Hinduism & Buddhism Test Review
5.0(1)Studied by 13 people
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:53 AM on 10/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
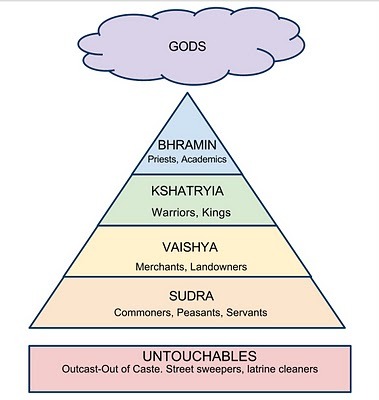
Caste system
-Castes are assigned by birth
-Your caste determined your job, who you could marry, who you could eat with
-Cleanliness became the most important aspect of caste
-Your caste determined your job, who you could marry, who you could eat with
-Cleanliness became the most important aspect of caste
2
New cards
Bhagavad Gita
The most important work of Indian sacred literature, a dialogue between the great warrior Arjuna and the god Krishna on duty and the fate of the spirit. The story is about assigned duty and destiny.
3
New cards
Omm
the sounds of the universe; the essence of all things; the Origins of all things
4
New cards
Moksha
The Hindu concept of the spirit's 'liberation' from the endless cycle of rebirths. Can attain it from:
Way of knowledge (Jnana)
Way of Karma: complete selflessness
Way of devotion & love (Bhakti): experiencing pure love towards the gods
Raja: controlling the mind; meditation, yoga, breathing exercises
Way of knowledge (Jnana)
Way of Karma: complete selflessness
Way of devotion & love (Bhakti): experiencing pure love towards the gods
Raja: controlling the mind; meditation, yoga, breathing exercises
5
New cards
Trimurti
Brahma (the creator)
Vishnu (the sustainer)
Shiva (the destroyer)
Vishnu (the sustainer)
Shiva (the destroyer)
6
New cards
Vedas
-Earliest sacred texts of Hinduism
-Oral traditions written down
-Compiled assorted texts:
Hymns to various gods
Instructions for sacrifices
Spells for everyday life
-Oral traditions written down
-Compiled assorted texts:
Hymns to various gods
Instructions for sacrifices
Spells for everyday life
7
New cards
Brahman
-The universal soul
-True reality
-The ultimate reality underlying all phenomena
-All things not Brahman are illusions... everything we see is a part of the illusion
-True reality
-The ultimate reality underlying all phenomena
-All things not Brahman are illusions... everything we see is a part of the illusion
8
New cards
Samsara
the cycle of reincarnation
9
New cards
Atman
a little bit of Brahman inside of people; our personal, eternal soul
10
New cards
Intuition
"we can come to know things through intuition, ours and that of wise men before us"
11
New cards
Hindu tolerance and Hindu intolerance
-Hinduism is tolerant of other faiths & accept all religions as true
-They are intolerant to converts (those leaving the Hindu faith)
-They are intolerant to converts (those leaving the Hindu faith)
12
New cards
Fire sacrifice
-earliest characteristic in Hinduism;
-people would have fire rituals for multiple things including warding off evil influences, for good health, to cancel negative energies, for self-confidence, etc.
-the Vedas claimed that this ritual "strengthened the gods" who then "strengthened the world"
-people would have fire rituals for multiple things including warding off evil influences, for good health, to cancel negative energies, for self-confidence, etc.
-the Vedas claimed that this ritual "strengthened the gods" who then "strengthened the world"
13
New cards
Similarities between Hinduism and Christianity
-Moral teachings promote moral lives
-There is life after death
-There is an "eternal individual soul" inside of every human being
-Spiritual devotion, action, and knowledge are all good
-There is life after death
-There is an "eternal individual soul" inside of every human being
-Spiritual devotion, action, and knowledge are all good
14
New cards
Differences between Hinduism and Christianity
-God is not everything; he created everything
-Morality is based on God's righteousness
Hindu morality is almost entirely subjective
-In Christianity, scripture judges our experience
The bible serves as a firm source of truth
In hinduism, experience validates the sacred texts
-Sin and Salvation are real in Christianity
Not just "bad karma" and "moksha"
-Christianity involves God genuinely interacting with time and space
Hinduism rejects time as a substance
-Morality is based on God's righteousness
Hindu morality is almost entirely subjective
-In Christianity, scripture judges our experience
The bible serves as a firm source of truth
In hinduism, experience validates the sacred texts
-Sin and Salvation are real in Christianity
Not just "bad karma" and "moksha"
-Christianity involves God genuinely interacting with time and space
Hinduism rejects time as a substance
15
New cards
Hindu thoughts on evangelism
they are non-evangelistic and encourage people to follow their own religion and not try to convert people from one religion to another
16
New cards
Karmic justice
promises perfect justice and reward for all action
17
New cards
Three (four) yogas
Jhana (knowledge), Karma (obedience), Bhakti (action), Raja (meditation)
18
New cards
Ganges River
the holiest river to Hindus
19
New cards
Gods in Hinduism
"hyper-polytheistic" with over 300,000,000 gods
20
New cards
Namaste
Tradition Hindu greeting which means "the God in me greets and meets the God in you"
21
New cards
Syncretism
the merging of different religions or schools of thought
22
New cards
Hinduism and woman
they see women as lower incarnation state; having children=good karma, but you are mistreated if you are a widow or single
23
New cards
Gandhi
This was a leader of the Indian independence movement in mid-20th century known for his nonviolent protests; he said "God is truth. The way to truth lies through non-violence."
