Biology Cell Transport/Communication Test
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Robert Hooke
Scientist who discovered the first cell in a piece of cork
Cell Theory
Theory that states:
1. All Living Things are made up of cells
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function
3. New cells are produced from pre-existing cells
Eukaryotic
Type of cell that has a nucleus
Prokaryotic
Type of cell that DOES NOT have a nucleus
Cytoplasm
Where DNA is found in unicellular organisms
Prokaryotic
What type of cell bacteria is
Asexual Reproduction
What type of reproduction bacteria does to reproduce
Budding
Type of asexual reproduction when a small part of the cell breaks off
Binary Fission
Type of asexual reproduction when the cell splits
Bacillus
Oval shape of bacteria
Coccus
Circular shape of bacteria
Spirillus
Spiral shape of bacteria
Autotrophic
Type of organism that creates its own food for energy, usually in the form of photosynthesis
Chemotrophic
Kind of organism that uses chemicals to obtain energy
Heterotrophic
Type of organism that has to eat to obtain energy
Extremophiles
Organisms (bacteria) that live in extreme areas, like super hot or cold, or acidic or basic areas
Pathogens
What bad bacteria in your body is called
Antibodies
What your body produces to fight pathogens
No
Is a virus a living thing? (Yes/No)
Head
Where RNA is stored in viruses
Base Plate
What part of a virus is used to anchor onto cells
No
Are viruses made of cells? (Yes/No)
Vaccines
What is used to prevent viruses
Passive Transport
Type of cellular transport that DOES NOT require energy
Active Transport
Type of cellular transport that DOES require energy
Diffusion
Process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Cell Membrane
Where diffusion goes through
Equilibrium
When the concentrations on both sides are equal (This is a STATE OF BEING)
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion of molecules that require the use of channel proteins. An example is water, because it is a polar molecule
Osmosis
Type of facilitated diffusion that uses aquaporins to diffuse water through the cell membrane
Concentration Gradient
The direction of the flow of molecules
Against
Which way does active transport go on the concentration gradient (With/Against)
With
Which way does passive transport go on the concentration gradient (With/Against)
Endocytosis
Type of Active Transport by which the cell membrane folds around a substance and creates a vesicle to transport around the cell
Exocytosis
Type of Active Transport by which the vesicle merges with the cell membrane and releases the substance out of the cell
Protein Pump
Active Transport that requires ATP energy shoot it out of the cell against the concentration gradient
Semi Permeable
When only certain substances are allowed to travel through something
Osmotic Pressure
Force exerted by the net movement of water in or out of the cell
Isotonic
When the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same
Hypertonic
When the concentration is greater in relation to another substance
Hypotonic
When the concentration is less in relation to another substance
Plasmolyzed
When the cell membrane shrivels up but the cell wall stays intact in bacteria
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Hydrophilic
Water loving
Glycerol
What part of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) is hydrophilic?
Fatty Acid
What part of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) is hydrophobic?
Cells
Smallest level of organization
Tissues
Level of organization made up of cells
Organs
Level of organization made up of tissues
Organ Systems
Level of organization made up of organs
Receptors
Part of cell membrane that will receive chemical signals
Signal Transduction Pathways
What converts signals received cell’s surface into cellular responses
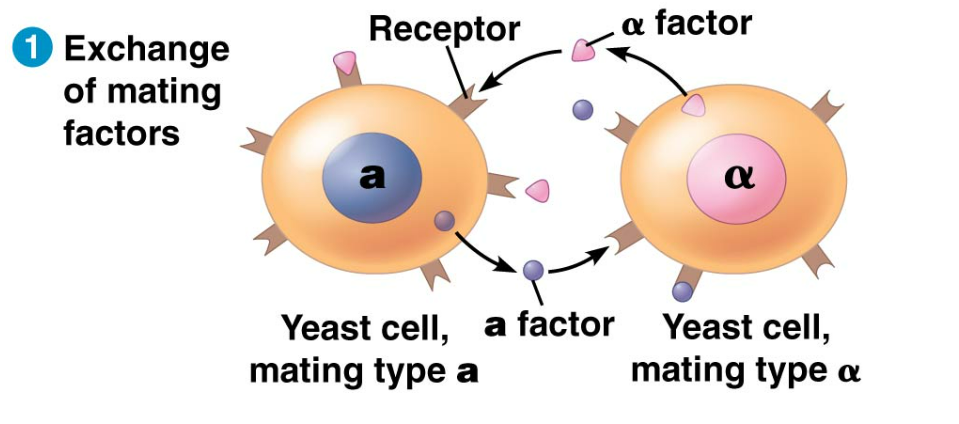
Exchange of Mating Factors
1st step in mating cells. Each cell type secretes a mating factor that binds to receptors on the other cell type.
Mating
2nd step in mating cells. Binding of the factors to receptors induces changes in the cells that lead to their fusion
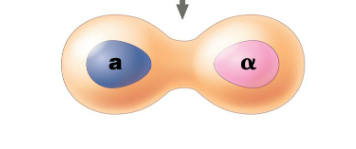
New Cell
Last step in mating cells. The nucleus of the fused cell includes all the genes from each of the two cells.

Quorum Sensing
A concentration of signaling molecules that allows bacteria to sense local population density
Cell Junctions
Allows molecules to pass readily between adjacent cells without crossing the cell membrane
Gap Junction
A cell junction in an animal cell
Plasmodesmata
A cell junction in a plant cell
Cell-Cell recognition
What it is called when 2 cells are able to communicate by molecules protruding touching each other from their surfaces
Growth Factors
Stimulate nearby target cells to grow and divide
Synaptic Signaling
Occurs in animal nervous system when a neurotransmitter is released in response to an electrical signal
Hormones
What is used in long distance signaling
Reception
1st stage of cell signaling. Target cell detects a signaling molecule that binds to a receptor protein on the cell surface
Transduction
Binding of signaling molecule alters the receptor and initiates a signal transduction pathway
Response
Transduced signal triggers a specific response in the target cell