Unit 5: Meteorology
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Water cycle and phase changes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
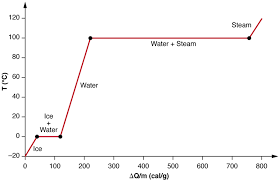
Why are there “flat places” in the curve?
Flat Places in the curve represent the time during which heat is being absorbed, but not enough heat has been absorbed to alter the current temperature.
This is called the latent heat stage and is where the phases are changing. Latent heat refers to the energy absorbed or released during a phase change, such as ice melting to water or water evaporating to vapor. (cannot add temperature and change phase at the same time.)
What is occurring to the phases of water at these stages?
The point in which energy is added or removed from the system. (depending on which way, and not enough heat) is absorbed to change the phase of water, resulting in transitions such as melting, freezing, or evaporating.
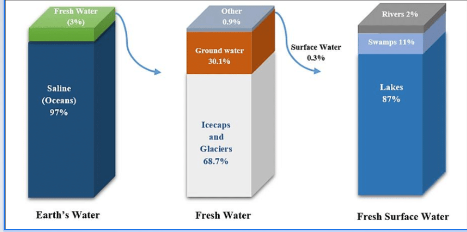
Water storage
Most of the time water is not moving along the water cycle, but being stored in the ocean. 70% of earth is covered in water! The ocean is the main storage of water (97%- look at graph on next slide) water is a polar bond
Accumulation
Where water gets collected & stored- in lakes, ponds, rivers, oceans, and other bodies of water
Evaporation:
Water goes from liquid to vapor (gas) state, because it is heated by the sun’s solar energy
Condensation
Water vapor (gas) cooling to liquid state
Clouds are a source of condensation. This is important because clouds produce precipitation.
Precipitation
Water released from clouds. Too much water coheres together and the water droplet falls back to earth. rain, hail, snow, ice)
Transpiration
The process by which water is absorbed by plants from the soil and then released as vapor (evaporation) through their leaves. It plays a significant role in the water cycle.
Surface Runoff
Water not absorbed by the ground, it travels on the earth’s surface.
Snowmelt Runoff
The runoff produced from melting snow, contributing to rivers and streams during warmer seasons. It is crucial for replenishing water supplies.
Infiltration
When precipitated water filters into the soil and is absorbed by the soil
Porosity
the amount of space between the grains of mineral/soil.
permeability.
The rate at which water moves through the ground (impermable water does not soak)
Groundwater
the term that describes the water underground
Stream discharge
when stream water goes to the ocean
Impervious
The name of a surface that water can’t pass through, and this carries pollutants into our drinking water:
Hight Pressure system
Cool air (more dense), not very moist air.
Low Pressure System
Warm air (less dense), very moist air.