ABI 103: Glycogen Synthesis
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are the 3 enzymes involved in Glycogen Synthesis?
UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase
Glycogen Synthase
Glycogen Branching Enzyme
Is Glycogen synthesis from G1P thermodynamically favorable?
By itself, it is thermodynamically unfavorable.
Are Glycogen synthesis and Glycogen breakdown separate pathways?
yes, they are separate pathways
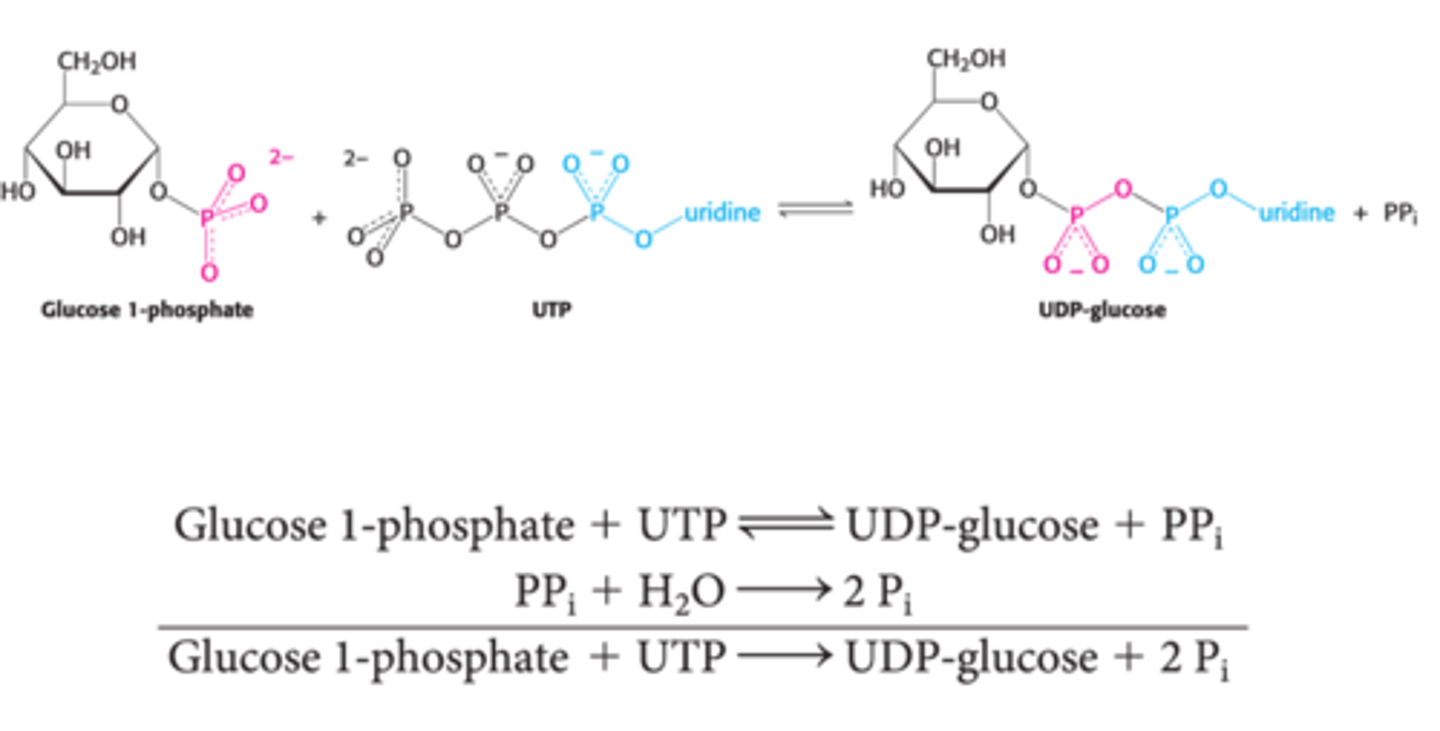
What does UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase do?
UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase activates glucosyl units, Uridine Diphosphate Glucose (UDPG).
What can an "activated" Uridine Diphosphate Glucose (UDPG) do?
It can donate a glucosyl unit to the growing glycogen chain.
