GI E2- IBD
1/77
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What are the 2 components of gust associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)?
Organized (peyer patches) & diffuse (single layer epithelial cells that separates lumen of intestines from laminate propria)
Which type of immune response?
Hard wired, rapid response to offending agents
TLRs (toll like receptors) & NLRs (NOD like receptors)
Innate
Which type of immune response?
delayed response involving memory
T cells & B cells
Adaptive
What is an active process of local and systemic unresponsiveness to orally ingested antigens such as food?
Oral tolerance
What maintains a balance between action and suppression of inflammation, tightly regulating the immune system?
GALT & oral tolerance
Who is IBC MC In?
Bimodal- 20-30 & 60 - 70
caucasians, developed nations, jewish ethnicity
What is a lifelong illness marked by remission & relapses, profound emotional & social impact, and has a strong genetic basis?
IBD
What is the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)?
Dysregulated mucosal immune response (hyperactivity or loss of tolerance) in genetically susceptible host to microbial antigens that normally reside w/in the intestines
What condition is a chronic, recurrent disease of patchy, transmural inflammation (skip lesions) involving any segment of GI tract from the mouth to the anus?
Crohn’s disease
Where parts of the GI tract are often affected in Crohn’s?
½ of pts localize to TI & cecum, also seen isolated in small bowel or colonic involvement
Rare in esophagus, stomach, duodenum
rectum is spared
What does the transmural mucosal inflammation in Crohn’s disease (CD) lead to?
Complications from perforating disease or progressive fibrosis and strictures
What are the 3 patterns of CD?
Inflammatory, structuring, perforating
What is the pathogenesis of CD?
Aphthous ulcers & focal crypt abscess → stellate ulcerations fuse longitudinally & transversely, demarcating normal islands of mucosa forming cobblestone appearance → noncaseating granulomas → lymphoid tissue aggregates → transmural inflammation + fissures, may form fistulas/abscesses
The following ssx are with what condition?
insidious onset
crampy, colicky abd pain, classically RLQ
Diarrhea (MC non bloody)
intermittent low fever, malaise, wt loss
fistulizing → draining perianal abscess or fistulas
stricturing → obstructive sx, pain, distension, N/V
frequent extra intestinal manifestations
recurring episodes w/ periods of remission
Crohn’s disease
The following labs are for what condition?
CBC- IDA, vit B12 malasorp
leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
dec albumin
inc ESR
IBD serology → ASCA > PANCA
Crohn’s disease
What is prometheus IBD serology 7?
7 tests combines serologic, genetic, & inflammatory markers to differentiate IBD vs non-IBD vs CD vs UC
Is P-ANCA more common in CD or UC?
UC
Is ASCA more common in CD or UC?
CD
What diagnostic studies can be used for CD?
Bx via colonoscopy, CT enterography (CTE), abd flat film, UGI w SBFT, BE, CT, MRE, capsule endoscopy
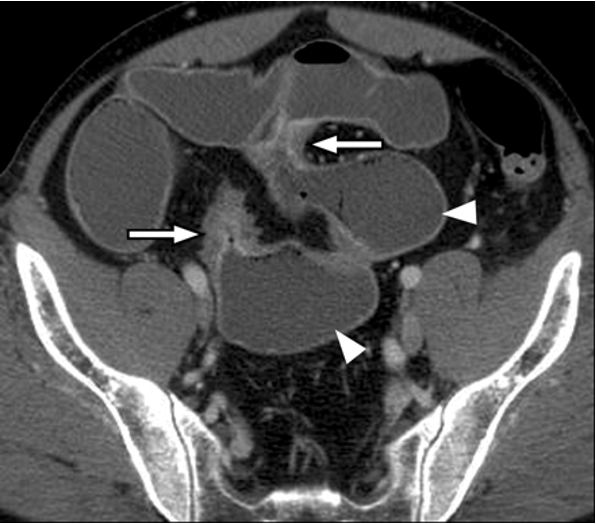
What are characteristic findings of CD that can be seen on CTE?
Skip lesions, small bowel strictures separated by segment of normal distended small bowel
What hepatobiliary extraintestinal complications can be seen in CD?
Gallstones, PSC, cholangiocarcinoma
What dermatologic extraintestinal complications can be seen in CD?
EN, pyoderma gangrenosum
What oral extraintestinal complications can be seen in CD?
aphthous ulcers- stomatitis
What ocular extraintestinal complications can be seen in CD?
Episcleritis, uveitis, iritis
What MSK extraintestinal complications can be seen in CD?
Arthropathy, sacroilitis, osteopenia, osteoporosis, ankylosing spondylitis
What classic skin condition associated w IBD presents as tender red nodules usually on the shins, causes fever & joint pain and often resolves in 3-6 weeks?
