Radio, UV, Infrared and X-ray telescopes
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA A-level physics options - astrophysics chapter 1 telescopes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Draw a diagram of a single-dish radio telescope.
dish must be parabolic
dish reflects signal to the antenna, the signal is amplified and then computer-analyzed.
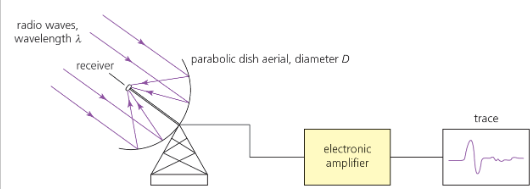
Why must the dishes be large on single-dish radio telescopes?
Radio telescopes collect EM radiation with very large wavelengths (10-0.5mm)
When wavelength is large, angular resolution is also large, resulting in large airy disks
Therefore, the diameter of the dish must be large to reduce angular resolution.
Large dish increases the resolving power and collecting power of the telescope
Advantages of radio telescopes
Can operate during the day as well as night
Many celestial objects active in the radio region (protostars, radio galaxies)
De-excitation produces radio radiation. Hydrogen gas is everywhere in the universe, therefore radio telescopes are useful in detecting hydrogen clouds
Disadvantages of radio telescopes.
Poor angular resolution compared to optical telescopes
Ionosphere can absorb signals below 30MHz
Water vapour absorbs singals above 60GHz
Man-made interference at radio wavelengths (phones, radio, tv) forces telescopes to isolated areas.
Require large structures for support and steering.
What are infrared telescopes?
telescopes that use the same design as optical telescopes (that detect visible light)
Detector is made from superconducting material
Used to observe cooler objects such as: cool stars, star formation regions, active galaxies, large-scale structures
Benefits of IR telescopes?
Used to observe cooler objects such as: cool stars, star formation regions, active galaxies, large-scale structures. Which cannot be observed with visible light
Disadvantages of IR telescopes?
detector material is sensitive and needs to be maintained just above 0K, and shielded from heat sources
Most only be used in space or above the atmosphere as the atmosphere absorbs infrared light
What are UV telescopes?
use the same design as IR and optical telescopes
Detect wavelengths in the UV region
Most used to observe warmer objects such as: hot massive stars, new white dwarves, core regions of active galaxies.
How do UV telescopes work?
They make use of the photoelectric effect to convert UV photons to electrons and convert the signal into a current.
Disadvantages of UV telescopes?
UV radiation below 300nm is absorbed by the atmosphere and therefore the telescope must be placed in space (if observing within that region)
What are X-ray telescopes
telescopes that detect in the X-ray region
X-ray are high energy so must be made from a combination of parabolic and hyperbolic mirrors to prevent them from passing through
Light rays are focused onto CCDs
Observe high-energy events such as active galaxies, black holes and neutron stars
Disadavantages of X-ray telescopes
all X-ray is absorbed by the atmosphere, so can only be used in space.
What are gamma-ray telescopes
telescopes that detect objects in the gamma region
gamma has such high-energy that it would pass straight through them, detector made of layers of pixels are used instead
gamma rays produce a signal in each pixel they come into contact with
What are CCDs?
charged coupled devices
an array of light-sensitive pixels, which become charged
when they are exposed to light by the photoelectric effect
convert light signals into electrical format
CCD advantages compared to photographic film
Quantum efficiency is over 75% compared to 5% for photographic film.
The image produced is in digital format which can be processed by a computer immediately.
Can handle large differences in signal intensity, therefore faint objects can be captured next to bright objects
Can detect wavelengths in infrared, UV and visible
Pixel and spacial resolution is higher
What is quantum efficiency?
What is pixel resolution?
the total number of pixels used to form the image on a screen.
A lot of small pixels will be able to resolve an image more clearly than a small amount of
large pixels
What is spatial resolution?
the minimum distance two objects must be apart in order to be
distinguishable. This is used to observe small details.