GCSE OCR Biology B6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:31 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Wall
Bacterial Cell have this - it prevents the cell from bursting
2
New cards
DNA Strand
Found in the Cytoplasm, controls cell actiivities and replication.
3
New cards
Plasmids
Small strands of DNA.
4
New cards
Flagellum
'Tail' of a bacteria - This helps them move.
5
New cards
Bacteria Shapes
Rods, Curved Rods, Spheres, Spirals.
6
New cards
Bacteria Survival
Can consume a huge number of organic nutrients. Some bacteria can produce their own nutrients. This means bacteria can survive in many different habitats.
7
New cards
Asexual Reproduction
Method of reproduction - replication of cells without another, different cell.
8
New cards
Binary Fission
Process of reproduction - means 'split in two'.
9
New cards
Bacteria Reproduction
Quick. Warm with a good source of nutrients.
10
New cards
Culturing Bacteria
Growing bacteria on an agar plate (or similar equipment)
11
New cards
Aseptic Techniques
Techniques to prevent youselve from infection. For example, sealing the petri dish.
12
New cards
Uses of Bacteria
Yoghurt, Insulin production
13
New cards
Virus Composition
Prortein coat with a strand of gentic material.
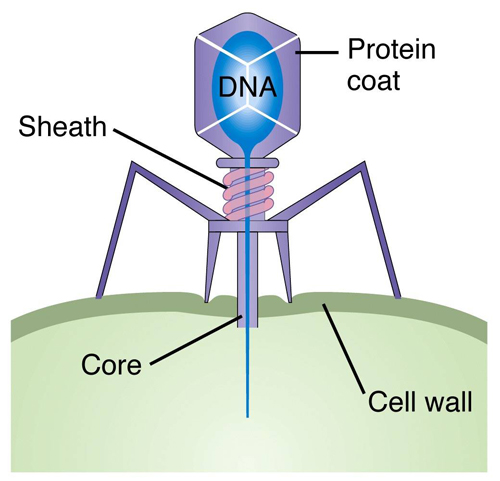
14
New cards
Reproduction of Viruses
Attaches to a host cell, infects, and break the cell, turning it into a virus 'powerhouse'
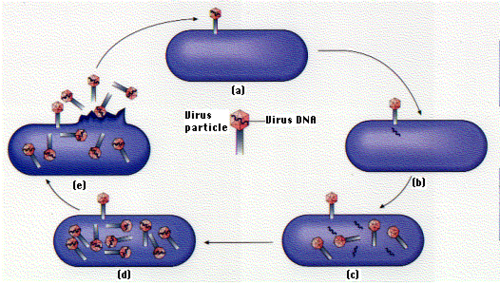
15
New cards
Disease Transmission
Food, Water, Airborne, Contact
16
New cards
Incidence of Disease
Number of new disease cases that occurs in a population in a certain time.
17
New cards
Natural Disasters lead to...
Bad sanitation, because everyone is cramped together. Also, hospitals are affected, therefore the healthcare will be worse.
18
New cards
Stages of Disease
Microorganism enters the body.
Reproduction
Toxin Production
Toxins cause symptoms.
Reproduction
Toxin Production
Toxins cause symptoms.
19
New cards
Antiseptics
Used outside the body, they prevent infection.
20
New cards
Antibiotics
Inside the body, they kill bacteria to treat an infection.
21
New cards
Bacterial Mutations
Mutations in DNA can cause a bacteria to have a genetic advantage to others, so will reproduce rather than die. This could be in the form of Antibacterial Mutations.
22
New cards
Rules of Antibiotics
Don't take anti-biotics when you don't need them - this increase will create an advantage for mutated bacteria to re-produce. Also, complete your dose of anti-biotics, as not doing so will increasethe chance of resistant bacteria re-producing more.
23
New cards
Louis Pasteur
Argued that microbes were in the air which caused disease and decomposition.
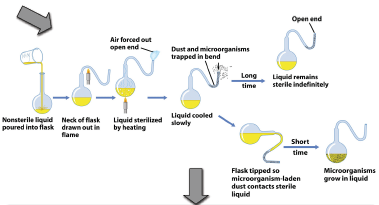
24
New cards
Joseph Lister
First to use antiseptics (he used carbolic acid) in surgery to prevent 'sepsis'.
25
New cards
Alexander Fleming
Accidently discovered Penicillin - this medicine is a very good bacteria.
26
New cards
Anaerobic Respiration
Respiration to create energy when there is no oxygen present. This is called fermentation with Yeast.