Erythema nodosum (EN)
What complications can be seen in CD?
Abscess, intestinal narrowing, fistulas, perianal disease, malabsorption, can recur at prior surgical resections
What is there in increased risk of developing in CD?
Colon carcinoma
What is recommended 8 years after being diagnosed with Crohn’s disease?
Screening colonoscopy & annual surveillance
What is the Christmas mnemonic for CD?
Cobblesetones
High temp
Reduced lumen
Intestinal fistulae
Skip lesions
Transmural (all layers, may ulcerate)
Malabsorption
Abd pain
Submucosal fibrosis
What condition is a chronic, recurrent disease limited to the mucosal layer of the colon w/ diffuse mucosal inflammation?
Ulcerative colitis (UC)
What parts of the GI tract are affected in UC?
Rectum almost always involve (dz begins here)
May extend proximally in continuous fashion to involve part or all of colon
What is UC limited to the rectum?
Ulcerative proctitis
What is UC in the rectum & sigmoid colon?
Proctosigmoiditis
What is UC involvement of rectum and entire colon?
Total colitis (pancolitis)
What is UC w ileal (distal) involvement?
Backwash ileitis
What is UC that involves only the left side of the colon?
Distal colitis
For the majority of pts w UC, the disease ______ over time
Does not progress
What is the pathophysiology of UC?
Crypt architecture distorted → mucosal vascular congestion w/ edema & focal hemorrhage
Neutrophils invade epithelium usually in crypts → cryptitis & crypt abscess → diffuse friability & erosions w/ bleeding
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
acute or subacute onset
characterized by flares & remissions
hallmark- bloody D w/ mucous & tenesmus, fecal urgency
lower abd cramps/pain, mild tenderness
Ulcerative colitis
In a pt w UC, severe abd pain, fever or tachycardia suggests what?
Fulminant colitis or toxic megacolon
The following labs are seen with what condition?
CBC- IDA
leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
inc ESR
hypoalbuminemia
negative stool culture
serology- + P ANCA
UC
What diagnostic studies can be used for UC?
Flex sigmoidoscopy (mucosa edema, friable, mucous, erosions), stool studies, plain abd film if severe, abd CT (colonic wall thickening), mucosal bx
What diagnostic study is not very useful in UC and may precipitate toxic megacolon?
Barium enemas (BE)
What is contraindicated with severe acute UC because of the risk of perforation and toxic megacolon?**
Colonoscopy
What is not possible in 10% of IBD patients?
Distinction bt UC and CD
What complications are seen with UC?
Massive hemorrhage, toxic megacolon
What condition is a rare, life threatening widening of the large intestine, where the colon dilates to diameter > 6 cm?
Toxic megacolon
What ssx are associated with toxic megacolon?
Fever, inc WBCs, tachycardia, hypotension, AMS
What is the treatment for toxic megacolon?
Meds first- steroids, abx, NPO, NG tube
IVF, surgery PRN
What is there an increased risk of in UC patients?
CRC
What is recommended 8 years after UC diagnosis?
Screening colonoscopy & annual surveillance
What are the goals of tx of IBD?
Relieve sx & prevent comps w/ 2 step approach (achieve & maintain remission)
What are the classes of meds for IBD?
5 ASAs/mesalamines, corticosteroids, thiopurines, MTX, anti-TNFs, abx, biosimilar therapies (newer)
What drug is an older agent used to induce remission in IBD (better in UC), is broken down in small intestine by bacterial AZO reductases, and has antibacterial and antiinflammatory properties?
Sulfasalazine
What SEs are seen in sulfasalazine d/t the sulfa component?
Rash, fever, hepatitis, agranulocytosis, pancreatitis, impairs folate absorption
What is needed when prescribing sulfasalazine?
Folate replacement 1 mg QD
What drugs are sulfa free & controls the site of delivery to the bowel & limits systemic toxicity?
Mesalamines
What mesalamine is released in the ileum & colon, induces remission in CD and maintains remission in UC?
Asacol
What mesalamine is released in the SI to the distal colon?
Pentasa
What should be used to treat UC colitis distal to splenic flexure?
Topical mesalamine enema - Rowasa
What should be used to treat procititis?
Mesalamine suppository - Canada
What is used for acute treatment of mod-severe UC?
Corticosteroids - prednisone for active UC unresponsive to 5-ASA
What dosage form of corticosteroids should be used for distal colitis?
Topical
How are glucocorticoids used to treat mod-severe CD?
NOT used for maintenance → taper once clinical remission is achieved (can take several months)
What SEs are seen with glucocorticoids?
Striae, fluid retention, hyperglycemia, osteonecrosis, wt gain, etc
What purine analogues are used in the treatment of IBD?
