2.1 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Bollards
Used to limit access by vehicles to a particular area and channel pedestrian traffic, avoiding injuries.
Access control vestibule
Space serving as an entryway to limit access to secured areas, typically includes a biometric scanner or badge reader.
Badge reader
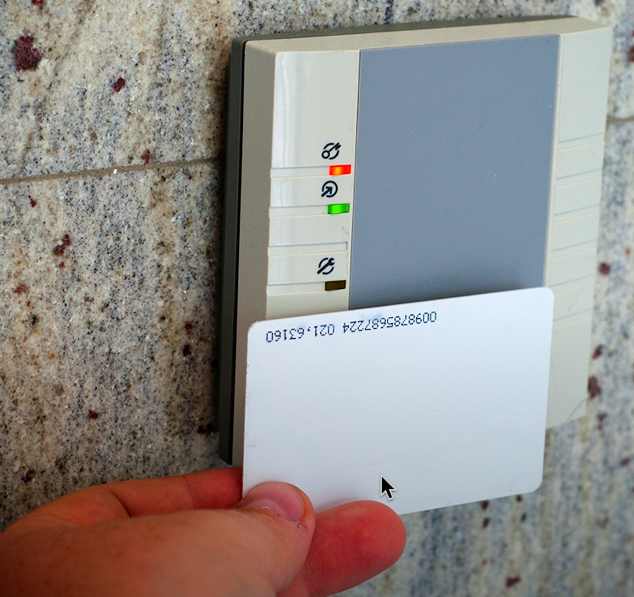

A device allowing authorized users access by scanning an identification badge, uses magnetic stripes, barcodes, or RFID.
Video surveillance

CCTV that allows observation of activity in a specific area without physical presence.
Alarm systems

Devices designed to alert to events requiring attention, like security breaches.
Circuit-based alarm systems
Alarms designed to ring when a circuit is opened or closed. Placed on doors, windows, or fences, and useful on the perimeter of a secured area.
Duress alarm
A specialized alarm system that is triggered by a user in distress, typically requiring only a discreet action or button press, often used in situations such as bank tellers or emergency service personnel to signal for immediate assistance.
Motion sensors
Devices designed to alert when motion is detected within a specific area.
Door lock
A security device that ensures a door stays in a closed position.
Conventional door lock
A door lock that uses a traditional lock and key to open.
Deadbolt
A door lock that uses a thumb turn/second key mechanism to provide enhanced security and prevent unauthorized access.
Electronic door lock
A door lock that uses a keyless/PIN mechanism to open.
Biometric lock
Locks that use biometric/physical features to provide access (e.g., fingerprints, retina/facial scans).
Equipment locks
Used to secure sensitive hardware, ensuring only authorized personnel can manage it.
Security guards
Personnel responsible for the physical protection of a facility and identification of access.
ID badge
A card or credential issued to employees that allows access to secured areas and systems within the facility. Contains the person’s name, picture, and other details - must be worn at all times.
Access list
Physical list of names/credentials that can enter a secured building - enforced by a security guard.
Fences
Barriers used to mark boundaries or control access, designed to be robust and difficult to cross.
Key fobs
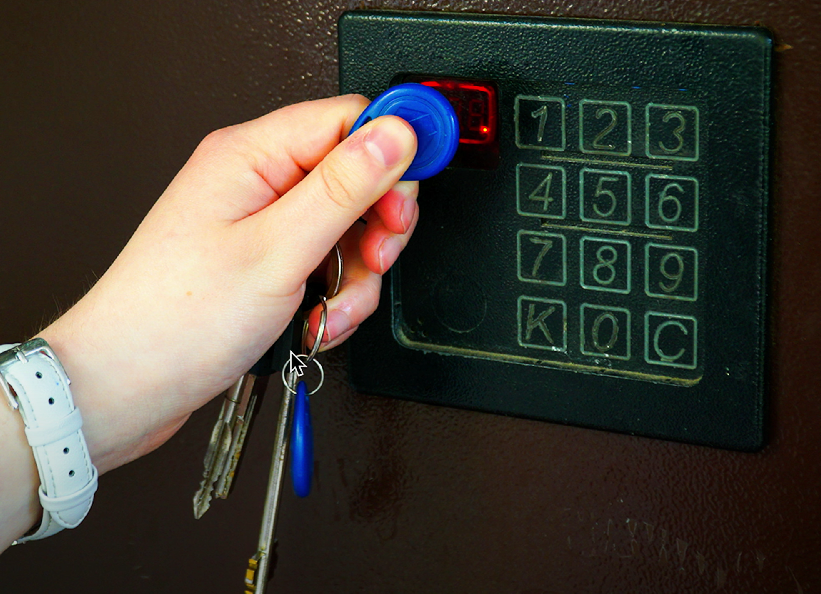

