Unit 1 Part 2: Sleep and Sensation
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 2 of Unit 1 (Biological Bases of Behavior) sleep and sensation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and the environment
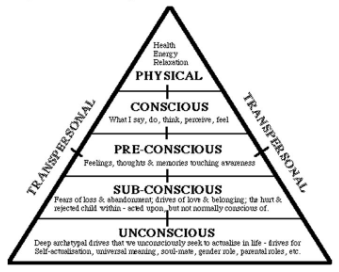
levels of consiousness
unconscious- deep drives that we unconsciously seek to actualize
subconscious- not currently of focal awareness, things we act upon but are not conscious of
preconscious- feelings, thoughts, and memories touching awareness
conscious- what we think, say, do, perceive, feel consciously
physical- health, energy, relaxation
circadian rhythm
24 hour sleep wake cycle

types of brain waves
alpha, theta, delta, beta
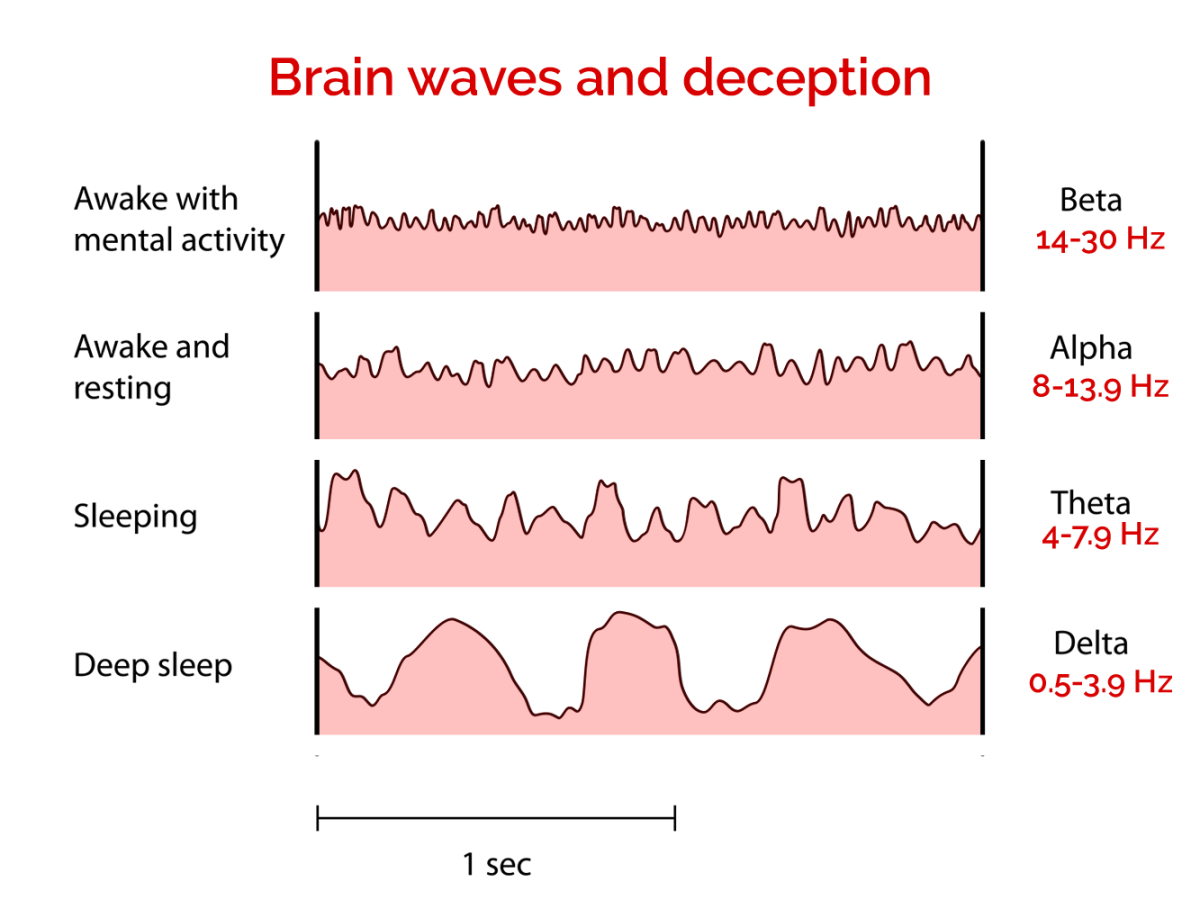
when are alpha waves produced?
NREM 1 and when zoning out
When are theta waves produced?
NREM 2
When are delta waves produced?
NREM 3
When are beta waves produced?
