Lecture 1 - Vectors and Kinematics
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is a scalar
A SINGLE number (with a unit) that describes PHYSICAL QUANTITY
What is a vector
A quantity with both SIZE and DIRECTION
Magnitude of a vector is drawn like WHAT
| A (with arrow on top) | or A
Vectors are equal if they have the same WHAT and WHAT
Vectors are equal if they have the same MAGNITUDE (size) and DIRECTION
If your subtracting vectors how do you do it
Flip the direction
If your multiplying vectors how do you do it
Break it down to the addition and add like normal tip to tail
Any vector can be represented as a sum of two WHAT
Perpendicular vectors (Px and Py)
^I is WHAT
Is a dimensional vector length of 1 that points in the POSITIVE x DIRECTION
^J is WHAT
Is a dimensional vector length of 1 that points in the POSITIVE y DIRECTION
^K is WHAT
Is a dimensional vector length of 1 that points in the POSITIVE z DIRECTION (3D)
What is direction
Given by the angle COUNTER clock-wise from the x-axis
Taking the ratio Ay/Ax gives tangent of an WHAT between the WHAT and the WHAT
Taking the ratio Ay/Ax gives tangent of an ANGLE between the HORIZONTAL DIRECTION and the VECTOR
R = A + B (how do you add them)
R = (A + B) x + (A+B) y
What are the equations for the scalar (dot) product of two vectors ( A dot B )
A dot B = A x B x Cos(θ)
or
A dot B = AxBx + AyBy + AzBz
or
A dot B = AxBx + AyBy
if θ = 90 the product is WHAT (dot)
Zero
if θ < 90 the product is WHAT (dot)
positive
if θ > 90 the product is WHAT (dot)
Negative
if θ = 180 the product is WHAT (dot)
Negative
if θ = 0 the product is WHAT (dot)
Positive
What are the equations for the scalar (cross) product of two vectors ( A x B )
A x B = A x B x Sin(θ)
or
A x B = (AxBy - AyBx) K
A x B = A x B x Sin(θ) direction is given by the WHAT
Right hand rule
Right hand rule = Point the fingers of your right hand along the WHAT vector in the cross product (WHAT), then curl them so they point to the WHAT vector (WHAT). Your thumb gives the direction of the WHAT
Right hand rule = Point the fingers of your right hand along the FIRST vector in the cross product (Vector A), then curl them so they point to the SECOND vector (Vector B). Your thumb gives the direction of the CROSS PRODUCT
Out of page = WHAT
Positive
Into page = WHAT
negative
