ATAR Economics - Microeconomics: Chapter One and Two
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Law of Demand
There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity. As price goes up, quantity demanded goes down and vice versa.
Movement Along the Demand Curve
A contraction or expansion will occur only when price change for the product or factor (constant income). The demand curve does not move ** note the degree or extent
Influence of Non-price Factor: Demand
Demand will either increase or decrease, the demand curve will either shift left or right.
Factors Affecting Demand
Levels of Disposable Income
The Price of Substitutes
Tastes and Preferences
Expectations
Population Factors
Other Factors: Advertising
Law of Supply
a higher price will lead producers to supply a higher quantity to the market. Because businesses seek to increase revenue, when they expect to receive a higher price for something, they will produce more of it
Non Price Factor: Supply
Price of Other Goods
Technology
Prices of Resources
Expectations of Products
Number of Sellers
Weather
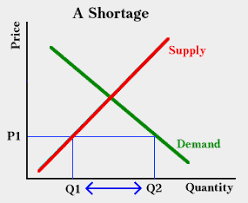
Shortage
A shortage in economics occurs when the quantity demanded for a good or service exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price, leading to a situation where not all consumers can obtain the desired product.
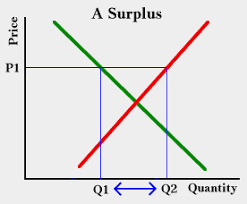
Surplus
A surplus in economics refers to the excess of a product or resource that remains after all needs have been met. It can lead to lower prices or increased consumption.
The Roles Of Market
A market exist when buyers and sellers exchange goods, services, or resources.
Market Consists of…
Buyers (Demand
Sellers (Supply)
Something to Exchange (goods or services)
Product Market
A product market refers to the marketplace where goods and services are bought and sold by consumers. It is where products are offered for sale and consumers make purchases.
Factor Markets
a factor market is where resources like labour, capital, land, and entrepreneurship are bought and sold to produce goods and services.
Competitive Market
According to the intensity of competition in the market
Firms: Price Takers
They must take the price that is established by the market
Firms: Price Settlers
Who have market power and can make their own price
Imperfect Market
Small numbers of firms
Product Differentiation
Price Settlers - Firm
Entry into the market is restricted
Opportunity Cost
Cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another
Equilibrium Price
The equilibrium price is where the supply and demand for a product are balanced, resulting in a stable price for that product.
Price Mechanism
The tendency to move toward the equilibrium price is known as the market mechanism
Law of Increasing Costs
as the production of a good increases, the opportunity cost also increases, because resources are not of the same quality
Inferior Good
a type of good whose demand decreases when consumer income rises. Examples include generic brands or public transportation.
Two reasons for Law of Demand
Substitution Effect
Income Effect
Market Equilibrium Changes
Market equilibrium increase in demand; P goes up, q goes up
Market equilibrium decrease in demand; p goes down, q goes down
Market equilibrium increase; p goes down, q goes up
Market equilibrium decrease; p goes up , q goes down
Combinations outside of the line:PPF
Impossible to produce since there are inefficient resources
Combinations inside of the line:PPF
Not all resources are being employed or not being used in the most efficient manner
Why is PPF in a negative slope
Law of opportunity cost; one of the two goods available needs to be sacrificed if the economy decides to increase the production of one of the goods, and scarcity of resources as it reallocates resrouces for production
Factors of Production
Land
natural resources used in the production process, such as water, minerals, and land itself. It is one of the essential components alongside labour, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Labour
the physical and mental effort exerted by humans in the production process. It includes the work done by individuals to produce goods and services.
Capital
man-made resources used in the production process, such as machinery, tools, buildings, and technology. It is essential for creating goods and services.
Enterprise
the abilities of individuals to combine other factors (land, labour, capital) to create goods and services.