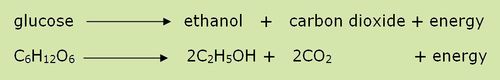
27
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
Respiration to create energy when there is oxygen present. This is preferred by the Yeast.
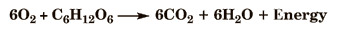
28
New cards
Fermentation vs Aerobic in Yeast
Aerobic Respiration is preferred by yeast, as it creates more energy in comparison to fermentation. However, fermentation produces ethanol.
29
New cards
Yeast Growth Rate
The faster the Yeast respires, this is increased.
30
New cards
Temperature
Warm = faster growth rate
Too hot = enzyme denature
Too hot = enzyme denature
31
New cards
More food
More glucose = faster production
32
New cards
Toxic Waste
Build up of this slows production
33
New cards
pH
This has to be just right.
34
New cards
Uses of Yeast
To clean 'sugary' water from factories.
35
New cards
Beer
Germinate Barley. Add Yeast. Clearing agents. Pasteurised. (detail in revision guide)
36
New cards
Distillation
The act of heating up alcohol to 78 Degrees to evaporate the alcohol but not the water. This is condensed in a cooling tube and you are left with a high concentrated spirit.
37
New cards
Biomass
Living or dead (recently) organic matrial. It is a store of energy.
38
New cards
Biogas
Usually 70% Methane, 30% Carbon Dioxide. Made by a digester.
39
New cards
Uses of Biogas
Burned to power a turbine to Generate electricity, or heat water. Even some cars can run out it.
40
New cards
Digester
A tank in which sludge is placed to allow decomposition by microorganisms. creates methane through process of anaerobic digestion.
41
New cards
Advantages & Disadvantages of Biofuels
Advantages - Sustainable. Doesn't rely on fossil fuels. Can be made quickly. Doesn't create pollution, as plants absorb the Carbon Dioxide produced (it balances out)
Disadvantages - Not much energy in comparison to Fossil Fuels. Large amounts of land is needed to create this - destroying wildlife.
Disadvantages - Not much energy in comparison to Fossil Fuels. Large amounts of land is needed to create this - destroying wildlife.
42
New cards
Ethanol
Used in alcohol, it can be also used a cleaner fuel in cars.
43
New cards
Gasohol
Usually 10% Ethanol and 90% Petrol. Produces less pollutants and is more sustainable than petrol itself. Good in fossil fuel poor areas.
44
New cards
Sandy Soils
Made up of large mineral particles, with large pores in the soil. Therefore, there is a high air content, and it is very permeable.
45
New cards
Pores
Gaps.
46
New cards
Permeable
Water can pass though this easily.
47
New cards
Clay Soils
Made up of Tiny mineral particles. Pak tightly, so small pores in the sol. Low air content and not very permeable
48
New cards
Loam Soils
Micture of sand and clay particles. Properties depend on levels of each type.
49
New cards
Humus
Decomposed, dead organic matter, which helps support life.
50
New cards
Humus & Water Content of Soil
Burn soil at 105 degrees until constant mass is acheived. This difference is water content. Heat at 550 degrees for 2 hours, and hummus will burn away. This difference is hummus content.
51
New cards
Air Content of Soil
Replace the air in soil with water - work out how much this is using a pipette. Water used to fill up soil until the top = air content.
52
New cards
Herbivore
Plant Eater
53
New cards
Carnivore
Meat Eater
54
New cards
Detritivores
Feed on dead organisms
55
New cards
Soil
Needed by plants for anchorage, water & minerals.
56
New cards
Conditions of Soil
Water and oxygen must be present. Presence of hummus is also important by giving off nurtients and minerals, and also increasing air content.
57
New cards
Worms
Are very useful in soil. They bury leaves which can be decomposed. They allow aeration. Allow drainage. Mix up the soil levels, distributing the nutrients equally. Neutralises soil acidity.
58
New cards
Aeration
Allowing air (oxygen) into the soil to help organisms respire.
59
New cards
Waterlogged Soil
A soil that is soaked or saturated with water.
60
New cards
Soil Acidity
These are less fertile than other pH's of soil.
61
New cards
Organisms with no Skeletal Systems
Water gives support for these organisms
62
New cards
Advantages & Disadvantages to living in water
Advantages - Plenty of Water. Less variation in temperature. Provides support (no skeletal system) good waste disposal.
Disadvantages - More resistant to movement than air. Water needs to be regulated (osmosis etc.). Fishing takes place.