Thiopurines → Azathioprine & 6 mercaptopurine (6 MP)
What drugs are immunosuppressive agents that are used to treat glucocorticoid dependent IBD?
Thiopurines
How long does it take to see results with thiourines?
3-4 weeks (taper steroids)
What is azathioprine converted to?
6 MP
What SEs are seen with thiopurines?
Leukopenia (MC), pancreatitis, hepatitis
What must be tested before starting treatment with thiopurines?
TPMT genotype aka thiopurine methyl transferase (enzyme that metabolizes the drug)
What folate antimetabolite used to treat IBD is an IM/SC weekly injection that results in impaired DNA synthesis?
MTX
What drugs are chimeric IgG monoclonal antibody that are very effective with CD?
Anti TNF drugs (Cimzia, Humira, Remicade)
What are surgical treatment options for CD?
SI dz → resect as little intestine as possible
Proctectomy w/ end to end colostomy
Total proctocolectomy & Ilesostomy
I&D of abscesses, fistulotomy
What is the most frequent continence preserving operation used for UC that spares the sphincter?
Ileoanal pullthrough, ileal pouch anal anastomosis (IPPA)
How does the IPPA procedure work?
Rectal mucosa dissected down to dentate line of anus → pouch created from ileum to neorectum → neorectum is sutured circumferentially to the anus (J shape)
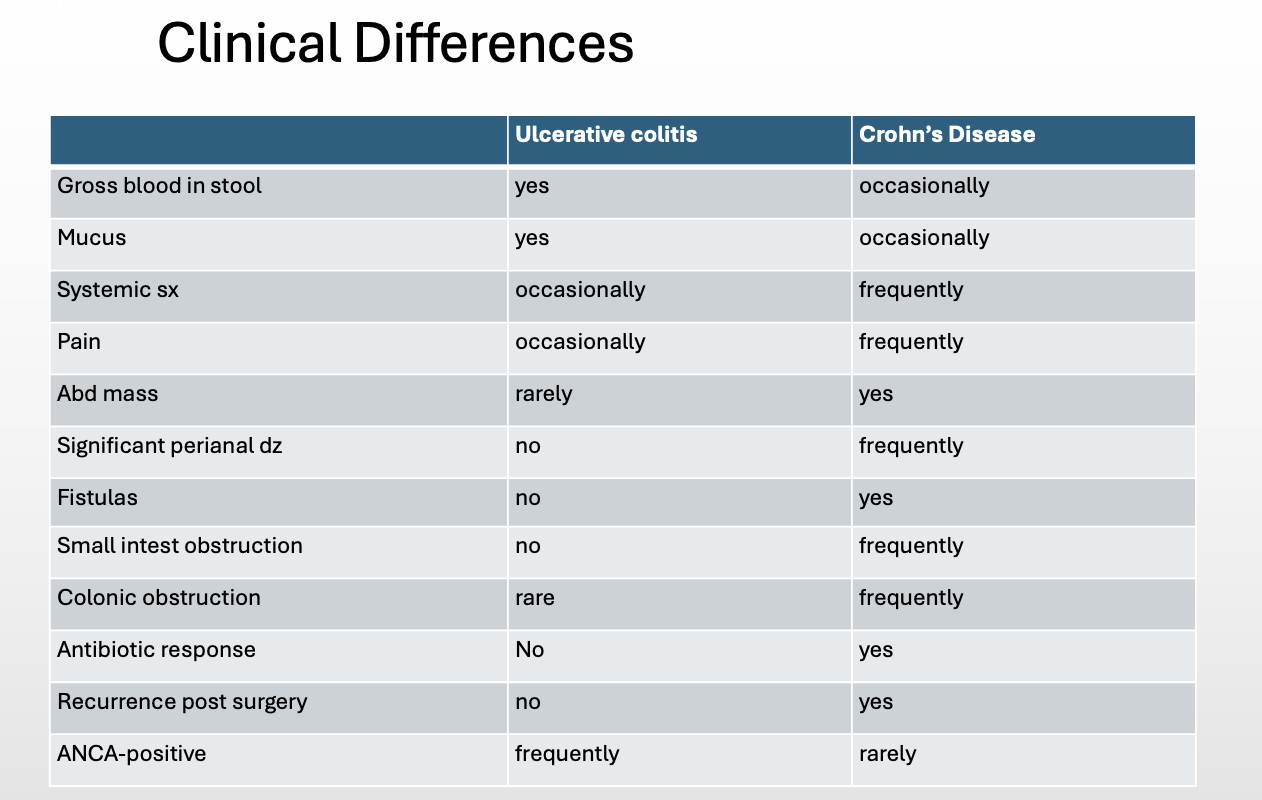
Quick reference clinical differences bt CD vs UC
:)