Small devices for granting access to secured areas, often using RFID technology.
Smart cards

Plastic cards with embedded digital circuits used for authentication based on digital certificates.
Mobile digital key
Uses a phone to replace digital keys for unlocking doors and accessing systems.
Keys

Shaped metal with incisions designed to insert into a lock to open or close it. Used to secure areas that should not be locked electronically for power loss risks (e.g., safes).
Biometrics
Authentication based on unique physical or biological characteristics.
Retina scanner
A device that reads and analyzes the unique capillary (blood vessel) patterns in the retina, helping to verify the identity of an individual accurately and securely.
Fingerprint scanner
A device that analyzes the ridge patterns of fingerprints to provide authentication.
Palm print scanner
A device that scans the shape of a person’s hand and fingers to provide authentication.
Facial recognition technology (FRT)
Technology that creates a digital “key” from facial features and uses that to provide authentication. Relatively secure method - 1/1,000,000 false positive rate.
Voice recognition technology
Technology that uses an individual’s voice to provide authentication - the system is typically “trained” by speaking phrases, then the results are evaluated and stored to create a biometric pattern of the user’s voice (i.e., mannerisms, pace, accents).
Lighting
Ensures adequate visibility for surveillance and acts as a psychological deterrent.
Magnetometers
Devices that measure magnetic fields to detect metal objects for security.
Logical security
Encompasses the safeguards put in place to protect digital data and resources from unauthorized access and exploitation.
Principle of least privilege
Concept stating users should have only the minimal access rights necessary.
Zero Trust model
Security model where no entity is trusted by default and every access must be verified.
Access Control Lists (ACLs)

Technology used to allow or deny traffic on a network based on predefined filters.
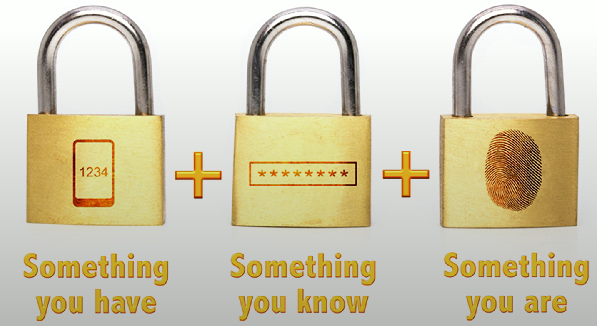
Multifactor authentication (MFA)
Use of two or more methods to verify a user's identity.
Email-based MFA
MFA method used to associate a person with a particular email address, often requiring verification through a one-time code sent to the email before access is granted.
Hardware token
A physical device that generates a one-time code for user authentication, ensuring that only the individual with the hardware token can access the application or service. Typically attached to a keychain for easy access.
Authenticator application
Application that provides a pseudo-random number token to log into an app/service.
Short Message Service (SMS)
Use of a stored phone number to send a login factor via a text message, allowing users to receive a one-time code that must be entered for authentication.
Voice call MFA
Provision of a security token via a phone call - the user receives a numeric code given from a phone call and enters it to provide authentication.
Time-based one-time password (TOTP)
A temporary numeric code generated based on the current time and a shared secret key, providing an additional layer of security for two-factor authentication.
One-time password/passcode (OTP)
One-time authentication code - can only be used once per session/authentication attempt.
Security Assertions Markup Language (SAML)
An open standard for authentication/authorization in third-party applications.
Single sign-on (SSO)
Authentication process allowing access to multiple applications with one set of credentials.
Just-in-time access
Granting temporary access privileges to minimize security risks.
Privileged access management (PAM)
Security approach for managing root/privileged account access - stores privileged account credentials in a digital vault, and these temporary account credentials are released from the vault by request.
Mobile device management (MDM)
Centralized management of company-owned and user-owned devices.
Data loss prevention (DLP)
Managing sensitive personal data to prevent unauthorized leakage or acquisition.
Identity access management (IAM)
Framework ensuring authorized access to data at the correct time.
Directory services
Database of network entities, primarily Windows-based using Active Directory for access control.