosoftening plastics
Thermosoftening plastics do not have covalent bonds between neighbouring polymer molecules, so the molecules can move over each other when heated and the plastic melts.
38
New cards
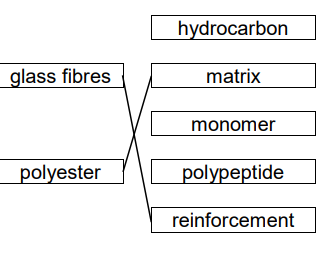
what type of material is glass fibers
fiber-reinforced plastic
39
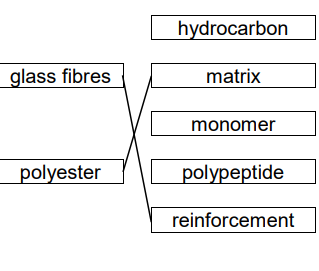
New cards
what type of material is polyester
matrix
40
New cards
The outer skin makes the surfboard more expensive. Suggest two reasons why an outer skin is added to the poly(styrene) core.
any two from: (to make the board)
• harder
• stronger
• tougher
• more rigid
• waterproof
• harder
• stronger
• tougher
• more rigid
• waterproof
41
New cards
what two pieces of measuring apparatus could the student use to find the rate of production of hydrogen gas
gas syringe
stop clock
stop clock
42
New cards
how does magnesium being fixed to steel ships prevent the ship from rusting
magnesium is more reactive, it provides a sacrificial reaction
43
New cards
explain why aluminium window frames do not corrode after they are made
coating of Aluminium oxide protects metal from further corosion
44
New cards
describe a test to show that the drinking water contained aluminium ions (3 MARKS)
1. dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide
2. dissolves in excess to form a colourless solution
3. white precipitate forms which dissolves in excess
45
New cards
describe a test to show that drinking water contains sulfate ions
1. barium chloride
2. hydrochloric acid
3. white precipitate
46
New cards
formula of ethanol
C2H5OH
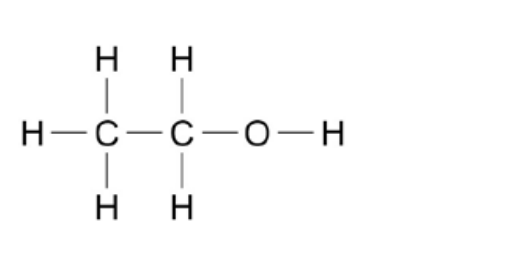
47
New cards
Methanol is used to produce methanoic acid. What type of substance reacts with methanol to produce methanoic acid?
oxidising (agent)
48
New cards
The mixture of gases from the reactor cools in the condenser. Suggest why ammonia condenses but the other gases do not. (harber process)
ammonia has a **higher** boiling point
49
New cards
50
New cards
plan an investigation to find the total mass of dissolved solids in an 100cm^3 sample of drinking water
• weigh (evaporating) basin / dish
• add measured volume of water
• weigh (evaporating) basin / dish and water
• heat to evaporate water
• reweigh
• repeat heating until constant mass obtained
• subtract mass of (evaporating) basin / dish from mass
• repeat and calculate a mean, discarding anomalous results
• calculate the mass in 100 cm3 water if necessary
• add measured volume of water
• weigh (evaporating) basin / dish and water
• heat to evaporate water
• reweigh
• repeat heating until constant mass obtained