What is the ΔG° of the formation of Uridine Diphosphate Glucose (UDPG)?
ΔG°≈0
What makes the overall reaction catalyzed by UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase to activate UDPG exergonic?
The subsequent exergonic hydrolysis of PPi by inorganic pyrophosphatase makes the overall reaction exergonic
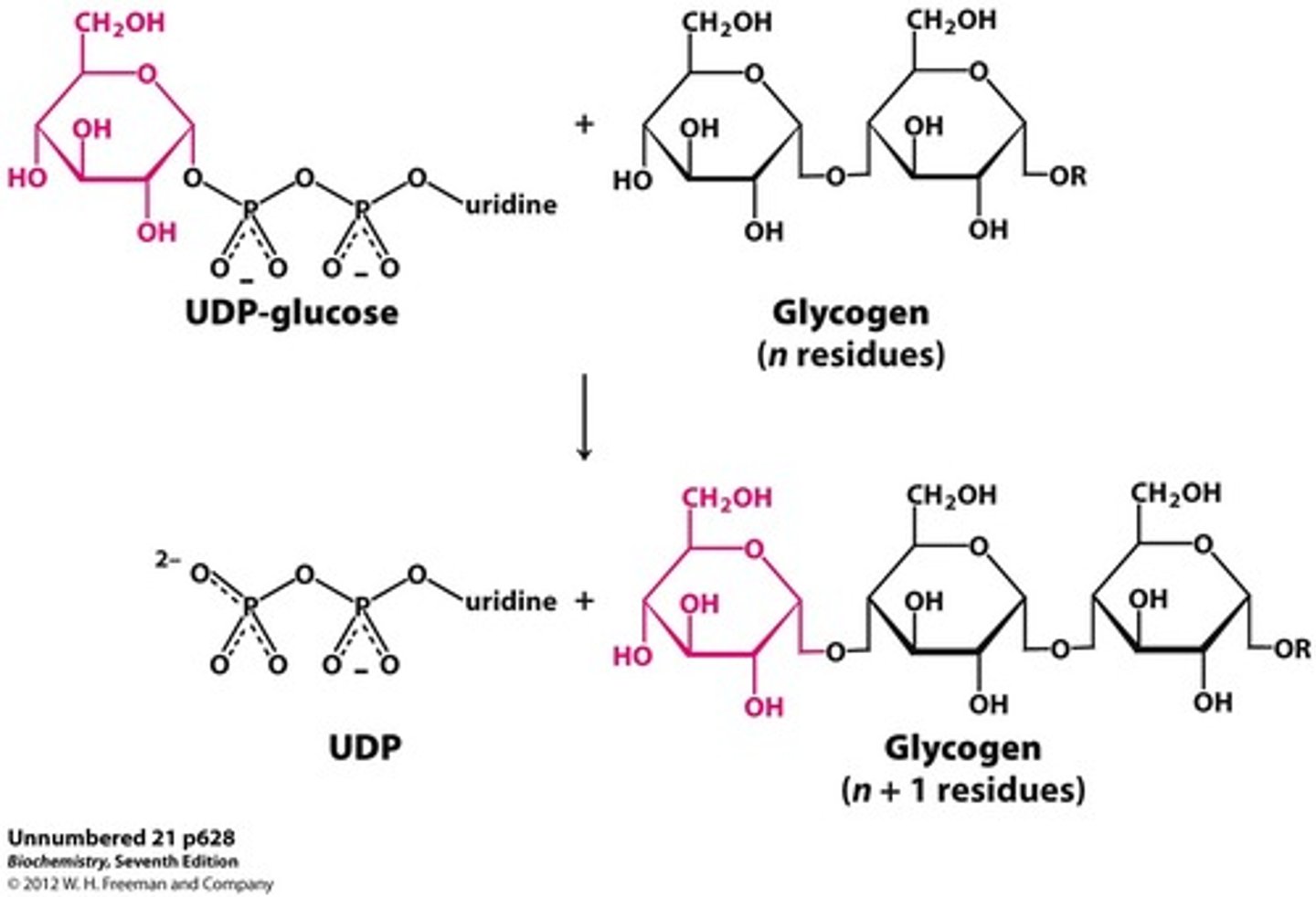
What does Glycogen Synthase do in Glycogen Synthesis?
it extends glycogen chains
What does Glycogen Synthase transfer and from where to where?
