Apologia Advanced Biology Module 10 Endocrine System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Endocrine System
Consists of hormone glands or hormonal cells that secrete hormones into the blood in order to regulate the body for homeostasis. Its goal is to regulate the body. It affects the body chemically, therefore slowly, the effects last long, they control all the cells in the body that have receptors to the specific chemicals, the strength of the signal varies, and can repair itself if damaged.
Nervous System
Regulates the body for homeostasis. The response is fast, the duration of influence is sudden and brief, controls the muscles and glads, its signal strength is fixed by the rate of the action potential and cannot be repaired if damaged.
Receptors
Are proteins made by target cells that bind to specific hormones which can then cause profound changes
Carrier protien
A kind of transport protein that can change shape to move material from one side to another, they bond and drag molecules through the membrane to the other side
Endocrine gland
Makes, stores, and secretes hormones
Neurosecretory cells
Neurons of the hypothalamus that secrete neurohormone rather than neurotransmitter
Prostaglandins
Biologically active lipids that produce many effects in the body including smooth muscle contraction, inflammation, and blood clotting.
Hypothalamus
A portion of the forebrain that controls homeostatic and endocrine functions by controlling the release of pituitary hormones.
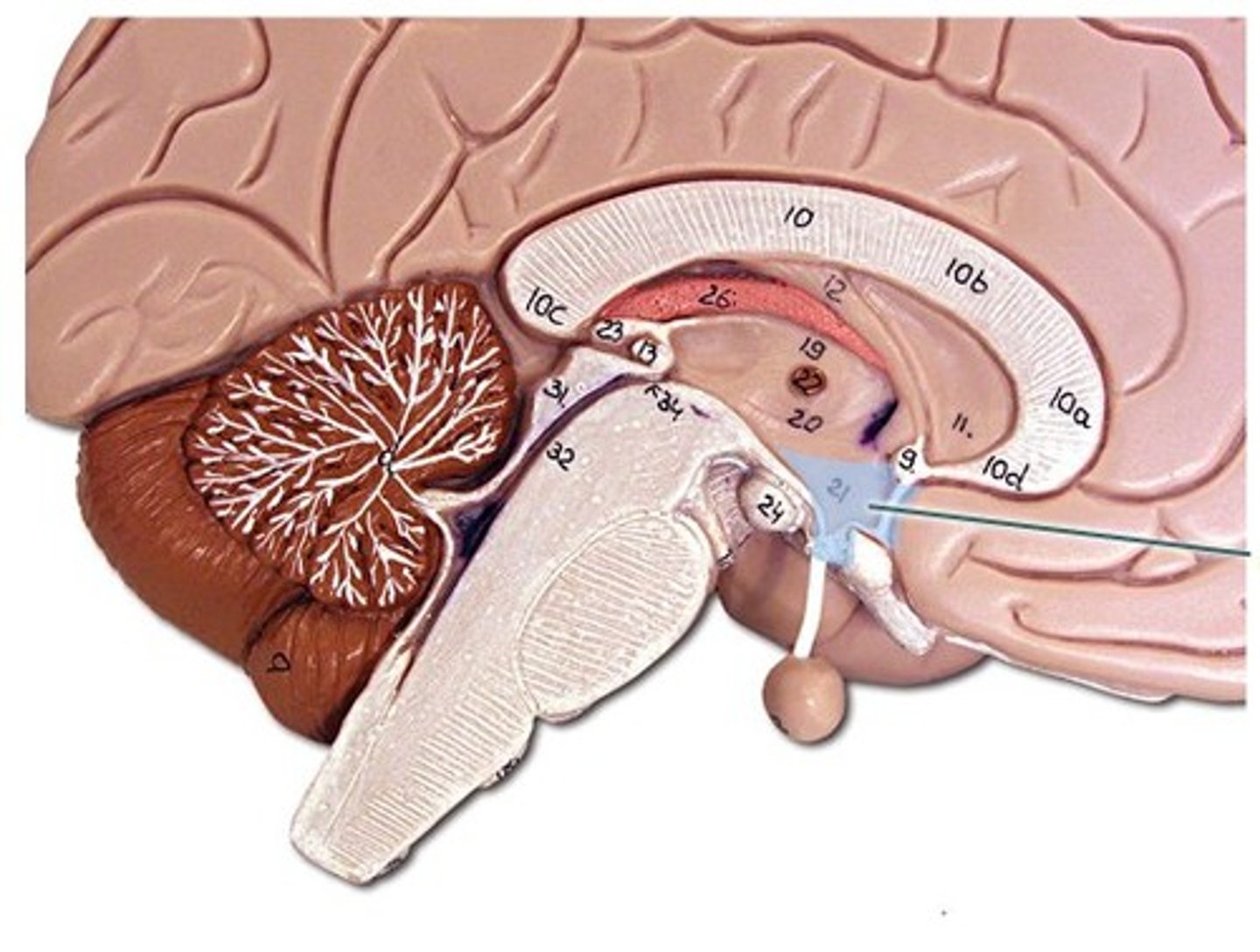
Anterior pituitary gland
The gland of the hypothalamus which secretes GH, TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH, PRL, MSH which in turn stimulate other endocrine glands.