• subtract mass of (evaporating) basin / dish from mass
• repeat and calculate a mean, discarding anomalous results
• calculate the mass in 100 cm3 water if necessary
51
New cards
explain how methane keeps titan warmer than other moons of saturn
(methane) allows short(er) wavelength radiation to pass through (from the sun)
(which is) re-emitted from the surface as long(er) wavelength radiation
(which is) absorbed (by methane in the atmosphere)
(which is) re-emitted from the surface as long(er) wavelength radiation
(which is) absorbed (by methane in the atmosphere)
52
New cards
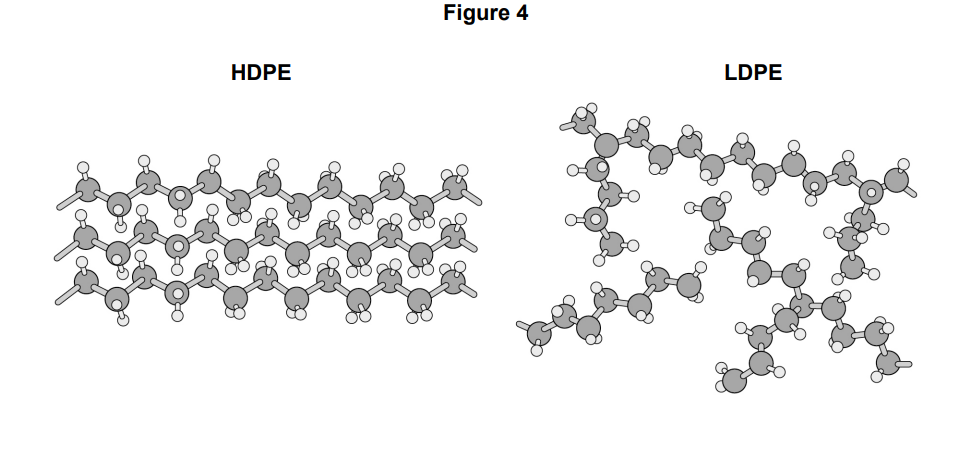
explain why HDPE has a higher density than LDPE
(in HDPE) polymer chains / molecules are closer together
(so) more atoms per unit volume
(so) more atoms per unit volume
53
New cards
give a test to identify the group 1 metal ion in potash alum
flame test
lilac (flame)
lilac (flame)
54
New cards
name one instrumental method that could identify the group 1 metal ion and show the concentration of the ion in a solution of ptash alum
flame emission spectroscopy
55
New cards
describe how copper is extracted from low grade iron ores by Phyto mining
grow plants (on land containing copper ores)
plants are burnt (to produce ash)
ash dissolved in acid (to produce a solution of a copper compound)
electrolysis of solution (containing a copper compound) **or** displacement (of copper) from solution (containing a copper compound)
plants are burnt (to produce ash)
ash dissolved in acid (to produce a solution of a copper compound)
electrolysis of solution (containing a copper compound) **or** displacement (of copper) from solution (containing a copper compound)
56
New cards
if the FOWARD reaction is exothermic, higher temperature is ________ yield
higher temperature gives %%***lower yield***%% because the reaction is exothermic
57
New cards
Give one other way of changing the rate of reaction between gases. You should not refer to pressure in your answer.
change the temperature
add a catalyst
add a catalyst
58
New cards
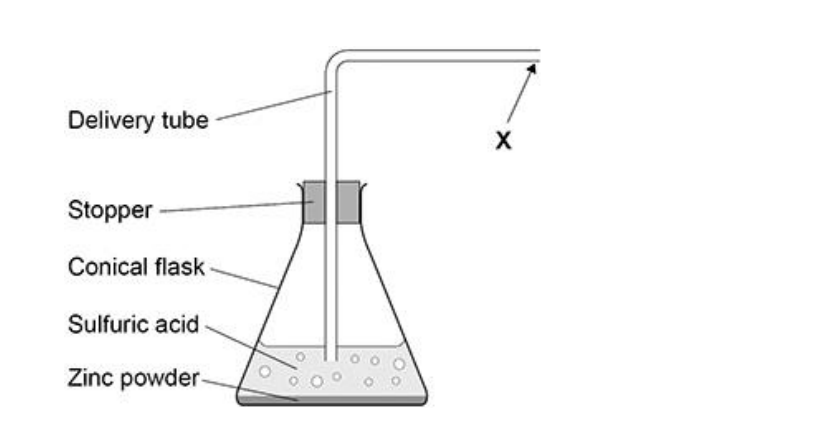
if the tube is dipped into the solution, what problem would be caused
(sulfuric) acid will travel up tube **or**
no hydrogen / gas will be collected
no hydrogen / gas will be collected
59
New cards
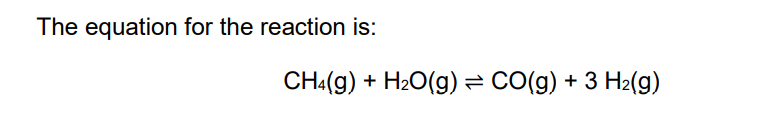
explain why a low pressure was used for this reaction
higher yield (of hydrogen or carbon monoxide or product)
(because) fewer moles / molecules / particles on left hand side
(because) fewer moles / molecules / particles on left hand side
60
New cards
What is meant by equilibrium?
