HP412 Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:20 AM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
trauma-related disorders
Acute stress disorder
Adjustment disorder
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD
Adjustment disorder
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD
2
New cards
Acute stress disorder
acute maladaptive reaction in days and weeks following traumatic event (under 1 month)
(2-4 weeks)
(2-4 weeks)
3
New cards
Adjustment disorder
A maladaptive response to some type of life stress (whether traumatic or not
4
New cards
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Prevalence: 9%
Gender differences: women more likely to get diagnosis
Risk factors for PTSD:
-women
-homeless, SUD, mental illness
Gender differences: women more likely to get diagnosis
Risk factors for PTSD:
-women
-homeless, SUD, mental illness
5
New cards
schizoid and schizotypal (A)
6
New cards
Histrionic and Narcissistic
7
New cards
Definition of traumatic event
An event involving some direct threat of death, severe bodily harm, or psychological injury to the self or another person.
8
New cards
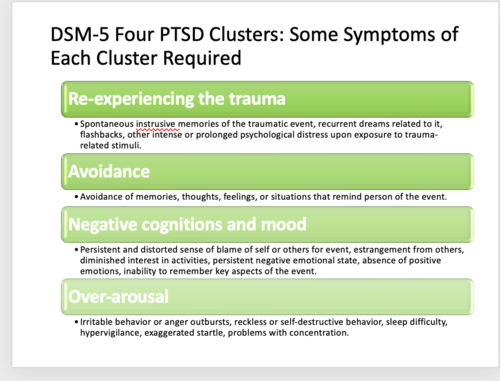
Diagnostic criteria for PTSD (4 clusters)
over 1 month
must have some from each cluster
Re-experiencing symptoms:
Avoidance symptoms:
negative cognitions and mood;
Heightened arousal symptoms:
must have some from each cluster
Re-experiencing symptoms:
Avoidance symptoms:
negative cognitions and mood;
Heightened arousal symptoms:
9
New cards
Other common symptoms of PTSD
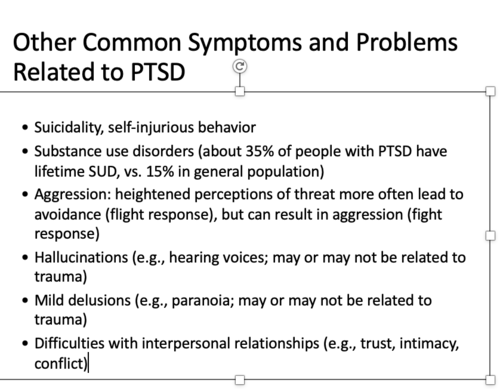
•Suicidality, self-injurious behavior
•Substance use disorders (about 35% of people with PTSD have lifetime SUD, vs. 15% in general population)
•Aggression: heightened perceptions of threat more often lead to avoidance (flight response), but can result in aggression (fight response)
•Hallucinations (e.g., hearing voices; may or may not be related to trauma)
•Mild delusions (e.g., paranoia; may or may not be related to trauma)
•Difficulties with interpersonal relationships (e.g., trust, intimacy, conflict)
•Substance use disorders (about 35% of people with PTSD have lifetime SUD, vs. 15% in general population)
•Aggression: heightened perceptions of threat more often lead to avoidance (flight response), but can result in aggression (fight response)
•Hallucinations (e.g., hearing voices; may or may not be related to trauma)
•Mild delusions (e.g., paranoia; may or may not be related to trauma)
•Difficulties with interpersonal relationships (e.g., trust, intimacy, conflict)
10
New cards
Factors related to trauma V.
