Env Sci II
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Sustainability
A system or process that can be continued indefinitely without depleting materials or energy resources required to keep it running
What does most of our energy go towards
Most energy usage is ELECTRICITY and HEAT
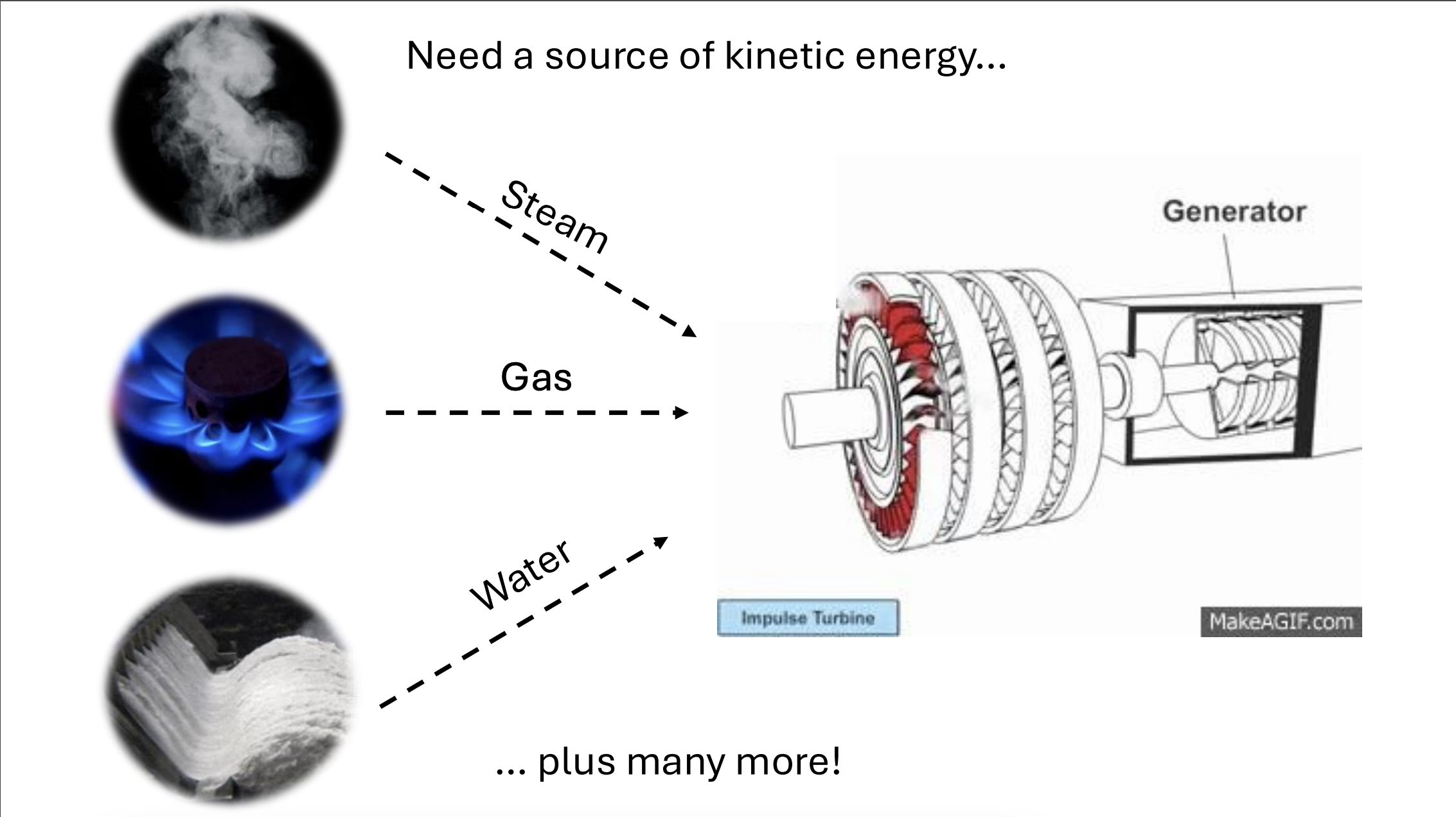
How do we generate electricity?
Turbine electricity generator
kinetic energy - energy in motion
harness kinetic energy
ex: steam, gas water, etc
Where does most of our energy come from?
80% comes from natural gas, oil, and coal
What are the two key elements of sustainable energy consumption?