Transfers glucosyl unit of UDPG to C4-OH group on one of glycogen's non-reducing ends
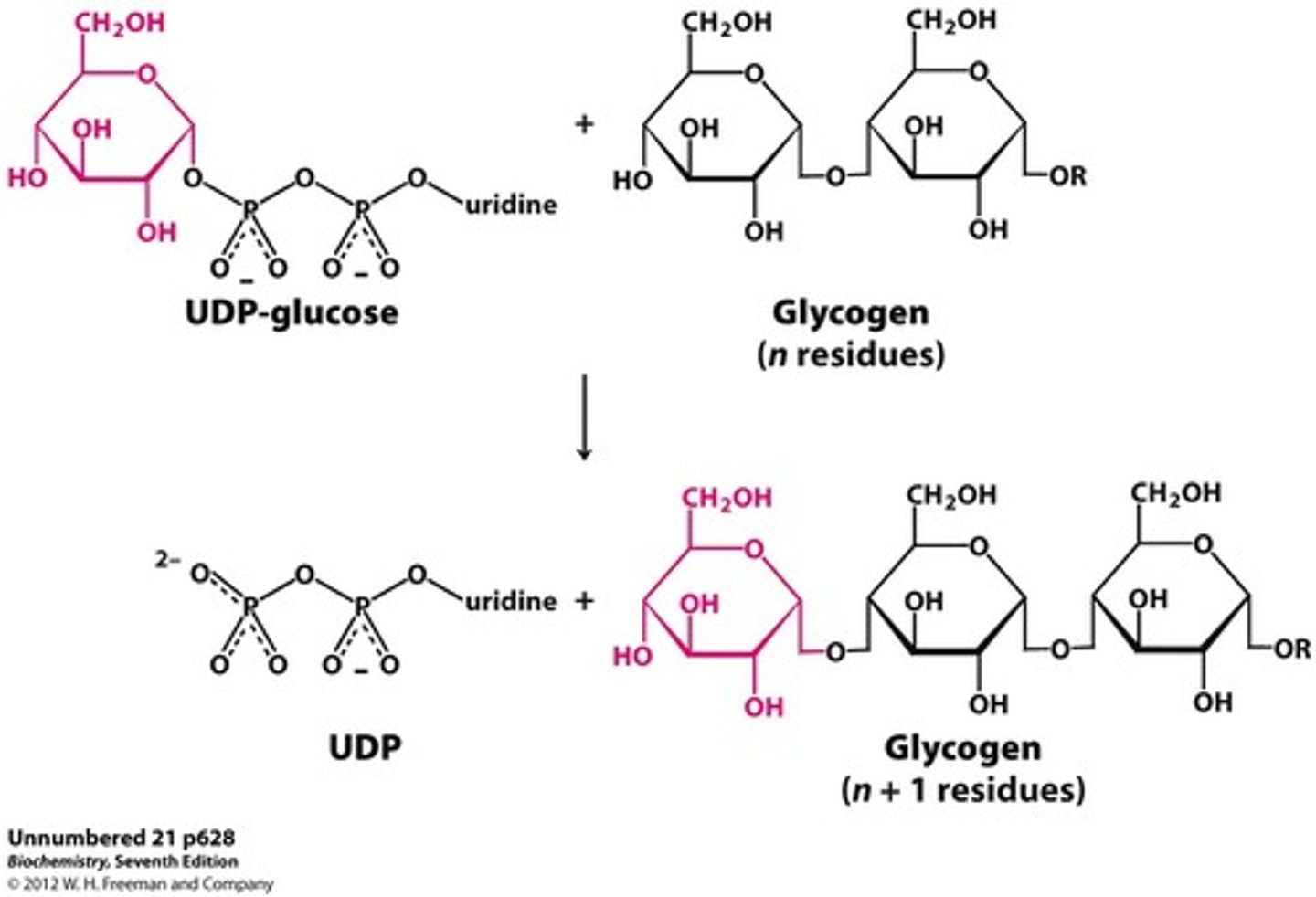
What bond is formed by Glycogen Synthase between the glucosyl unit of UDPG and glycogen's non-reducing end?