Factors related to person or situation
Factors related to person or situation
Increased risk for PTSD in serious mental illness
factors related to event:
-degree of exposure to trauma
-severity of trauma
factors related to person:
-history of abuse
-lack of social support
-genetic predisposition
-feeling of shame
-prior psychiatric history
-lack of coping
-detachment/ dissacociation
factors related to event:
-degree of exposure to trauma
-severity of trauma
factors related to person:
-history of abuse
-lack of social support
-genetic predisposition
-feeling of shame
-prior psychiatric history
-lack of coping
-detachment/ dissacociation

11
New cards
treatment for PTSD
1) Exposure therapies* (e.g., prolonged exposure therapy)
2) Cognitive restructuring* (e.g., cognitive processing therapy)
EMDR: eye movement following
SSRIs
Other treatments
Yoga and meditation
Brief therapies
Journaling
Present centered therapy
2) Cognitive restructuring* (e.g., cognitive processing therapy)
EMDR: eye movement following
SSRIs
Other treatments
Yoga and meditation
Brief therapies
Journaling
Present centered therapy
12
New cards
Theory underlying exposure therapies
Mower 2-factor theory (1950): classical and operant conditioning combined create PTSD
emotional processing theory: foas and kozak:
designed to reduce associations between CS (memories of event, similar situations) and CR (fear) by preventing reinforcement of avoidance of CS, resulting in habituation of fear
emotional processing theory: foas and kozak:
designed to reduce associations between CS (memories of event, similar situations) and CR (fear) by preventing reinforcement of avoidance of CS, resulting in habituation of fear
13
New cards
basic treatment for exposure therapy:
-prolonged exposure: imaginal + in vivo (most studied treatment)
-tell story, rate stress out of 100, tell again
-tell story, rate stress out of 100, tell again
14
New cards
basic treatment for cognitive restructuring
cognitive processing therapy
•Second most empirically supported treatment for PTSD (after exposure therapy)
•Individual or group therapy formats feasible
•12-16 sessions
•Most programs provide psychoeducation and strategies for coping with anxiety
•Primary focus is on teaching cognitive restructuring as skill for examining thinking related to upsetting feelings, and then using skill to address trauma-related thoughts and beliefs
•Homework collaboratively agreed upon to practice skills between sessions
•Some cognitive restructuring programs also include an exposure component
•Research indicates cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy are equally effective
•Combining cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy not more effective than either one alone
•Second most empirically supported treatment for PTSD (after exposure therapy)
•Individual or group therapy formats feasible
•12-16 sessions
•Most programs provide psychoeducation and strategies for coping with anxiety
•Primary focus is on teaching cognitive restructuring as skill for examining thinking related to upsetting feelings, and then using skill to address trauma-related thoughts and beliefs
•Homework collaboratively agreed upon to practice skills between sessions
•Some cognitive restructuring programs also include an exposure component
•Research indicates cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy are equally effective
•Combining cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy not more effective than either one alone
15
New cards
classical conditioning (learned by association)
Traumatic event (unconditioned stimulus) produces an unconditioned response (fear, pain) → previously innocuous stimuli that where present when this pairing occur of traumatic event can be conditioned through association (conditioned response- seeing certain things, triggers associated with response)
16
New cards
