BIO 214 : Seed plants Chap 26
1/71
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
anther
sac-like structure at the tip of the stamen in which pollen grains are produced
Anthophyta
Phylum to which angiosperms belong
Barcoding
Molecular biology technique in which one or more short gene sequences taken from a well characterized portion of the genome is used to identify a species
Basal angiosperms
A group of plants that probably branched off before the separation of monocots and eudicots
Calyx
Whorl of sepals
Carpel
Single unit of pistils
Conifer
Dominant phylum of gymnosperms with the greatest variety of trees
Corolla
Collection of petals
Cotyledon
Primitive leaf that develops in the zygote; monocots have one cotyledon, and dicots have two cotyledons
Crop
Cultivated plant
Cycads
Gymnosperm that grows in tropical climates and resembles a palm tree; member of the phylum Cycadophyta
Dicot
(Also eudicot) related group of angiosperms whose embryos possess two cotyledons
Dioecious
Describes a species in which the male and the female reproductive organs are carried on separate specimens
Filament
Thin stalk that links the anther to the base of the flower
Flower
Branches specialized for reproduction found in some seed-bearing plants, containing either specialized male or female organs or both male and female organs
Fruit
Thickened tissue derived from ovary wall that protects the embryo after fertilization and facilitates seed dispersal
Ginkgophyte
Gymnosperm with one extant species, the Ginko bilbao: a tree with fan-shaped leaves
Gnetophyte
Gymnosperm shrub with varied morphological feathers that produce vessel elements in its woody tissues; the phylum includes the genera Ephedra, Gnetum, and Welwitschia
Gymnosperm
Seed plant with naked seeds (seeds exposed on modified leaves or in cones)
Gynoecium
(Also, carpl) structure that constitutes the female reproductive organ
Heirloom seed
Seed from a plant that was grown historically, but has not been used in modern agriculture on a large scale
Herbaceous
Grass-like plant noticeable by the absence of woody tissue
Herbivory
Consumption of plants by insects and other animals
Integument
Layer of sporophyte tissue that surrounds that megasporangium, and later, the embryo
Megasporocyte
Megaspore mother cell; larger spore that germinates into a female gametophyte in a heterosporous plant
Microsporocyte
Smaller spore that produces a male gametophyte in a heterosporous plant
Monocots
