Concepts of Auditing Lecture 1 Ch 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Independence
Includes two categories - independence of mind and independence of appearance
Independence of appearance
the avoidance of circumstances that would cause a reasonable and informed third party, having knowledge of all relevant information, including safeguards applied, to reasonably conclude that the integrity, objectively, or professional skepticism of a firm or a member of the attest engagement team has been compromised
Independence of mind
the state of mind that permits the performance of an attest service without being affected by influences that comprises professional judgment, thereby allowing an individual to act with integrity and exercises objectivity and professional skepticism
Material
The omission of an item in a financial report is material if, in light of surrounding circumstances, the magnitude of the item is such that it is probable that the judgment of a reasonable person relying on the report would have been changed or influenced by the inclusion or correction of the item
Types of Services
assurance service - The broad range of information
enhancement services that are provided by certified public
accountants (CPAs).attestation - increase the reliability of information
Other Assurance Services—Putting information into a form
or context that facilitates decision making.
Non assurance services
tax services
management consulting services
Attest
to bear witness to; certify; declare to be correct, true, or genuine;
declare the truth of, in words or writing, especially affirm in an official capacity
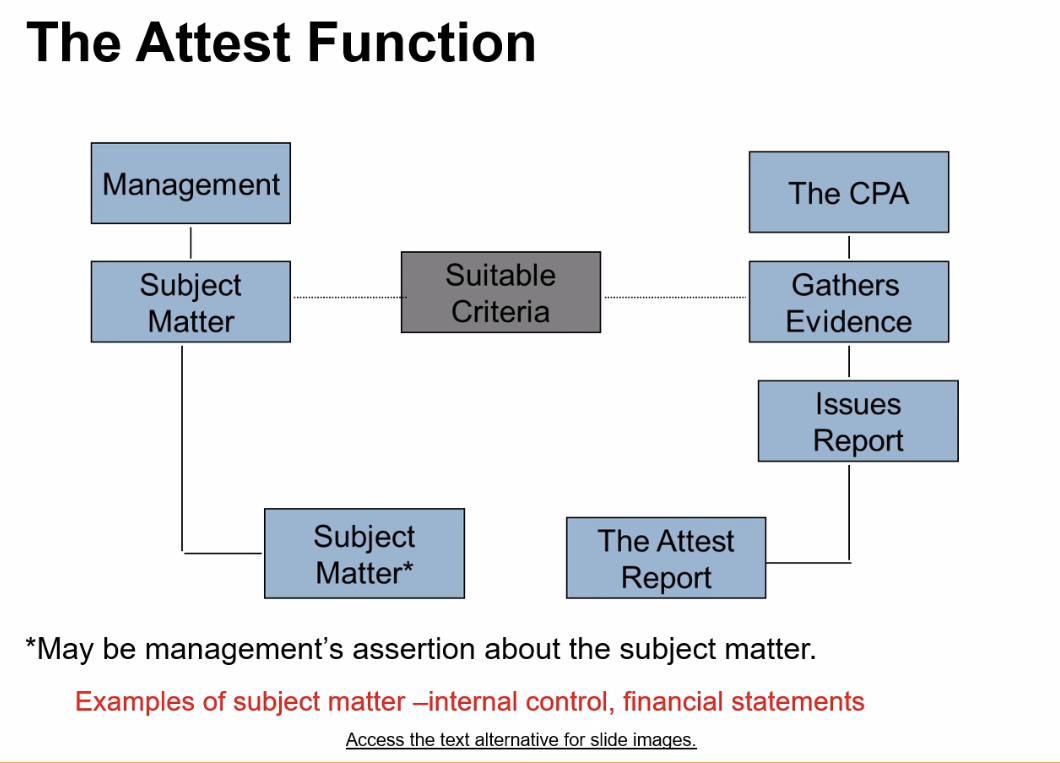
Attest Engagement
To attest to information means to provide assurance as to its
reliability.An examination, review, or agreed-upon procedures
engagement performed under the attestation standards related
to subject matter or an assertion that is the responsibility of
another party
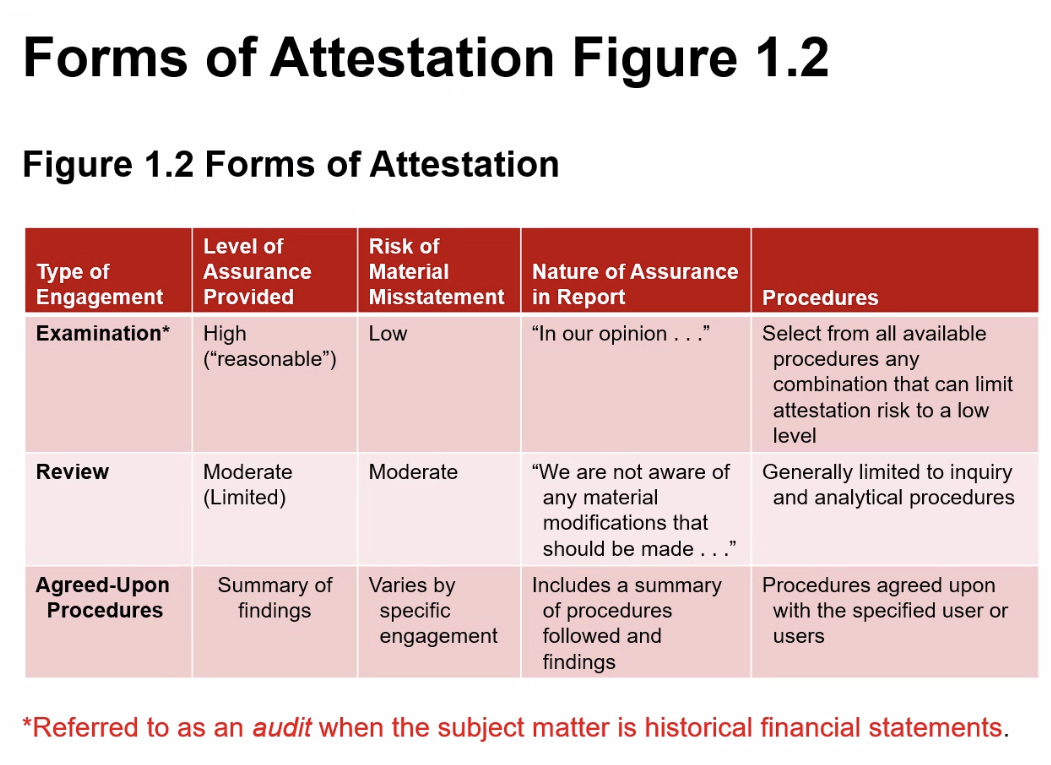
Forms of Attestation
The attest function
Suitable criteria
Standards established or developed by groups of experts.
Example: Internal control audit – standards established by
the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO)
framework.Example: Financial statement audit – for a financial
statement audit suitable criteria are referred to as the
“applicable financial reporting framework.” In the U.S. this
is typically Generally Accepted Accounting Standards.