Efficiency
reducing energy lost as waste per unit input
Conservation
reducing demand for energy
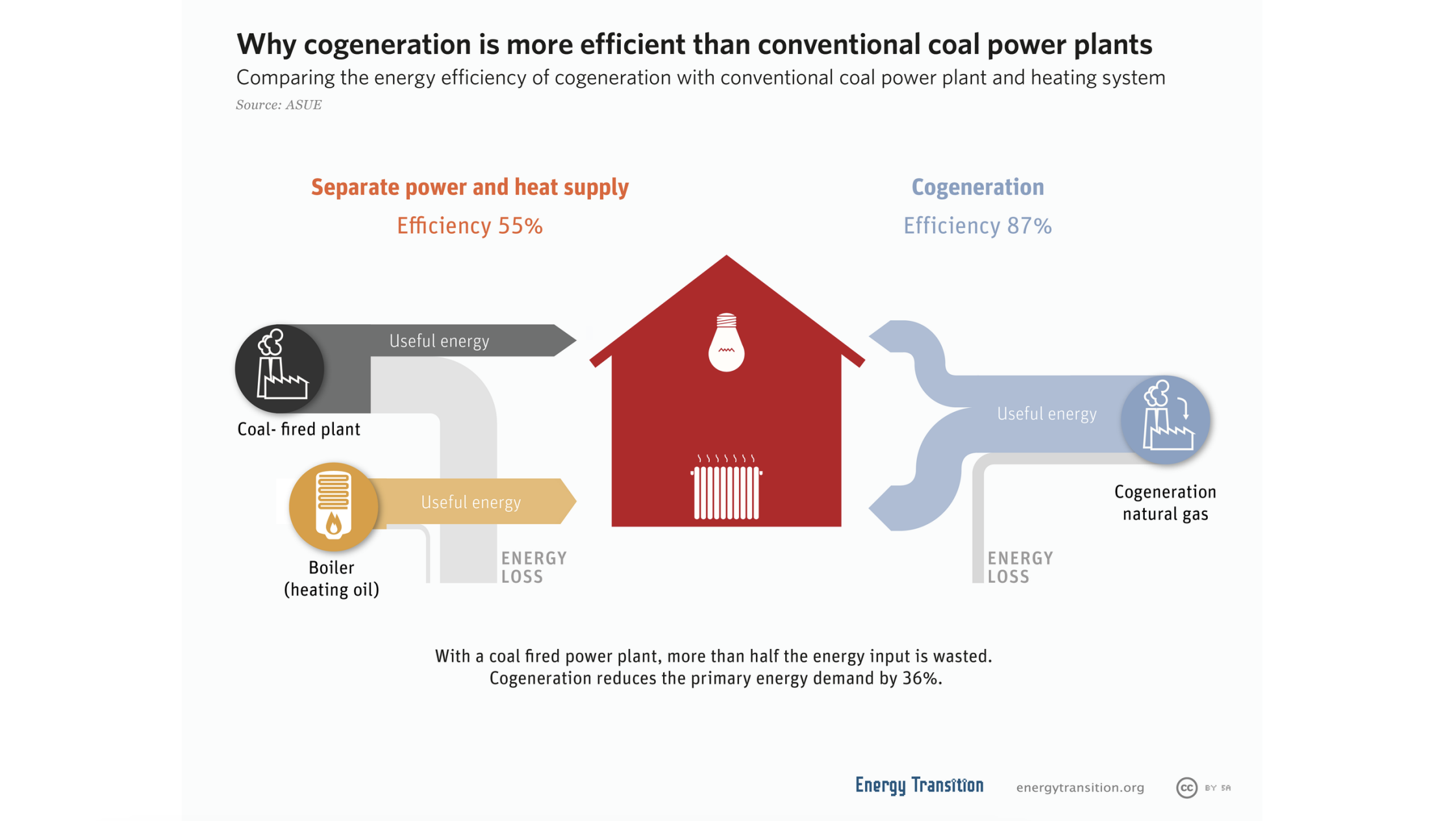
What is cogeneration?