IN A CLOSED SYSTEM
the forwards and backwards reactions are equal
the forwards and backwards reactions are equal
61
New cards
The Earth's early atmosphere
1. One theory suggests that during the first billion years of the Earth’s existence, there was intense volcanic activity that released gases that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans.
2. At the start of this period, the Earth’s atmosphere may have been like the atmospheres of Mars and Venus today, consisting of mainly **carbon dioxide** with **little or no oxygen gas**. Volcanoes also produced **nitroge**n which gradually built up in the atmosphere and there may have been small proportions of **methane** and **ammonia**.
3. When the oceans formed carbon dioxide dissolved in the water and carbonates were precipitated producing sediments, and **reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.**
62
New cards
why is evidence for the earths early atmosphere limited
Evidence for the early atmosphere is limited because of the time scale of 4.6 billion years.
63
New cards
explain why increasing the use of biofuels may cause food shortages
fertile land is used for biofuels
less space for actual food
less space for actual food
64
New cards
The percentages of nitrogen and of oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere today have changed from the percentages in the Earth’s early atmosphere.
how much has nitrogen & oxygen increased
how much has nitrogen & oxygen increased
nitrogen Increased by about 40 times
oxygen increased by about 21%
oxygen increased by about 21%
65
New cards
Solar energy may not be able to replace the generation of electricity from fossil fuels completely. Suggest two reasons why.
• sunshine is unreliable
• increased demand for energy '
• lack of space
*ignore references to cost*
• increased demand for energy '
• lack of space
*ignore references to cost*
66
New cards
what does an exothermic reaction profile look like
reactants up
products down
products down
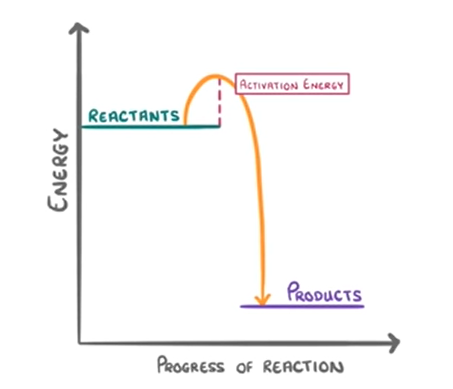
67
New cards
what does an endothermic reaction profile look like
reactants down
products up
products up
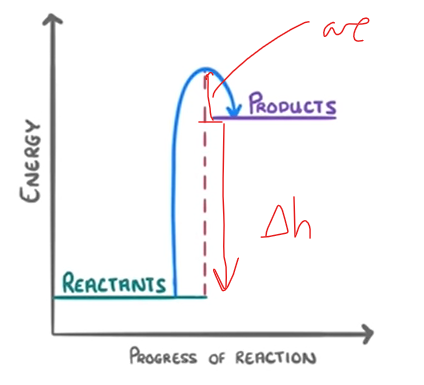
68
New cards
test for carbon dioxide
turns limewater milky
69
New cards
affinity
tendency of a chemical species to react with another to form a chemical compound
70
New cards
desalination
the process of removing salt from seawater.
71
New cards
effluent
liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea.
72
New cards
leachate
1. water that has percolated through a solid and leached out some of the constituents.