if θ = 180 the product is WHAT (cross)
zero
if θ = 90 the product is WHAT (cross)
zero
if θ < 90 the product is WHAT (cross)
A x B < AB
if θ = 90 the product is WHAT (cross)
A x B = AB
if θ > 90 the product is WHAT (cross)
A x B < AB
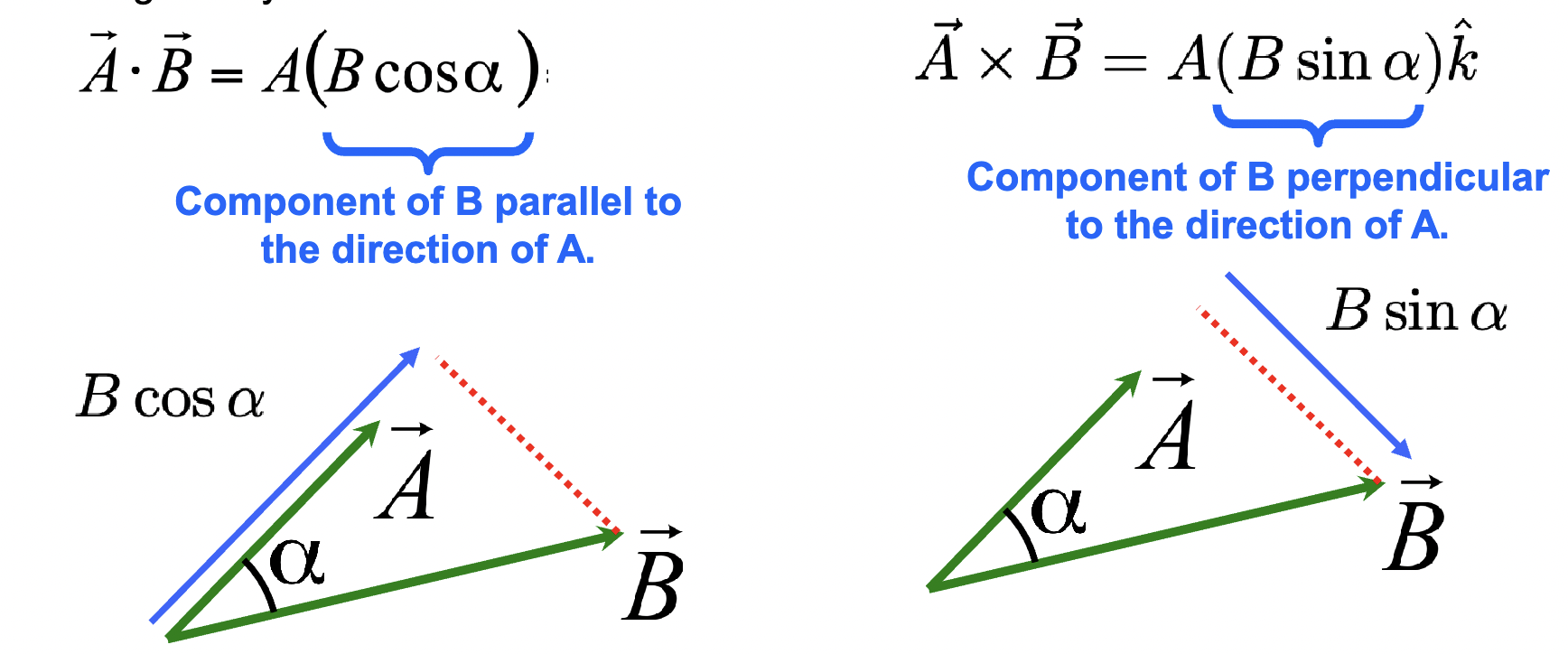
Dot vs cross product:
A (dot) B = A(B cos(a)) = component of B is WHAT to the direction of A
A x B = A (B sin(a)) = Component of B WHAT to the direction of A
Dot vs cross product:
A (dot) B = A(B cos(a)) = component of B is PARALLEL to the direction of A
A x B = A (B sin(a)) = Component of B PERPENDICULAR to the direction of A
Motion diagrams show representation/image of an object at WHAT
Fixed time intervals
If an object is speeding up the distance gets WHAT
Larger
If an object is SLOWING DOWN the distance gets WHAT
Smaller
If an object is at constant motion the distance is WHAT
The same
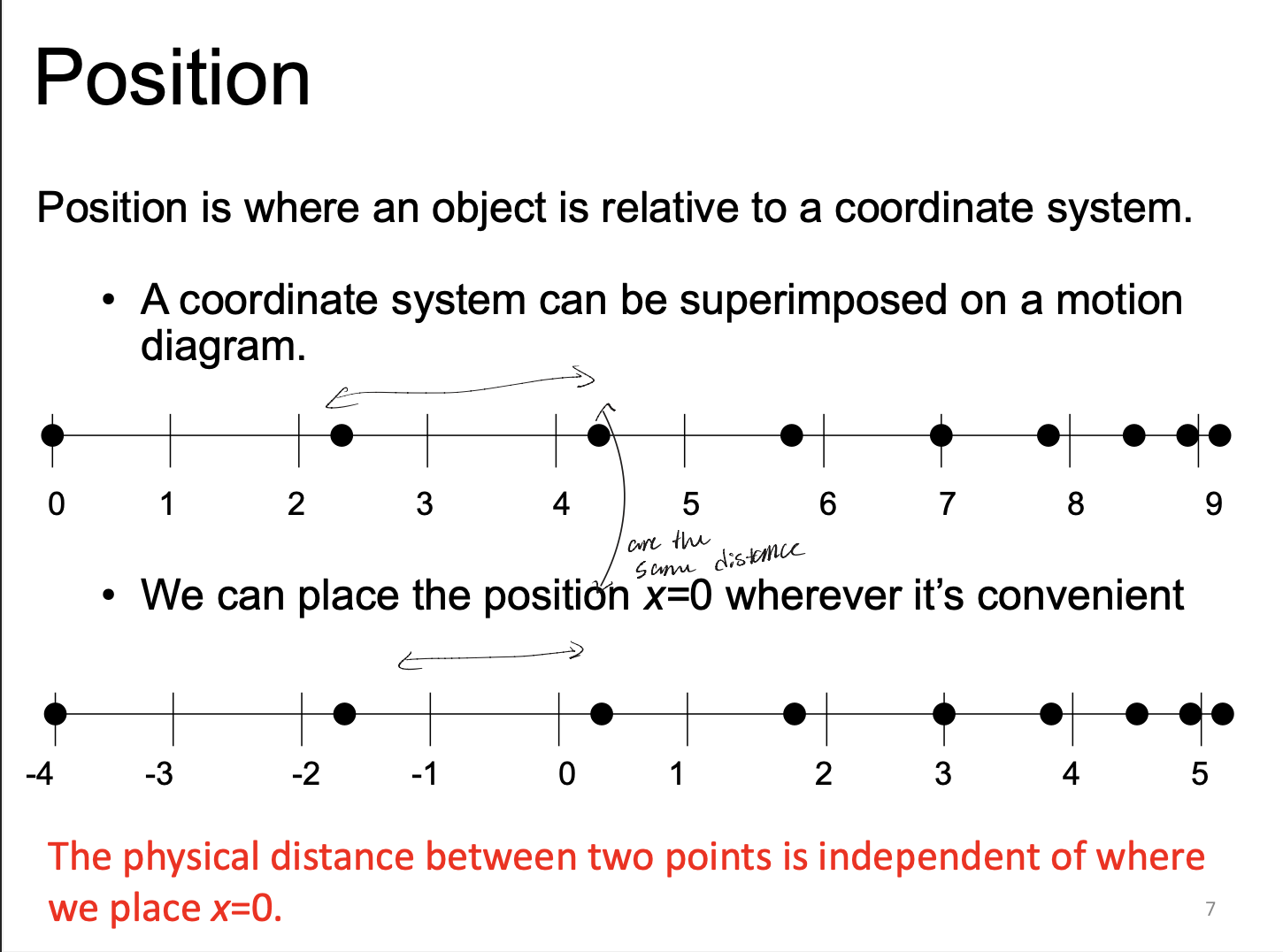
What is position
Position is where an object is relative to a COORDINATE SYSTEM
A coordinate system can be placed on a WHAT diagram
motion
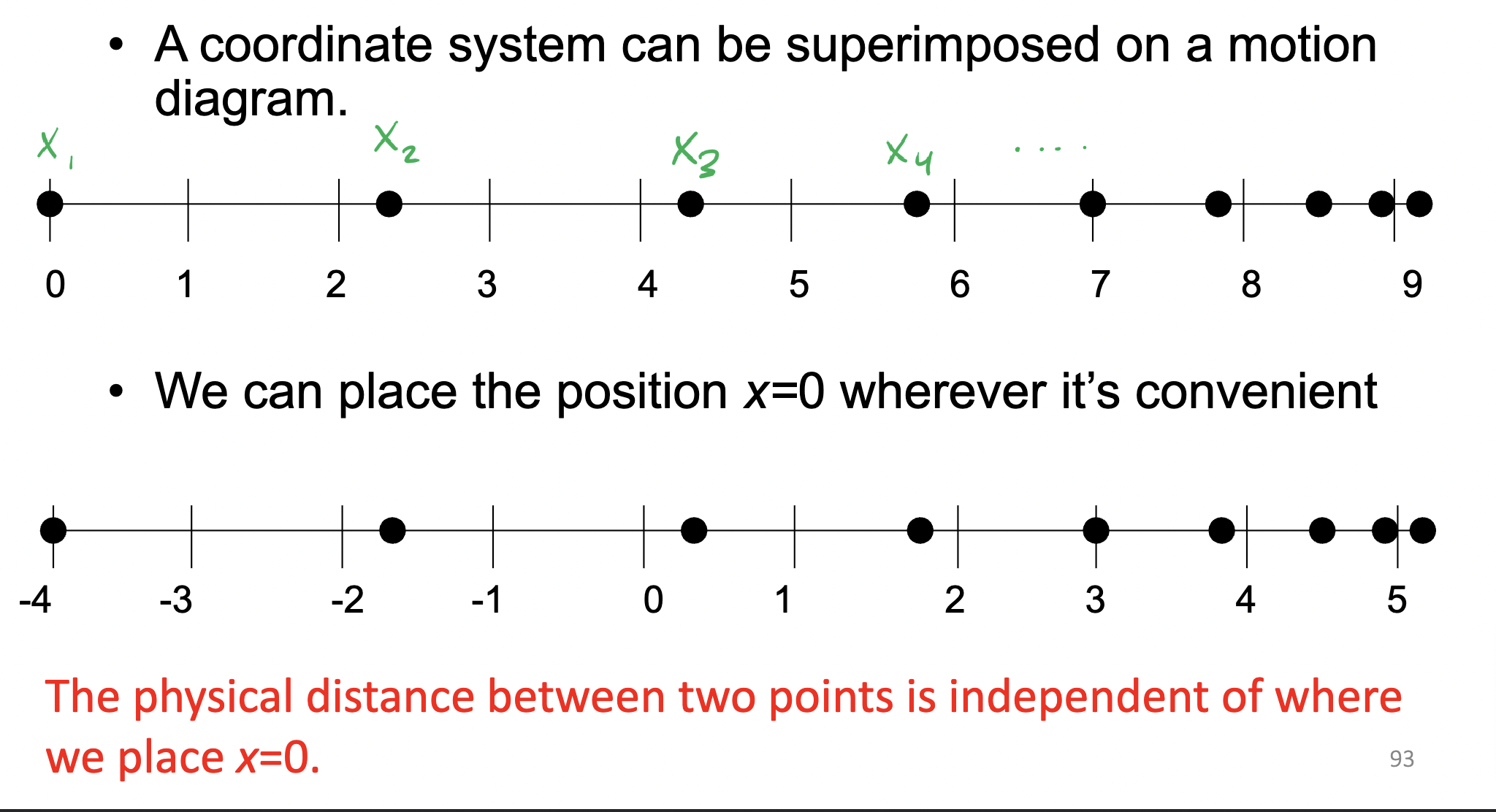
We can place the position X = WHAT wherever
X = 0