operant conditioning (learned by consequences)
avoidance of dear inducing stimuli (CS) such as driving car, leads to reduction in anxiety (negative reinforcement) and increased avoidance
17
New cards
Theory underlying cognitive restructuring therapies
Horowitz; Ehlers & Clarkb
-Difficulty integrating new and old beliefs leads to intrusions related to traumatic events
Traumatic events challenge previously held beliefs about self, others, or world
Giving people tools for examining thinking→ used to process and integrate trauma
Combination of 2 is not more effective than individual treatments alone
-Difficulty integrating new and old beliefs leads to intrusions related to traumatic events
Traumatic events challenge previously held beliefs about self, others, or world
Giving people tools for examining thinking→ used to process and integrate trauma
Combination of 2 is not more effective than individual treatments alone
18
New cards
Substance use disorders (SUD)
Diagnostic criteria for SUD:
-hazerdous. use
-social/ interpersonal problems
-neglect major roles
-withdrawal
-tolerance build up
-using more amounts
-repeated attempts to regulate/ quit
-much time spent using
-physical or psychological problems
-activities given up to use
-craving
Severity of SUD:
mild: 2-3 symptoms
moderate: 4-5 symptoms
severe: 6+ symptoms
Gender differences:
-hazerdous. use
-social/ interpersonal problems
-neglect major roles
-withdrawal
-tolerance build up
-using more amounts
-repeated attempts to regulate/ quit
-much time spent using
-physical or psychological problems
-activities given up to use
-craving
Severity of SUD:
mild: 2-3 symptoms
moderate: 4-5 symptoms
severe: 6+ symptoms
Gender differences:
19
New cards
psychological dependence
the feeling that a drug is needed to continue a feeling of emotional or psychological well-being
20
New cards
Physiological dependence
-use of increasingly greater amounts of drug to experience same effect (tolerance)
-negative physical response when the substance is no longer used (withdrawal)
-negative physical response when the substance is no longer used (withdrawal)
21
New cards
General categories of SUD
Depressants
Alcohol use disorder
Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol related brain damage: Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, dementia
Stimulant use disorder (cocaine, amphetamine-type)
Opioid use disorder
Cannabis use disorder
Hallucinogen use disorder
Inhalant use disorder
gambling disorder
Alcohol use disorder
Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol related brain damage: Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, dementia
Stimulant use disorder (cocaine, amphetamine-type)
Opioid use disorder
Cannabis use disorder
Hallucinogen use disorder
Inhalant use disorder
gambling disorder
22
New cards
Alcohol related brain damage: from long term use
Wernicke-Korsakoff:
dementia
dementia
23
New cards
Comorbidity of SUD with other psychiatric disorders
Severity of disorder= proportional to greater risk of substance disorder
Anxiety disorders and depression have rates of SUD 25-35%
PTSD has rates of 30-40%
Antisocial personality disorder= HIGHEST RISK (>50%)
Schizophrenia, schiozo effective, BPD, major depression
Anxiety disorders and depression have rates of SUD 25-35%
PTSD has rates of 30-40%
Antisocial personality disorder= HIGHEST RISK (>50%)
Schizophrenia, schiozo effective, BPD, major depression

24
New cards
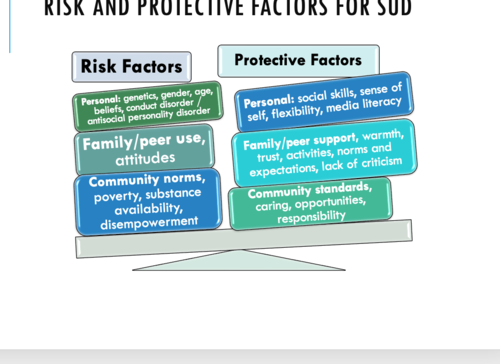
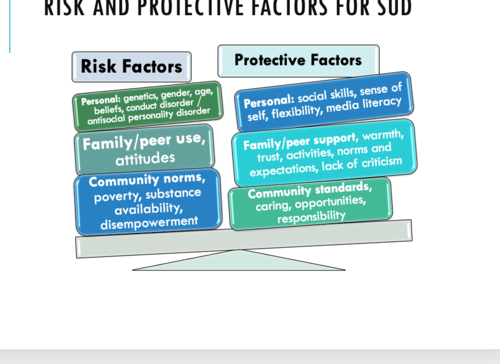
Risk factors for SUD
-personal: genetics, age, gender, belief, conduct disorder, antisocial personality disorder
-family/ peer use/ attitudes
-community norms, poverty, substance availability, disempowerment
-family/ peer use/ attitudes
-community norms, poverty, substance availability, disempowerment
25
New cards
protective factors for SUD
personal: social skills, sense of self, flexibility, media literacy
