1.1 Cells and Magnification 🔬
1/77
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Light microscope
uses light to detect and magnify small objects
Using a light microscope
start with low power objective lens (wide field of view) to locate cells
once centred, switch to higher power lens for detailed viewing
Magnification
How much an image appears to have increased in size by
Total magnification
overall magnification of eyepiece and objective lenses
Total magnification equation
Total magnification = eyepiece magnification x objective lens magnification
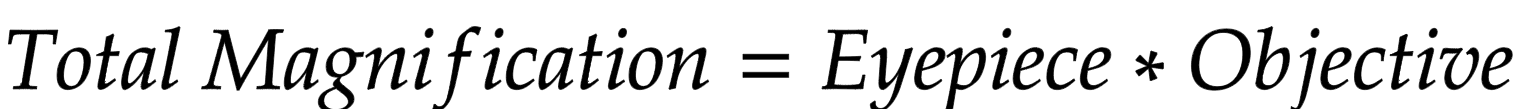
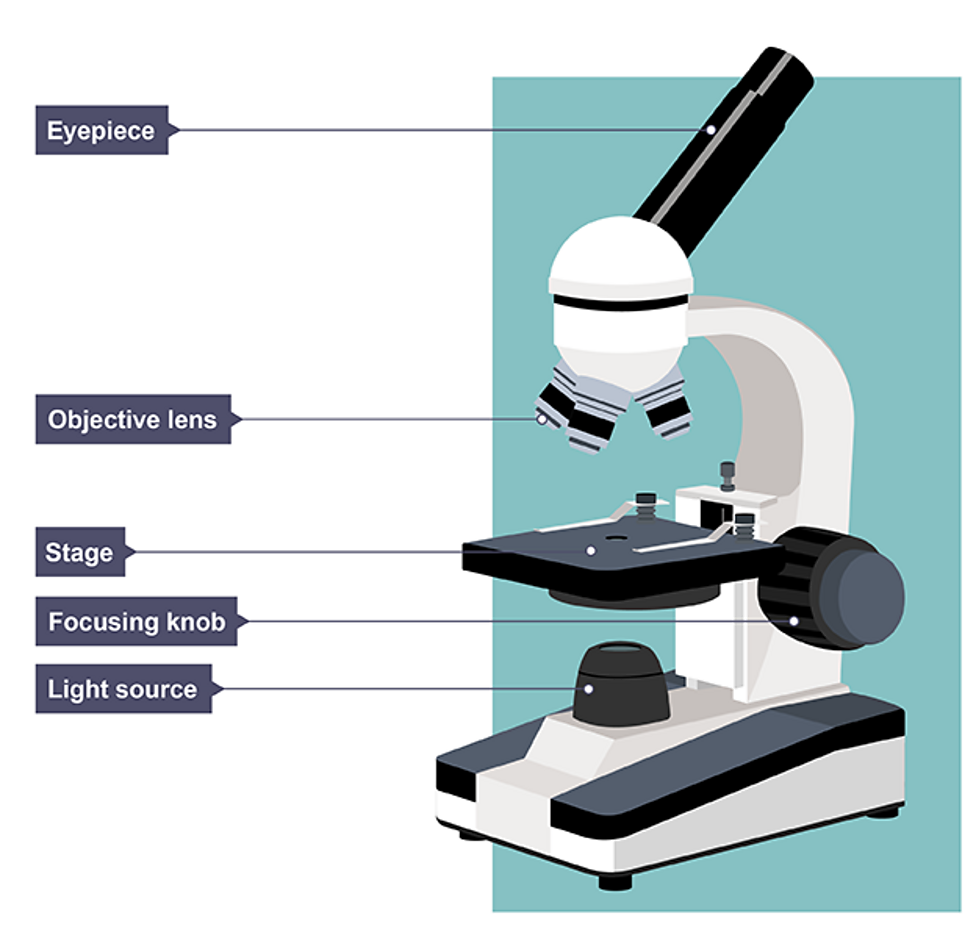
Eyepiece lens
closest to the eye when viewing
Objective lenses
above stage that can be manually adjusted for higher magnification
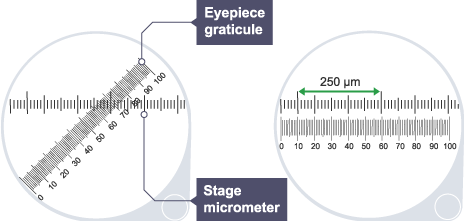
Graticule
scale with many divisions on eyepiece lens to measure object's size
Focusing wheel
twistable wheel to adjust focus of object by changing height of stage
Microscope slide