REM and when awake
stage NREM 1
the lightest stage of sleep, where a person can be easily awakened and may experience drifting thoughts
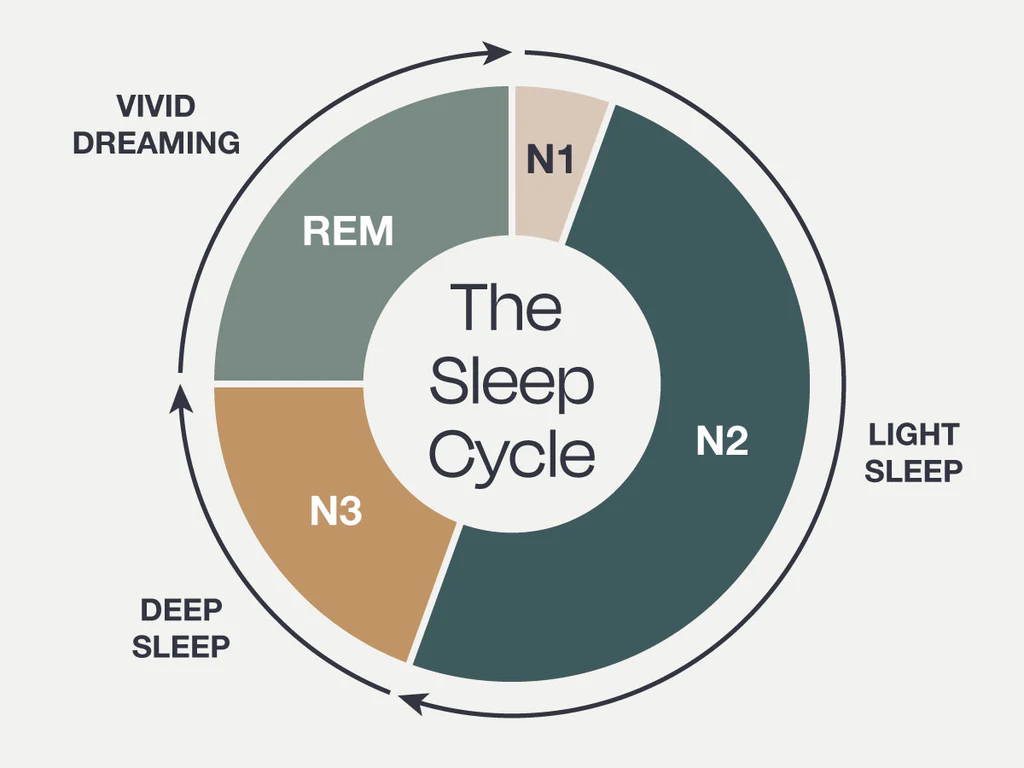
stage NREM 2
a period of light sleep where sleep spindles occur, typically lasting about 20 minutes
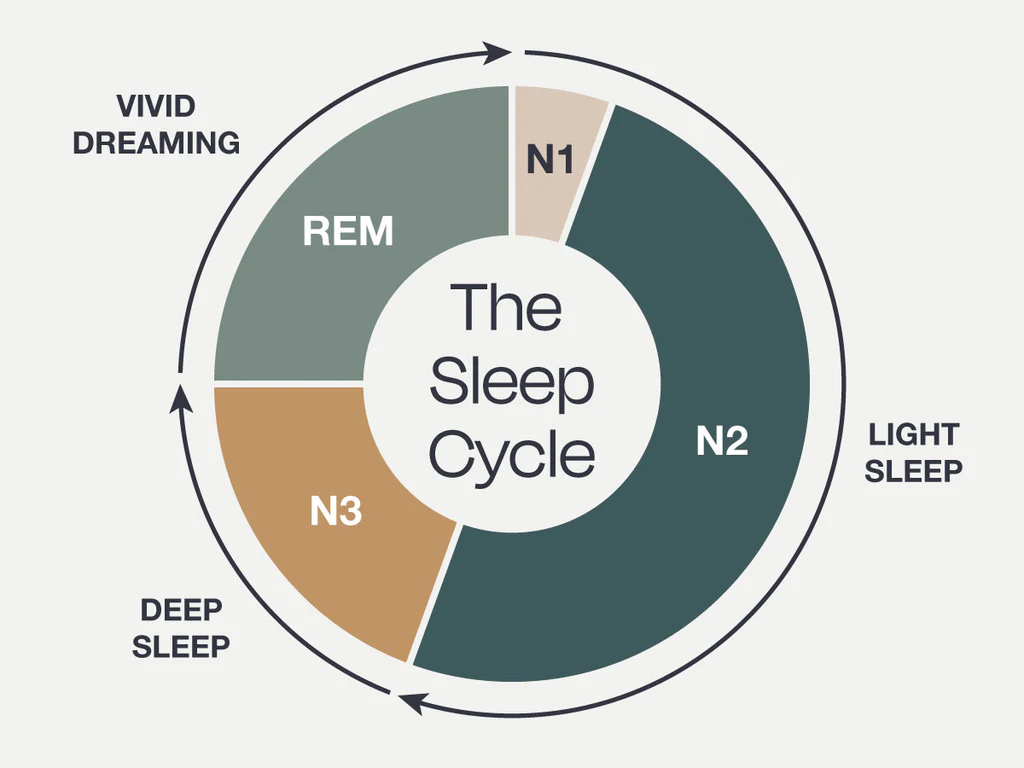
stage NREM 3
the deepest stage of sleep, characterized by slow brain waves and difficulty waking
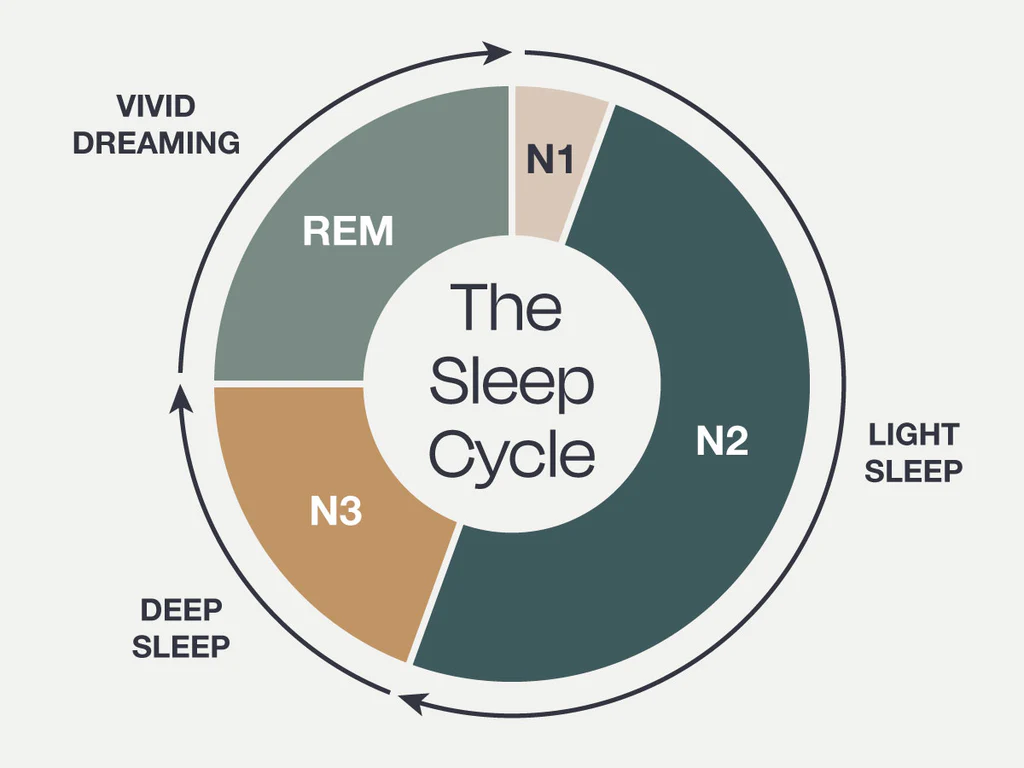
REM
a stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movement, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming often referred to as paradoxical sleep due to the brain's activity resembling that of wakefulness
your muscles are paralyzed
REM rebound
the phenomenon where a person experiences increased REM sleep following a period of sleep deprivation resulting in more intense dreams and longer REM periods
happens after sleep deprivation, body’s way of trying to catch up on REM sleep
restoration or resources
sleep helps your body repair itself and restore resources you used during the day
activation synthesis
dreams are the cerebral cortex's attempt to make sense of random neural activity during sleep
consolidation theory of dreams
the idea that dreams play a role in processing and consolidating memories from the day
move memories from short to long term
REM sleep behavior disorder
a condition in which individuals act out their dreams during REM sleep, often resulting in disrupted sleep and potential injury
shift work
a work schedule that differs from the traditional 9-to-5 hours, often leading to sleep disturbances and circadian rhythm disruptions
sleep apnea
a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue
somnambulism
sleepwalking
night terrors
episodes of intense fear and panic during sleep, often accompanied by screaming or thrashing, typically occurring in children
jet lag
a temporary sleep disorder resulting from traveling across multiple time zones, causing fatigue and disorientation
hypnogogic sensations
vivid hallucinations occurring while falling asleep, often involving sensations of falling or floating
insomnia
a condition characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, leading to daytime fatigue and impaired functioning
memory consolidation
the process by which short-term memories are transformed into long-term memories during sleep
narcolopsy
a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks
sensation
the process by which sensory receptors and nervous systems receive and interpret stimuli from the environment
sensory deprivation
reduced sensitivity to a constant stimulus over time
transduction
