Ch 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from Section 1.1: Systems of Linear Equations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
System of Linear Equations
A collection of one or more linear equations involving the same variables x_1,\ldots,x_{n} .
Linear Equation
An equation that can be written as a_1x_1 + a_2x_2 + … + a_nx_n = b, where the coefficients a_1,\ldots,a_{n} and the constant b are real or complex numbers.
Solution
A tuple (x_1,…,x_n) of numbers that makes every equation in the system true when substituted.
Solution Set
The complete set of all solutions to a linear system.
Equivalent Systems
Two systems that have the same solution set.
Consistent
A system that has at least one solution (one or infinitely many).
Inconsistent
A system that has no solution.
No Solution
A situation where no assignment of values satisfies all equations in the system.
Exactly One Solution
A system that has a single, unique solution.
Infinitely Many Solutions
A system that has an infinite number of solutions.
Coefficient Matrix
The rectangular array containing only the coefficients of the variables from a linear system.
Augmented Matrix
The coefficient matrix with an added column containing the constants from the right-hand sides.
Matrix Size
The dimensions mxn of a matrix, read as 'm by n' (m rows, n columns).
Elementary Row Operations
The three operations used to simplify a system: replace a row by the sum of itself and a multiple of another row; interchange two rows; and multiply a row by a nonzero constant.
Row Equivalence
Two matrices are row equivalent if one can be transformed into the other by a sequence of elementary row operations; they have the same solution set for their associated systems.
Triangular Form
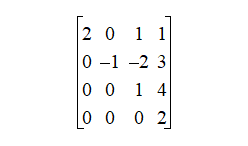
A form of the augmented matrix (or the system) where equations are arranged so that the leading (first nonzero) entry moves to the right as you go down, enabling step-by-step solving.
Existence and Uniqueness Questions
Two questions used to classify a linear system: (1) Is the system consistent? (2) If consistent, is the solution unique?
Check Solution
Substituting the found solution back into the original equations to verify correctness.
Floating Point Arithmetic
Real-number arithmetic on computers with finite precision, which can introduce rounding errors; software often uses floating point representations.