Symmetry & skewness
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Symmetry & skewness
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Symmetrical distribution
it is symmetrical if it can be divided into two equal sizes of the same shape
Skewed distribution
contrast of what symmetrical distribution is, thus refers to asymmetry
The distributions can be skewed to the left or skewed to the right
we read skewness based on the direction of which the datapoints cluster
Distribution skewed to the left
long tail that trails towards the left
Distribution skewed to the right
long tail that trails towards the right side
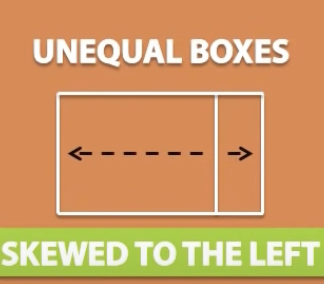
The skew in a box-plot
the side of the box that is larger determines the skew
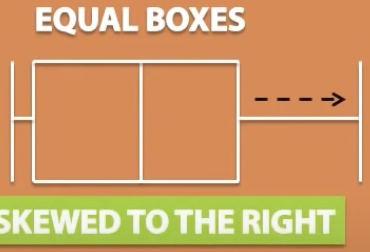
The skew in a box which is equal in size
we will have to look at the whiskers to determine the skew
the longer whisker will determine the skew
Finding the skew, if the boxes are equal and the same whisker length
the distribution is set to be symmetrical
symmetrical distribution & median
The plane of symmetry will always be at the median, because the median is the middle point of the data
symmetrical distribution & mean
the mean is the balance point of a distribution
the mean is equal to the value of the median in symmetrical distribution
Skewed distribution & median
if it is skewed to the left, the mean is less than the median (the mean will be closer to the left side of distribution, and the median will be closer to the right side of distribution)
if it is skewed to the right, the mean is greater than the median (the mean is closer to the right side of distribution, & the median will be closer to the left side of distribution)