AP Macroeconomics Unit 1
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
(1.2) What happens when the PPC is linear and concave to the origin, respectively?
Linear PPC = Constant Opportunity Cost
PPC Concave to the Origin = Increasing Opportunity Cost
(1.2) What is the Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)?
The Production Possibilities Curve is a model capable of illustrating trade-offs and the resulting opportunity costs.
(1.3) What is absolute and comparative advantage?
Absolute advantage considers who can produce more, while comparative advantage considers who can produce more efficiently.
(1.4) Law of Demand?
Price and Quantity Demanded are inversely related
(1.4) Shift vs change in price on the demand curve?
Changes that affect M.E.R.I.T will shift the demand curve and changes in price will cause movement along the curve
(1.4) What are the 5 main factors that change/shift the Demand curve?
M.E.R.I.T

(1.4) Slope of Demand?
Downward sloping demand model
(1.5) Law of supply?
Price and quantity supplied is positively related.
(1.5) Slope of Supply model?
Upward sloping supply model
(1.5) What are the five factors that change/shift the Supply Curve?
T.R.I.C.E.

(1.6) Relationship between demand, supply, price and quantity?
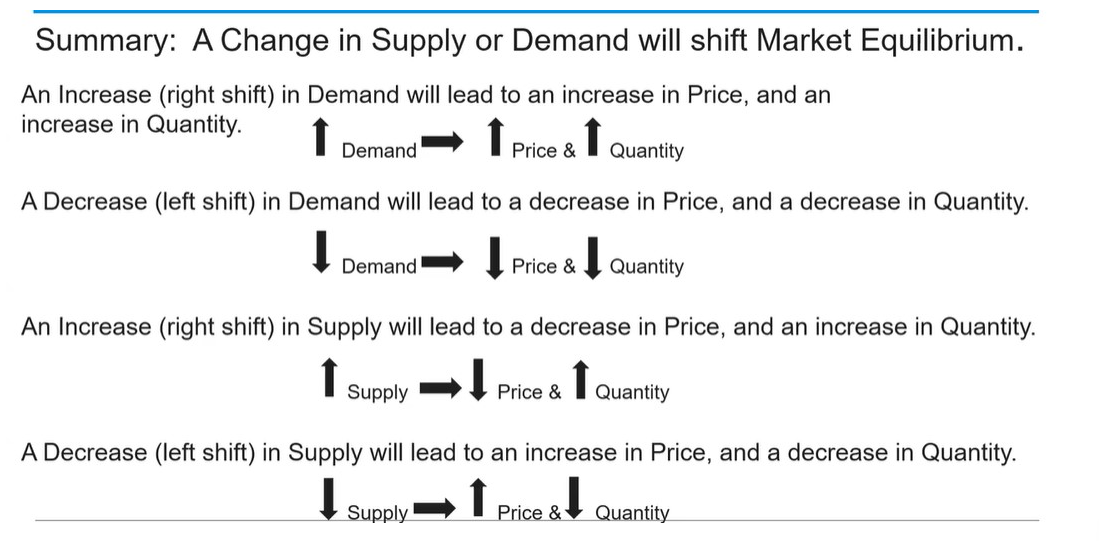
(1.6) Shortage?
QD > QS → Shortage
(1.6) Surplus?
QS > QD → Surplus