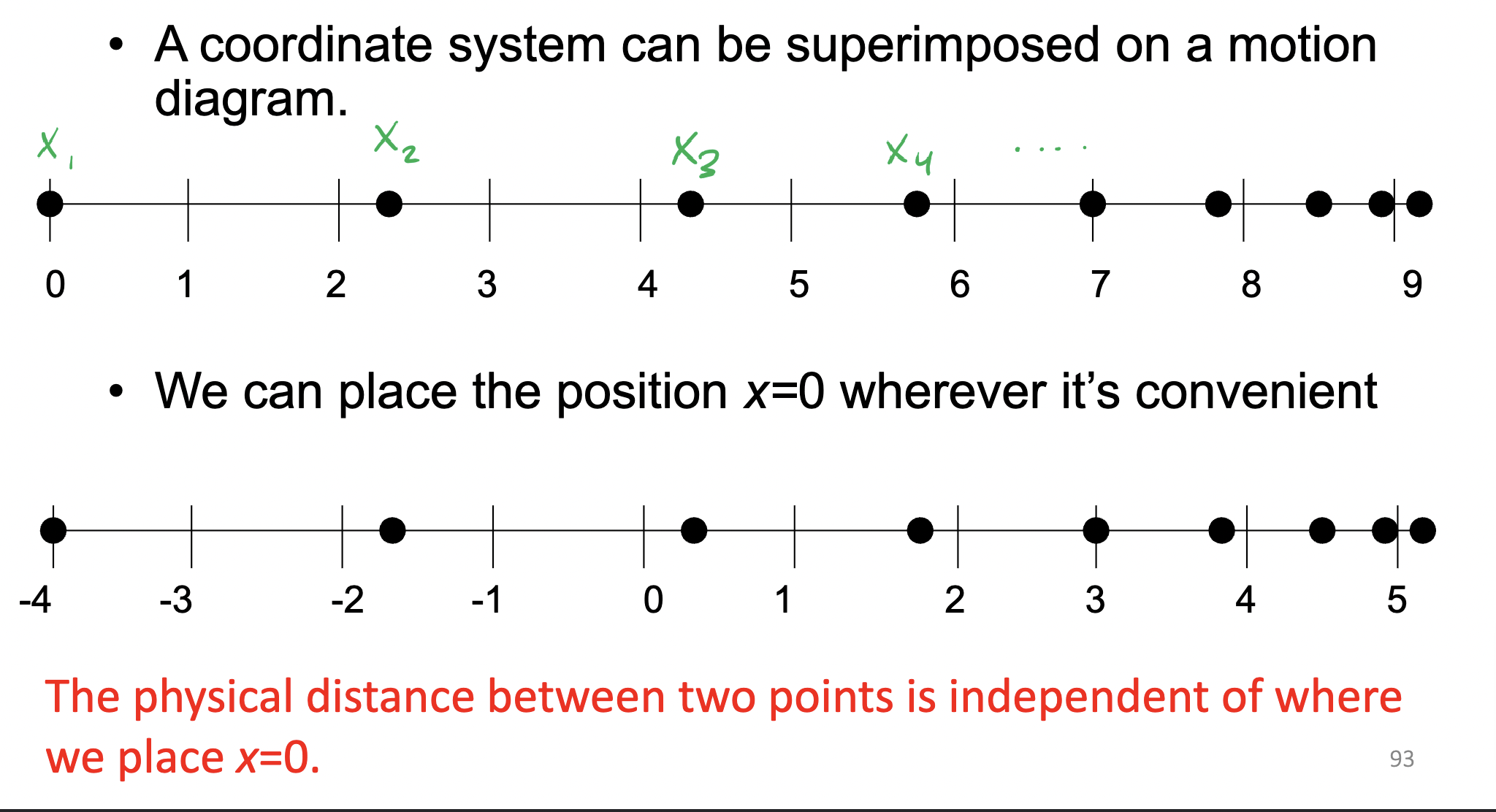
The physical WHAT between two points is independent of where we place WHAT
The physical DISTANCE between two points is independent of where we place X = 0
What is mechanism
The study of the MOTION of objects and related concepts of FORCE and ENERGY
What is kinematics
Describes HOW objects move
What is dynamics
Describes WHY objects move
A position vector always extends from the WHAT to the WHAT
A position vector always extends from the ORIGIN to the LOCATION
Displacement is the WHAT
Change in position (final minus initial)
Δr = rf - ri
Position:
Defines the WHAT of on object
Represented by WHAT
Is a VCTOR pointing from the WHAT to the WHAT
Position:
Defines the LOCATION of on object
Represented by r
Is a VECTOR pointing from the ORIGIN to the OBJECT
Displacement:
Separation between two WHAT
Represented by WHAT
Is a VECTOR pointing from WHAT to the WHAT
Displacement:
Separation between two POSITION VECTORS
Represented by Δr = rf - ri
Is a VECTOR pointing from START to the FINISH
Distance:
The WHAT path-length traversed by the object
Represented by WHAT
Is a WHAT
Distance:
The TOTAL path-length traversed by the object
Represented by d
Is a SCALAR
Speed is “how WHAT” an object is moving
Speed is “how FAST” an object is moving
Velocity is “how WHAT and in what WHAT” is an object moving
Velocity is “how FAST and in what DIRECTION” is an object moving
What is teh equation for speed
speed = distance/ Δt
What is the equation for velocity
v = displacement / Δt
Therefor speed is a WHAT and velocity is a WHAT
Therefor speed is a SCALAR and velocity is a VECTOR
What is the equation for acceleration
Vavg = Δr/Δt = displacement/ Δt
Velocity always points in the same direction as WHAT
Δr
Any change in an objects VELOCITY is called an WHAT
Acceleration
If a runners speed is increasing acceleration = WHAT and points where
a doesnt = 0 →
If a car is slowing down acceleration = WHAT and points where
a doesnt = 0 ←
Direction depends on the direction of the WHAT relative to the direction of the WHAT
Direction depends on the direction of the VELOCITY relative to the direction of the ACCELERATION
if → +V
than
→ +a (WHAT)
← -a (WHAT)
if → +V
than
→ +a (speeding up)
← -a (slowing down)
if ← -V
than
→ +a (WHAT)
← -a (WHAT)
if ← -V
than
→ +a (Slowing down)
← -a (speeding up)