73
New cards
bronze is an alloy of and , used for making _________ and
copper
tin
statues
decorative things
tin
statues
decorative things
74
New cards
brass is an alloy of and , used for making _________ and
copper
zinc
taps
door fittings
zinc
taps
door fittings
75
New cards
gold is used for made of , and
jewellery
silver
copper
zinc
silver
copper
zinc
76
New cards
pure gold is __ carrats
24
77
New cards
18 carrat gold is ___% gold
75%
78
New cards
high carbon steel is ______ but
____________
\
____________
\
stong
brittle
brittle
79
New cards
low carbon steel is ________ and
_____________ shaped
_____________ shaped
softer
more easily
more easily
80
New cards
steels containing _________ __and__ _________ are stainless steels.
and is ________and____________ to corrosion
and is ________and____________ to corrosion
chromium and nickel
hard and resistant
hard and resistant
81
New cards
what is borosilicate glass made from
sand, boron, trioxide
82
New cards
borosilicate glass melts at ____________ temps than soda lime glass
higher
83
New cards
Most composites are made of two materials:
a matrix or binder surrounding
84
New cards
binding together fibres or fragments of the other material is called what
reinforcement
85
New cards
sewage treatments

86
New cards
what is bioleaching
when you use bacteria to produce leachate solutions that contain metal compounds
87
New cards
aluminium magnesium alloys are _____ __density and used in__ ____________ manafacturing
low
aerospace
aerospace
88
New cards
test for carbonate ions
• add hydrochloric acid
• effervescence / fizzing
• bubble gas through limewater
• limewater becomes cloudy
• effervescence / fizzing
• bubble gas through limewater
• limewater becomes cloudy
89
New cards
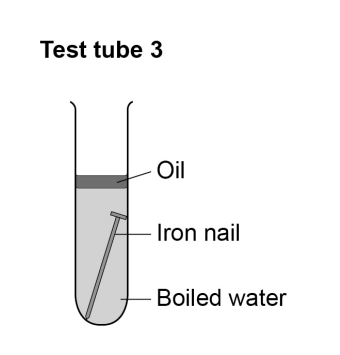
does the iron nail rust?
Tube 3: (nail) does not rust because no air / oxygen
90
New cards
Magnesium is fixed to some steel ships.
Explain how this prevents the steel from rusting.
Explain how this prevents the steel from rusting.
magnesium is more reactive (than iron) (so magnesium) provides sacrificial protection
91
New cards
Plan an investigation to find the total mass of dissolved solids in a 100 cm3 sample of the drinking water.
• weigh (evaporating) basin / dish
• add measured volume of water
• weigh (evaporating) basin / dish and water
• heat to evaporate water
• reweigh
• repeat heating until constant mass obtained
• subtract mass of (evaporating) basin / dish from mass
• repeat and calculate a mean, discarding anomalous results
• calculate the mass in 100 cm3 water if necessary
• add measured volume of water
• weigh (evaporating) basin / dish and water
• heat to evaporate water
• reweigh
• repeat heating until constant mass obtained
• subtract mass of (evaporating) basin / dish from mass
• repeat and calculate a mean, discarding anomalous results
• calculate the mass in 100 cm3 water if necessary
92
New cards
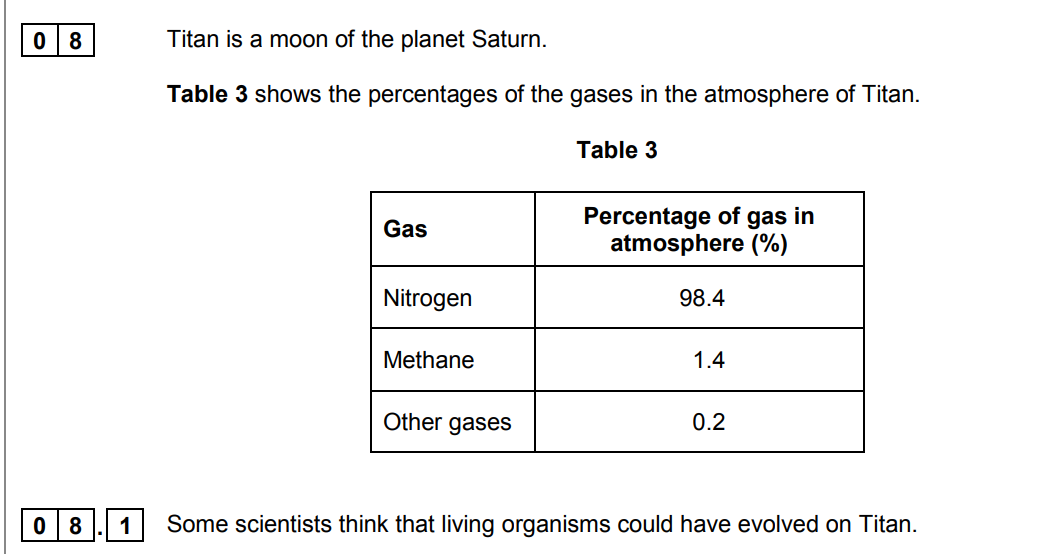
Explain why these organisms could not have evolved in the same way that life is thought to have evolved on Earth.
