Physics Yr 10 Mocks
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What are the forces acting on a plane flying forwards in the air?
Thrust
Air resistance
Gravity
Lift
What are contact forces?
Forces only act when objects are touching. (all the rest)
What are non contact forces
Forces that can act from a distance
(weight, magnetic, and electrostatic)
What is the effect of balanced forces on an object?
The object stays the same, still or remains at a constant speed
What is the affect of unbalanced forces on an object?
The resultant force acts in the direction of the bigger force meaning the object will move/speed up
What is terminal velocity?
Velocity is speed in a certain direction meaning it is a vector. Terminal velocity is when the sum of the upward force equals the sum of the downward force meaning the object stays at the same speed. It is the maximum speed the object can reach. It varies depending of mass and surface area/shape
Describe the forces acting on a man jumping out of a parachute.
Man jumps out of plain. Weight pulls him down to the ground, air resistance pushes him back with a smaller force, slowing him down. His speed increases until the air resistance pushes = the weight. He has now reached terminal velocity. The man opens the parachute. Air resistance increases due to the increased surface area slowing him down. He falls until terminal velocity again until he decelerates to the floor.
Hookes law required practical
attach the clamp to the stand near to top using a boss
Place the clamp stand near to the edge of a bench/table
Clamp the base to the bench using a g clamp
Hang the spring from the top clamp and adjust the ruler so it is vertical
place the 100 g on the spring and write down the extension
add more weight measuring the extension each time
What does this practical teach us?
the extension of the spring is directly proportional to the forced applied to it (hookes law) as the graph shows a straight line through (0,0)
What is an elastic limit?
All springs have an ‘elastic limit’ if you stretch them much further than that it will deform and never go back to its original shape
What are the 8 energy stores?
Thermal, Kinetic, Sound, Light, GPE, EPE, chemical, electrostatic and magnetic
What are the 4 energy pathways?
Heating, Radiation (waves), Mechanical (work done) and Electrical
Explain the movement of heat by conduction
As particles heat up, they vibrate more. Each particle collides into the next one transferring energy. This process is continued passing energy throughout the material.
Explain the effect of material on infrared radiation
Black rough matt materials are much better emitters and absorbers of radiation than shiny smooth silver ones because they do not reflect as much light and the rough texture increases surface area for incoming radiation.
Infrared radiation required practical
get two cans, one shiny and silver, the other matt black.
set next to two bulbs painted black
fill each can simultaneously with the same temperature water (warm or cold depending on weather your measuring absorption or emissions)
place in two thermometers
after each minute record the temperature on the thermometers. Do this until ten minutes has passed.
Asses effectiveness of Loft insulation
Quite effective, contains trapped air meaning no convection current can be set up and creates an insulating layer between lost and house. Heat can escape through roof by convection though.
Asses effectiveness of double glazing
Very effective, Slows down thermal transfer by conduction. creates a vacuum and a vacuum means no convection or conduction
Asses the effectiveness of curtains
Quite effective, prevent heat leaving through windows, reduce head loss by infrared radiation (if opaque). Cheap.
What is energy efficiency and why is it important?
When you do the same task but use less energy (e.g using LED bulbs). This saves money and uses less un-renewable energy and increases resilience and reliability of electric grid.
Describe how a power station works in terms of energy transfers
Chemical energy is stored in coal which is burned in a furnace to create steam from water. The chemical energy transfers to thermal energy in steam which then turns some turbines transferring energy into kinetic energy which turns the generator which creates electricity and sends it out through the national grid
Explain 3 different ways that electricity can be generated
Fossil fuels - releases ghg into atmosphere, low costs, finite resources
Nuclear energy - low co2 emissions, risk of nuclear accident and radiation
wind power - no ghg emissions, dependent on wind, visual and noise impacts on locals
Work done is
when you push or pull something and it moves
What does work done on frictional forces cause?
Heat
What does work done against gravity increase?
Gravitational Potential Energy
What energy does a moving object have?
Kinetic
What happens when an object falls from a height?
It gains speed and transfers GPE into kinetic energy. The GPE lost will equal the kinetic energy gained.
What energy does a spring store when it is squashed or stretched?
Elastic Potential Energy
What is the spring constant?
A measure of how stiff a spring is
What is specific heat capacity?
The energy required to heat 1kg of something by 1 degree C without a change of substance
Specific Heat Capacity required practical
Place a hot block of metal into water
As the block cools down, the water heats up
Energy is transferred into the water from the metal
We presume that all energy goes into the water and none escapes
we can use this to find the SHC
Key facts about energy
Can be stored and transferred or dissipated but not created or destroyed.
The most common way for energy to be wasted/dissipated is dissipated as heat.
To avoid this use thermal insulation and lubricate moving parts.
