MCDB 436 (9): T-cell Mediated Immunity
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
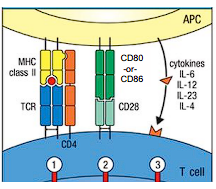
co-stimulatory molecules
- T-cell: CD28
- APCs: CD80/86
binding of CD28:80/86 = REQUIRED for activation of naive T cells
- APCs: CD80/86
binding of CD28:80/86 = REQUIRED for activation of naive T cells
2
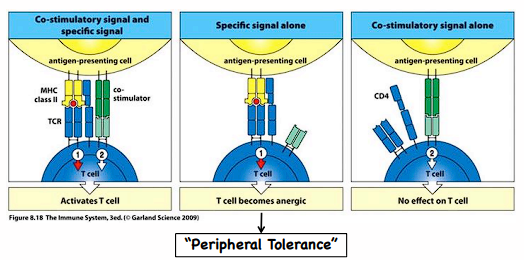
New cards
effects of co-stimulation/lack of on T cell
- MHCII:TCR + co-stimulator = activated T cell
- MHCII:TCR without co-stim = anergic
- co-stim without MHCII:TCR = no effect
- MHCII:TCR without co-stim = anergic
- co-stim without MHCII:TCR = no effect
3
New cards
peripheral tolerance
T cell interacts with APC with only MHCII, no co-stim molecules
4
New cards
immature DCs
- round, smooth surface
- more phagocytic
- lower levels of CD80/86
- lower levels of MHC II
- lower levels of cytokine secretion - IL-12, IL-10, TNFa
- more phagocytic
- lower levels of CD80/86
- lower levels of MHC II
- lower levels of cytokine secretion - IL-12, IL-10, TNFa
5
New cards
____ and ____ activate vascular endothelium
IL-1b :: TNFa
6
New cards
_____ stimulates dendritic cell migration to lymph nodes and maturation
TNFa
7
New cards
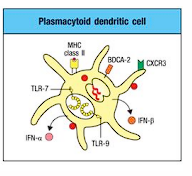
plasmacytoid DCs
produce abundant type I IFNs, may act as helper cells for Ag presentation by conventional dendritic cells
- express TLR7&9, RLR, type I IFNs
- not thought to be involved in ag-specific activation of naive T cells but rather early viral infection sentinels
- express TLR7&9, RLR, type I IFNs
- not thought to be involved in ag-specific activation of naive T cells but rather early viral infection sentinels
8
New cards
conventional DCs
activated by MAMPs in peripheral tissues, where they encounter pathogens ->
TLR signaling induces CCR7 expression AND enhances processing of pathogen-derived Ags
resident: highly phagocytic, macropinocytic; do not express co-stimulatory molecules
TLR signaling induces CCR7 expression AND enhances processing of pathogen-derived Ags
resident: highly phagocytic, macropinocytic; do not express co-stimulatory molecules
9
New cards
TLR signaling effect on conventional DCs
- induce CCR7 (chemokine receptor)
- increase processing of Ags taken up into phagosomes
- increase processing of Ags taken up into phagosomes
10
New cards
CCR7 signaling
respond to CCL19 and CCL21, directing them to the draining lymphoid tissue ->
CCL19 + 21 provide further maturation ->
co-stimulatory CD80/86 + MHC ->
conventional DCs activate naive T cells, no longer phagocytic ->
express CD80 + 86, MHCI/II, adhesion molecules (LFA/ICAM)
CCL19 + 21 provide further maturation ->
co-stimulatory CD80/86 + MHC ->
conventional DCs activate naive T cells, no longer phagocytic ->
express CD80 + 86, MHCI/II, adhesion molecules (LFA/ICAM)
11
New cards
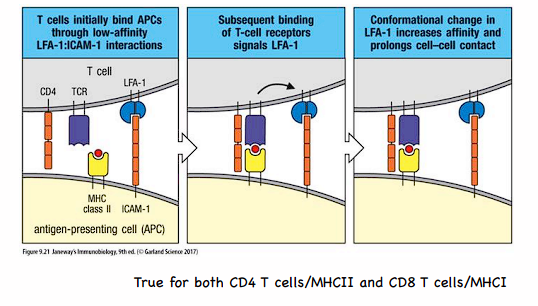
transient adhesive interactions