Disadvantages - More resistant to movement than air. Water needs to be regulated (osmosis etc.). Fishing takes place.
63
New cards
Amoebas
Single-celled organism that control waer levels with a contractile vacuole.
64
New cards
Contractile Vacuoles
Collects the water that diffuses in by Osmosis, and then opens up at the edge of the cells to 'throw' water out again.
65
New cards
Plankton
Microscopic Organisms that live in fresh and salt water.
66
New cards
Phytoplankton
Microscopic Plants.
67
New cards
Zooplankton
Microscopic animals. They feed on Phytoplankton.
68
New cards
Photosynthesis factors
Temperature, Light Intensity, and Availability of Nitrates.
69
New cards
Plankton Population in the year
Winter - Low. Temp & Light Intensity is low. Mineral content is high, but this can't do photosynthesis.
Summer - High. Temp & Light Intensity is high. Mineral content is low, limiting photosynthesis.
Summer - High. Temp & Light Intensity is high. Mineral content is low, limiting photosynthesis.
70
New cards
Producer
Organism that produces it's own food.
71
New cards
'Marine Snow'
Dead, decomposing matter that has fallen from nearer the surface. Major source of Nutrients.
72
New cards
Eutrophication
Algae growing rapidly in water, dying, decomposing, and the bacteria starves animals in water from oxygen.
73
New cards
Pollution from Chemicals
If water is polluted with chemicals, these aren't always broken down by the organisms. When they are eaten the chemical passes on - an Otter eats lots of fish, so they would get a lot of this chemical.
74
New cards
Insoluble Chemicals
Starch, Proteins, Fats.
75
New cards
Non-biological Washing Powders
Break up Stains via Chemicals.
76
New cards
Biological Washing Powders
Contains Chemicals but also Enzymes to break up the 'stubborn' stains.
77
New cards
Amylases
Break down Carbohydrates into Simple Sugars. (Jam, Chocolate)
78
New cards
Lipases
Break down Lipids (fat) into fatty acids and Glycerol. (Butter & oil)
79
New cards
Proteases
Break down Proteins into Amino Acids (Blood, Grass)
80
New cards
Temperature of Biological Powders
Need to be washed at moderate wash temperature to pevent denaturing, however more resiliant enzymes are being developed.
81
New cards
pH of Biological Powders
Water needs to be neutral - Enzymes might not work at extremes of pH.
82
New cards
Special Stain Removers
Might contain solvents, or even specialised enzymes to break a stain down (blood, wine)
83
New cards
Diabetes
Diagnosed by presence of sugar in urine.
84
New cards
Benedict's Solution
When this is heated with urine, the colour of the solution goes from blue to orange if sugar is present. (Chemical Properties)
85
New cards
Reagent Strips
Strips of paper with Enzymes and Chemicals on it. They change colour if urine is present. Based on a sequence of enzyme reactions.
86
New cards
Low Calorie Food
Sucrase is aded to sucrose to make Glucose and Fructose, a much sweeter sugar.
87
New cards
Sucrose
Sugar we use at home
88
New cards
Sucrase
An enzyme that breaks down sucrose.
89
New cards
Rennet
Enzyme that causes milk to clot.
90
New cards
Pectinase
Used in fruit juice extraction. Breaks down Pectin that causes a release of juices.
91
New cards
Immobilised Enzymes
Enzymes that don't need to be seperated out of the mixture after the reaction has taken place.
92
New cards
Encapsulate
Enclose in a capsule
93
New cards
Alginate Beads
Formed by mixing the enzyme with Alginate, then dropping the mixture into a calcium chloride solution.
94
New cards
Avantages of Immobilising Enzymes
Enzymes don't contaminate the product. Immobilised enzymes in Alginate Beads can be used in continuous flow proccessing.
95
New cards
Lactose Intolerance
Gut Bacteria cannot be broken down by Lactase (produces Glucose and Galactose), so the gut bacteria ferment it. This causes Abdominal pain, Wind, Diarrhoea.
96
New cards
Lactose Free Milk
The Lactase in immobilised lactase breaks down the milk into glucose and galactose (simple sugars)
97
New cards
Immobilised Enzymes & Reagent Strips
Reagent strips use immobilised enzymes to quickly identify the glucose concentration in the blood
98
New cards
Genetic Engineering
Altering the genetic code of an organism. 'Good' genes are removed and interted into a different organism.
99
New cards
Transgenic Organism
A genetically modified Organism.
100
New cards
Gene Transfer
Is possible because DNA is universal. They all use the same 4 bases.