(Titan has) little / no oxygen
(so) photosynthesis has not occurred (on Titan)
little carbon dioxide present **OR** oxygen-using animals cannot have evolved
(so) photosynthesis has not occurred (on Titan)
little carbon dioxide present **OR** oxygen-using animals cannot have evolved
93
New cards
Titan is warmer than the other moons of Saturn because its atmosphere contains the greenhouse gas methane. Explain how this greenhouse gas keeps Titan warmer than the other moons of Saturn
(methane) allows short(er) wavelength radiation to pass through (from the sun)
(which is) re-emitted from the surface as long(er) wavelength radiation
(which is) absorbed (by methane in the atmosphere)
(which is) re-emitted from the surface as long(er) wavelength radiation
(which is) absorbed (by methane in the atmosphere)
94
New cards
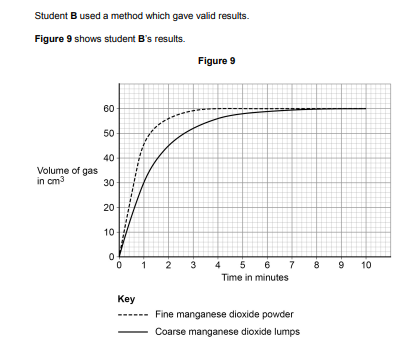
Determine the mean rate of reaction in cm3 /s between 2 and 4 minutes for coarse manganese dioxide lumps.
0\.092
95
New cards
what is phytomining
plants are grown in soil that contains low grade ore.
the plants absorb metal ions through their roots and concentrate these ions in their cells.
the plants are harvested and burnt.
the ash left behind contains metal compounds.
the plants absorb metal ions through their roots and concentrate these ions in their cells.
the plants are harvested and burnt.
the ash left behind contains metal compounds.
96
New cards
how does iron rust
iron + oxygen + water → **hydrated iron(III) oxide**
**Hydrated iron(III) oxide** is the orange-brown substance seen on the surface of rusty objects.
**Hydrated iron(III) oxide** is the orange-brown substance seen on the surface of rusty objects.
97
New cards
ways to prevent corrosion
* painting
* oiling and greasing
* coating with plastic
* Electroplating
* **Sacrificial protection**
* oiling and greasing
* coating with plastic
* Electroplating
* **Sacrificial protection**
98
New cards
Electroplating
**Electroplating** involves using **electrolysis** to put a thin layer of a metal on the object:
99
New cards
sacrificial protection
Iron can be protected from rusting if it is in contact with a more **reactive** metal, such as zinc.
The more reactive metal **oxidises** more readily than iron, so it ‘sacrifices’ itself while the iron does not rust.
Once the **sacrificial metal** has corroded away, it can simply be replaced.
The more reactive metal **oxidises** more readily than iron, so it ‘sacrifices’ itself while the iron does not rust.
Once the **sacrificial metal** has corroded away, it can simply be replaced.
100
New cards
Galvanising
When iron is coated in zinc, the process is called **galvanisation**. The zinc layer stops oxygen and water reaching the iron. Zinc is more reactive than iron, so it also acts as a sacrificial metal.