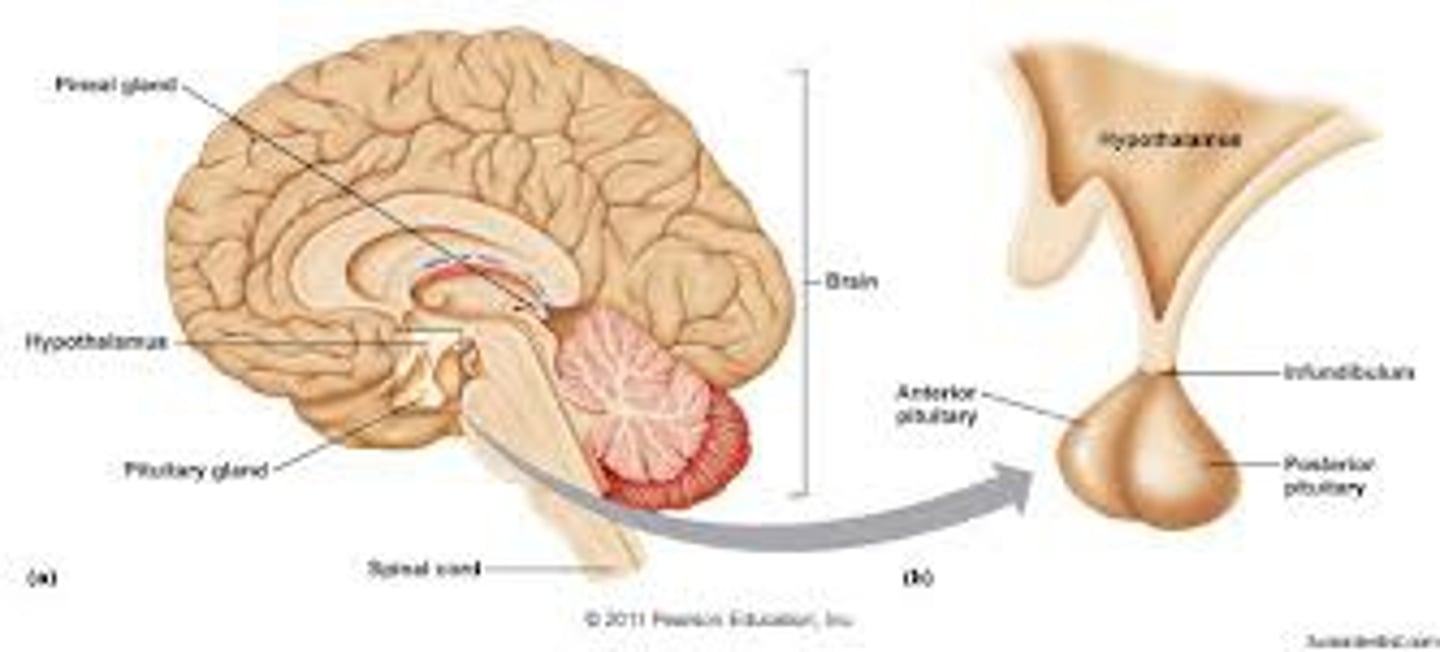
Posterior pituitary gland
This is made of nervous tisssue and stores and secretes two hormones made by the hypothlamus; oxtytocin and ADH. The posterior pituitary is controlled by action potentials from the hypothalamus.
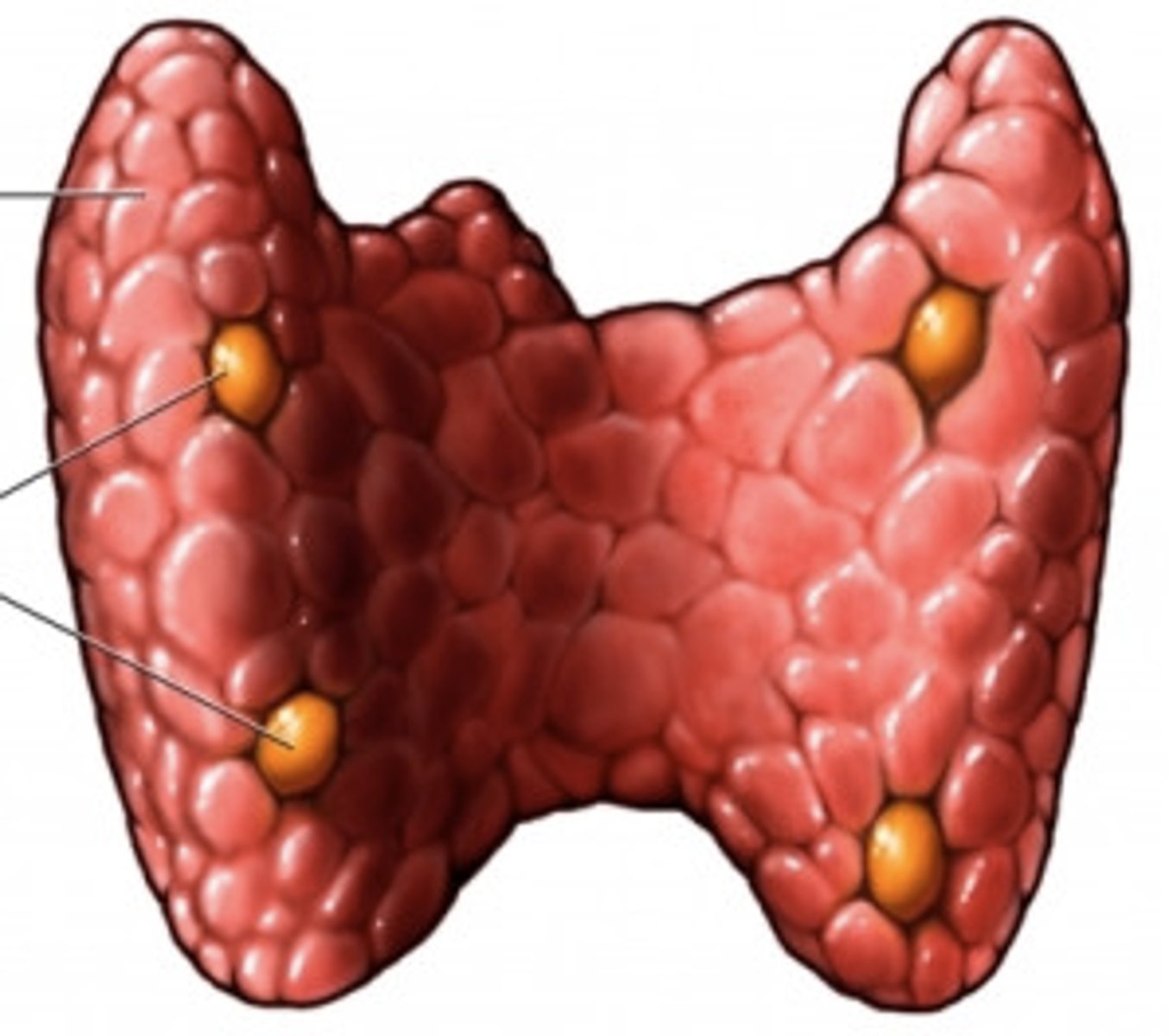
Thyroid