between T cells and APCs (CD4/MHCII and CD8/MHCI)
- LFA-1 on T cell, ICAM-1 on APC
- ensures the T cell doesn't bind too strongly
- LFA-1 on T cell, ICAM-1 on APC
- ensures the T cell doesn't bind too strongly
12
New cards
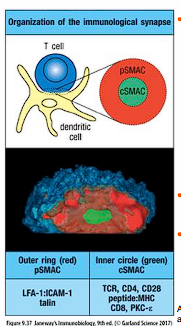
immunological synapse
area of contact b/t T cell and APC; aka supramolecular activation complex (SMAC)
- outer (pSCMAC) + inner (cSMAC)
provides structure for directed secretion of T cell cytokines
- outer (pSCMAC) + inner (cSMAC)
provides structure for directed secretion of T cell cytokines
13
New cards
pSMAC vs cSMAC
pSMAC - enriched for LFA-1 and talin (cytoskeletal protein)
cSMAC - higher levels of TcR, CD4/CD8, CD28, CD2, PKC-e
cSMAC - higher levels of TcR, CD4/CD8, CD28, CD2, PKC-e
14
New cards
APC signals to naive T cells
deliver signals for clonal expansion and differentiation
- for both CD4 and CD8
- differentiation results in generation of effector T cells (diff from naive T)
- provide cytokines that induce naive CD4 into distinct subsets also
- for both CD4 and CD8
- differentiation results in generation of effector T cells (diff from naive T)
- provide cytokines that induce naive CD4 into distinct subsets also
15
New cards
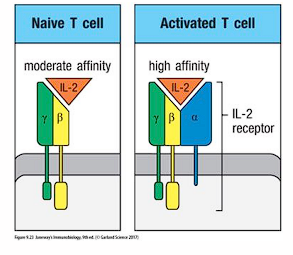
CD28-dependent co-stimulation of activated T cells
induces expression of IL-2 and IL-2R
- activated T cell has alpha chain, whereas naive T cell just has beta and gamma
- IL-2 comes from T cells themselves; therefore, autocrine process
- activated T cell has alpha chain, whereas naive T cell just has beta and gamma
- IL-2 comes from T cells themselves; therefore, autocrine process
16
New cards
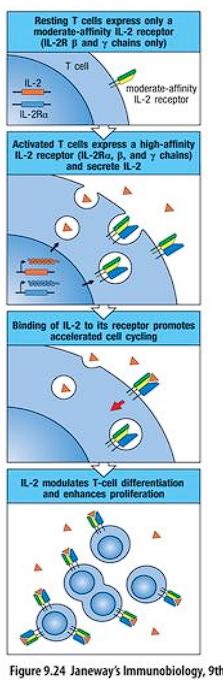
activated T cell
stimulates differentiation pathway of T cells
17
New cards
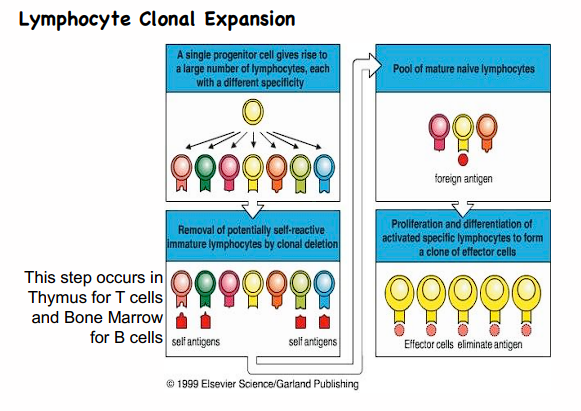
lymphocyte clonal expansion
progenitor ->
large # of lymphoctes ->
removal of self-reactive immature lymphocytes by clonal deletion (thymus for T, bone marrow for B) ->
pool of mature naive lymphocytes ->
proliferation + differentiation of activated specific lymphocytes form a clone of effector cells
large # of lymphoctes ->
removal of self-reactive immature lymphocytes by clonal deletion (thymus for T, bone marrow for B) ->
pool of mature naive lymphocytes ->
proliferation + differentiation of activated specific lymphocytes form a clone of effector cells
18
New cards
T/F: once a T cell becomes an effector cell, encounter with its specific Ag results in immune effector functions without need for co-stim
true
19
New cards
APC cytokine secretion
APCs secrete cytokines that drive the differentiation of T cells into different subsets and effector functions
- include APCs and innate immune cells
- by environmental conditions - PRR-MAMP/DAMP binding
- include APCs and innate immune cells
- by environmental conditions - PRR-MAMP/DAMP binding
20
New cards
CTLA-4