24
New cards
Four Noble Truths
1. life is suffering
2. the cause of suffering is desire
3. the cure for suffering is to remove desire
4. to remove desire, follow the Eightfold path
2. the cause of suffering is desire
3. the cure for suffering is to remove desire
4. to remove desire, follow the Eightfold path
25
New cards
Concepts shared between Hinduism and Buddhism
reincarnation, karma, escape from reincarnation
26
New cards
Anatman
"no self"; a permanent self does not exist; we are an ever-changing self
27
New cards
Buddhist thoughts on evangelism
Evangelism is a natural and immediate response to the Gospel
28
New cards
Theravada
Individuals must find the way to Nirvana on their own; Theravada Buddhism has been a much smaller movement and is only practiced by intense monks in SE Asia (Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand). "Small raft"
29
New cards
Mahayana
Others -especially the Buddha and bodhisattvas- must help the individual find Nirvana. "Large raft"
30
New cards
Pure Land
Buddhism in China that focuses on being reincarnated in the "pure land"; cooperates well with Daoism and other native relations
31
New cards
Zen
Buddhism in Korea and Japan that focuses on "nothingness" meditation; they sometimes use beatings and riddles to focus the mind
32
New cards
Tibetan
Buddhism in Tibet and Nepal; most political and mystical; the face of this type of Buddhism is the Dalai Lama
33
New cards
Soka Gakkai
-also known as Nichiren Buddhism
-they chant the phrase "Nam-myoho-renge-kyo" which answers the questions "Who am I?" & "Where am I?"
-they say that chanting empowers, improves, and focuses their lives
-they chant the phrase "Nam-myoho-renge-kyo" which answers the questions "Who am I?" & "Where am I?"
-they say that chanting empowers, improves, and focuses their lives
34
New cards
Story of Siddhartha
Sheltered from outside world, went out one day saw an old man, a sick man, a dead man, and an ascetic monk; he could not understand how bad life was, and so he became an ascetic but gave up after many years, he sat under a bodhi tree and meditated but then found enlightenment after finding the middle path.
35
New cards
Buddha's final words
"decay is inherent in all things; work out your salvation with diligence!"
36
New cards
Buddhism and the nature of reality
The Buddha saw the world as it truly was, without ignoring the real pain and suffering of humanity, The World is Real and Rational, Though Buddhism is at its core an atheistic belief system, its view of reality is somewhat pantheistic, We are in a rational - not illusory - world filled with pain which we produce ourselves by bad karma.
37
New cards
Buddhism and what is a human being
The Buddha's Three Marks of Existence:
-Anatman (no Atman) - "no self"; a permanent self does not exist; we are an ever-changing self
-Dukkha: suffering; dissatisfaction
-Impermanence: we are all passing away and changing with the universe
-Anatman (no Atman) - "no self"; a permanent self does not exist; we are an ever-changing self
-Dukkha: suffering; dissatisfaction
-Impermanence: we are all passing away and changing with the universe
38
New cards
Buddhism and intuition
Buddhism is much more suspicious of the self in comparison to Hinduism; Intuition looks too much like desire
39
New cards
King Ashoka
Built thousands of stone pillars with Buddhist teachings carved into it and sent Buddhist missionaries all over Southeast Asia
40
New cards
Nirvana
The state of englightenment for Buddhists; "extinguished; blown out"
41
New cards
Desire
they believe desire is the cause of suffering
42
New cards
Eight-fold path
1. Right View
2. Right Intention
3. Right Speech
4. Right Action
5. Right Livelihood
6. Right Effort
7. Right Concentration (Meditation)
8. Right Mindfulness
2. Right Intention
3. Right Speech
4. Right Action
5. Right Livelihood
6. Right Effort
7. Right Concentration (Meditation)
8. Right Mindfulness
43
New cards
Asceticism
avoiding all forms of comfort and worldly pleasures
44
New cards
Budda and the gods
Budda isn't a god and they don't worship any gods; they are an atheistic religion
45
New cards
Siddhartha's four sights
1. old age
2. sickness
3. death
4. an ascetic monk
2. sickness
3. death
4. an ascetic monk
46
New cards
The three poisons
greed, hatred, ignorance
47
New cards
Bodhisattvas
"buddha-to-be"; has attained enlightenment but chooses to remain in the world to bring enlightenment to the world
48
New cards
Dukkha
suffering and dissatisfaction
49
New cards
Dalai Lama
The face/leader of Tibetan Buddhism, a lifelong bodhisattva