thin piece of glass to hold specimens when observed
Microscope stage
Where slide is placed with stage clips
Field of view
maximum area visible when looking through a microscope
Drawing cell structures
Drawn in pencil with firm, continuous lines (no sketching)
Large and proportionate to observed cell
Clearly labelled
Given title with magnification or size
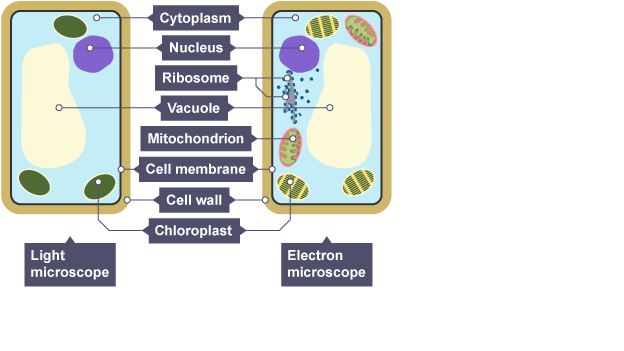
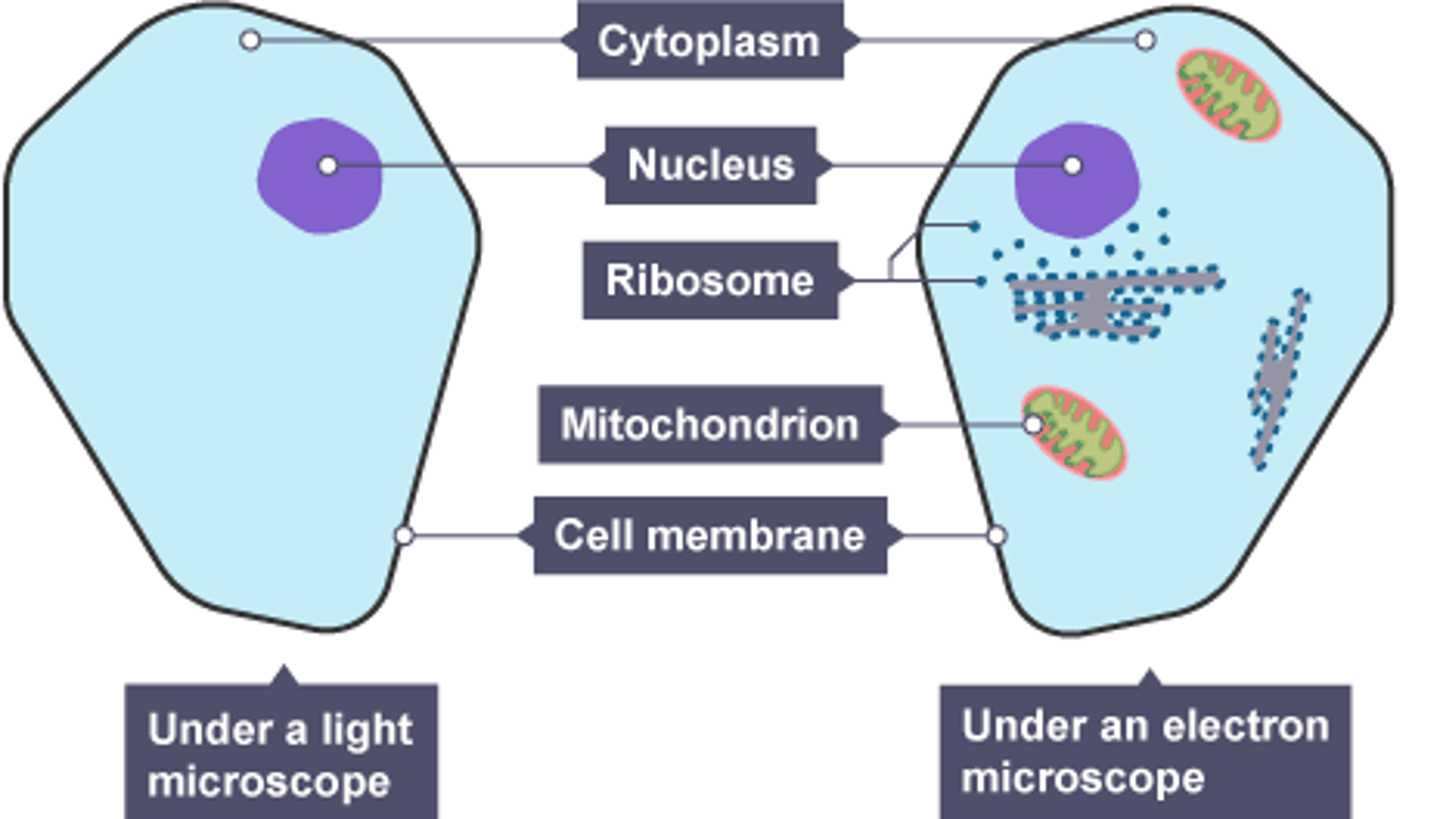
Electron microscope
focuses beams of electrons for higher resolution and magnification