α(1→4) glycosidic bond
What is the ΔG° for the Glycogen Synthase reaction? Is it spontaneous?
-13.4 kJ/mol
spontaneous
What is the energetic price of Glycogen Synthesis?
1 UTP is cleaved to UDP for each glucose residue incorporated into glycogen.
How is UTP replenished in Glycogen Synthesis? What enzyme mediates it?
UTP is replenished using ATP as substrate through a phosphoryl-transfer reaction mediated by Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase.
UTP consumption is energetically equivalent to...
ATP consumption
Can Glycogen Synthase link together just any two glucose residues?
No. Glycogen Synthase CAN NOT simply link together two glucose residues.
Glycogen Synthase can only act on what to do Glycogen Synthesis?
It can ONLY extend already existing α(1→4)-linked glucan chains.
What happens in the 1st step of glycogen synthesis?
Glycogenin acts as glycosyltransferase.
What does Glycogenin attach to when it acts as a glycosyltransferase?
It attaches glucose residue donated by UDPG to OH group of its Tyr 194.
Glycogenin extends the glucose chain by up to how many additional UDPG-donated glucose residues?
extends it by 7 additional UDPG-donated glucose residues
In glycogen synthesis, what does Glycogenin extending the glucose chain by 7 UDPG-donated glucose residues make?
It forms a glycogen "primer"
What enzyme can work now that the glycogen "primer" is made? What does it do?
Glycogen Synthase can now extend the primer
Each glycogen molecule is associated with what two enzymes?
Each glycogen molecule is associated with 1 molecule glycogenin and 1 molecule glycogen synthase.
In Glycogen Synthesis, the Glycogen Branching Enzyme transfers glycogen segments with how many glucose residues?
Glycogen Branching Enzyme transfers 7-residue glycogen segments.
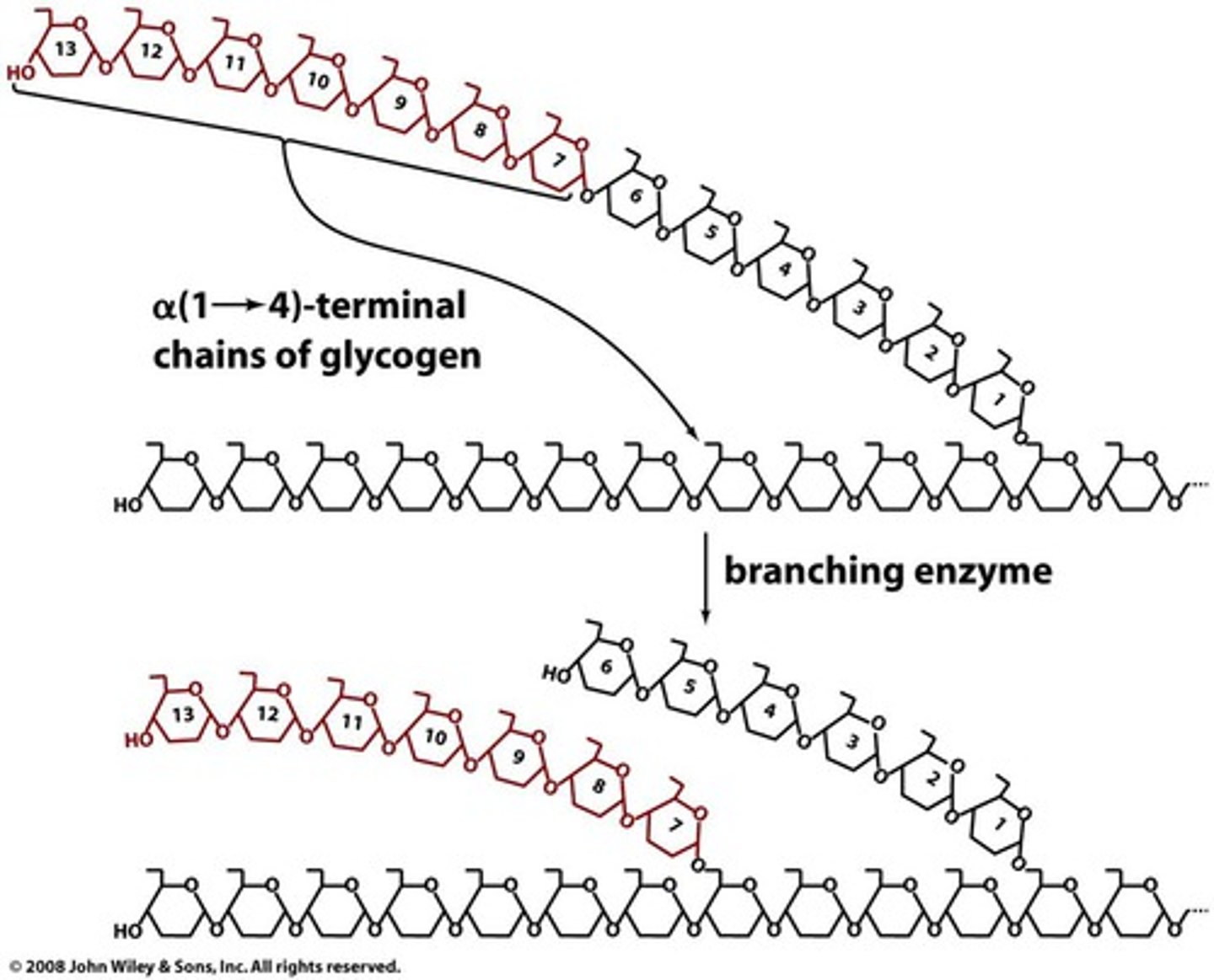
Glycogen Synthase generates only what type of linkages? What type of polymer does that produce?
Glycogen synthase generates only α(1→4) linkages to yield α-amylose. (no branches)
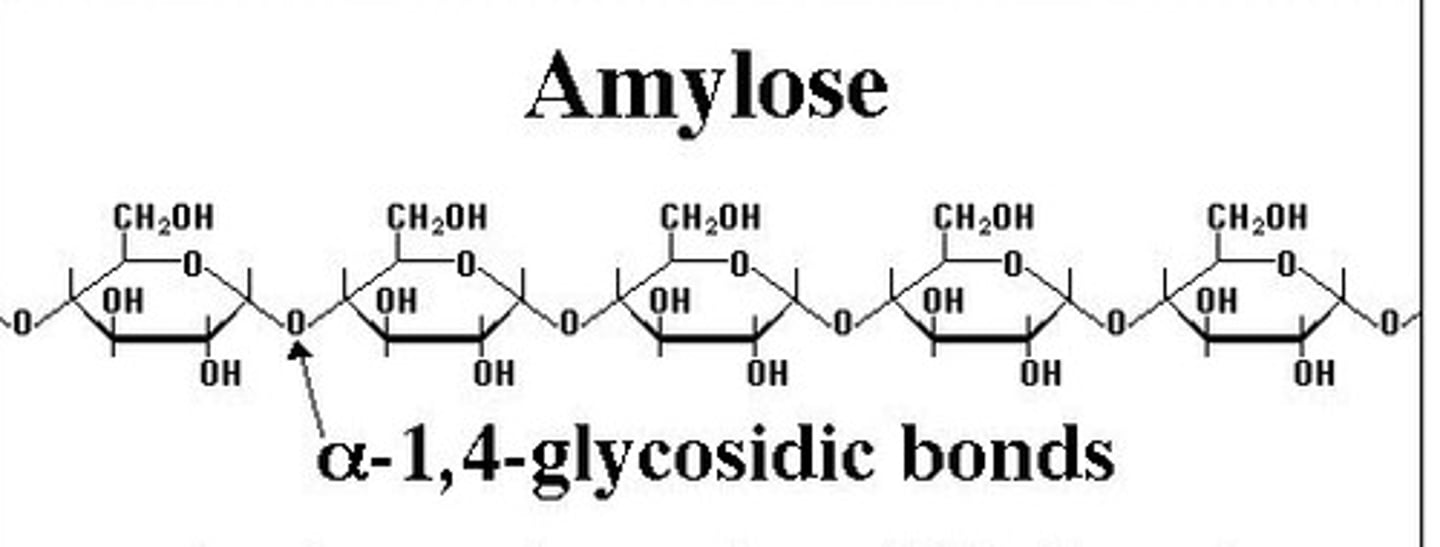
What is another name for the Glycogen Branching Enzyme?
amylo-(1,4→1,6)-transglycosylase
A branch is created by the Glycogen Branching Enzyme when transferring a 7-residue segment from where to where?