Secretes TH which INCREASES the metabolism/metabolic rate. It also secretes Calcitonin which LOWERS the blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclasts to break down bone.
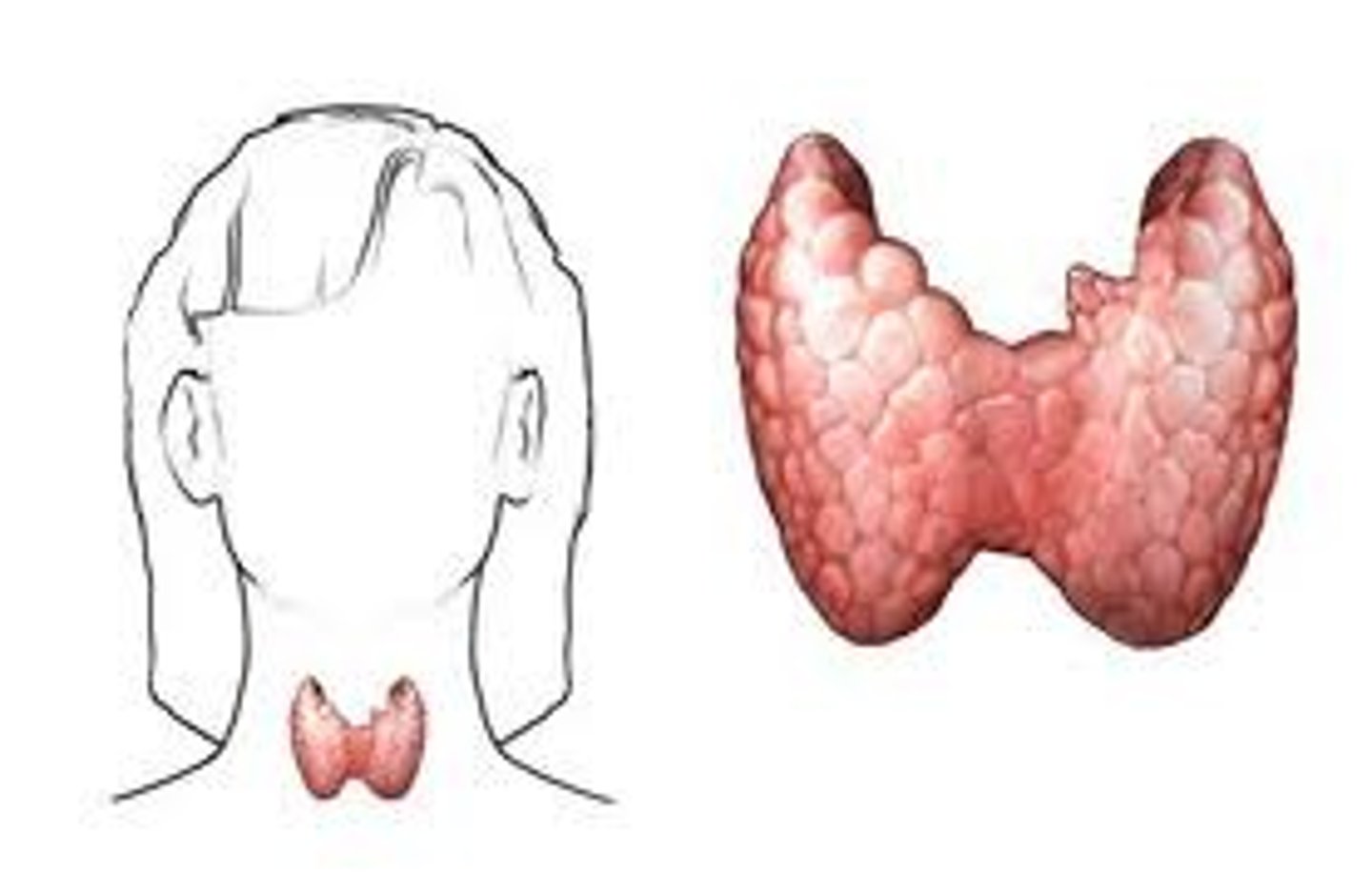
Parathyroid glands
Located at the edges of the ________ and secrete PTH which opposes Calcitronin. PTH stimulates osteoclasts activity, RAISING the blood calcium levels.