Uses of electron microscopes
clearer and more detailed view of cells (ribosomes)
revealing structures of smaller organelles (mitochondria/ chloroplast)
Resolution
degree of detail visible in an image
Magnification equation
Magnification = Image size/ Actual size
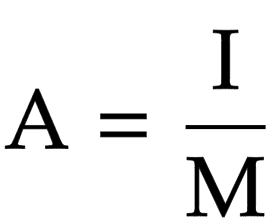
Micrometre (μm)
10-6

Micrometres to millimetres
1000μm = 1mm
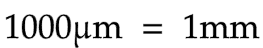
Image size
size of object after magnification
Actual size
real size of object before magnification
Sub-cellular structures
Structures or organelles that are found in the cell
Staining techniques
using dyes to better see cells by making parts more obvious e.g iodine/ methylene blue
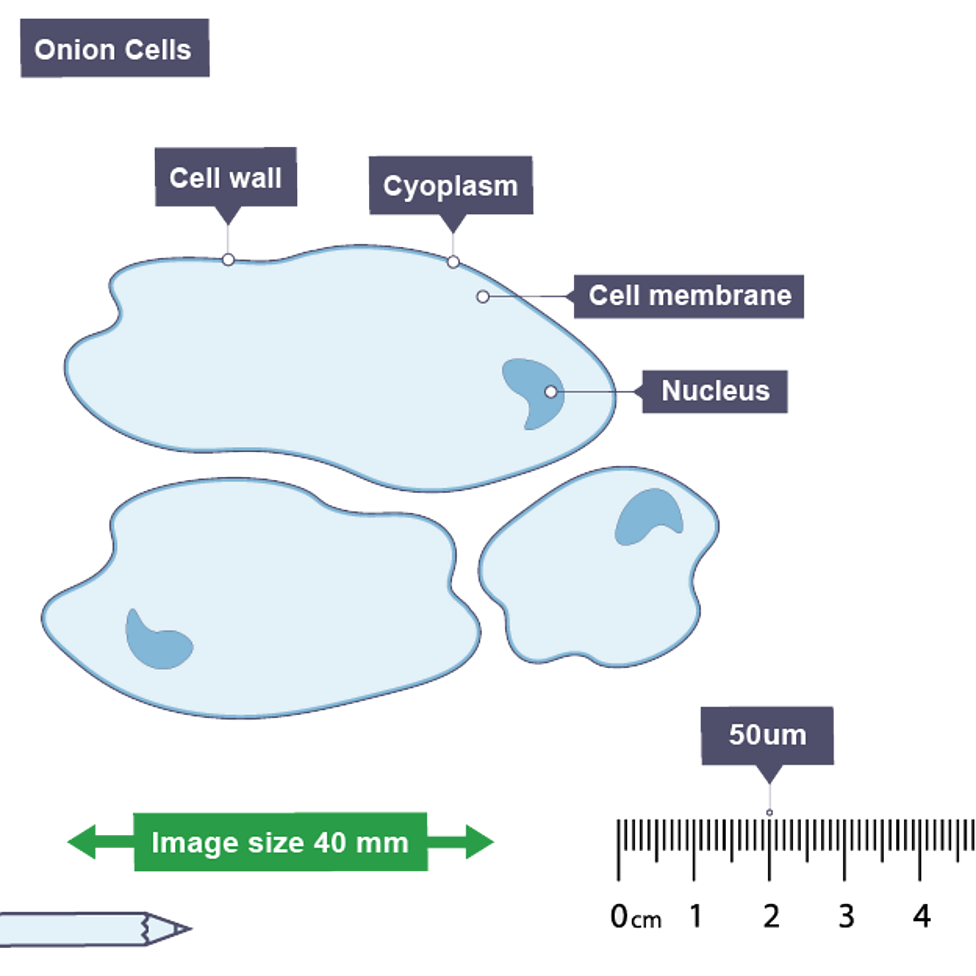
Using a scale bar
Measure length of scale bar using ruler
Convert to micrometres
Calculate magnification (measured length/ given length)
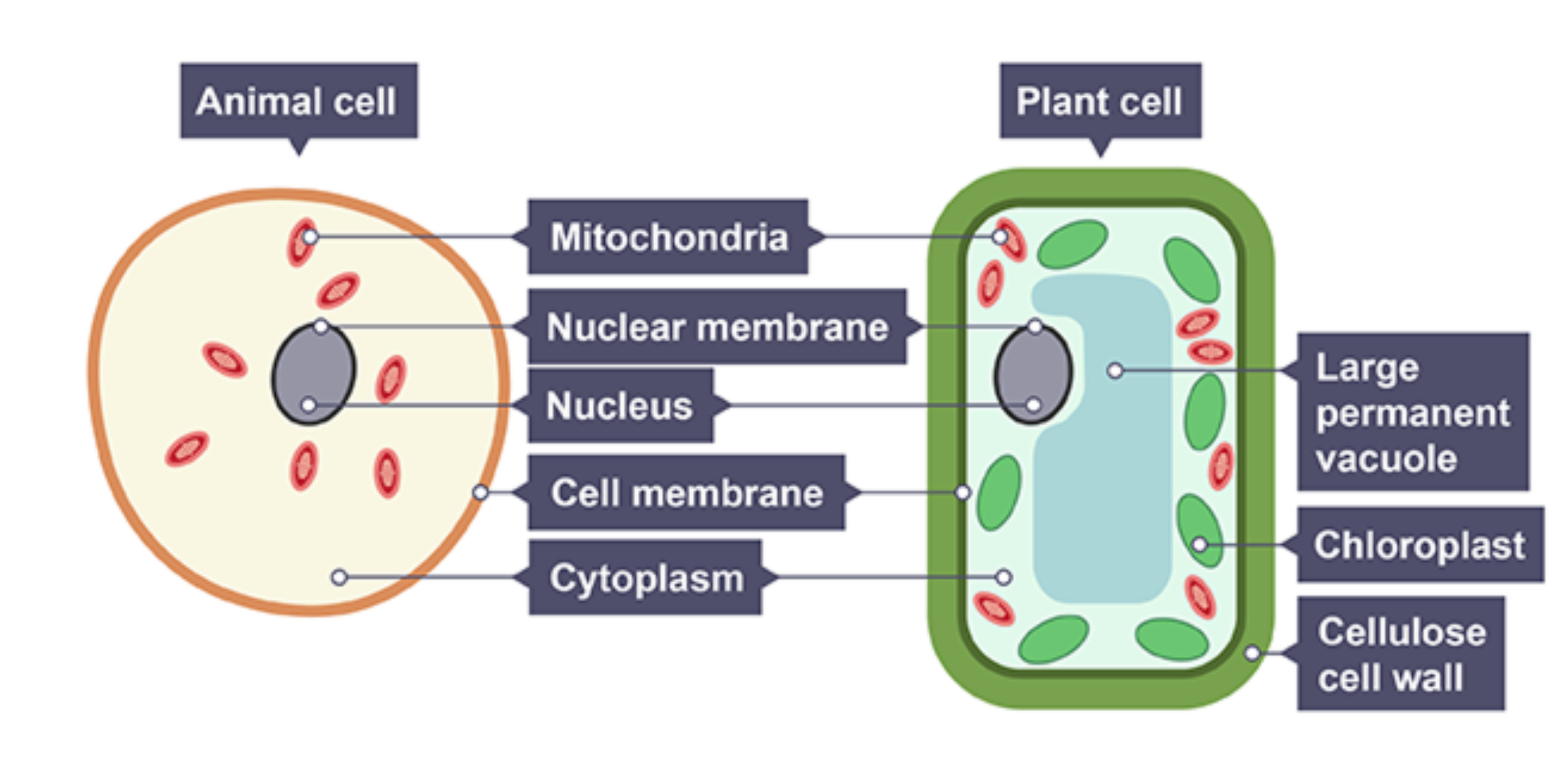
Animal cell