Related group of angiosperms that produce embryos with one cotyledon and pollen with a single ridge
Monoecious
Describes a species in which the male and female reproductive organs are on the same plant
Nectar
Liquid rich in sugars produced b flowers to attract animal pollinators
Ovary
Chamber that contains and protects the ovule or female megasporangium
Ovulate cone
Cone containing two ovules per scale
Ovule
Female gametophyte
Paraphyletic group
Not all descendents of a single common ancestor are included in the group
Perianth
Part of the plant consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals)
Petal
Modified leaves interior to the sepals; colorful petals attract animal pollinators
Pistil
Fused group of carpels
Pollen grain
Structure containing the male gametophyte of the plant
Pollen tube
Extension from the pollen grain that delivers sperm to the egg cell
Pollination
Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma
Progymnosperm
Transitional group of plants that resembled conifers because they produced wood, yet still reproduced like ferns
Sepal
Modified leaf that encloses the bud; outermost structure of a flower
Spermatophyte
Seed plant
Stamen
Structure that contains the male reproductive organs
Stigma
Uppermost structure of the carpel where pollen is deposited
Strobilus
Plant structure with a tight arrangement of sporophylls around a central stalk, as seen in cones or flowers; the male strobilus produces pollen, and the female strobilus produces the eggs
Style
Long, thin structure that links the stigma to the ovary
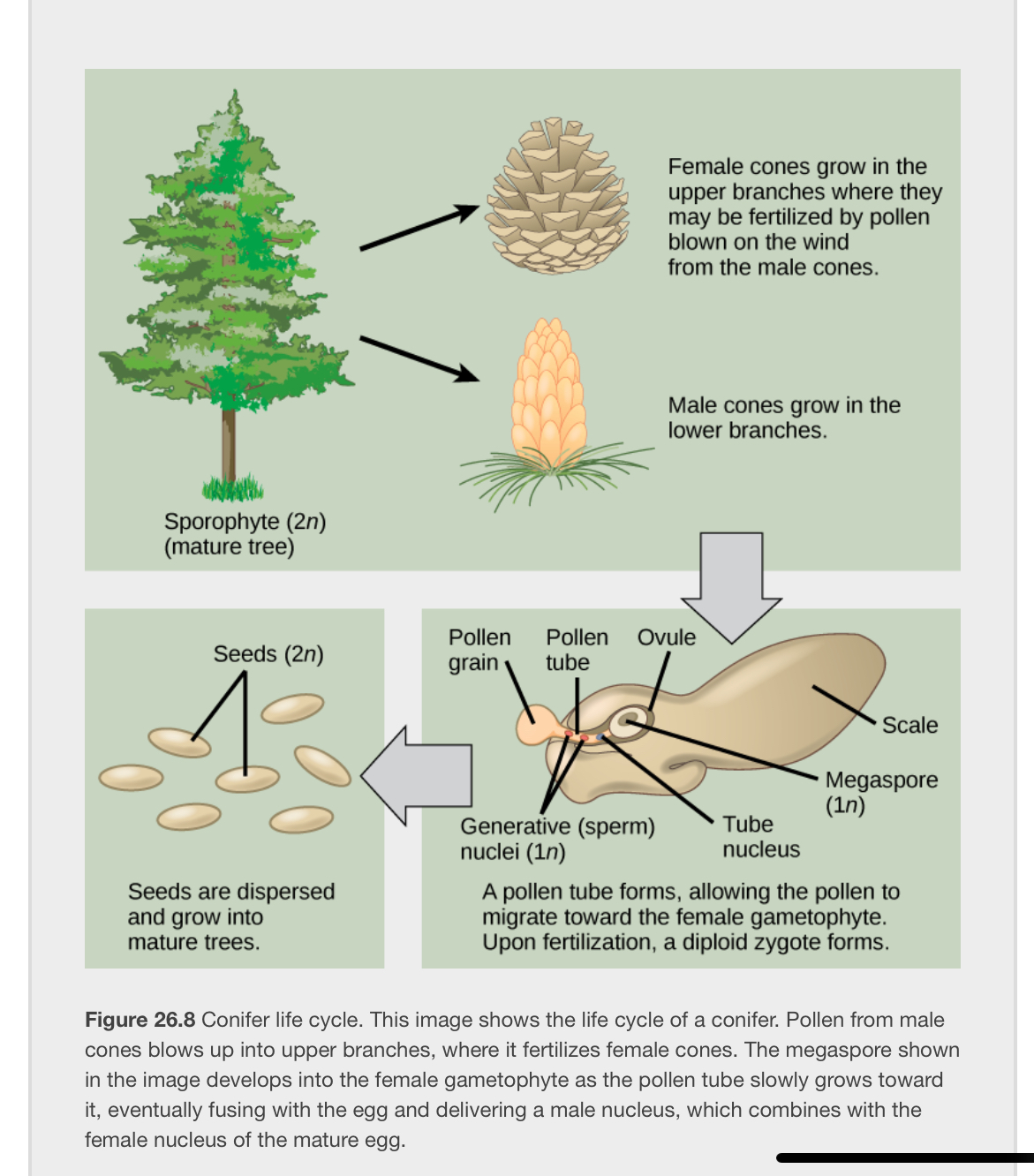
At what stage does the diploid Zygote form?
At fertilization
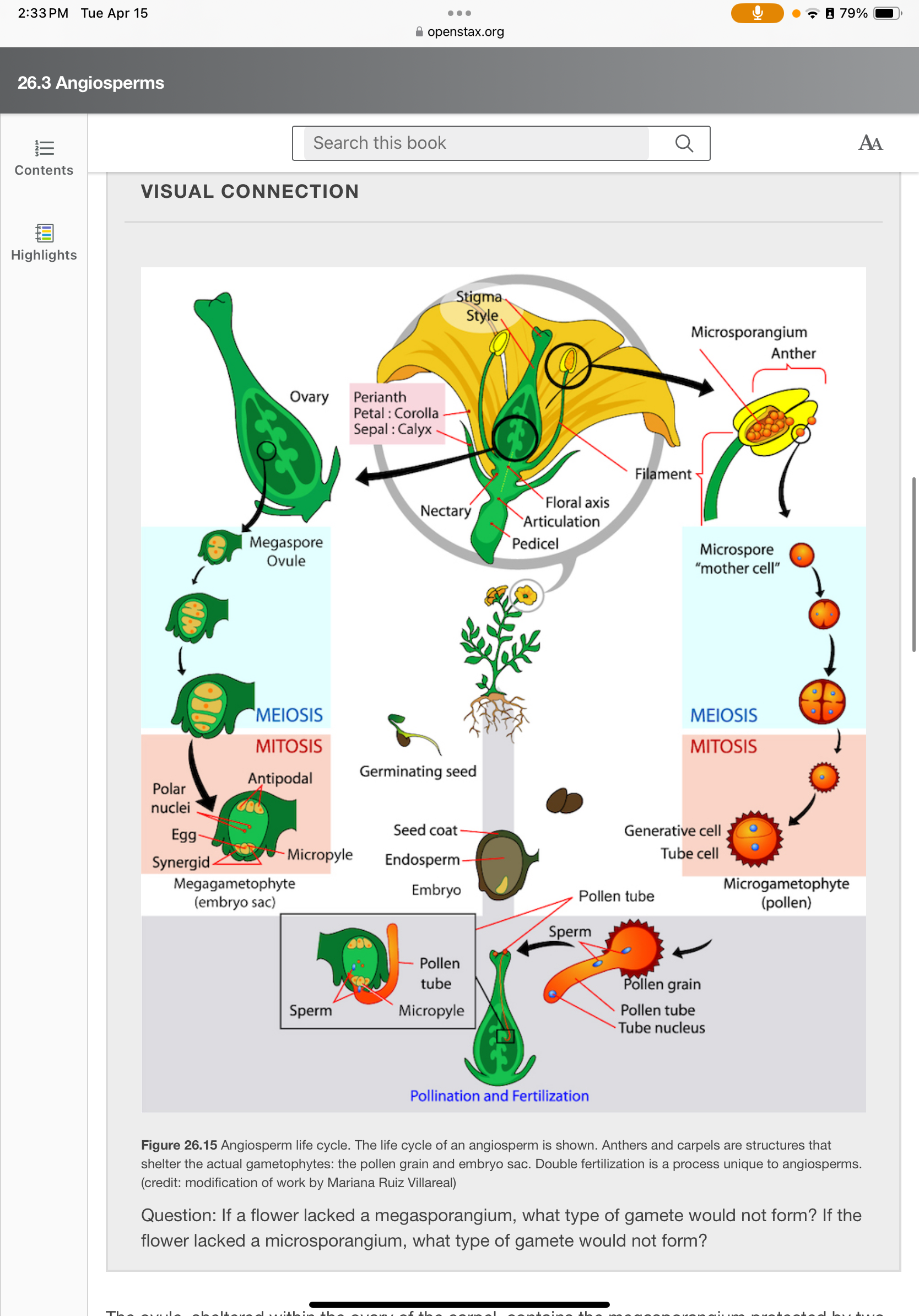
If a flower lacked a megasporangium, what type of gamete would not form? If the flower lacked a microsporangium, what type of gamete would not form?
f a flower lacked a megasporangium, it would not produce egg cells (female gametes). If it lacked a microsporangium, it would not produce sperm cells (male gametes).
Seed plants are
All heterosporous
Besides the seed, what other major structure diminishes a plant’s reliance on water for reproduction?
Pollen
In which of the following geological periods would gymnosperms dominate the landscape?
Permian
Which of the following structures widens the geographic range of a species and is an agent of dispersal?
Seed
Which of the following traits characterizes gymnosperms?
The plants carry exposed seeds on modified leaves