It converts waste heat emitted during electricity production into useful heat
fuel input → generator → heat recovery (from exhaust, gases, or steam)
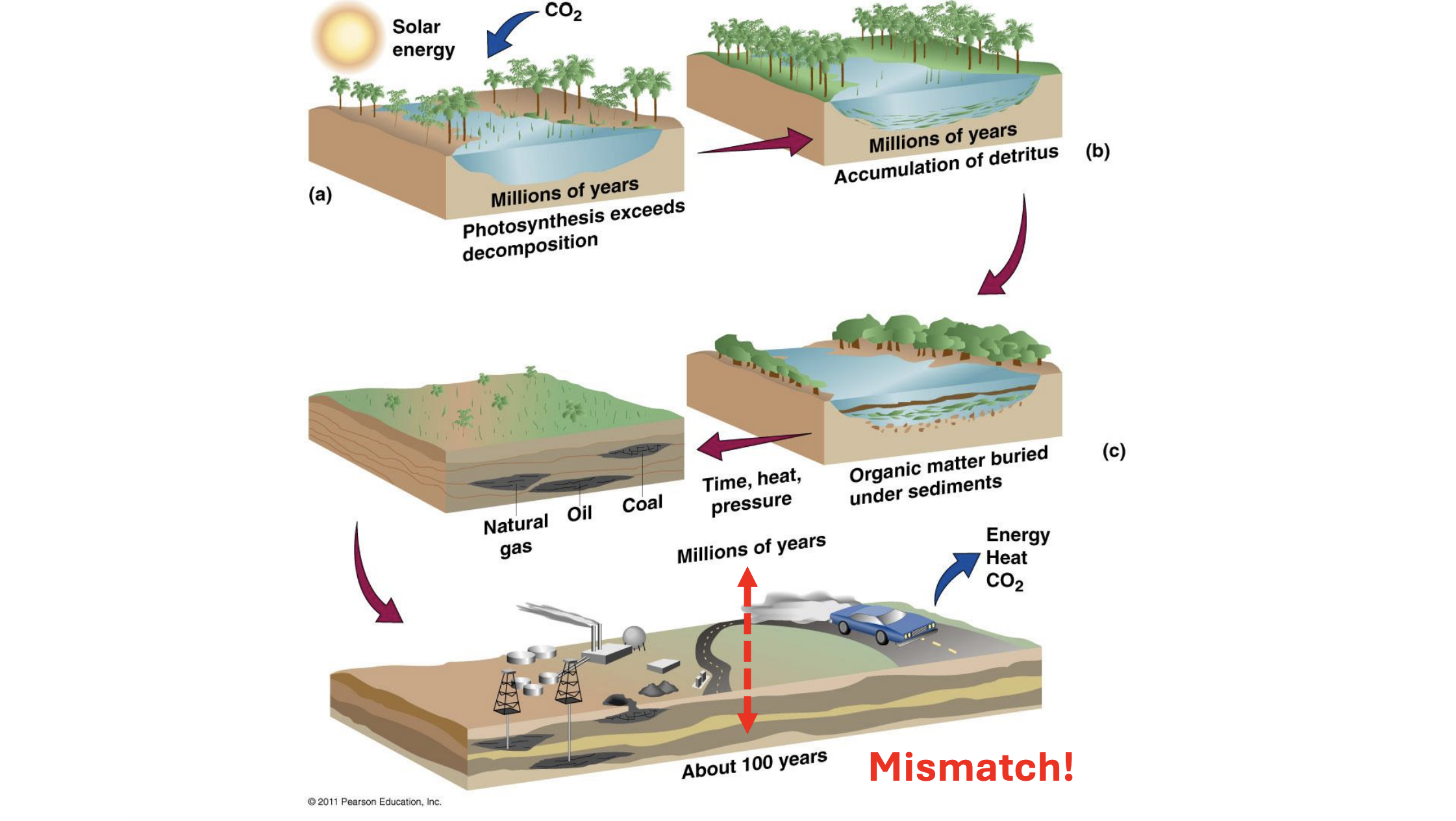
What are fossil fuels?
they are ancient organic material buried underground
hundreds of millions of years old
burned for energy
three main types:
coal, oil, natural gas
What is coal?
ancient plants (300 mya) compressed into sedimentary rock laters by heat and pressure
extracted via mining
to make coal, plants must not have decomposed quickly, how?