What happens when materials are rubbed together?
The can gain a static charge by the transfer of electrons
Charge key facts
A charge has an electrical field around it
Like charges repel, opposites attract
Current definition
the rate of flow of charge
What does the current in a component depend on?
Resistance and potential difference
Required practical : IV characteristics or a filament lightbulb, LED and resistor

Required practical - resistance

Components in series circuits
the current in each component is the same
the total voltage of the power supply is shared between each component
the total resistance of 2 components is equal to their resistances added together
Components in parallel circuits
the total voltage across each component is the same
the total current in the whole circuit is the sum of all components current added together
the total resistance of two components is less than the resistance in the smaller resistor
What colour is the neutral wire
BLUE 💙🥶🦋🐟🔵🚙🚎👖🈳🐬🥏🧞♂🧢🥣👥🔷🐳🅿🦕
What colour is the earth wire?
GREEN AND YELLOW 💚🍀🤑🔫🌲🐍☘🐸🌿🌴🥑🥒🌱🦖🌳🚛🐢⭐️💛🌟⭐️💐🌝🌻🐝🍌🐣🌼🐥🌙🍍💊🍋🥎🌽🌕🍯🦜🧀🟨🟡🏵📒
What colour is the live wire?
BROWN 🐻🐴🐶🥔🐴🐌🍂🐡🦘🐗🐂👝🦌🥥🦗🟤🤎🍄🟫🟫🌰🛕👜📦💼🧅
Why do some devices not need earth wires?
They are made of non conductive plastic preventing any live wires from touching the outside and the causing the shock
How does a fuse work?
A fuse is a small safety box with a wire inside that is designed to melt if the current gets to high and breaks the circuit, stopping the electricity
What is a transformer?
A device that transfers energy from one alternating current circuit to one or more other circuits either stepping up (increasing voltage and decreasing current) or stepping down (decreasing the voltage and increasing the current)
What is the national grid?
the system that delivers gas and electricity to homes and businesses across britain
Why is the efficiency of electrical appliances is an important consideration?
More efficient appliances use less electricity so less fossil fuels are burnt, there’s less of a strain on the grid and it saves money
according to the nuclear model most of the atom is …
empty space
relative mass of protons electrons and neutrons
protons = 1
electrons = very small
neutrons = 1
relative charge of protons electrons and neutrons
protons = +1
electrons = -1
neutrons = 0
Why do atoms have no overall charge
they have the same amount of protons and neutrons
What happens when atoms loose or gain electrons
atoms loose or gain electrons to fill their outer shells and form ions
Which one is the atomic number
Bottom number (also known as proton number)
Mass number
top number
Isotope definition
2 atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
What is radioactive decay
when unstable atoms randomly give out radiation from their nuclei. the decaying is completely spontaneous and cannot be affected by external factors
what is the unit for radiation and what can it by measured with?
Becquerel (Bq) and a Geiger counter
nuclear equation for alpha radiation
a a-4 4
X → Y + (alpha)
z z-2 2