inhibitory co-receptor signal expressed after T-cell activation
- structurally similar to CD28 but not the "gas pedal"
- CTLA-4 binds to CD80/86 for inhibition
- MUCH higher affinity than CD28
- structurally similar to CD28 but not the "gas pedal"
- CTLA-4 binds to CD80/86 for inhibition
- MUCH higher affinity than CD28
21
New cards
CTLA-4 effects
- decreases production of T-cell derived IL-2
- results in limiting proliferative response of activated T cell
- shuts down activation of T cell
- results in limiting proliferative response of activated T cell
- shuts down activation of T cell
22
New cards
effector T cell
respond to target cells without costimulation
naive T recognizes Ag on APC -> secretes and responds to IL-2 -> clonal expansion -> differentiation -> effector function
for both CD4 and CD8
naive T recognizes Ag on APC -> secretes and responds to IL-2 -> clonal expansion -> differentiation -> effector function
for both CD4 and CD8
23
New cards
high endothelial venules (HEV)
specialized post-capillary venous swellings; cuboidal endothelial cells
- enable lymphocytes circulating in blood to directly enter lymph node/secondary lymphoid tissues
- found in all secondary lymphoid organs (except spleen) - tonsils, PIs, pharynx, etc
- express receptors to interact with leukocytes; enable naive lymphocytes to move in and out of the lymph nodes from the circulatory system
- enable lymphocytes circulating in blood to directly enter lymph node/secondary lymphoid tissues
- found in all secondary lymphoid organs (except spleen) - tonsils, PIs, pharynx, etc
- express receptors to interact with leukocytes; enable naive lymphocytes to move in and out of the lymph nodes from the circulatory system
24
New cards
recruitment of leukocytes in the development of secondary lymphoid organs
1) stromal cells + HEVs secrete CCL21
2) DCs have CCR7 to bind CCL21, migrate into developing lymph node
3) DCs secrete CCL19, attracting T cells with CCR7 to developing lymph node
4) B cells initially attracted by CCL19 also with CCR7
5) B cells induce differentiation of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), secreting CXCL13 for attracting more B cells on CXCR5
2) DCs have CCR7 to bind CCL21, migrate into developing lymph node
3) DCs secrete CCL19, attracting T cells with CCR7 to developing lymph node
4) B cells initially attracted by CCL19 also with CCR7
5) B cells induce differentiation of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), secreting CXCL13 for attracting more B cells on CXCR5
25
New cards
CCR7
binds CCL21/19; on B, T, and DCs
26
New cards
CXCR5
binds CXCL13 (from FDC); on B cells
27
New cards
if a T cell DOESN'T encounter its specific Ag in the lymph node...
they leave the lymph node through efferent lymphatics to return to the circulation to enter another secondary lymphoid organ
28
New cards
if a T cell DOES encounter its specific Ag in the lymph node...