nutrients stored in plants but now decomposing fast enough
carboniferous conditions were great for plants, not good for decomposing
U.S. has the most coal reserves
coal was the first fossil fuel to emerge around the 1850s
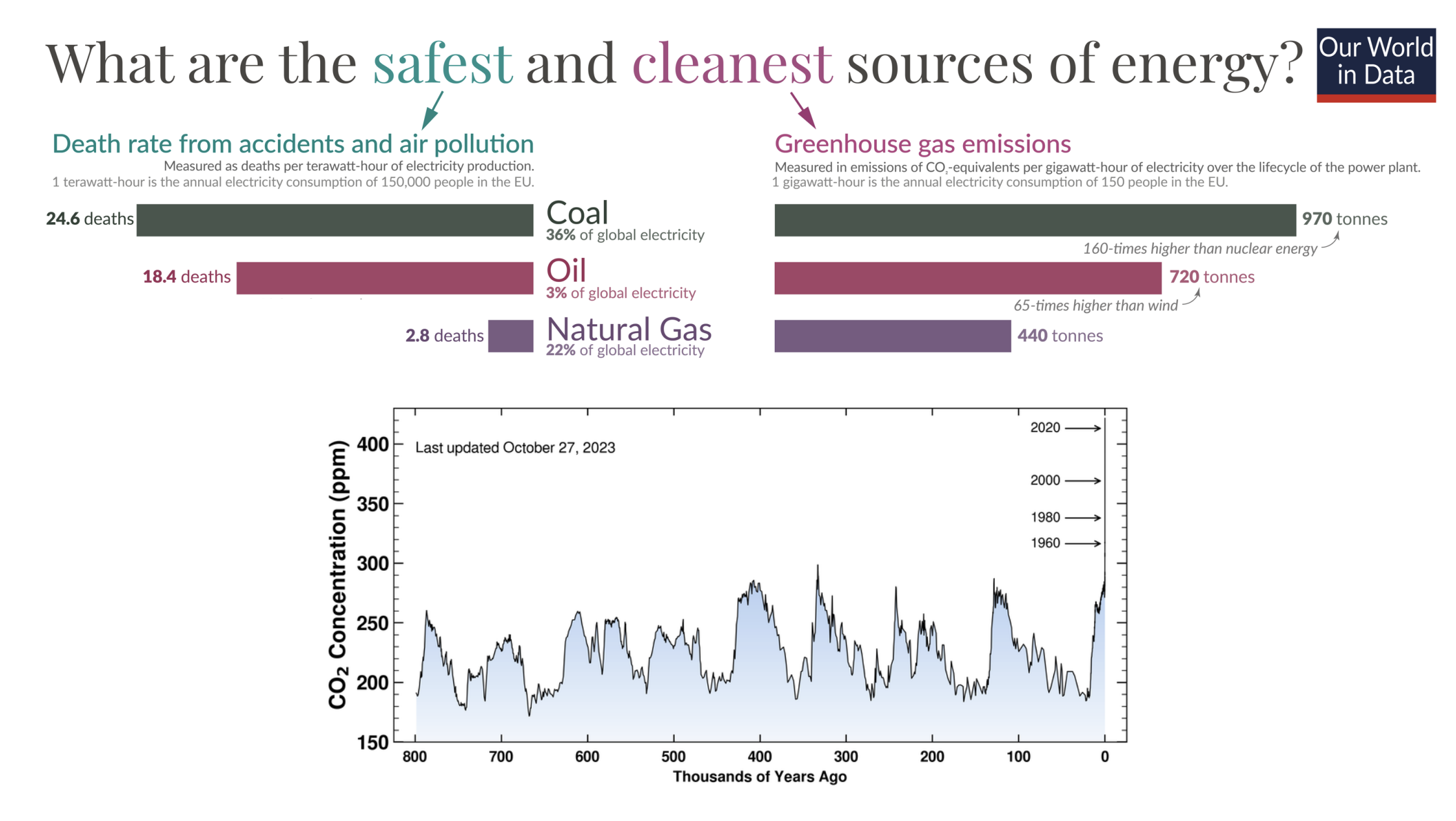
What is oil and natural gas?
