5) Radical Halogenation of Alkanes + features of halogenation rxns
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
page 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
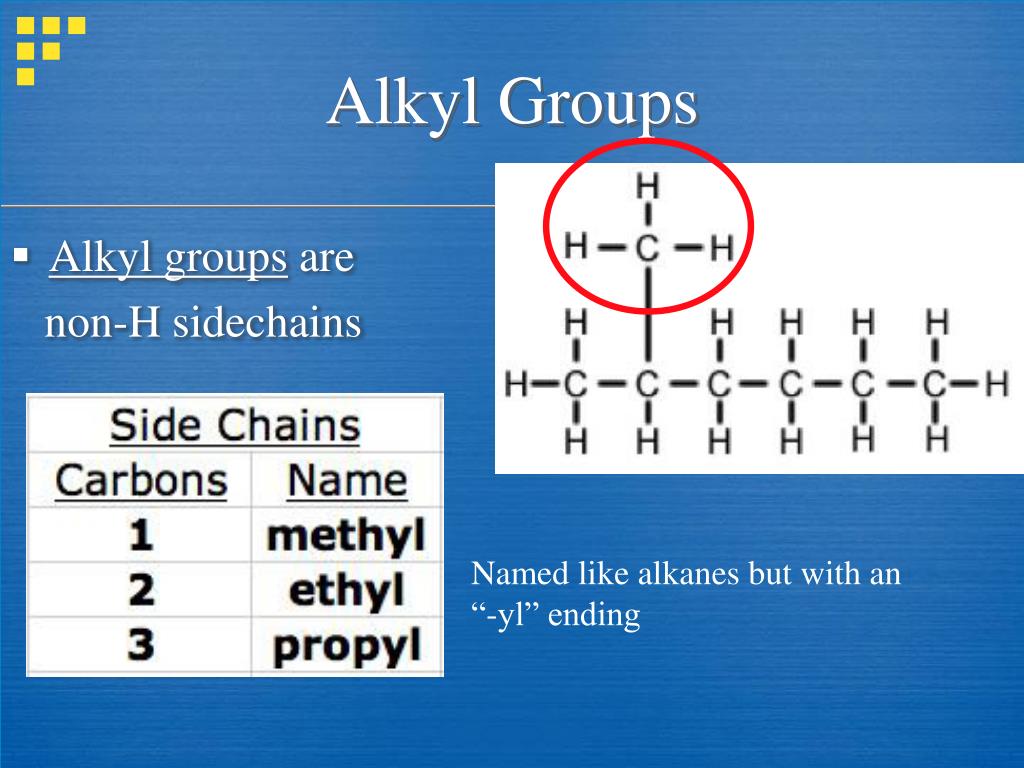
What is an alkyl?
An alkane missing 1 hydrogen; this allows a substituent to attach
What is a halide?
A halogen atom bonded to another element, typically carbon
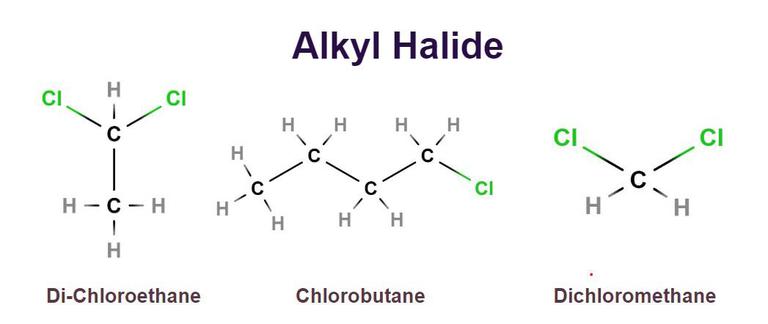
What is an alkyl halide?
Where a halogen is bonded to a carbon atom in an alkyl group
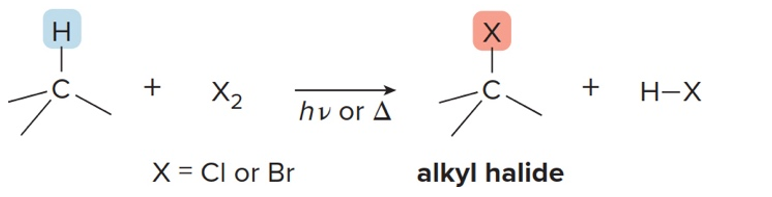
We use what halogens for radical halogenation?
Cl2 and Br2
Why don’t we use F or I atoms?
F reacts too violently and I reacts too slowly
What is radical halogenation?
A halogen (like Cl₂ or Br₂) replaces a hydrogen atom in an alkane
Mechanism of radical halogenation def
A step by step reaction of a halogen replacing a hydrogen atom
Alkanes with multiple types of C–H bonds (1°, 2° carbons) create?
a mixture of alkyl halide products
mixture of alkyl halide products def
a halogen has replaced a hydrogen on different carbon atoms (primary, secondary, etc) in the molecule
What are C-H bonds?
the alkane (saturated hydrocarbon chain, contains only C and H)
If the halogen is added in excess
multiple substitutions will occur, can connect to primary, secondary carbons and so on
If the alkane is in excess
monohalogenation will occur
What is monohalogenation?
Only one hydrogen atom in the alkane is replaced by one halogen atom
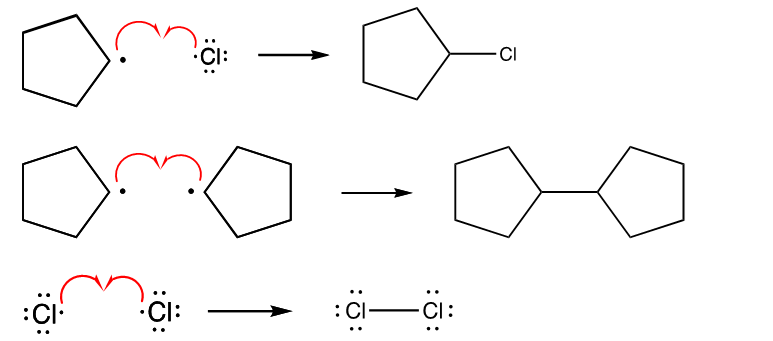
What is Initiation?
Two radicals are formed by homolysis of a sigma bond
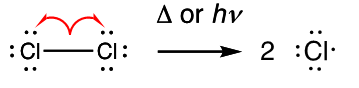
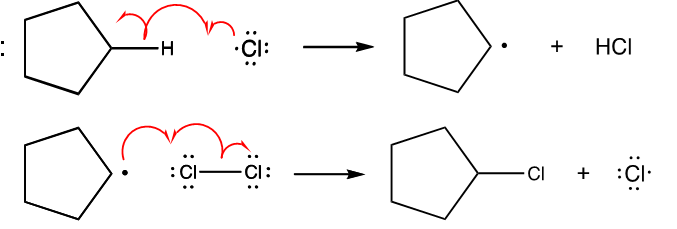
What is propagation?
A radical reacts with another reactant to form a new sigma bond and another radical
What is termination?
Two radicals react to form a stable bond, which stops the reaction.