From chain end to C6-OH group of a glucose residue on the same or another glycogen chain.
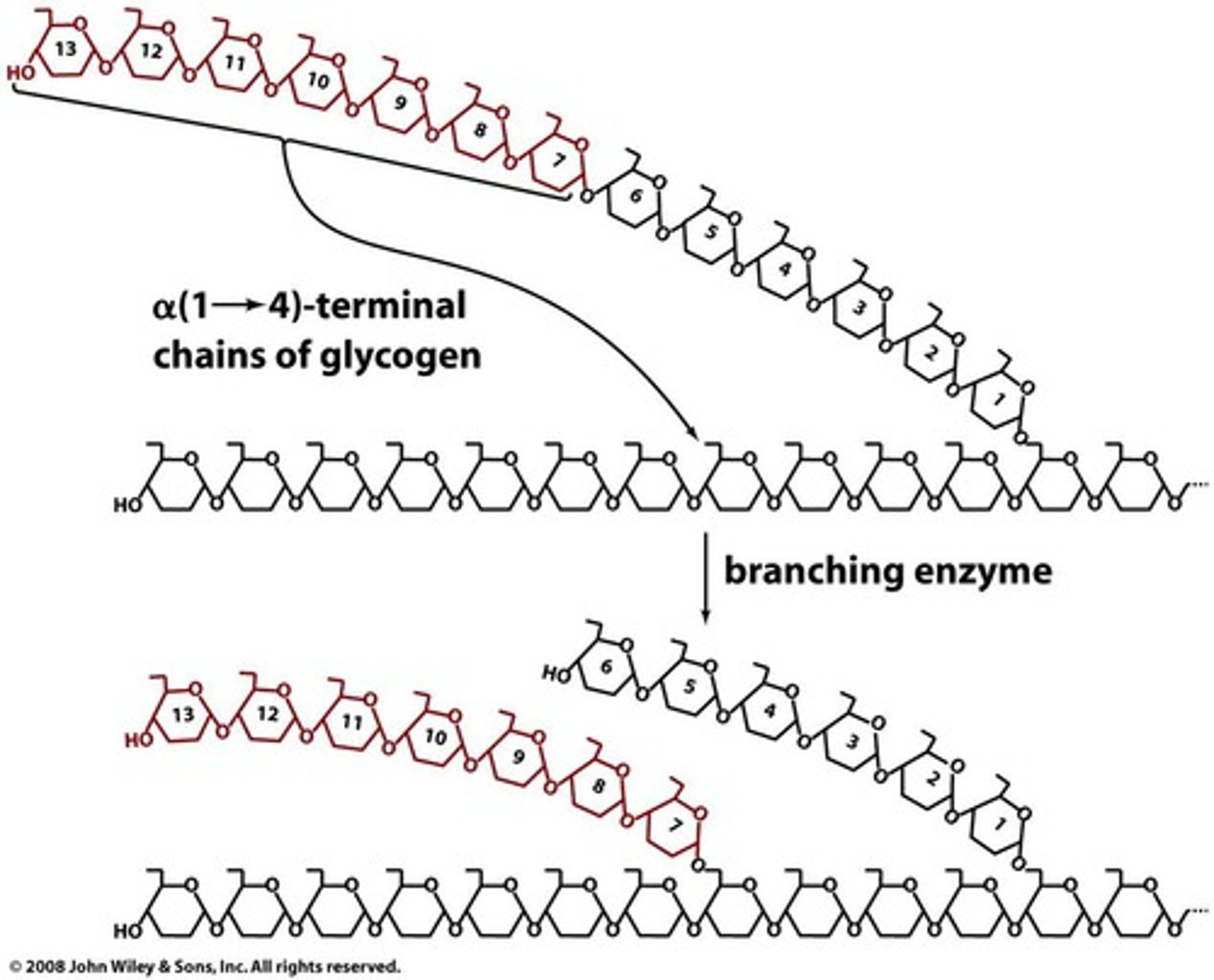
Each transferred segment by the Glycogen Branching Enzyme must come from a chain of at least ____ residues.