has a nucleus, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, mitochondria and cytoplasm
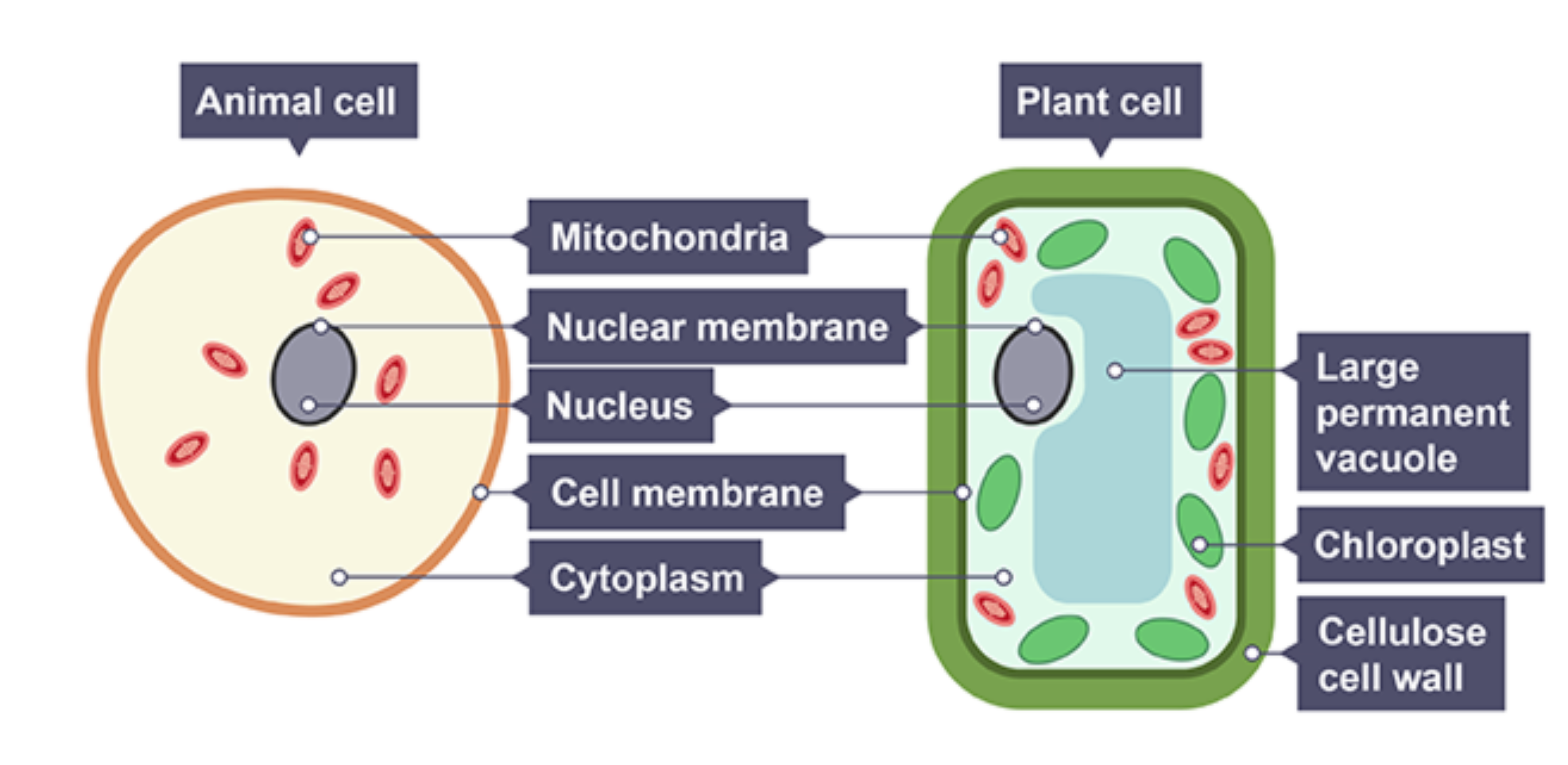
Plant cell
has a nucleus, nuclear membrane, vacuole, cell membrane, mitochondria, chloroplasts, cell wall and cytoplasm
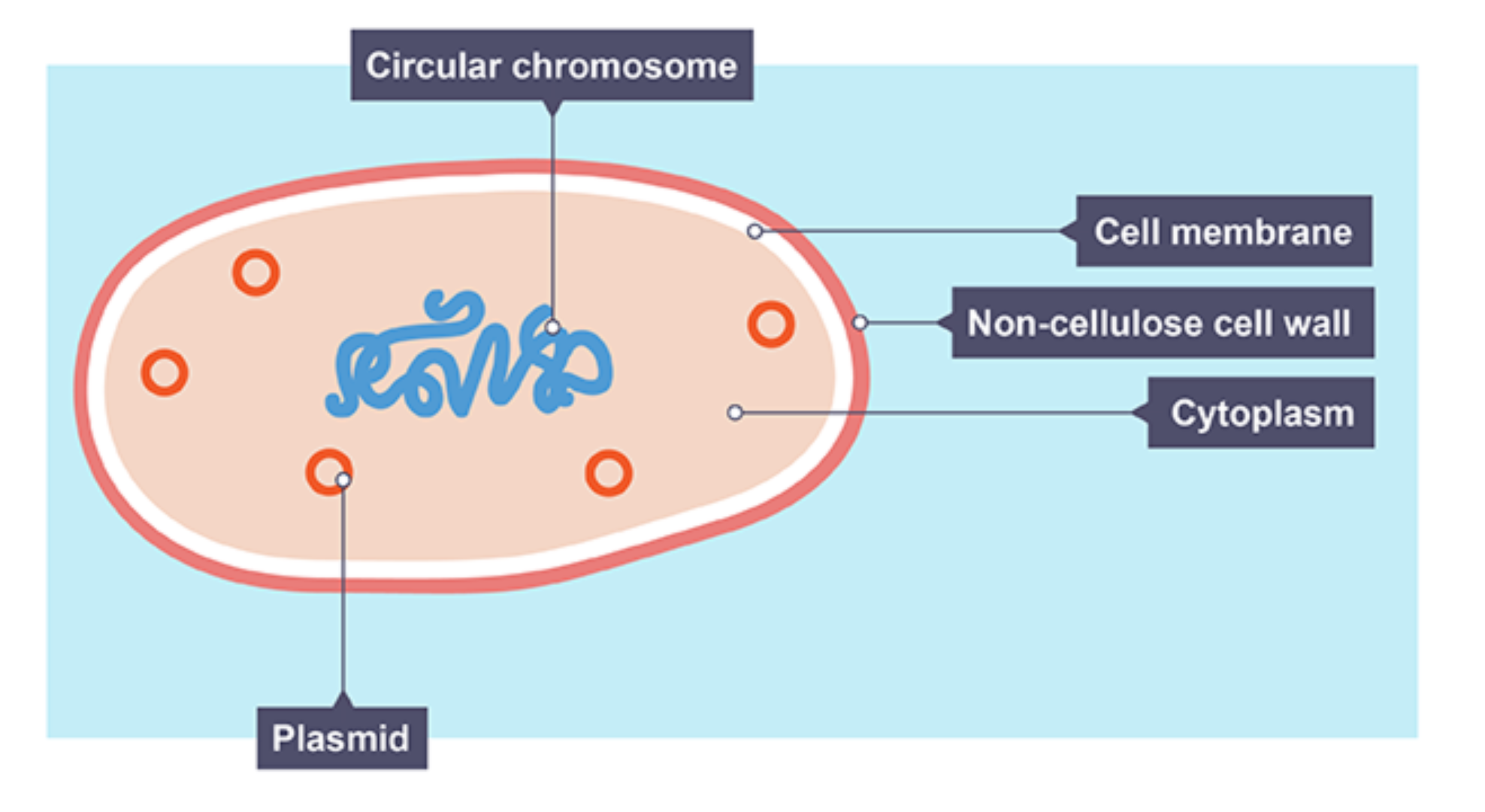
Bacterial cell
has cell wall, cell membrane, flagella (tail), but no nucleus as genetic material is free within cytoplasm/ plasmids
Cell membrane
Controls the entry of substances into and outside of the cell
How is the cell membrane adapted?