- T cells lose their ability to exit from the node and become activated to proliferate and differentiate into effector T cells
- after several days: regain expression of receptors to exit node
- after several days: regain expression of receptors to exit node
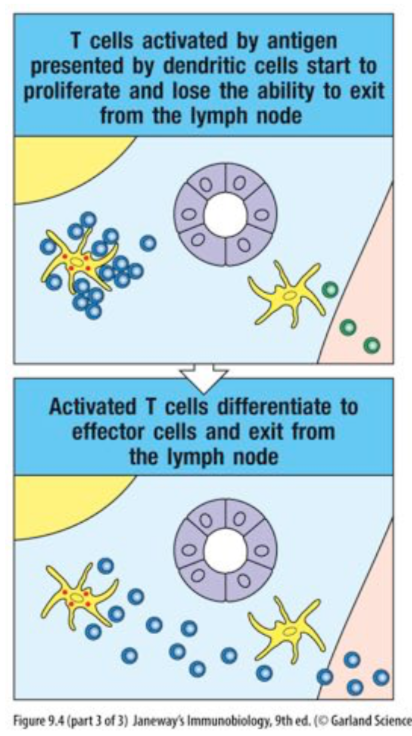
29
New cards
trapping of naive T cells in lymphoid tissue
bind to DCs, activated through TcRs
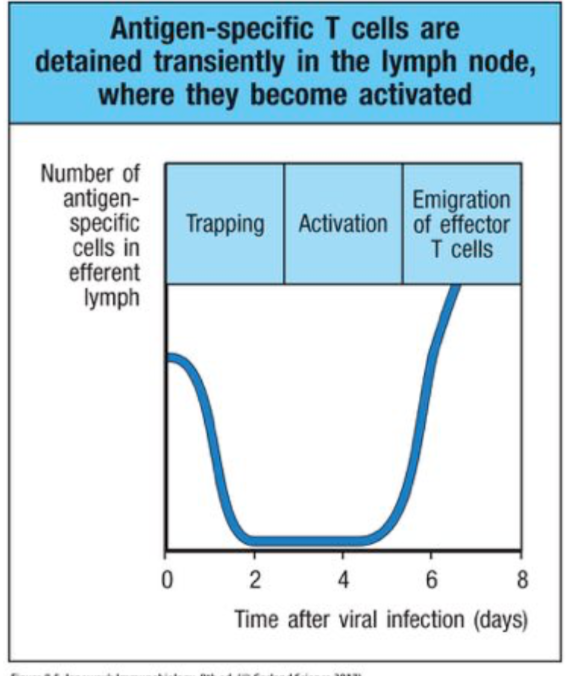
30
New cards
sailyl-Lewis X with T- and B-lymphocytes
- at rest: lack expression
- upon activation: strongly express s-LeX. bind to L-selectin
- upon activation: strongly express s-LeX. bind to L-selectin
31
New cards
L-selectin
expressed on naive T cells; binds to sulfated s-LeX moieties on vascular addressins
32
New cards
vascular addressins
CD34 - on HEV cells
GlyCAM-1 - on HEVs
MAdCAM-1 - on mucosal endothelium, guides lymphocytes to MALT
use vascular addressins to get into HEV or mucosal endothelium
GlyCAM-1 - on HEVs
MAdCAM-1 - on mucosal endothelium, guides lymphocytes to MALT
use vascular addressins to get into HEV or mucosal endothelium
33
New cards
lymphocyte entering lymphoid tissue - process
1) circulating lymphocyte enters HEV
2) L-selectin to GlyCAM-1 + CD34 + sLeX, allowing rolling interaction
3) LFA-1 activated by CCR7 signaling in response to CCL21 bound
4) activated LFA-1 binds to ICAM-1
5) extravasation (encouraged by intracellular chemokine gradient)
2) L-selectin to GlyCAM-1 + CD34 + sLeX, allowing rolling interaction
3) LFA-1 activated by CCR7 signaling in response to CCL21 bound
4) activated LFA-1 binds to ICAM-1
5) extravasation (encouraged by intracellular chemokine gradient)
34
New cards
sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)
bioactive lipid; establishes a gradient between lymphoid organ and circulatory fluids. allows exit of lymphocytes from lymphoid tissue
- major source = hematopoietic cells, mostly erythrocytes
- establish gradient through S1P degradation (erythrocytes die, no degrading enzyme)
- lymphatic sys: source = lymph endothelial cells
- LPP1 and LPP3 degrade; localized enzymes to plasma membrane, function as ecto-enzymes (degrade extracellularly)
- major source = hematopoietic cells, mostly erythrocytes
- establish gradient through S1P degradation (erythrocytes die, no degrading enzyme)
- lymphatic sys: source = lymph endothelial cells
- LPP1 and LPP3 degrade; localized enzymes to plasma membrane, function as ecto-enzymes (degrade extracellularly)
35
New cards
S1PR1
expressed on naive T cells, responsive to S1P gradient
- no Ag recog: S1PR1 promotes movement to efferent flow
- Ag recog: decrease S1PR1 expression, retained in T-cell zone
- effector T cells: re-express S1PR1
- no Ag recog: S1PR1 promotes movement to efferent flow
- Ag recog: decrease S1PR1 expression, retained in T-cell zone
- effector T cells: re-express S1PR1
36
New cards
CD69
T cell activation marker
- inc CD69 = dec S1PR1 (activating)
- dec CD69 = inc S1PR1 (effector or naive)
- inc CD69 = dec S1PR1 (activating)
- dec CD69 = inc S1PR1 (effector or naive)
37
New cards
polarizing mileu
effect of external factors on naive CD4+ T cell differentiation
- environment, infection, hygiene, nutrition, epigenetics, genetics, etc.
