34: Estuaries
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
benefits of the sea
supporting, regulating, cultural, provisioning
sea covers ___% of earth
70
sea provides __% of space for life on earth
98
majority of sea is
deep sea (>200m)
marine biodiversity has the ______ 'phylogenetic' level
greatest
there are ____ animal phyla in marine systems
>30
how many freshwater/terrestrial phyla are there?
11-14
how many phyla are found only in marine ecosystems?
15
there are an estimated 600,000 to ___ million species associated with tropical coral reefs
9 million
ecosystem functioning
how nature provides clean water, air, food etc.
biodiversity relates to ecosystem functioning and thus provides
clean water, air, food etc
loss of predator species, not intermediate consumers, triggers rapid and dramatic
extinction cascades
what enables marine communities to resist warming?
herbivory
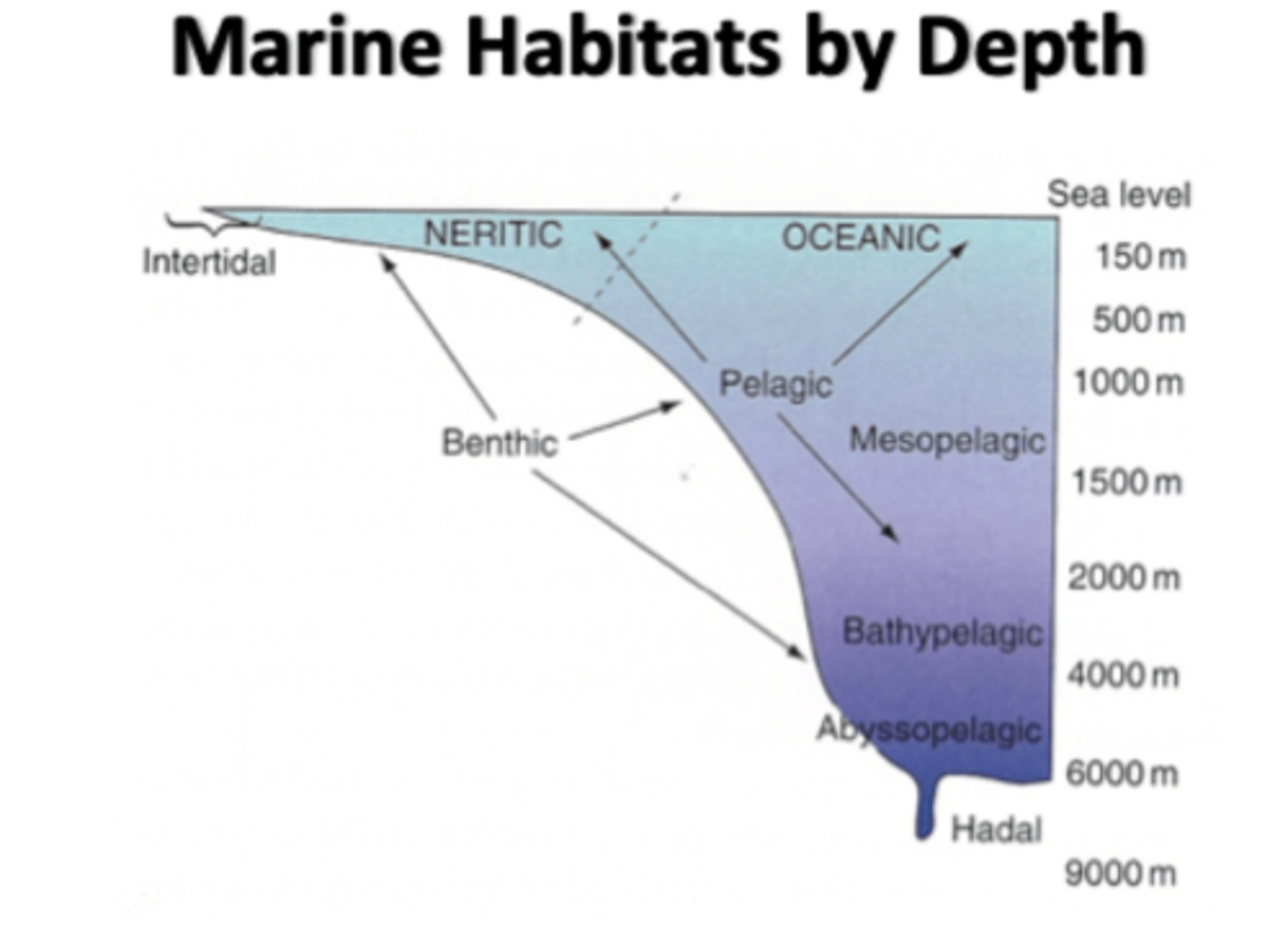
marine habitats by depth
estuary
where rivers meet the sea
how to define an estuary
difficult - usually based on salinity
topographical classification of estuaries
- coastal plains with eustatic sea level rise or fjords
- offshore deposits can cause barriers across bays or inlets
- isostatic variation driven by tectonic activity
large estuaries tend to have _____ tidal ranges
large
1 multiple choice option
estuaries can be defined by
salinity, topography, tidal range
tidal range classifications
microtidal (<2m)
mesotidal (2-4m)
macrotidal (4-6m)
hypertidal (>6m)
tidal prism
difference between volume of water when tide is in and ot
tidal range moderates the variability of
extreme environments
tidal range can be altered by
urbanisation
tidal range is a source of
renewable energy
what key environmental factors influence organisms in estuaries?
- salinity
- sediment
- dissolved oxygen
- temperature
which is not a key environmental factor influencing organisms in estuaries?
light
3 multiple choice options
salinity is measured using
dimensionless measure: practical salinity unit
salinity ______ along an estuary, dramatically in ___-estuary
varies, mid
________ salinity profiles are used to classify estuaries
vertical
intertidal mudflats
river sediment
- soft fine silt, difficult to walk in
- rich in organic material
- high secondary production
- deposit feeders can thrive
temperature _______ vary with tidal cycles
doesn't
1 multiple choice option
zones within estuaries
1: head
2: upper reaches
3: middle reaches
4: lower reaches
5: mouth
estuarine organisms
fish, chironomids, nematodes, crustaceans, bivalves, amphipods, diatoms, green algae
plants ____ common in estuaries
aren't (only seagrass)
are estuaries important habitats for birds
yes
bioturbators
organisms that move/mix sediment while burrowing or feeding