Megasporocytes will eventually produce which of the following?
Female gametophytes
What is the policy of the following structures: gametophyte, seed, spore, sporocyte?
1n, 2n, 1n, 2n
In the northern forests of Siberia, a tall tree is most likely a:
Conifer
Which of the following structures in a flower is not directly involved in reproduction?
The sepals
Pollen grains develop in which structure?
The anther
In the course of double fertilization, one sperm cell fuses with the egg and the second one fuses with _________.
The polar nuclei of the center cell
Corn develops from a seedling with a single cotyledon, displays parallel veins on its leaves, and produces monosulcate pollen. It is most likely a:
A monocot
Which of the following plant structures is not a defense against herbivory?
Nectar
White and sweet-smelling flowers with abundant nectar are probably pollinated by:
Bees and butterflies
Abundant and powdery pollen produces by small, indistinct flowers is probably transported by:
Wind
Plants are a source of ________.
a food
b fuel
c medicine
d all of the above
d all of the above
Because insects pollinated flowers and flowers provided food, both benefited—leading to mutual adaptations like flower shapes and insect feeding structures.
What role did seed and pollen adaptations play in seed plant expansion?
Seeds protect embryos and allow dormancy; pollen allows fertilization without water, enabling reproduction in diverse environments.
What adaptation makes conifers suited to Mediterranean climates?
Their needle-like leaves reduce water loss, making them drought-resistant—ideal for dry, hot summers.
What are the four modern phyla of gymnosperms?
Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, Ginkgophyta, and Gnetophyta.
How can a botanist tell cycads from palm trees?
Cycads have cone-bearing structures and unbranched trunks with stiff leaves; palms have flowers and fruits, not cones.
What two structures help angiosperms dominate land ecosystems?
Flowers (for pollination) and fruits (for seed protection and dispersal).
Why do plants invest so much energy in attracting pollinators?
Animal pollination increases efficiency, genetic diversity, and chances of successful fertilization over long distances.
What is biodiversity and why is it important?
Biodiversity is the variety of life in an ecosystem; it boosts resilience, stability, and productivity by supporting complex food webs and adaptation.