ancient marine organisms buried in the ocean floor and compressed by heat and pressure
gas and oil deposits form together, ration depends on the type of organic material and conditions
highly concentrated in petro states: along Arabian peninsula, Venezeula, etc
their economies depend on oil
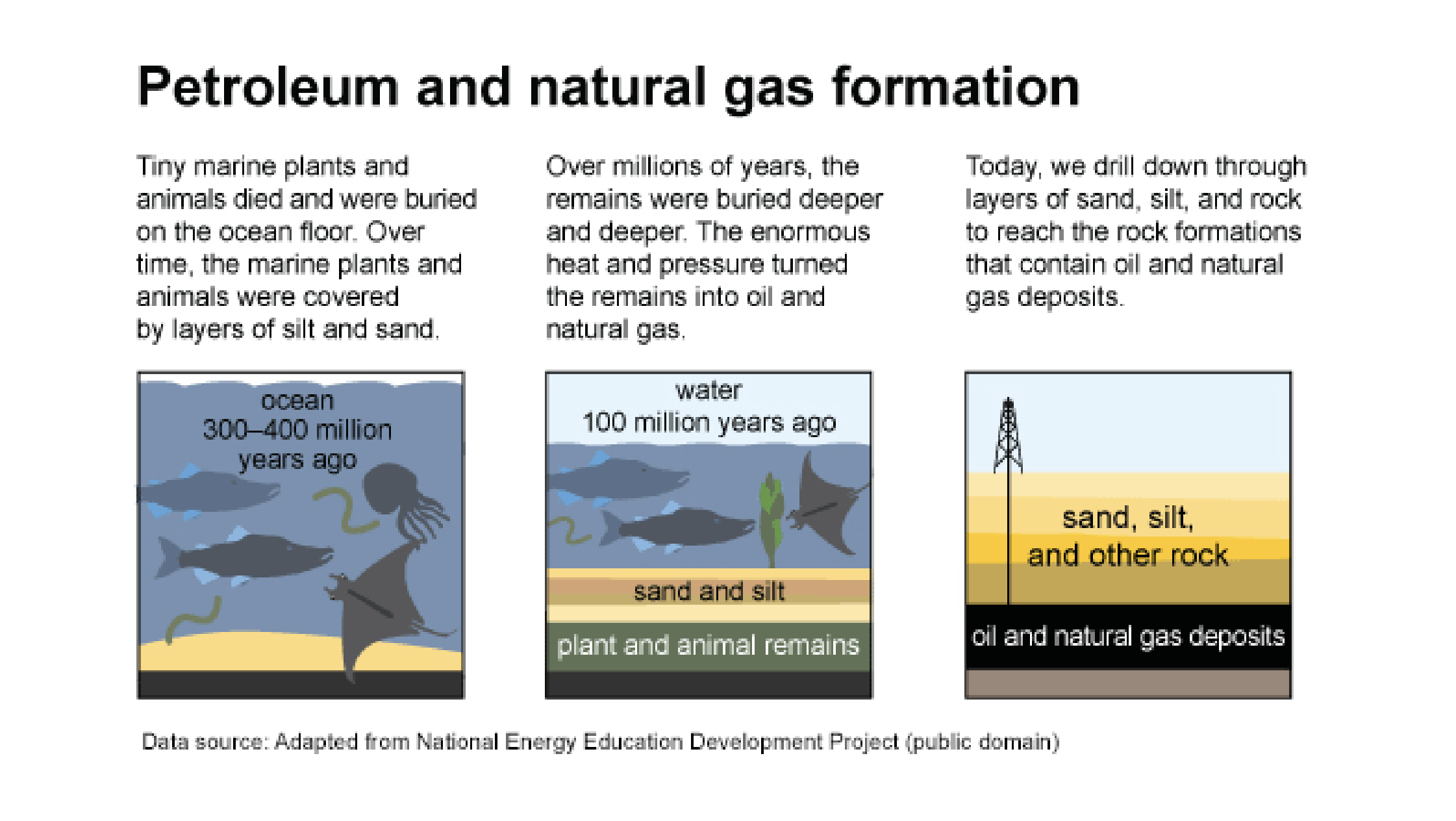
What is fracking?
fluid blasted deep into the earth
pipe drilled horizontally to make more contact with rock
fractures in the earth let gas flow into the pipe
potential for fracking to cause instability and lead to earthquakes, sinkholes, and leakages
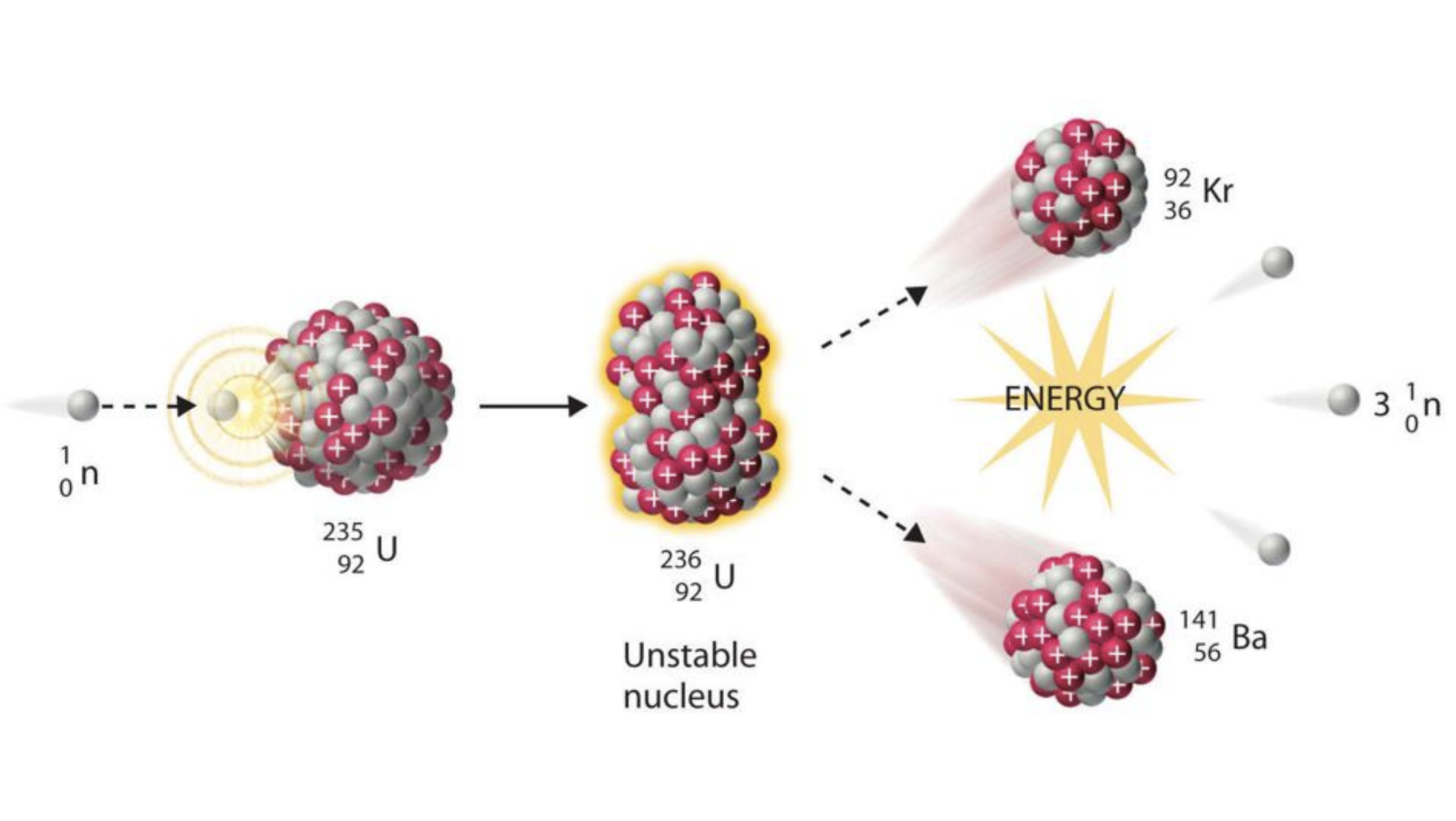
How is nuclear energy made?
unstable nucleus
unstable atom, add more unstable parts until it breaks apart and creates a lot of energy
fission chain reaction
what makes nuclear so powerful
fuel rod: made of enriched uranium
control rod: moderate pace of the reaction
how does nuclear energy work?
harness energy produced by fission reaction to generate steam and power a generator
powerful, versatile, and reliable
high capacity factor
clean (essentially no carbon emissions)
has the highest capacity factor
what is a capacity factor?
Capacity factor is a measure of how often a power plant runs at full capacity
What are the cons of nuclear energy
safety
ex: 3 Mile Island and Charnobyl
cost
cost has increased over time
high cost in terms of up front investments
waste
a lot of nuclear waste
What is risk?
the probability of a hazard causing harm, account for likelihood of occurrence and vulnerability of subject