Nuclear equation for beta decay
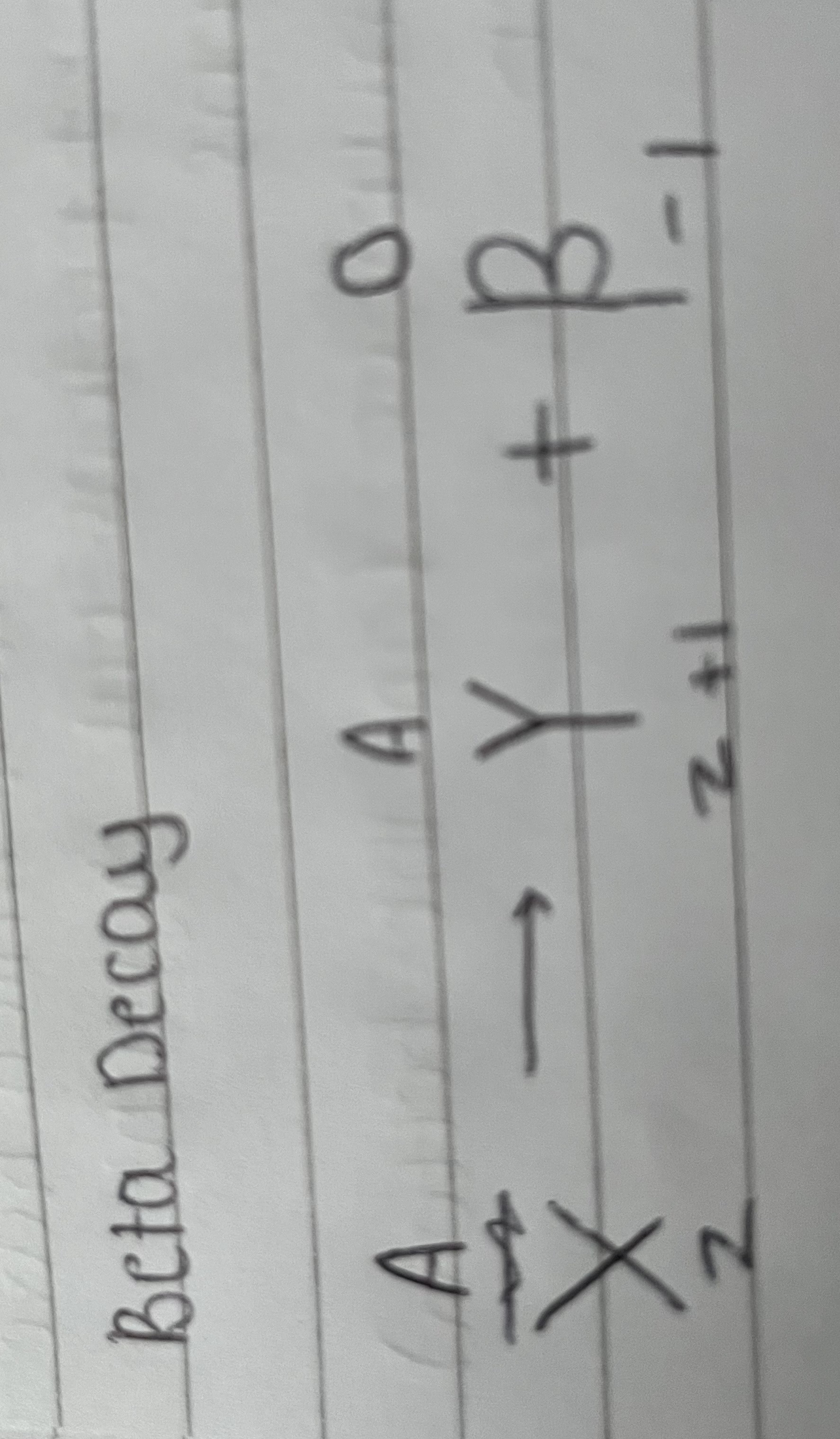
ionising power of alpha, beta and gamma
alpha : strong
beta : weak
gamma : very weak
what does ionizing power mean
how much radiation it emits from unstable nuclei
what can alpha beta and gamma be stopped by
alpha : paper
beta : alluminium
gamma : metres of concrete or few cm of lead
What measures can be taken to reduce exposure to radiation
reduce time spent in areas
increase distance between you and radioactive material
use appropriate shielding materials like lead or concrete
lower dosage of radiation
Irradiation definition
being exposed to radiation but not necessarily becoming radioactive
contamination definition
radioactive material getting into food we eat or on surfaces and making it radioactive
Half-life definition
the time taken for the amount of unstable nuclei in a material in an isotope sample to drop by half. the more radioactive, the shorter the half-life
Where does background radiation come from?
Natural sources like rocks and cosmic rays
Radon gas in the earth
Nuclear weapons and nuclear accidents
Medical
What jobs face high radiation?
dentists, radiographers, nuclear workers, uranium workers
How can radiation be used in medicine?
Gamma radiation can be used as a tracer which is drank/injected into patient and is used to measure the flow of a substance through an organ or to take pictures of internal organs
gamma radiation can be directed to cancerous tumours in narrow beams to destroy them
Gamma radiation is used as it is not as ionizing as alpha and cannot be deposited in the bodies organs and tissues
What are the two main fissionable substances commonly used in nuclear reactors?
Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239
define nuclear fission
The splitting of a parent nucleus into 2 daughter nuclei, releasing 2 or 3 moving neutrons and energy
What must happen for this to occur
an unstable nucleus must absorb a neutron (or can rarely happen spontaneously)
Describe nuclear fission in 3 steps
a nuetron is fired at an unstable nucleus
this makes the nucleus more unstable so it splits into 2 daughter nuclei
2 or 3 moving neutrons are released which are absorbed into more unstable nuclei forming a chain reaction
How can nuclear fission generate energy?
When fission occurs, heat energy is released which is sent to the boiler where it turns water into steam and turns the turbines and gets sent to the generator then the transformer and then to people’s houses as electricity
nuclear fusion definition
when 2 smaller nuclei join together to form one larger nucleus, releasing energy
how does nuclear fusion lead to the formation of elements inside stars?
stars begin their lives by fusing hydrogen into helium. this releases lots of energy which makes stars shine. when stars run out of hydrogen they fuse helium nuclei which forms carbon and oxygen
why does nuclear fusion release energy
some of the mass of the smaller nuclei is converted to energy and it is heated to a very high temp in order to have enough energy to collide