AKC
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CBSE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Why aldehydes are easily oxidised to carboxylic acids?
due to the presence of H on the carbonyl group, which can be converted into OH group without the cleavage of any bond.
Aldehydes act as strong _____ agents
strong reducing
strong oxidizing agents
HNO3, KMnO4, K2Cr2O7
mild oxidizing agents
tollens reagent fehlings reagent
can ketones be easily oxidized?
NO, the oxidize under vigorous conditions
tollens reagent
[Ag(NH3)2]+
tollens test
confirm the presence of aldehydes
how tollens reagent prepared
ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate prepared by adding ammonium hydroxide + silver nitrate —→ ppt formed of AgO , till the ppt first formed is redissolved
fehiling sol A
aq copper sulphate
fehling sol B
alkaline sodium potassium tartarate (roschelles salt)
who will give fehling test?
all aldehydes except aromatic aldehydes
who gives iodoform test?
all methyl ketones (or anything ending with ch3)
alpha H
the acidity of alpha h atoms of carbonyl group is due to strong EW effect (-I effect) and resonance stabilization of conj base.
aldol condensation
same compounds ——>NaOH←—- aldol —→ heat——→ aldol condensation product
who will give aldol condesnation reaction?
aldehyd and ketones having one alpha-H
Mesityl oxide
4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
cross aldol condensation
1 +2
2+1
1+1
2+2
4 products
canizarros reaction
ald+ald——conc KOH—→ alchohol (+h) + potassium alkanoate(-H)
clemensons reaction
benzaldehyde —zn/hg hcl—→ toulouene
prepping carboxylic acid from alchohols
jones reagent CrO3.H2SO4
jones reagent
CrO3.H2SO4
prepping carboxylic acid from alkyl benzene
COOK reaction/jk
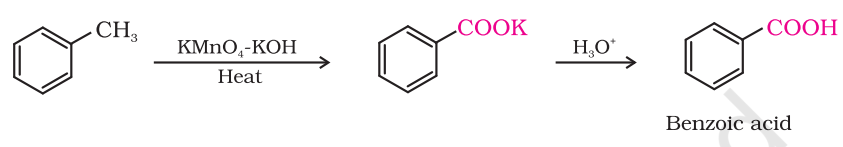
who doesnt give COOK reaction
ones with no benzyllic H
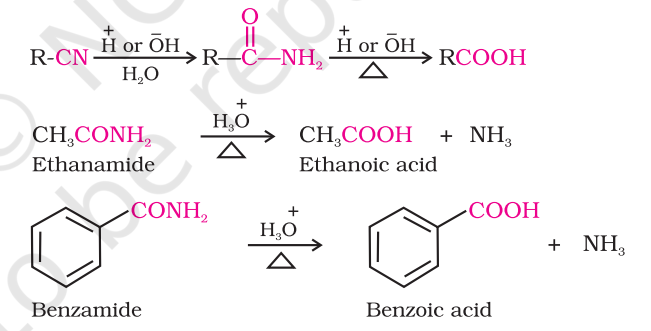
prepping carboxylic acid from nitriles and amides
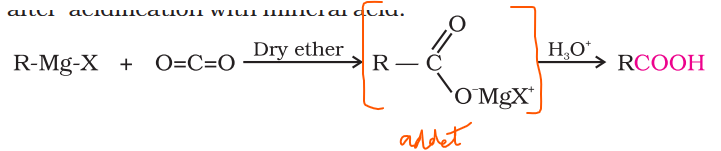
prepping carboxylic acid from grignards reagent
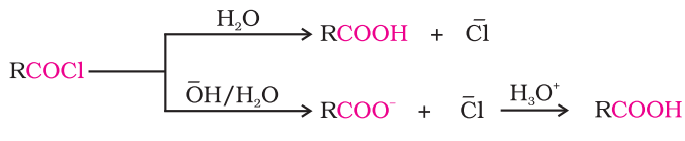
prepping carboxylic acid from acyl chloride
prep carboxylic acid from ester
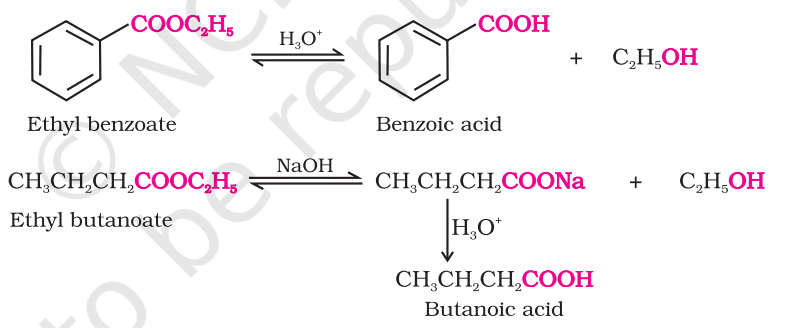
caboxlic acids upto 9 C
colourless
liquids
unpleasant odour
carboxylic acid above 9 C
wax like
solid
odourless-why?- less volatile
Why does carboxylic acids have higher BP than alchols
due to more extensive association with each other due to intermolecular H bonding
Are hydrogen bonds are not broken completely even in the vapour phase?
True
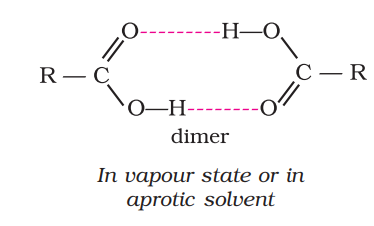
most carboxylic acids exist as ____ in the vapour phase or in the aprotic solvents.
dimer
aliphatic compunds upto ___ carbons are ____ in water
4, miscible and form H-bonds
solubility decreases with —— in carbon atoms
increase (coz higher carbons means they become hydrophobic part more interactions)
benzoic acid is nearly ____ in cold water
insoluble
carboxylic acid in general is ___ in less protic solvent
soluble
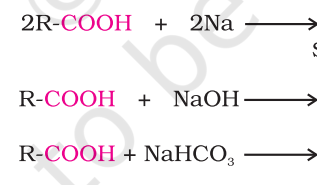
Products?
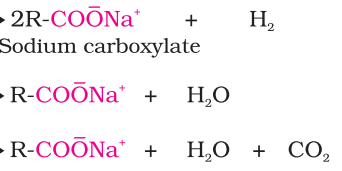
Keq

