Unit 2 Level 75 Review
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Polarity of Water?
Water is a polar molecule
Cause of Water Polarity
Water is a polar molecule because it has a partial positive charge on one end (hydrogen) and a partial negative charge on the other end (oxygen).
Interact or Not: Water
Water molecules interact with one another
How does water molecules interact?
Water molecules interact through hydrogen bonding, where the partially positive hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the partially negative oxygen of another water molecule.
Emergent property of water
Cohesion
Cohesion Info
The property of water that allows water molecules to stick to each other, forming hydrogen bonds and creating surface tension.
Emergent property of water (2)
Adhesion
Adhesion Info
The property of water that allows it to stick to other substances, such as when water sticks to the walls of a plant's xylem vessels.
Emergent property of water (3)
High specific heat
High Specific Heat Info
Water has a high specific heat, meaning it can absorb and store a large amount of heat energy without a significant change in temperature.
Emergent property of water (4)
Neutrality
Water Neutrality
Neither Acidic or Basic
Emergent property of water (5)
Low Density as Solid
Density of Water Info
Water expands when it freezes, which is unusual for most substances. This expansion creates less dense ice, allowing it to float on water bodies.
Emergent property of water (6)
Versatility as a solvent
Versatility as Solvent Info
Water is a versatile solvent, meaning it can dissolve a wide range of solutes due to its polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds.
Endothermic reaction
Is a chemical reaction that absorbs heat energy from its surroundings, resulting in a decrease in temperature. (Anabolic)
Exothermic reaction
Is a chemical reaction that releases heat energy to its surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature. (Catabolic)
Anabolic reaction
Is a metabolic reaction that builds larger molecules from smaller molecules, requiring energy input.
Catabolic reaction
Is a metabolic reaction that breaks down larger molecules into smaller molecules, releasing energy.
Energy vs. time curves for anabolic and catabolic reactions
Anabolic reactions have energy vs. time curves that show an increase in energy as the reaction progresses, while catabolic reactions have energy vs. time curves that show a decrease in energy.
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur.
Catalyst
Is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy, without being consumed in the process.
Enzyme
Is a biological catalyst, usually a protein, that speeds up specific chemical reactions in living organisms.
Lock-and-key (induced fit) model
Describes how enzymes bind to their specific substrates, where the enzyme's active site (lock) undergoes a conformational change to fit the substrate (key) and facilitate the reaction.
Denaturation
Is the process in which proteins lose their structure and function due to extreme conditions such as high temperature or pH.
Dehydration synthesis
Is a chemical reaction that links monomers together by removing a water molecule, forming a covalent bond and creating a larger polymer.
Hydrolysis
Is a chemical reaction that breaks down polymers into monomers by adding a water molecule, breaking the covalent bond.
ATP
Is a high-energy molecule used by cells to store and release energy during cellular processes.
Phospholipid
A molecule composed of a hydrophilic head (phosphate group) and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains), forming the main component of cell membranes.
Hydrophobic
Repel or do not mix with water due to their nonpolar nature.
Hydrophilic
Are attracted to or mix well with water due to their polar nature.
Bilayer
Refers to the arrangement of phospholipids in a cell membrane, where two layers of phospholipids align with their hydrophobic tails facing inward and their hydrophilic heads facing outward.
Passive transport
Is the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy, driven by concentration gradients.
Simple diffusion
Is the passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, down their concentration gradient.
Facilitated diffusion
Is the passive movement of molecules across a cell membrane with the help of transport proteins, down their concentration gradient.
Osmosis
Is the passive movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane, from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
Active transport
Is the movement of substances across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring the use of energy (usually ATP).
Pumps
Are membrane proteins involved in active transport, using ATP to move ions or molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient.
Endocytosis
Is the process by which cells engulf external substances by forming a vesicle from the cell membrane and bringing the substances inside the cell.
Exocytosis
Is the process by which cells release internal substances by fusing a vesicle containing the substances with the cell membrane and expelling the contents outside the cell.
Carbohydrate (Functions)
Functions: Energy storage, structure (especially plants), cell communication
Protein (Functions)
Structure, movement, enzymes, transport,
some hormones, immune system, receptors
Lipid (Functions)
Functions: Energy storage, insulation/padding, hormones, cell membranes (phospholipids)
Nucleic Acid (Functions)
Function: Store and transmit genetic information
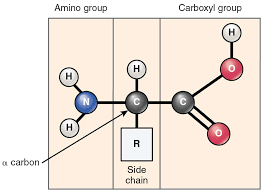
Protein (Structure)
Structure: Chains of amino acids
- Joined by peptide bonds Dipeptide Polypeptide
(Monomers Dimers Polymers)
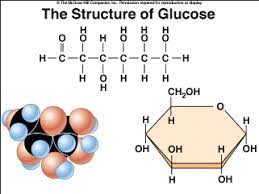
Carb (Structure)
monosaccharide disaccharide polysaccharide
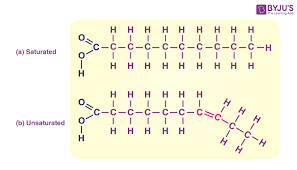
Lipids (Structure)
Triglycerides, Steroids
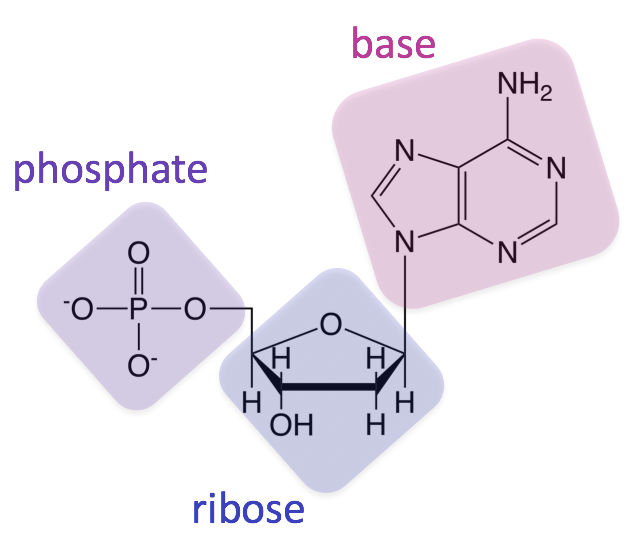
Nucleic Acid (Structure)
Structure: Phosphate and 5-C sugar (backbone); nitrogenous base
(A, T, C, and G)
How to know if something is water soluble?
It has to be polar (Contains N or O)
Lipid (monomers)
glycerol and fatty acids
Lipid (polymers)
diglycerides and triglyceride
Protein (polymers)
polypeptides
Protein (monomers)
amino acids
Carbohydrates (polymers)
polysaccharides and disaccharides
Carbohydrates (monomers)
monosaccharides
Nucleic Acids (polymers)
DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acids (monomers)
nucleotides
Carrier proteins
bind the specific solute to be transported and undergo a series of conformational changes to transfer the bound solute across the membrane
Channel Proteins
interact with the solute to be transported much more weakly
Glycolipid
Help with cell recognition
Glycoprotein
Help as receptors for chemical signals