family/ peer support
community standards: caring, opportunities etc.
family/ peer support
community standards: caring, opportunities etc.
26
New cards
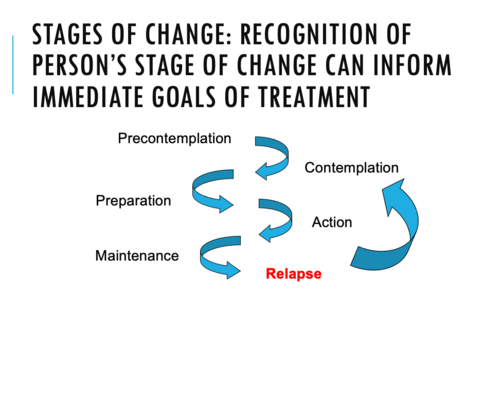
Stages of change: recognition of persons stage of change can inform immediate goals of treatments:
Precontemplation
Preparation
Action
Maintenance
*relapse*
Contemplation
Preparation
Action
Maintenance
*relapse*
Contemplation
27
New cards
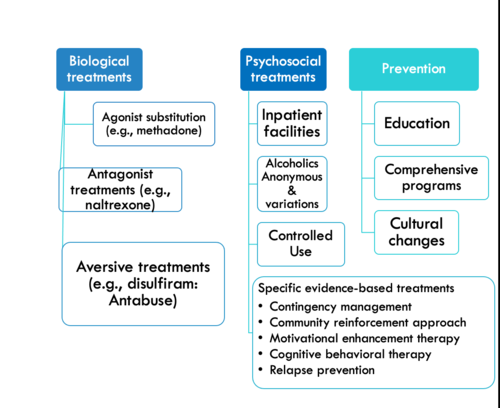
Treatment for SUD
BIOLOGICAL:
Agonist substitution (same or similar effect as drug but safer or less harmful: mimicks neurotransmitter
Eg: heroin addiction→ methadone agonist
Antagonist (blocking effects of substance, such as naltrexone for alcohol use
disorder or opioid addiction)
Aversive (causes negative reactions when substance used, such as disulfiram for
alcohol use disorder)
PHYSCOSOCIAL:
Self-help (e.g., AA)
Psychosocial
(evidence-based)
Contingency management: positive reinforcement for not using substances (pay someone to stop using)
Community reinforcement approach: work with natural support, work to enforce natural reinforcers , make one realize negative consequences of using
Motivational enhancement therapy: Motivate people to change behavior based on ones personal goals in life→ helping them see the interference of substance use
CBT
Relapse prevention therapy: identify situations of when is most likley to have relapse→ prevent those
Self-control strategies for substance use
("Modifying ABCs of Substance Abuse")
Stages of change: One goes through series of stages when going through stages→ ID stage ones at to help them get to next stage
Agonist substitution (same or similar effect as drug but safer or less harmful: mimicks neurotransmitter
Eg: heroin addiction→ methadone agonist
Antagonist (blocking effects of substance, such as naltrexone for alcohol use
disorder or opioid addiction)
Aversive (causes negative reactions when substance used, such as disulfiram for
alcohol use disorder)
PHYSCOSOCIAL:
Self-help (e.g., AA)
Psychosocial
(evidence-based)
Contingency management: positive reinforcement for not using substances (pay someone to stop using)
Community reinforcement approach: work with natural support, work to enforce natural reinforcers , make one realize negative consequences of using
Motivational enhancement therapy: Motivate people to change behavior based on ones personal goals in life→ helping them see the interference of substance use
CBT
Relapse prevention therapy: identify situations of when is most likley to have relapse→ prevent those
Self-control strategies for substance use
("Modifying ABCs of Substance Abuse")
Stages of change: One goes through series of stages when going through stages→ ID stage ones at to help them get to next stage
28
New cards
Features of personality disorders
Early onset: precursors in adolescence
Stable over time
Pervasive: evident across many aspects of individuals life: personal, social, occupational situation
Clinically significant impairment: personal distress or impairment in social/ occupational function
Stable over time
Pervasive: evident across many aspects of individuals life: personal, social, occupational situation
Clinically significant impairment: personal distress or impairment in social/ occupational function
29
New cards
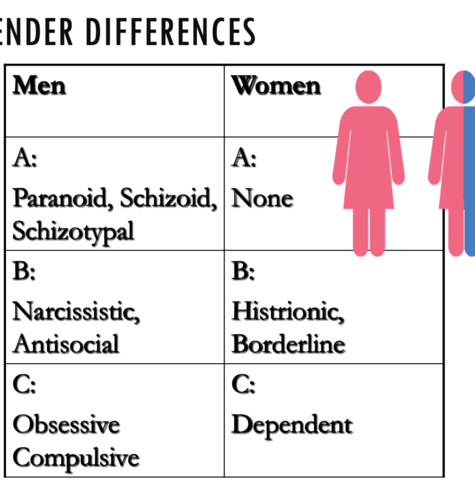
Gender differences of personality disorder:
Antisocial personality disorder - men
Schizoid / paranoia: men
Histrionic personality disorder: women
Borderline personality disorder: women
Schizoid / paranoia: men
Histrionic personality disorder: women
Borderline personality disorder: women
30
New cards
3 clusters of personality disorders
A: Odd or eccentric behaviors (specific personality disorders)
-paranoid personality disorder
-schizoid personality disorder
-schizotypical personality disorder
