Computer science.
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1-2.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Unit 3
(i) What does RAM stand for….
What is the use of it.
Random access memory.
Primary memory unit that can be written and to read from only.
(ii) What does ROM stand for.
What is the use of it.
Read only memory.
Primary unit that can only be read form.
What does DRAM stand for ? and the defination.
Dynamic RAM.
Type of RAM chip that needs to be constantly refreshed.
What does SRAM stand for and what is the use of it ?
Static RAM
Type of Ram chip which uses flip-flop and does not need to be refreshed.
(PROM) stands for.
and what is the defination of it.
Programmable ROM
Type of ROM chips that needs to be programmed once.
EPROM stands for.
Defination.
Erasable ROM
Type of ROM chip that needs to be programmed once using Ultraviolet light.(UV light)
HDD stands for.
Defination.
Hard disk drive.
type of magnetic storage device that uses spinning disk.
SSD
Defination..
Solid state drive
media storage that has no moving parts which relies on the movemnet of the electron.
For chosing the right device what are the 4 main things to remember ?
User Skills
user needs
Environment
Cost
In RAM the data user can change the ____.
Data
RAM is ___. (volatile,non-volatile)
Volatile (memory contents are lsot on powering off the computer. )
Each DRAM chips consists of a number of ________ and _________.
Transistors and capacitors.
Role of transistors.
Acts like switches they allow the chip control circuity to read the capacitors values.
Role of Capacitors.
holds the bits of information (0 or 1)
Why does the capacitor need to be charged after every 15 nanosec ? (if it is not refreshed)
They capacitor charge will leak away very quickly, leaving every capacitor with the value of 0.
Write the diferences between DRAM and SRAM.
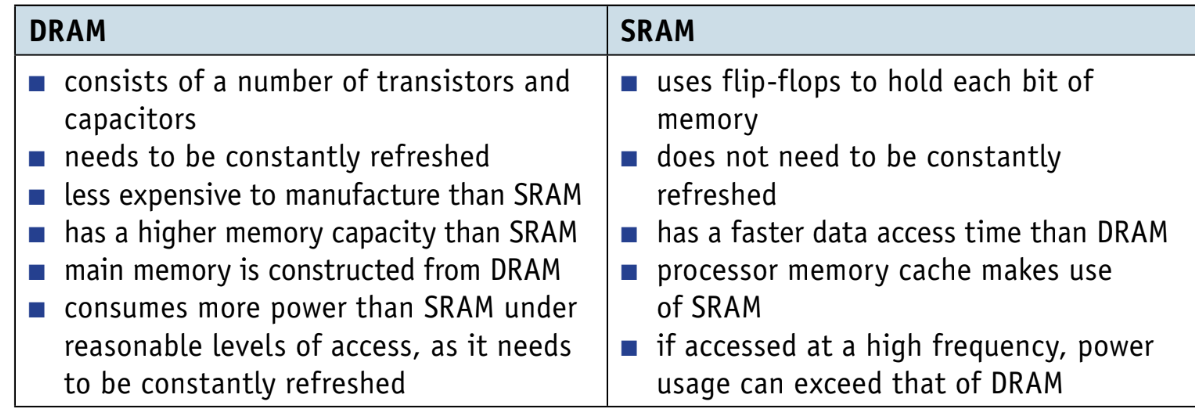
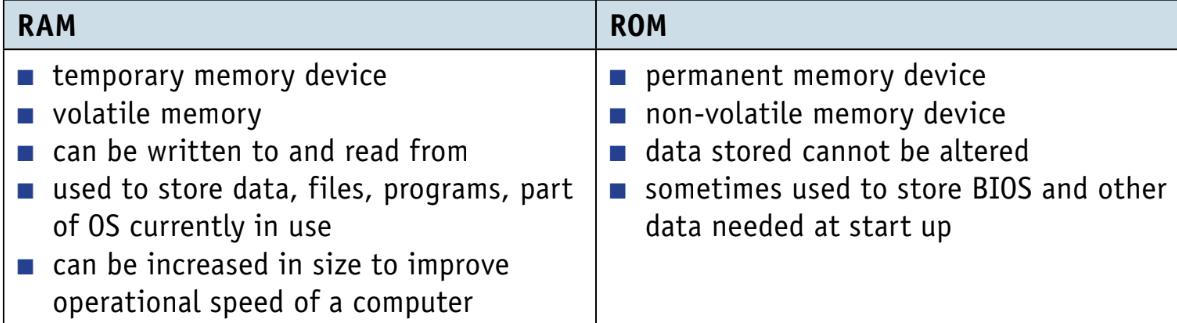
What is the difference between RAM and ROM.
