Module 1 Terms
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
anterior
to the front/in front
cuadad
tail end
cephalad
in the front/toward front
distal
far away
inferior
below
superior
above
proximal
close to
posterior
the back
medial
toward/ in the middle
lateral
to the side
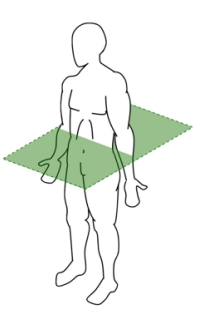
transverse plane
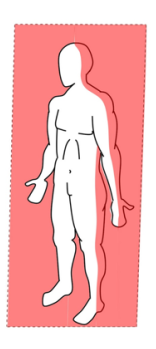
Frontal plane
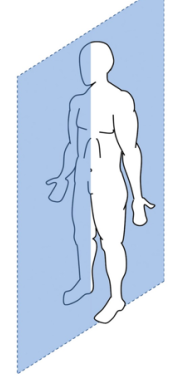
sagittal plane
organ
a structure that is composed of two or more tissues, has a definite shape, and performs specific functions organ system
organ system
a group of organs that functions in a coordinated manner to perform specific functions
Alkalosis (basic)
tissue pH greater than 7.4
7.35
normal blood pH
Acidosis (acidic)
tissue pH less than 7.35
buffers
molecules that reduce or increase the pH in the body in an effort to maintain normal pH levels
Break down and don’t work
what happens to enzymes when normal pH is not maintained
Hydrophobic molecules
molecules that do not dissolve in water
hydrophilic molecules
molecules that dissolve in water
hydophilic
are carbohydrates hydrophobic or hydophilic
Water’s role in the human body
protects cells, tissues, and organs, Helps to process body waste, helps with digestion, and helps regulate temperature
adenosine triphosphate
macromolecule that breaks apart molecules to make molecules
Carbohydrate
used for energy, body structure, monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide; go to for quick energy
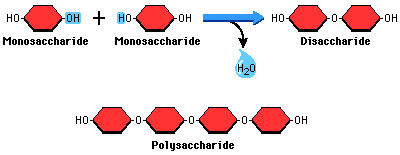
glucose
monosaccharide, C6H12O6, major molecule needed for energy in the human body
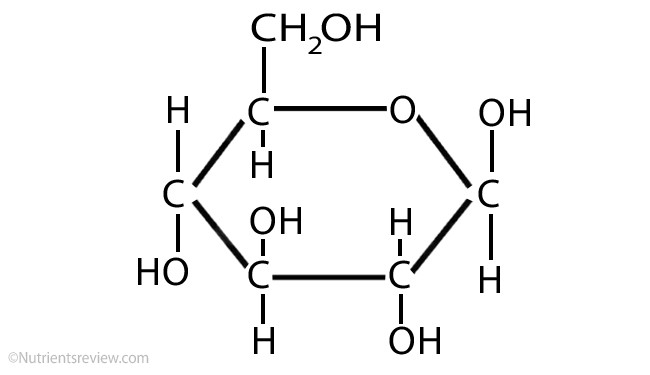
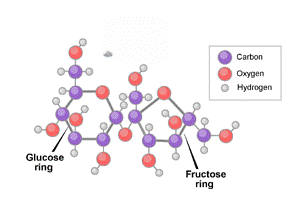
sucrose
disaccharides, can be broken down into monosaccharides
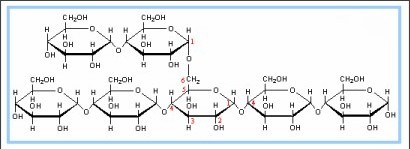
glycogen
polysaccharides, found in muscles and liver, storage molecule of humans
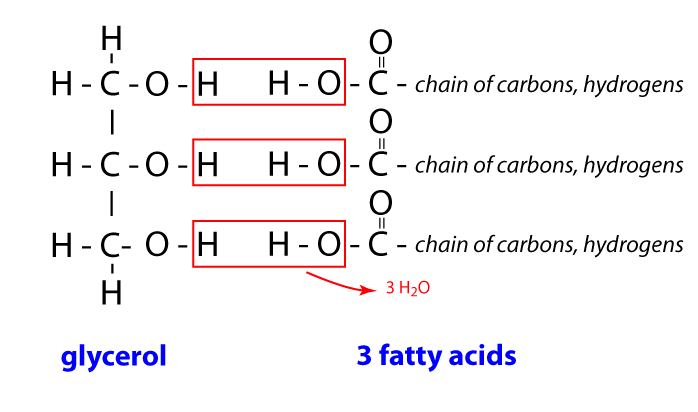
lipids
storage energy, insulates body, protects organs, provides structure for the body, hydrophobic in water, can be saturated or unsaturated; hormones; cholesterol; composed of glycerol and fatty acids; HYDOPHOBIC
unsaturated fats
contain one or more double bonds in the carbon chain, liquids at room temp
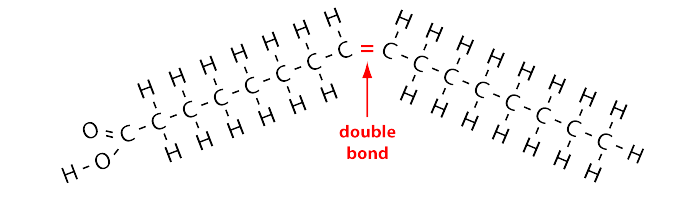
saturated fats
contain single bonds throughout their carbon chains, solids at room temperature
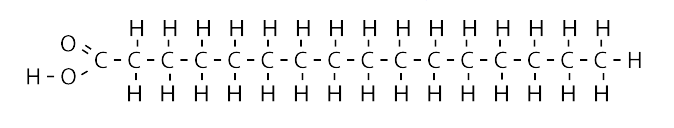
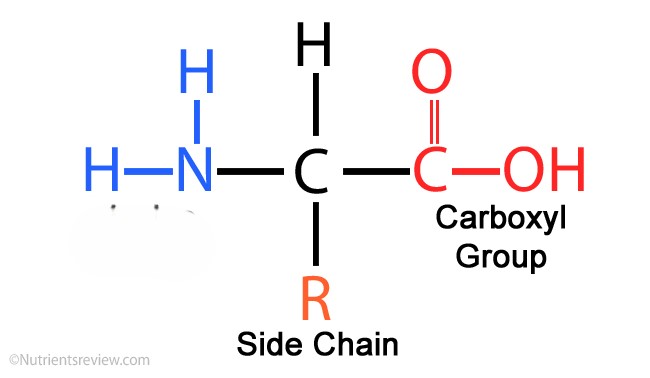
amino acid