Risk = Probability of Hazard (for nuclear, this is extremely low) x Vulnerability
What metal is used in nuclear energy?
Uranium
How do we store waste?
nuclear waste lasts tens of thousands of years
need to consider
environmental impact
proximity to people
national security
by-product can be used in nuclear weapons
our best solutions (far): bury it in a geological formation FAR AWAY from life
Renewable Energy
energy sources are replenished at a rate faster than they are depleted
several (diverse) types:
hydropower
solar
wind
biomass
geothermal
What is solar energy?
Sunlight hitting metal in a photovoltaic cell cause electrons to be emitted when light is absorbed
Pros of solar energy
pros:
low cost (both initial and recurring)
produce little pollution
can exist in remote areas
Cons of solar energy
intermittent energy source
duck-curve problem
space intensive
What is the duck-curve problem?
not using as much energy during the peak hours of solar energy production
using the most in the evening, bit in morning, big drop midday
What is hydropower?
Water flows through penstock from high elevation to low elevation, pushing turbine
Pros of hydropower
stable energy source
provides freshwater source
Cons of hydropower
expensive
interrupts flow of river systems
note the salmon canon
susceptible to droughts
What is Wind Energy
Turbine pushed by wind, kinetic energy of spinning turbines converted to electricity
What is wind?