Audit of Financial Statements
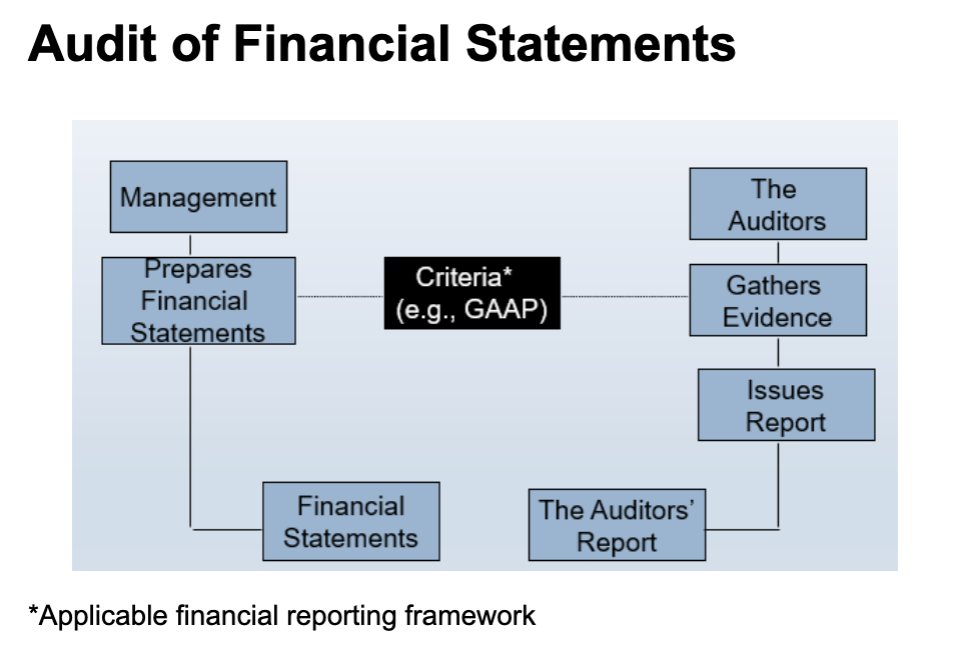
Financial Statement Audit
Auditors gather evidence and provide a high level of
assurance (referred to as reasonable assurance) that the
financial statements follow GAAP, or some other
appropriate accounting framework.Audit involves searching and verifying accounting records
and examining internal and external evidence.Sufficient evidence is gathered to issue an audit report that
states the auditors’ opinion.
Audit Evidence
Evidence focuses on whether financial statements are presented in
accordance with GAAP; examples:
Balance sheet.
All included assets and obligations exist.
Includes all assets and obligations.
Assets and obligations are properly valued.
Income statement.
Sales actually occurred.
Sales have been recorded at appropriate amounts.
Recorded costs and expenses are applicable to period.
All expenses have been recognized.
Financial statement amounts.
Accurate, properly classified and summarized.
Notes are informative and complete.
How an audit works
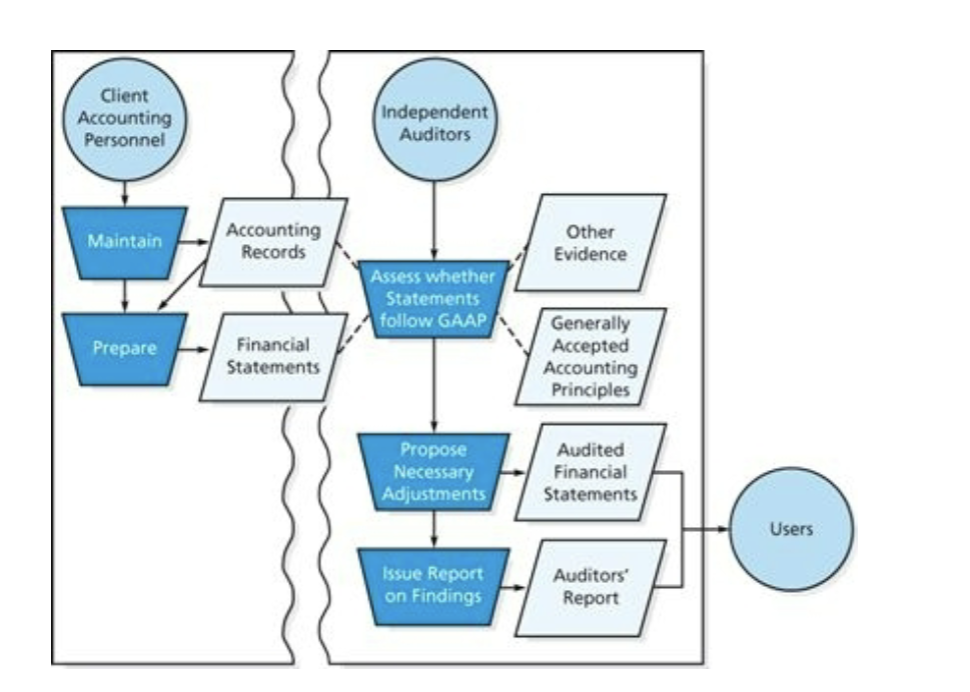
What creates the demand for audits?