B: Dramatic, emotional, or erratic behavior (specific personality disorders)
-Antisocial
-Borderline pd
-Histionic
-narcissistic
C: Anxious or fearful behavior (specific personality disorders)
-avoidant personality disorder
-dependent personality disorder
-obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
-paranoid personality disorder
-schizoid personality disorder
-schizotypical personality disorder
B: Dramatic, emotional, or erratic behavior (specific personality disorders)
-Antisocial
-Borderline pd
-Histionic
-narcissistic
C: Anxious or fearful behavior (specific personality disorders)
-avoidant personality disorder
-dependent personality disorder
-obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
31
New cards
Specific personality disorders
Personality disorders clustered into 3 clusters: A=Odd, B=Dramatic, C=Anxious
32
New cards
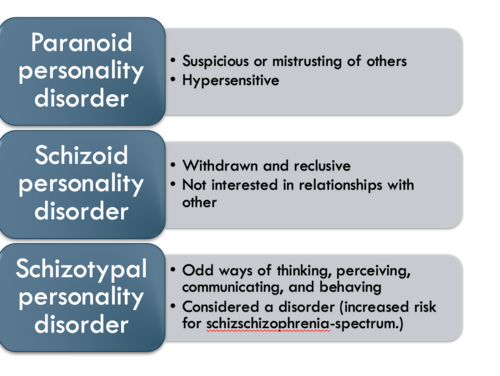
paranoid personality disorder
hypersensitive, suspicious, mistrusting
33
New cards
Schizoid personality disorder
•Withdrawn and reclusive
•Not interested in relationships with other
•Not interested in relationships with other
34
New cards
Schizotypal personality disorder
•Odd ways of thinking, perceiving, communicating, and behaving
•Considered a disorder (increased risk for schizschizophrenia-spectrum
•Considered a disorder (increased risk for schizschizophrenia-spectrum
35
New cards
Borderline personality disorder
•Threaten and engage in self-destructive behavior
•Impulsive
•Unstable relationships, dependency on and manipulation of others
Persuasive pattern of instability of interpersonal relationships, self image, affects, marked impulsivity, 5+ of following
Frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment
Unstable
Unusual perceptual experiences
Impulsivity in at least 2 areas that are potentially self damaging
Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestrures, threats, self injurious, self mutilating behavior
Affective instability
Chronic feeling of emptiness
Intense anger
Transient stress related paranoia or dissociation
•Impulsive
•Unstable relationships, dependency on and manipulation of others
Persuasive pattern of instability of interpersonal relationships, self image, affects, marked impulsivity, 5+ of following
Frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment
Unstable
Unusual perceptual experiences
Impulsivity in at least 2 areas that are potentially self damaging
Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestrures, threats, self injurious, self mutilating behavior
Affective instability
Chronic feeling of emptiness
Intense anger
Transient stress related paranoia or dissociation
36
New cards
Comorbidity with other psychiatric disorders (including PTSD & SUD)
PTSD: 50%
substance abuse: 67%
depression: 20%
eating disorder: 25%
suicide: 6%
substance abuse: 67%
depression: 20%
eating disorder: 25%
suicide: 6%

37
New cards
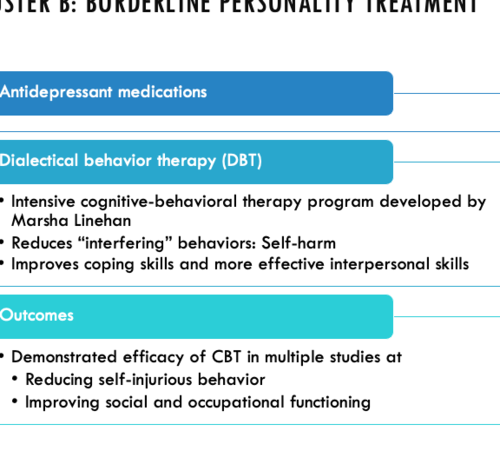
Treatment for borderline personality disorder:
Antidepressants
Dialectical behavior therapy:
•Intensive cognitive-behavioral therapy program developed by Marsha Linehan
•Reduces "interfering" behaviors: Self-harm
•Improves coping skills and more effective interpersonal
Dialectical behavior therapy:
•Intensive cognitive-behavioral therapy program developed by Marsha Linehan
•Reduces "interfering" behaviors: Self-harm
•Improves coping skills and more effective interpersonal
38
New cards
Conduct disorder
must have conduct diagnosis before 15 to have Antisocial disorder (18+)
3+ of the following over 12-mpnth period:
Bullies, threatens, intimidates others
Initiates fights
Used harmful weapons
Physically cruel
Forced sexual activity
Stealing
Run away from home overnight at least twice
3+ of the following over 12-mpnth period:
Bullies, threatens, intimidates others
Initiates fights
Used harmful weapons
Physically cruel
Forced sexual activity
Stealing