selectively permeable, only allowing some substances in and out
Nucleus
Control centre of cell which contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes
Cytoplasm
contains organelles and is where chemical reactions take place
Ribsomes
responsible for synthesising proteins
Mitochondria
Where cellular respiration takes place, abundant in cells requiring energy
Permanent vacuole
filled with cell sap and pushes cell membrane to provide support
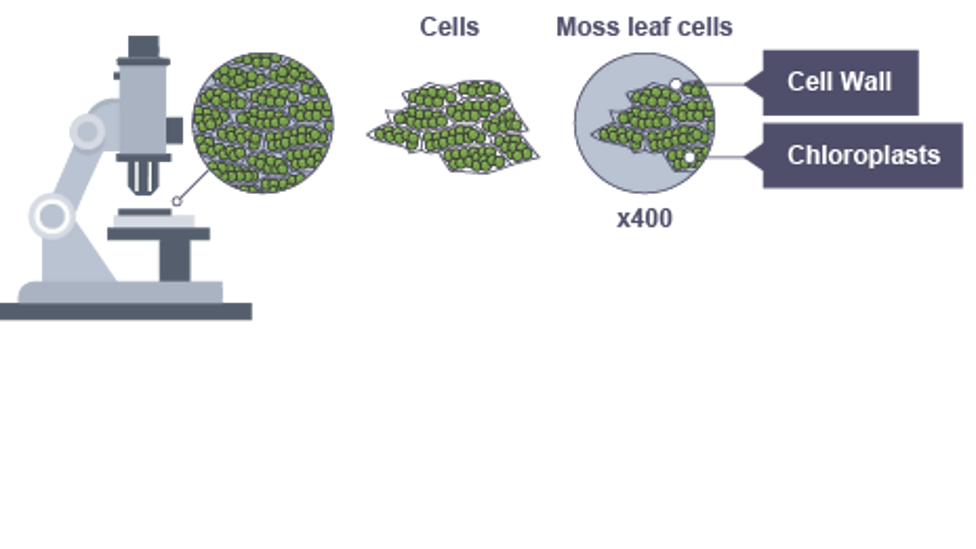
Cell wall
rigid outside structure which strengthens and supports cell
Material of cell wall
plant cells are cellulose while bacterial are non-cellulose
Plasmids
Small circular rings of DNA in cytoplasm
Chloroplasts
Contains chlorophyll and is where photosynthesis takes place
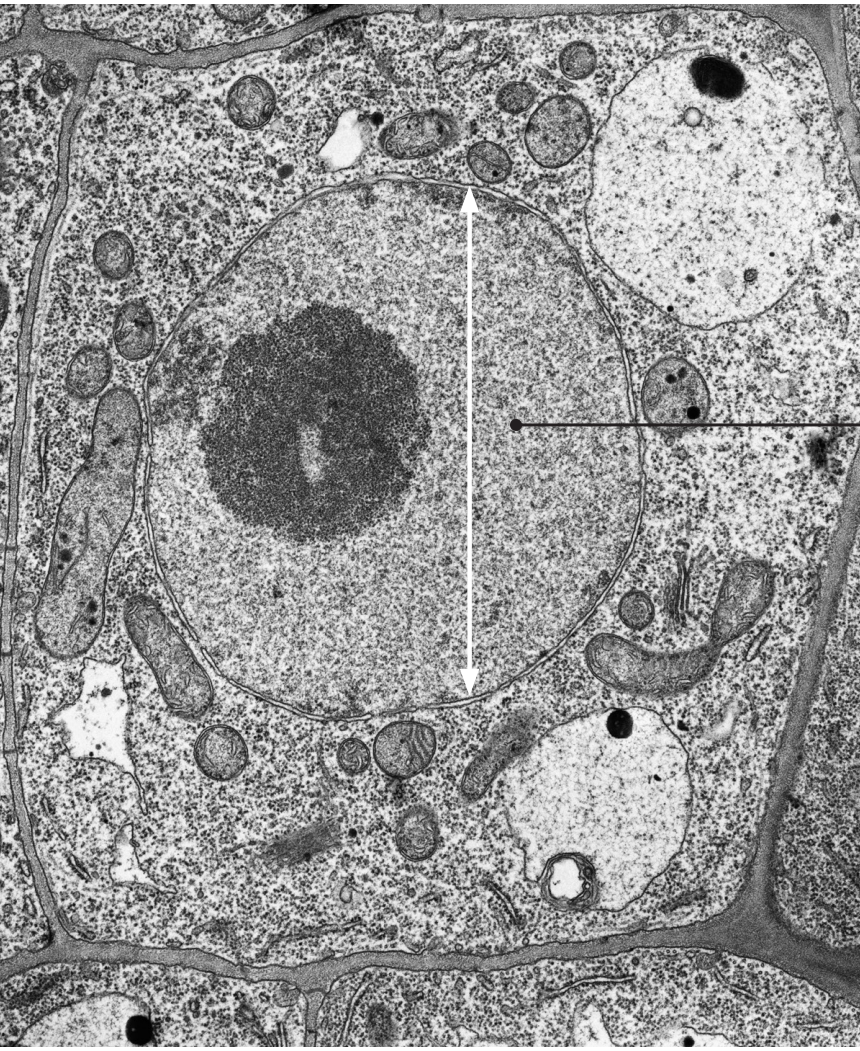
Why are there no chloroplasts visible in this photograph
root hair cell, which contains no chloroplasts
Chlorophyll
green pigment in the chloroplast which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
What is used to make chlorophyll?