Function: structure for the body, chemical messengers, promote chemical reactions, used by nucleic acids
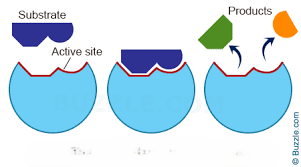
Enzyme
proteins: biological catalysts, speed up chemical reactions, lock and key mechanism
Vitamins
macromolecules needed for chemical reactions
Neurotransmitters
macromolecules that are chemical messenger in the nervous system
Hormones
chemical messengers for the body; released directly into the blood stream; speeds up chemical reactions
Transcription
process where m-RNA is made from DNA
Translation
process where DNA is read to make amino acid chains
Proteins
long chains of polypeptide chains that have a specific function, biological molecules responsible for creating and maintaining human structures; hormones; uses lock and key model; produced by nucleic acids
Peptide bond
amino acids are bonded together by this
Nucleic Acid
DNA and RNA are classified as this type of biological material, provides the genetic basis for all living things
Proteins and nucleic acid
two general types of biological molecules that contain nitrogen
RNA
nucleic acid that is single stranded and contains uracil
DNA
nucleic acid that is double stranded and contains thymine, made of nucleic acids, and countians that blueprint for maintaining the organism and provides the genetic basis for all living things
Lock and key model
the model used to describe how proteins interact with other molecules
Lactase
enzyme needed to break down lactose
non essential amino acids
amino acids that can be manufactured within the body
essential amino acids
amino acids that must be obtained through your diet
types of lipids
prostaglandin, phospholipid, saturated fats, unsaturated fats, cholesterol
plaque
sticky cholesterol deposits found on blood vessel walls
hypercholesteralemia
elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood stream
ketone bodies
molecular waste from breaking down triglycerides for energy
types of carbohydrates
cellulose, starch, glycogen
macromolecules
large molecular units; all contain C
aerobic
oxygen is present
anaerobic
oxygen is not present
electrolytes
ions that are found in the human body; important in fluid balance
Polyomer
Composed of many simple molecules that are repeating structural units called monomers
example: DNA and protiens
monomers
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
example: glucose
Surfactants
necessary for lung inflation and preventing lung collapse
Gylcogen
storage molecule of humans