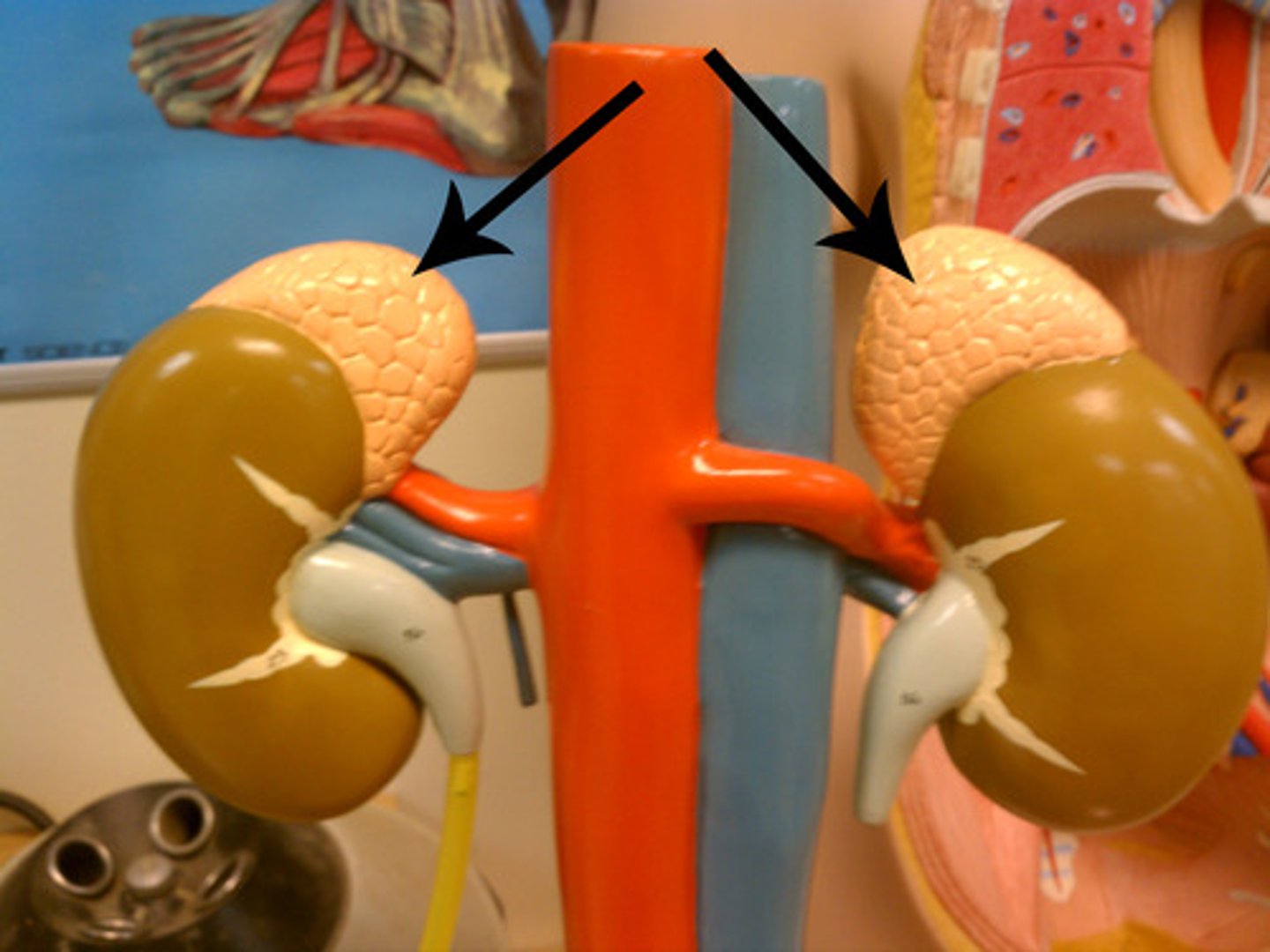
Adrenal glands
Two glands in one that sit near the top of each kidney.