PROM is made up of ?
How does Programming work in PROM ?
What are the things they are used in ?
Matrix of fuses.
Which uses an electric current to alter specific cells by burning fuses in the matrix.
They are often used in mobile phones or in RFID tags.
What does EPROM use other then fuses ?
And what does EPROM use to program
examples ?
Uses floating capacitors and transistors other then fuses.
Ultra violet (UV light)is used to program an EPROM through quartz window.
Used in application which are under development, such as the new game consoles.
What is a Embedded system ?
It involves installation of microprocessors into device to enable operation to be controlled in a more efficient way.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of controlling in this manner (embedded systerm)
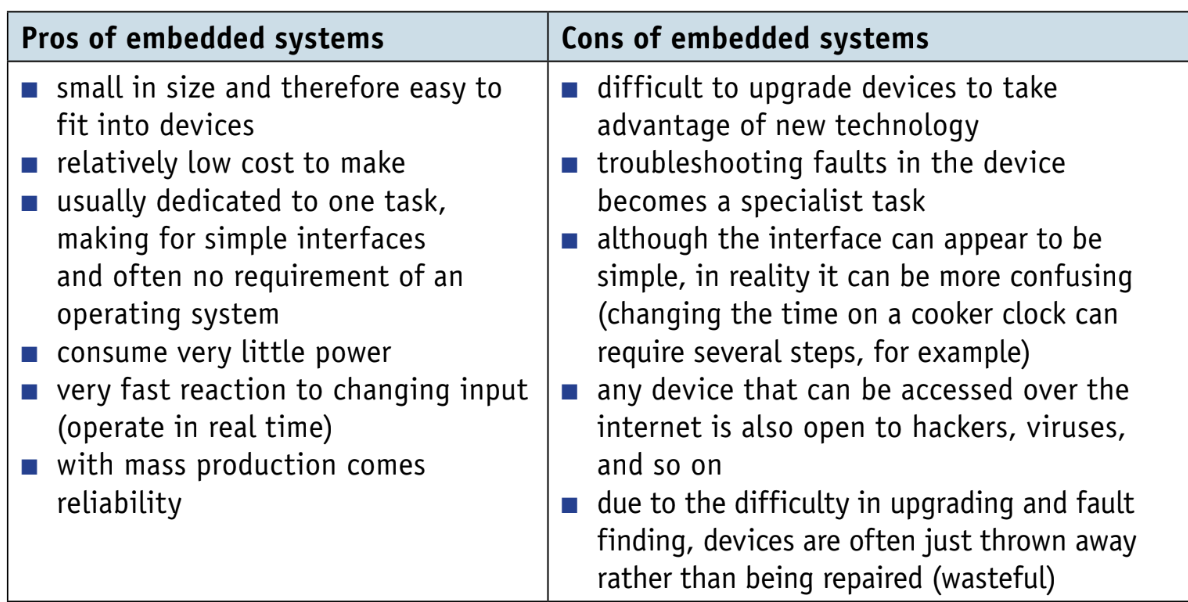
Example of embedded systems. (9)
Heating thermostats
hospital equipment
washing machines
dishwashers
coffee machines
satellite navigation system
factory equipments
security system
traffic lights.
What are the things that are stored in secondary storage device ?
All application,the operating system, device drivers and general files (for example, documents, photos,music)