Cool air over the water moves in → land heats up faster than water → war air over the land rises
Pros of wind energy
lost cost, especially onshore
land efficient, especially offshore
solar and wind energy are cheaper than fossil fuels
Cons of wind energy
noise and aesthetic makes people rlly mad
limited to windy places, intermittent
risk posed to migrating species and marine life
only .23 of birds die by wind turbines
compared to outdoor cats with 2,400 & building collisions with 599
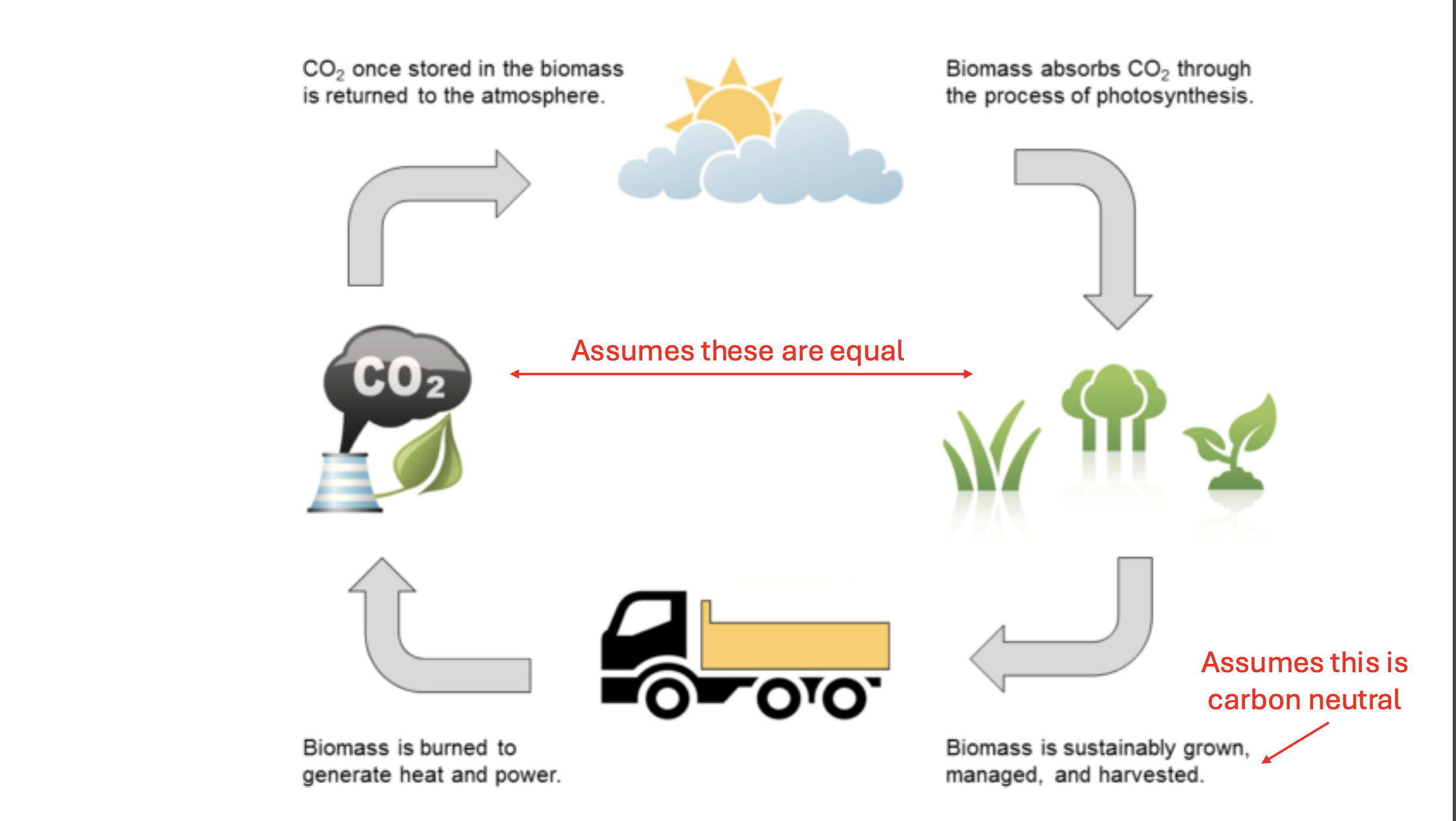
What is biomass?
organic material burned for fuels
Pros of biomass
highly available, can make waste productive
extremely low cost
Cons of biomass
air pollution source
carbon neutrality is complicated
What is Geothermal?