Audits lend credibility to information by reducing information risk,
the risk that information is materially misstated.
Financial statement misstatements arise due to--
Accidental errors.
Lack of knowledge of accounting principles.
Unintentional bias.
Deliberate falsification (fraud).
Audits do not directly address business risk, the risk that a
company will not be able to meet its financial obligations due to
economic conditions or poor management decisions.
United States v. Arthur Young—Supreme Court described the
auditors’ role as being that of a public watchdog, requiring both
total independence and complete fidelity to public trust.
Other types of audits and auditors
Types of audtis
Compliance Audits.
Example: IRS audit of taxpayer’s return.
Operational Audits.
Example: Effectiveness of operations of receiving department of a manufacturing company.
Integrated Audits.
Example: Assurance on both the financial statements and
effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting.
Types of auditors
Internal Auditors.
Government Accountability Office Auditors.
Tax Auditors.
AICPA’s Traditional Role
Establish Standards.
Research and Publication.
Continuing Professional Education.
Self-Regulation.
Note: Much of the standards setting and regulation roles
relating to public companies (referred to as “issuers”) has
been taken over by the SEC and the PCAOB
Establishes Standards—Examples
AICPA Auditing Standards Board:
Issues official pronouncements on auditing and attestation
matters for nonpublic companies (“nonissuers”).Statements on Auditing Standards (SASs).
Statements on Standards for Attestation Engagements
(SSAEs), which provides guidance for attesting to information
other than financial statements such as financial forecasts.Accounting and Review Services Committee.
Issues Statements on Standards for Accounting and
Review Services (SSARS) which are standards for
compilations or reviews, not audits of financial statements.
Professional Regulation
Regulations of Individual CPAs.
Code of Professional Conduct – ethical rules for C PAs.
Requirements for regular membership in A ICPA.
Regulation of Public Accounting Firms:
Peer reviews of a firm’s accounting and auditing practice must
follow AICPA Peer Review Program.CPA firms not registered and inspected by the PCAOB are subject
to peer reviews administered by the State CPA Societies under the
direction of the AICPA Peer Review Board.The AICPA National Peer Review Committee administers peer
reviews of CPA firms registered and inspected by PCAOB.Center for Audit Quality works to foster high-quality performance.
State Boards of Accountancy
Issue CPA certificates.
All boards require successful completion of CPA
examination.Education and experience requirements vary.
National Association of State Boards of Accounting
(NASBA)Other Parties
FASB.(Financial Accounting Standards Board)
Sets GAAP for entities other than federal, state and local governments.
GASB.(Government Accounting Standards Board)Sets accounting standards of financial accounting for state and local government entities.
FASAB (Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board)
Sets accounting standards for the US government.
IFAC. International Federation of Accountants
Sets international accounting standards.
PCAOB Role
Adopt auditing, attestation, quality control, ethics, and
independence standards relating to the preparation of audit
reports for SEC registrants.
Oversee and discipline CPAs and CPA firms that audit public
companies (issuers), including:
Register firms.
Perform inspections of firms.
Conduct investigations and disciplinary proceedings of firms.
Sanction registered firms.
Securities and Exchange Commision (SEC)
Agency of the US government.
Oversight responsibility for the PCAOB.
Objectives:
Protect investors and public by requiring full disclosure of
financial information by companies offering securities for sale to
the public.Prevent misrepresentation, deceit, or other fraud in the sale of
securities
Registration and Regulation of the Sale of Securities by the SEC
Registration statements:
Qualify securities for sales.
Contains audited financial statements.
Makes SEC major user of financial statements.
Periodic reporting requirements, for example, Form 10-Ks,
Form 10-Qs, etc.Regulation S-X.
Sets forth basic accounting regulation.
Types of Professional Services
Attestation and Assurance.
Tax.
Consulting.
Accounting.
Personal Financial Planning.
Litigation support.
Fraud Investigation
Industry Specialization
Firms with detailed knowledge and understanding of a
client’s industry.
Helps firms.
Be more effective at collecting and evaluating audit
evidence.Make valuable suggestions to improve client’s operations.
Provide client consulting services.