11 residues
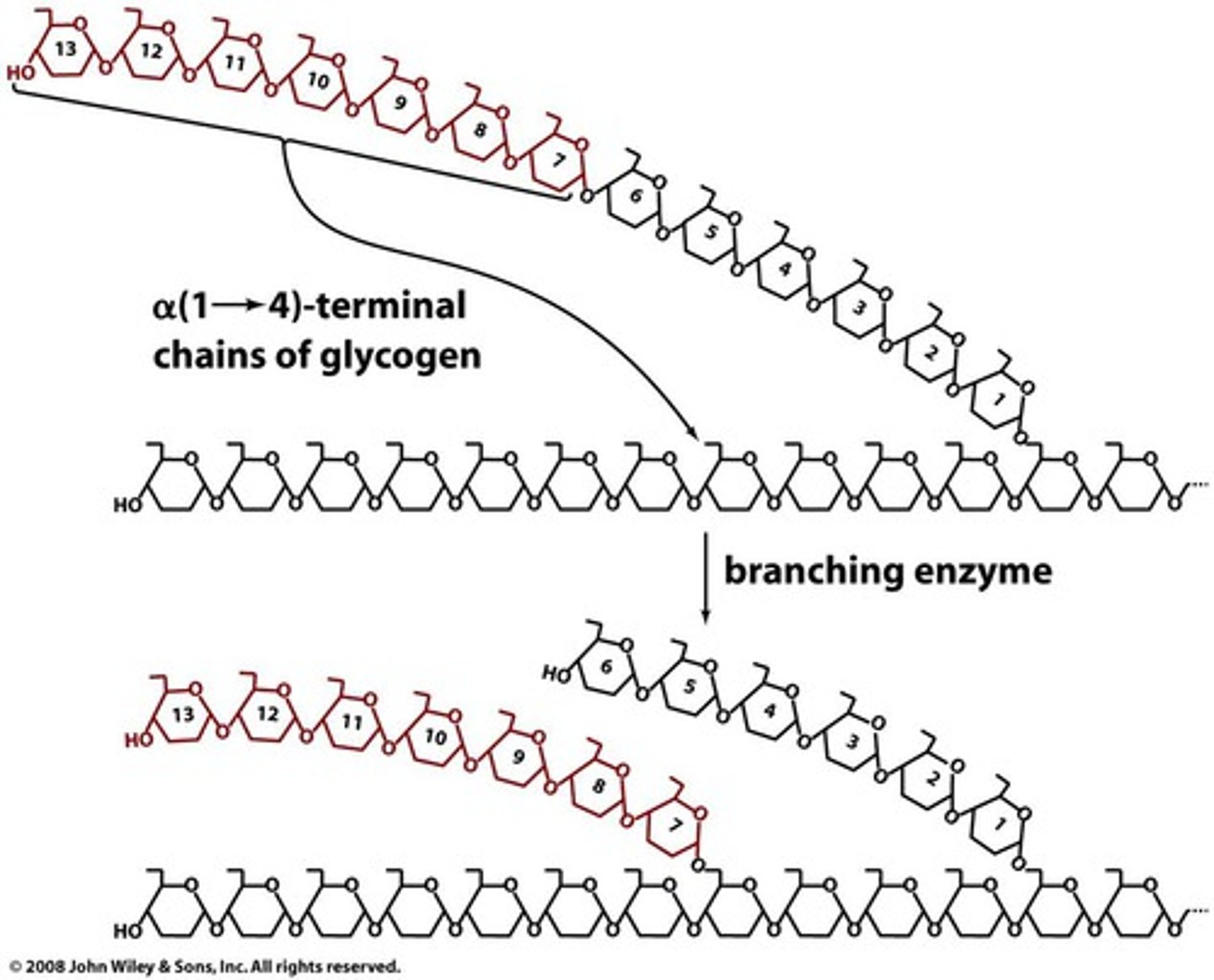
Each branch point of glycogen must be at least ____ residues away from other branch points.