Steam generation by pumping water down below earth’s surface
Pros of geothermal
very stable energy source
small land footprint
safe
Cons of geothermal
expensive
highly location dependent
require drilling into the Earth
Future renewables?
other sources of kinetic energy..
earths tides
nuclei merging together (nuclear fusion)
clean
static energy in water vapor
seismic activity (earthquakes)
these solutions don’t scale currently, but may in the future
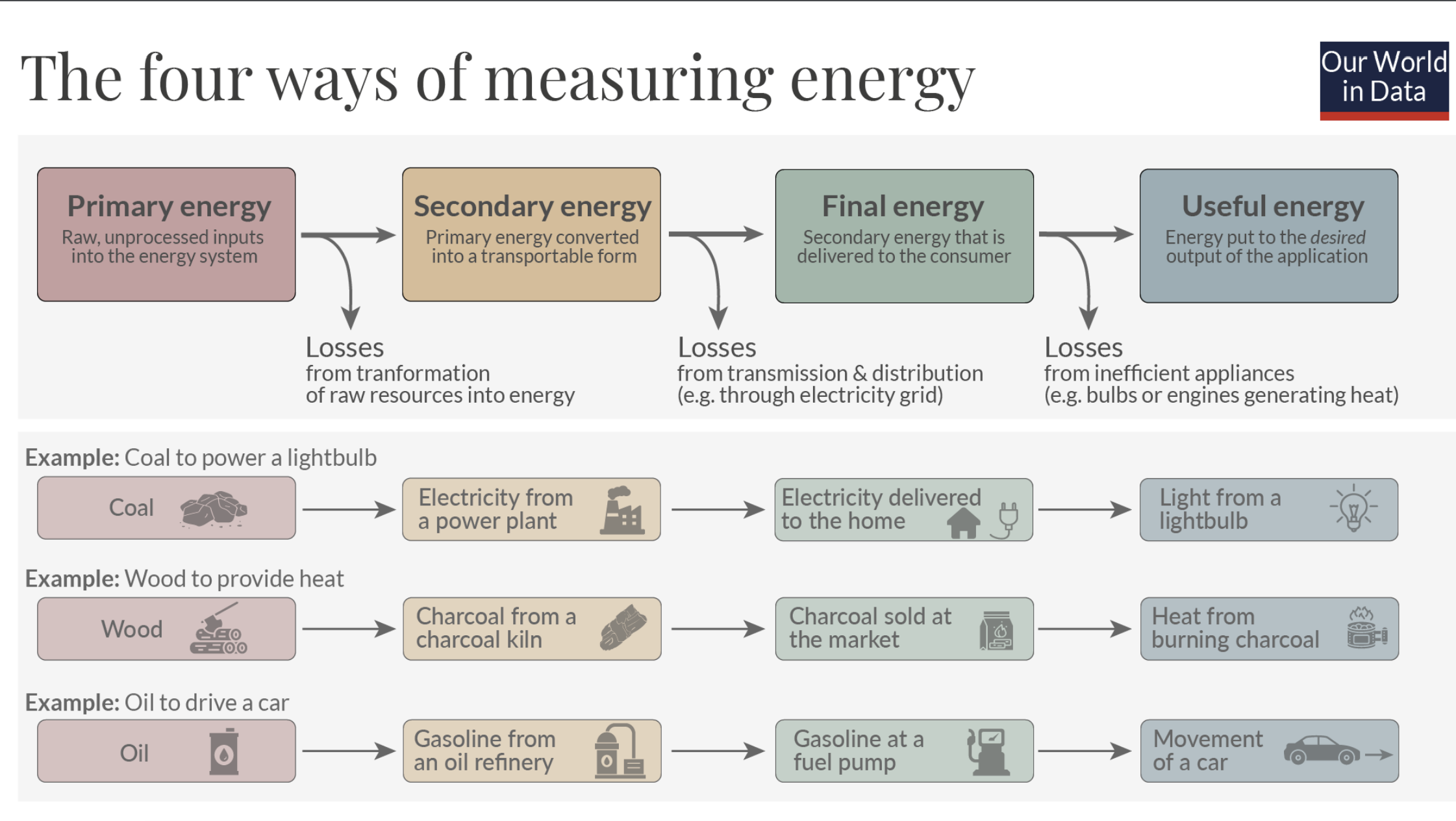
What are the four ways of measuring energy?
Primary Energy, Secondary Energy, Final Energy, and Useful Energy