the process of converting sensory stimuli into electrical signals
absolute thresholds
the minimum amount of stimulation that is detectable by an individual 50% of the time
accomodation
the ability of the eyes to focus on objects that are near or far
afterimages
an image that continues to appear in the eyes after a period of exposure to the original image
blind spot
where the optic nerve connects to the retina, no photoreceptors
amplitude
a measurement of the vertical distance of the wave from the average
cones
require more light, see color and detail, red green and blue
ganglion cells
specialized neurons located in the retina at the back of the eye
just-noticeable difference (JND)
the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticable
lens
clear, curved structures at the front of the eye behind the pupil; focuses light rays that enter the eye
opponent-process theory
the theory that opposing retinal processes enable color vision; for example, some cells are enabled by red and inhibited by green, and vice versa; red is activated so green is suppressed, vice versa
photoreceptors
specialized cells in the retina that detect light (rods and cones)
retina
converts light into electrical signals the brain can read
rods
work in dim light, peripheral vision, black and white
trichromatic theory
explains color vision based on three types of cones (r, g, b); they combine to create all colors
optic nerve
sends visual information to the brain
wavelength
distance between two consecutive peaks on a wave
Weber’s Law
the principle stating that the minimum difference in stimulation needed to detect a difference is proportional to the original stimulus intensity
farsightedness
distant objects are seen clearly, nearby objects are blurry
nearsightedness
nearby objects are clear, distant objects are blurry
blindsight
ability of blind people to respond to visual stimuli
monohromatism
can only see black/white
dichromatism
can only see two colors
propagnosia
“face blindness” faces can’t be recognized, even though vision and cognition are fine
synesthesia
stimulation of one sense leads to automatic experience of another sense
pitch
how high/low a sound is
middle ear
between the eardrum and chochlea
cochlea
converts sound vibrations into electrical signals
loudness
the intensity or volume of a sound (determined by amplitude)
eardrum
thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves hit it
sensorineural deafness
hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve
conduction deafness
caused by problems in the outer or middle ear mechanisms
place theory
different frequencies of sound stimulate different locations on the cochlea’s basilar membrane