magnesium ions
DNA loop
single molecule of DNA free in cytoplasm
Flagella
long whip-like filament to aid movement
Stem cell
undifferentiated cell which can divide to form cells of the same type and differentiate
What happens to stem cells when the are transported into the body?
they divide and differentiate into new white blood cells
Pre-treatments of stem cells
chemotherapy or radiotherapy
kills cancer cells
may kill some healthy cells e.g white blood cells
reduces immunity so more susceptible to infection
side effects e.g forming tumours
Differentiated
change to specialise a specific function
Embryonic stem cells
can become any type of cell, found in umbilical cord
Bone marrow stem cells
can become a limited range of cells (blood cells)
Meristem
where mitosis occurs and source of stem cells in apices
Apices
A term used to describe the tips of shoots or roots
How are plant stem cells useful
adult plant stem cells retain ability to differentiate to any type of cell
useful for cloning techniques, helping to protect rare species from extinction
modified disease resistance crops
Uses of stem cells
produce insulin cells for diabetes
treat paralysis from spinal cord injuries
Therapeutic cloning
embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient
General issues of stem cells
Lead to formation of tumours or unwanted cell types
Pre-treatments (chemo/radiotherapy) involves risky procedures
possible transfer of spreadable viruses or diseases
anti-rejection drugs must be taken
left vulnerable to other illnesses
ethical or religious objections
Advantages of bone marrow stem cells
treat leukaemia
less ethical concerns than embryonic
easier to obtain
Disadvantages of bone marrow stem cells
requires voluntary donors
extraction can cause pain and requires consent
may have a risk of infection or rejection
can only form cells such as blood cells
Advantages of embryonic stem cells
No consent required
obtainable via discarded embryos in IVF
can be used to make any type of cell
less risk of rejection if using therapeutic cloning
Disadvantages of embryonic stem cells
potential loss of life or harm to embryo
less easily obtained
risk of rejection
moral or ethical objections
Cell
basic building block of all living organisms
Cells adapted to their function
nerve cell- long fibre to carry signals across large distances
sperm cell- tail to move them towards egg cell
red blood cell- no nucleus to provide space for haemoglobin
root hair cell- long thin extension to increase surface area for absorption
Tissue
group of cells with similar structure and function working together
Organ
Collections of tissues performing specific functions
Organ system
group of organs which work together to form organisms
Organism
living thing such as a plant, animal or single-celled life form
Single celled
all life process carried out by one cell
Multicellular
made of multiple cells that differentiate to perform specific functions
Need for transport systems
larger cells are unable to directly obtain substances
Transport system
used for transporting substances around multicellular living organism
Surface area
total area of the surface of an object
Surface area to volume ratio
amount of surface area in relation to how large and object is
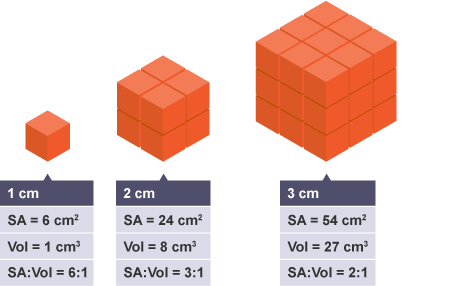
Large surface area to volume ratio
faster diffusion rates, as more room to diffuse through membrane
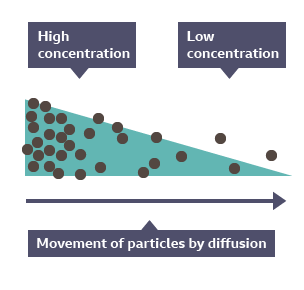
Diffusion
random movement of substances from an area of high concentration to a low e.g gas exchange
Adapted for exchanging materials
Small intestine- ciliated epithelial cells
lungs- alveoli
plant roots/ leaves- root hair cells
Passive process
Substances cross membrane without energy input from the cell
Net movement
overall movement of particles in diffusion
Concentration gradient
difference in concentration of a substance, a steeper gradient has faster diffusion
effect of temperature on diffusion
provide the particles with more kinetic energy, causing them to move, speeding up diffusion