Ka
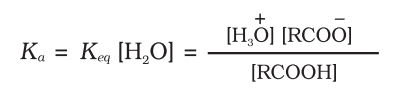
pKa
pKa of Hcl
-7
pKa of trifluoracetic acid
0.23
pKa of benzoic acid
4.19
pKa of acetic acid
4.76
pKa and strength of acid
CArboxylic acids are much stronger than alcohols
carboxylic acid and carboxylate are stabilized by resonance
CArboxylic acids are stronger than phenols?
phenol- 2 charges
carboxylate ion- 1 charge——> more stabilized
EWG effect
increases acidity
EDG effect
decreaswes acidic
hybridisation and acidity
sp>sp2>sp3
Formation of anhydride
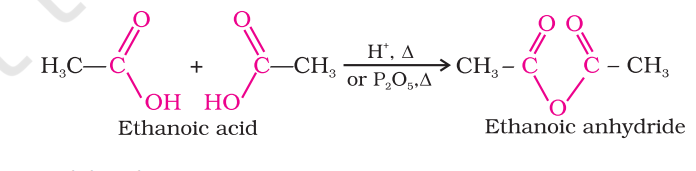
esterification

why water or ester removed form esterfication reaction?
Le Chatlier principle, move it forward
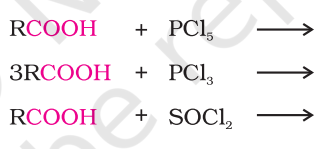
products?

carboxylic acid and ammonia reaction

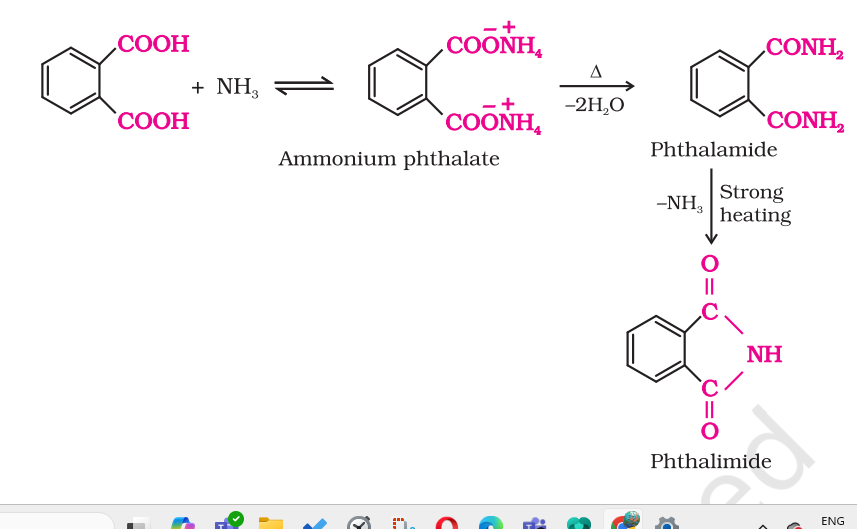
PHTHALIC ACID TO PHTHALIMIDE
carboxylic acid reduction
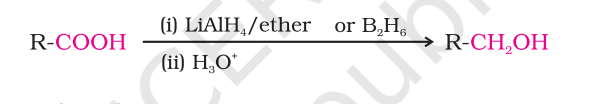
carbocylic acid decraboxylation

sodalime
3:1 NaOH: CaO
kolbes electrolysis
HVZ
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
carboxylic acid halogenatioon

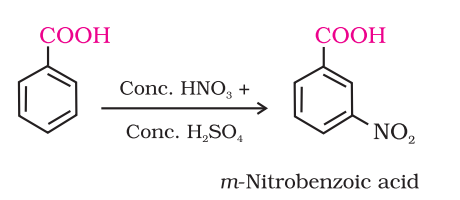
carbyoxylic acid ring subst for nitration
carbyoxylic acid ring subst for halogenation/br

can carboxylic acid undergo friedel craft reactions?
NO NO, (because the carboxyl group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminium chloride (Lewis acid) gets bonded to the carboxyl group)
for HVZ recation we require…..(hydrogen)
alpha hydrogen