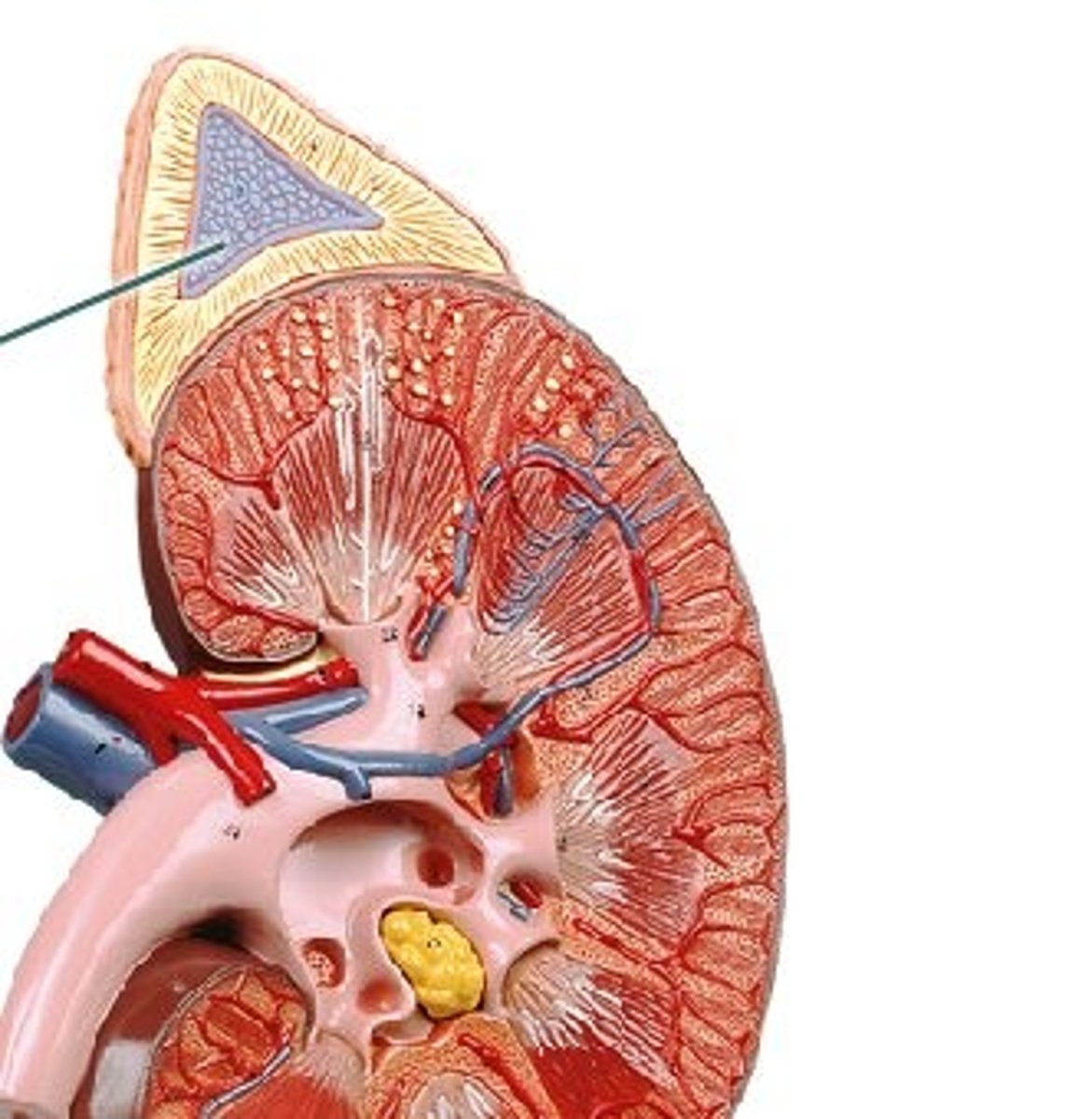
Adrenal Medulla
The inner region of the adrenal gland. The adrenal medulla is part of the sympathetic nervous system, and releases epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine into the blood when stimuated. These hormones augment and prolon the effects of sympathetic stimulation in the body.
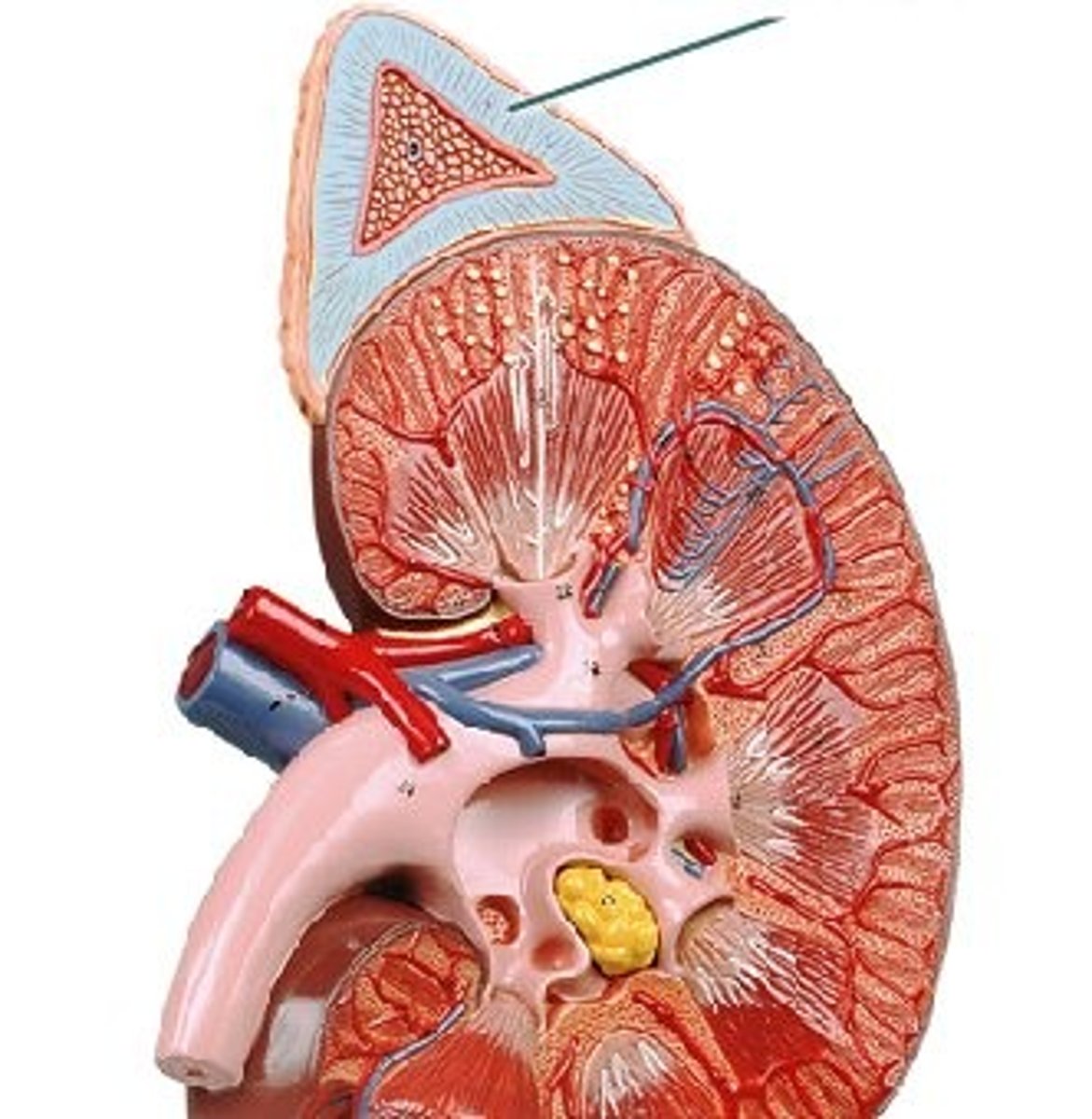
Adrenal Cortex
Produces about 50 hormones, including Cortisol and Aldosterone. Cortisol's