frequency theory
the rate at which the basilar membrane vibrates matches the frequency of the sound; nerve fires more when frequency is higher
vestibular sense
detects balance and spatial orientation using inner ear structures
volley theory
suggests that groups of neurons fire in a volley, as individual neurons can’t fire fast enough
olfactory system
sense of smell
warm/cold receptors
thermoreceptors that sense hot and cold
gate-control theory
non-painful input closes the nerve "gates" to painful input, which prevents pain sensation from traveling to the central nervous system.
nociceptors
pain receptors
phantom limb
a condition in which patients experience sensations in a limb that does not exist.
pitch perception
perceiving and differentiating between high and low pitches
semicircular canals
a structure in the inner ear that contains equilibrium receptors that respond to movement of the head and keep you balanced
gustation
sense of taste
nontasters
taste less flavor in foods
medium tasters
have a regular sense of taste
supertasters
people who are particularly sensitive to tastes
taste receptors
cell receptors on your tongue that recognize the 6 different tastes
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami, oleogustus
the six tastes out taste receptors recognize
(umami=savory/meat, oleogustus=fat)
kinesthesia
the ability to sense motion and sense your location in a space
pheromones
a chemical substance produced and released into the environment by an animal, especially a mammal or an insect, affecting the behavior or physiology of others of its species
Acts like a satellite dish or concert shell to help focus the signal into the ear hole
ear vibrations are carried to it from the ear canal
snail shell shaped
filled with fluid
The stirrup/stapes bangs against the oval window, that sets up a wave in the fluid inside the cochlea
When a wave of cochlear fluid crashes on a place of the organ of corti, cilia are stimulated
A nerve cell attached to the root of the cilia sends a signal to the brain
The brain knows that if certain cilia are stimulated, it should interpret that as different pitch
explains high pitch well
Highest frequency 20,000 Hz
ppl turn to u when u call them
Vibrations are not making it to the cochlea maybe there is swelling, blockage, damage
can be treated with medicine, maybe even surgery
maybe its from inherited disease, over use of loud noises, regular long use of normal noises,
Can be treated with hearing aid or cochlea implants
Your lens should focus the images to pinpoint clarity onto the center of your retina (fovea)