- environment, infection, hygiene, nutrition, epigenetics, genetics, etc.
38
New cards
TH1 cells
- fate-specifying cytokines: IFN-gamma, IL-12, and receive from ILC1
- produce: IFN-gamma
- regulate: TFH cell pathway
effect: macrophage activation, inflammation, opsonizing IgG isotypes
effect onto: macrophages -> kill dead intracellular bacteria
- produce: IFN-gamma
- regulate: TFH cell pathway
effect: macrophage activation, inflammation, opsonizing IgG isotypes
effect onto: macrophages -> kill dead intracellular bacteria
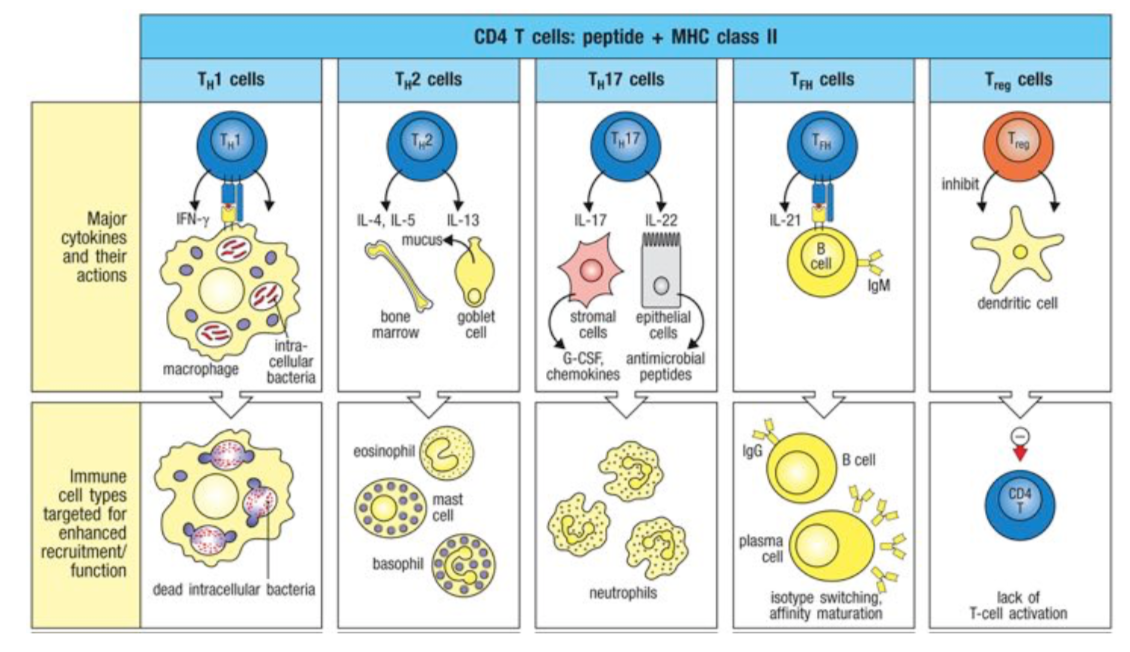
39
New cards
TH2 cells
- fate-specifying cytokines: IL-4, and receive from ILC2 (and IgE)
- produce: IL-4, IL-5, IL-13
- regulate: TFH cell pathway
effect: allergic and helminth responses
effect onto: bone marrow -> eosinophil (IL-5), mast cell, basophil
+ (IL-13) goblet cell -> mucus
- produce: IL-4, IL-5, IL-13
- regulate: TFH cell pathway
effect: allergic and helminth responses
effect onto: bone marrow -> eosinophil (IL-5), mast cell, basophil
+ (IL-13) goblet cell -> mucus
40
New cards
TH17 cells
- fate-specifying cytokines: TGF-beta, IL-6, IL-23, and receive from ILC3
- produce: IL-17, IL-22
effect: inflammation
effect onto:
- stromal cells -> G-CSF, chemokines -> neutrophils
- epithelial cells -> AMPs -> neutrophils
IL17 = proinflammatory cytokine; cascade effect
IL-22 = acts on epithelial to produce AMPs
- produce: IL-17, IL-22
effect: inflammation
effect onto:
- stromal cells -> G-CSF, chemokines -> neutrophils
- epithelial cells -> AMPs -> neutrophils
IL17 = proinflammatory cytokine; cascade effect
IL-22 = acts on epithelial to produce AMPs
41
New cards
TFH cells
- fate-specifying cytokines: IL-6
- produce: IL-21
effect: germinal centre help
effect onto: B cell -> isotype switching, affinity maturation
- produce: IL-21
effect: germinal centre help
effect onto: B cell -> isotype switching, affinity maturation