main function is to increase the breakdown of protein and fats to support glucose to the brain during stress. Aldosterone stimulates the kidneys to retain sodium to cause the body to hold water.
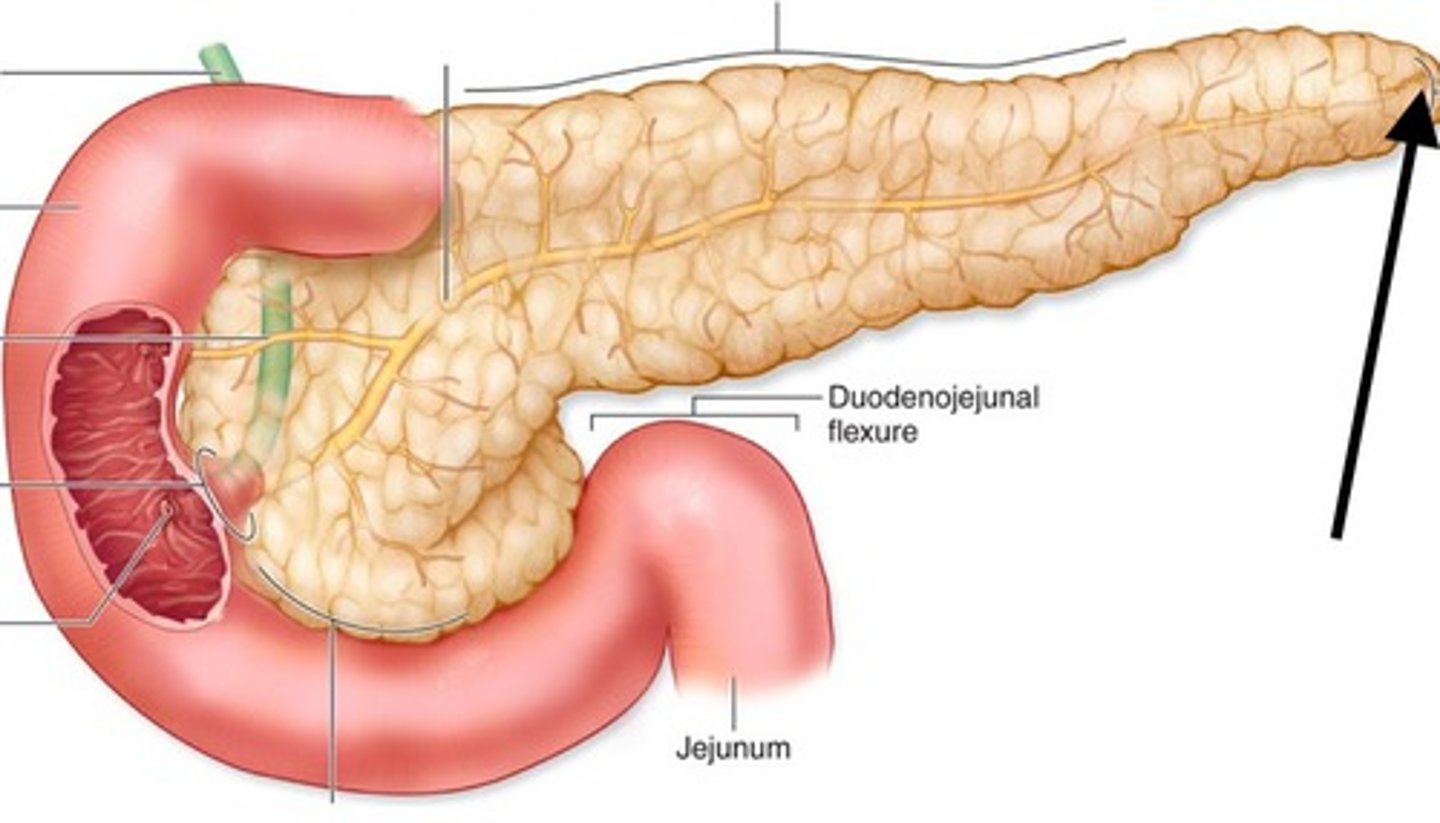
Pancreas
Produces Insulin to decrease the sugar level in the blood by stimulating cells to take in glucose from the blood. It produces Glucagon to increase the sugar level in the blood by causing the liver to release glucose into the blood.