at least 4 residues away
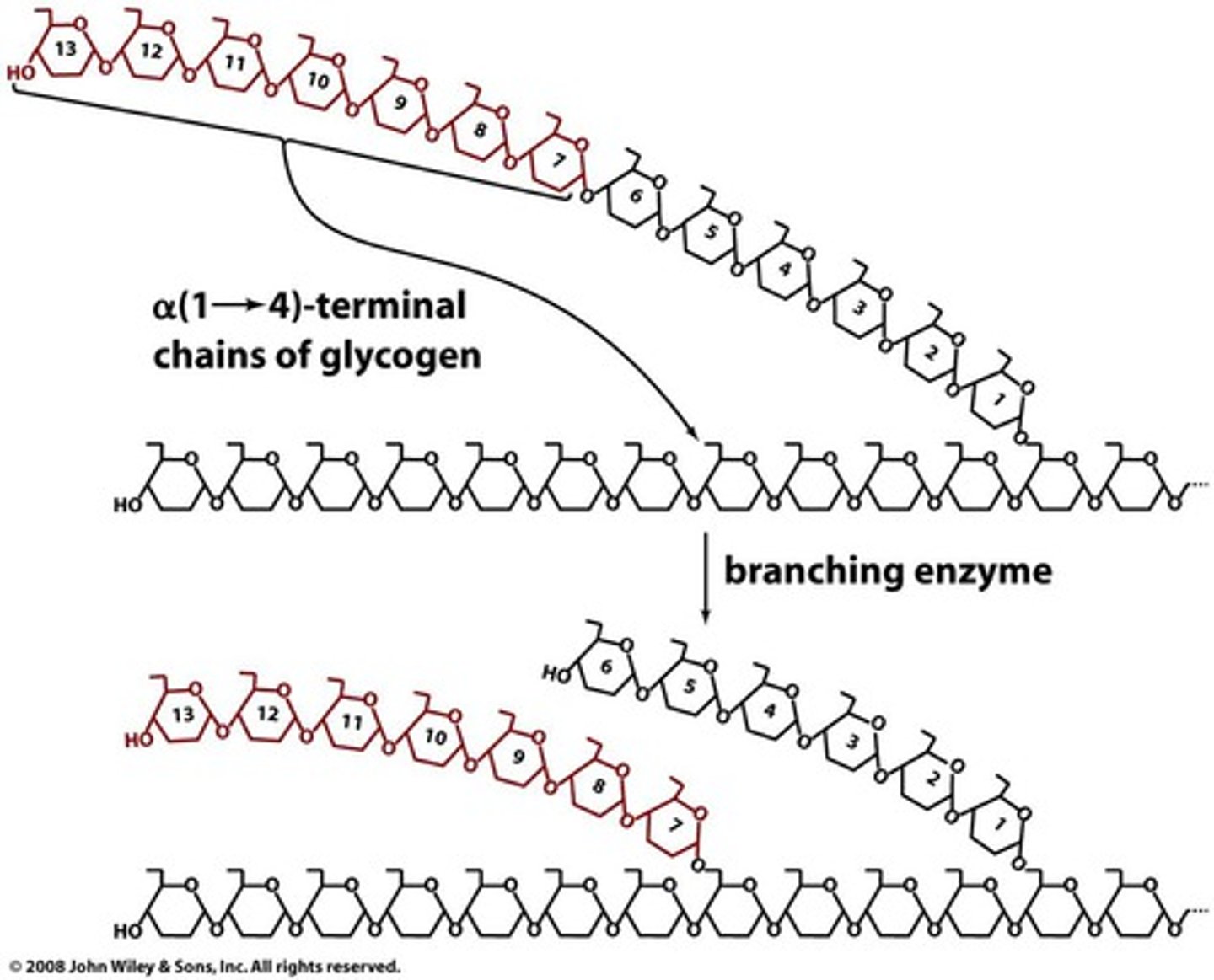
The branching pattern of glycogen has been optimized by evolution for what 2 things?
efficient storage and mobilization of glucose