Run away from home overnight at least twice
39
New cards
DSM-5 criteria for antisocial personality disorder:
-pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others since age 15 (conduct disorder diagnosis)
-at least 18
3+ over 12 mo:
Often bullies, threatens, intimidates others
Often initiates fights
Has used weapon that can cause serious harm to others
Has been physically cruel to others
Has been physically cruel to animals
Has forced someone into sexual activity
Deliberate fire setting in order to cause damage
Deliberate destruction of others' property
Broken into someone's house or building, stole car
Often lies to obtain good, favors, or to avoid obligations
Often stolen items of value
Stays out all night despite parental prohibitions
Has run away from home overnight at least twice
Often truant from school beginning age 13
-at least 18
3+ over 12 mo:
Often bullies, threatens, intimidates others
Often initiates fights
Has used weapon that can cause serious harm to others
Has been physically cruel to others
Has been physically cruel to animals
Has forced someone into sexual activity
Deliberate fire setting in order to cause damage
Deliberate destruction of others' property
Broken into someone's house or building, stole car
Often lies to obtain good, favors, or to avoid obligations
Often stolen items of value
Stays out all night despite parental prohibitions
Has run away from home overnight at least twice
Often truant from school beginning age 13
40
New cards
antisocial comorbidity with SUD
over 50%
41
New cards
Distinction between antisocial personality, psychopathic personality, &
sociopathy
sociopathy
ASPD: diagnoses in DSM-5, defined in behavioral terms
psychopathic: diagnosed in ICD-10, emphasis on personality characteristics, manipulation of others, superficial
Sociopathy is not a term used in psychiatric diagnosis (in DSM-5 or ICD-10), but generally refers to some combination of traits typically included in ASPD and psychopathy
psychopathic: diagnosed in ICD-10, emphasis on personality characteristics, manipulation of others, superficial
Sociopathy is not a term used in psychiatric diagnosis (in DSM-5 or ICD-10), but generally refers to some combination of traits typically included in ASPD and psychopathy

42
New cards
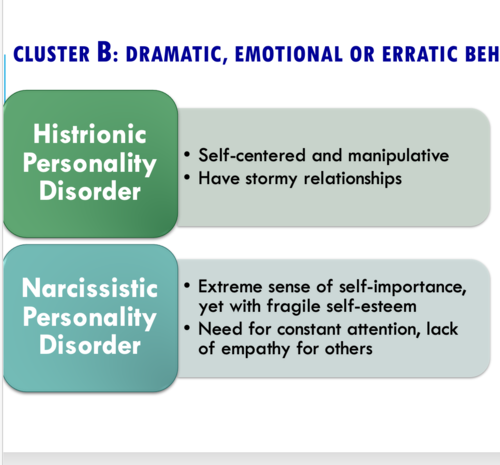
Narcissistic personality disorder
•Extreme sense of self-importance, yet with fragile self-esteem
•Need for constant attention, lack of empathy for others
•Need for constant attention, lack of empathy for others
43
New cards
Histrionic personality disorder
•Self-centered and manipulative
•Have stormy relationships
: 5+ symptoms (overdramatized, on stage, how people interact with ppl in world)
Overly dramatic
Impulsive
Impressionistic
Sensational
Attention seeking
Vague, superficial
Sexuall provocative
Appearance focused
Common in female
•Have stormy relationships
: 5+ symptoms (overdramatized, on stage, how people interact with ppl in world)
Overly dramatic
Impulsive
Impressionistic
Sensational
Attention seeking
Vague, superficial
Sexuall provocative
Appearance focused
Common in female
44
New cards
Avoidant personality disorder
•Low-self esteem
•Worry about negative evaluation by others, but desire affection and relationships
•Avoid social interaction
•Worry about negative evaluation by others, but desire affection and relationships
•Avoid social interaction
45
New cards
Dependent personality disorder
•Lack confidence in ability to function independently
•Subordinate their needs to wishes of others to maintain relationship
•Subordinate their needs to wishes of others to maintain relationship
46
New cards
OCD personality disorder
•Extreme perfectionism
•Rigid approach to doing things
•Lack of ability to express warm emotions
•Rigid approach to doing things
•Lack of ability to express warm emotions
47
New cards
Beliefs associated with different personality disorders