Ovaries
Primary function is to secrete Estrogen and Progesterone. Estrogen controls the development of eggs and adult female characteristics. Progesterone maintains and enhances the uterine lining for the possible implantation of a fertilized ovum.
Testes
The primary function is to secrete Testosterone, the male hormone that stimulates the growth of genital and secondary sexual characteristics.
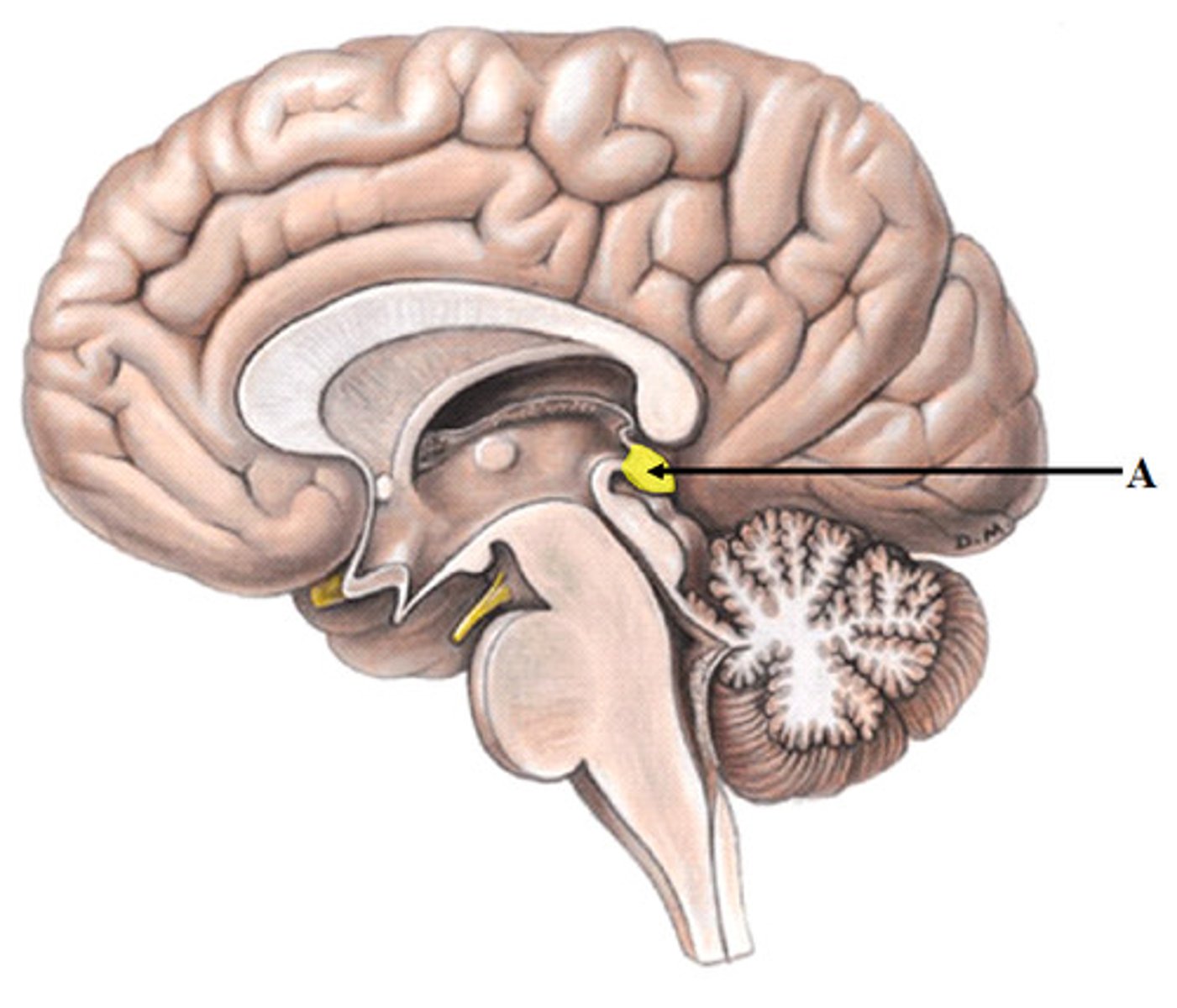
Pineal body
A structure found between the cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates and is considered an endocrine gland. Secretes melatonin. Plays a role in circadian rhythm - regulation of this. Sleep/wake cycles or night/day cycles.