42
New cards
induced Treg cells
- fate-specifying cytokines: TGF-beta, IL-2
- produce: TGF-beta, IL-10
effect: regulation, suppression of inflammatory responses
- produce: TGF-beta, IL-10
effect: regulation, suppression of inflammatory responses
43
New cards
innate lymphoid cells (ILC)
cells of lymphoid lineage which lack specific Ag receptors (no TcR/Ig) and lack co-receptor complexes
- migrate from bone marrow and populate lymphoid tissues + peripheral organs
- fewer in # than B/T
- migrate from bone marrow and populate lymphoid tissues + peripheral organs
- fewer in # than B/T
44
New cards
Id2
transcription factor in the common lymphocyte progenitor (CLP) required for the development of all ILCs
45
New cards
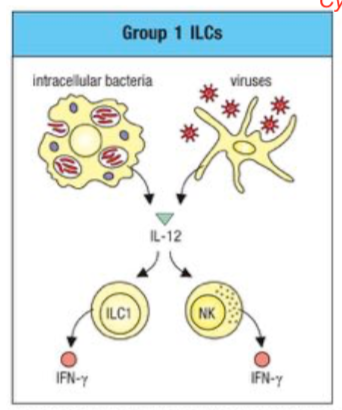
group 1 ILCs
intracellular bacteria + viruses -> IL-12 -> ILC1 + NK -> IFN-gamma
for TH1
for TH1
46
New cards
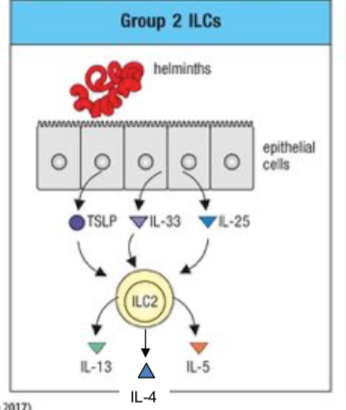
group 2 ILCs
helminths -> epithelial cells -> TSLP + IL-33 + IL-25 -> ILC2 -> IL-13, IL-4, IL-5
for TH2
for TH2
47
New cards
group 3 ILCs
intracellular bacteria -> IL-23 -> ILC3 -> IL17, IL-22
48
New cards
ILC-cytokine inducing responses
- MAMPs by different types of microorganisms (direct/indirect)
- DAMPS
- cytokine signals from other cells
- environmental signals (pollutants, etc)
- DAMPS
- cytokine signals from other cells
- environmental signals (pollutants, etc)
49
New cards
CD4 effector T cell help
enhance effector functions - innate, isotype switching, etc
50
New cards
thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP)
produced in response to helminths; alarmins
- cytokines primarily produced by epithelial cells that sense molecular patterns of helminths (chitin)
- cytokines primarily produced by epithelial cells that sense molecular patterns of helminths (chitin)
51
New cards
T/F: ILCs require priming and differentiation to acquire effector functions
false