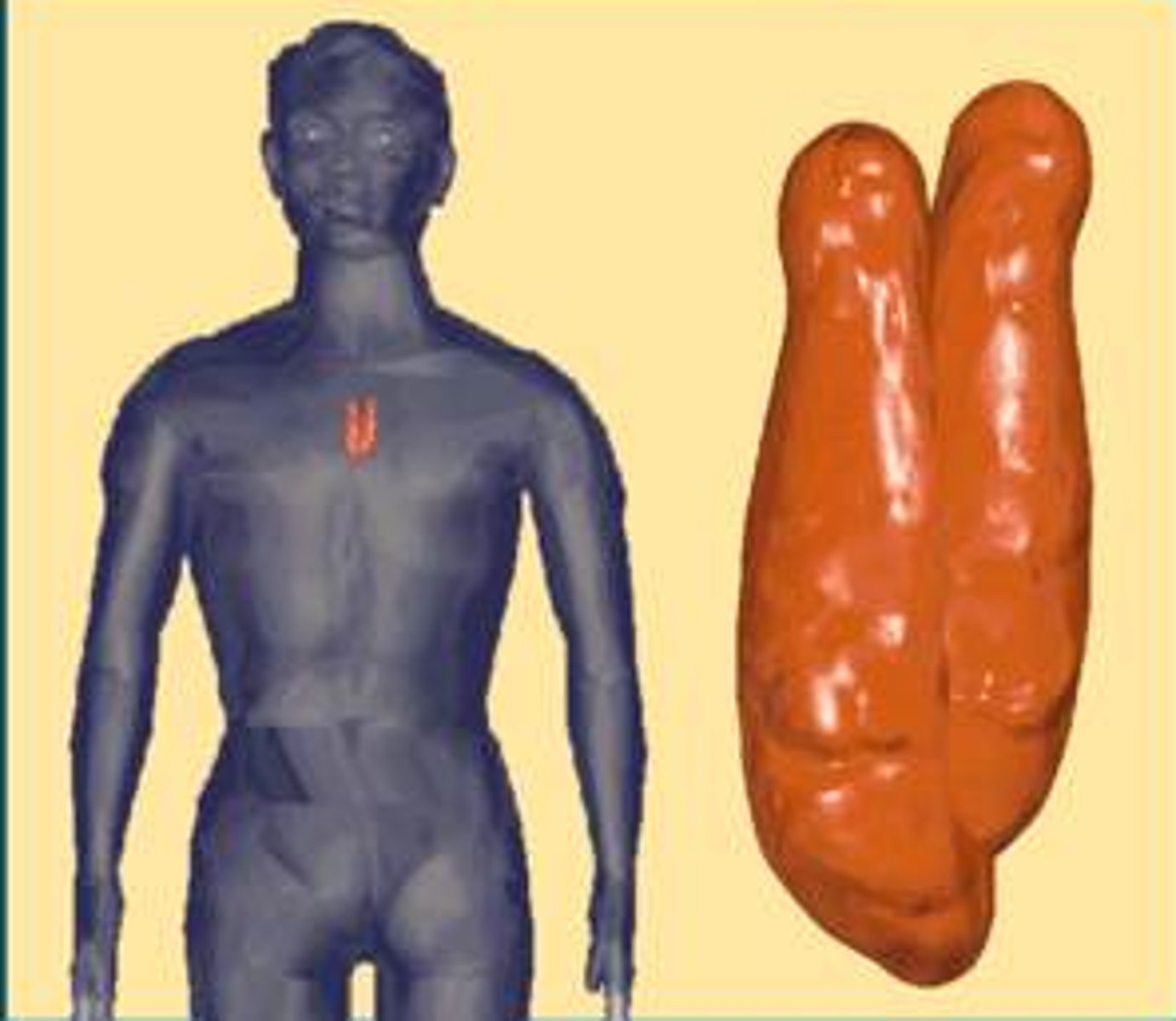
Thymus gland
Gland found in the thoracic cavity above the heart where T lymphocytes mature. It produces several hormones which stimulate development of cells important in immunity.
Hormone classification
- Amines: made from amino acid
- Steroids: made from cholesterol
- peptide/proteins: long/short chains of amino acids
Three ways the secretion of hormones is controlled
- Non-hormonal control (chemicals but not hormones)
- Direct neural control (nervous system controlled by neurotransmitters or neurohormones)
-hormonal control (actual hormones)
Hormone secretion patterns
- Constant (produced evenly)
- Cyclic (produced on a cycle)
- Acute (produced suddenly)
Hormone receptors
- Membrane-bound [found on the surface of the cell (works like a lock and key)]
- Nuclear receptors [(not on the surface) of the cell membrane. It can actually diffuse into the cell, travel through the cytoplasm and right into the nucleus. It activates a specific gene in the DNA. Helps the cell produce a new protein or enzyme that produces the response in the target cell.]