HST Microbiology & Infection Control
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Nucleus
Located near the center of the cell, contains nuclear pores and chromosomes, etc DNA
Cell Wall
Structural layer in some cells that provides the cell with structural support and protection, as well as filtering
Cell Membrane
Outer limit of a cell, selectively permeable, composed of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and a few carbohydrates
Cytoplasm
Made of water, proteins, ions, and nutrients, houses the organelles
Ribosomes
Responsible for photosynthesis
Mitochondria
the center for respiration, provide energy for the cell
Lysosomes
digestive function
Nucleolus
Produce and assemble the cell’s ribosomes
Reservoir
Ex: People, animals, food, soil, water
Portal of exit
Ex: mouth, cuts, diapering
Mode of transportation
Ex: contact, droplets, airborne
Portal of entry
Ex: mouth, cuts, eyes
Susceptable host
Ex: babies, children, elderly, unimmunized, anyone
Fomite
inanimate reservoir of pathogenic organisms, Ex: Clothing, bedding
Vector
living organism that carries microorganisms from infected to noninfected Ex: Mosquitoes, ticks
Carrier
Host that is unaware of pathogen prescense and spreads the disease
Nosocomial Infection (Healthcare-Associated Infection)
pathogens found in a healthcare environment
Biohazardous waste examples
Blood products, body fluids, human tissues, vaccines, table papers, used medical tools, specula, inoculating loops, used gloves
Requirements an employer must follow under the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard
A written OSHA exposure control plan, training, and Hepatitis B vaccine
Exposure Control Plan requirements
1) When an incident occuts, the physician must be notified stat
2) after exposure, patient receives free medical evaluation
3) employee be tested for HBV
After persorming a leak test, what are the five steps to disinfecting an endoscope
1) Clean
2) Disinfect
3) Rinse
4) Dry
5) Store
When should biological indicators be used
1) If a new type of packaging material is used
2) If you have a new autoclave
3) After autoclave maintenance or repair
4) On a weekly basis as a general quality control measure
Medical asepsis
Any practice that reduces the number and spread of microorganisms.
Surgical asepsis
The process that eliminates completely all microorganisms and their spores from the surface of an object
What color are biohazard bags
Red
At how full should a sharps container be replaced
2/3
For how long are double layer autoclaved packages considered sterile
30 days
For patients with TB (tuberculosis) what type of precautions should be used
airborne precautions
How would you classify a stethoscope: noncritical, semicritical, or critical
noncritical
How would you classify an endoscope: noncritical, semicritical, or critical
semicritical
Physical act of cleaning instruments
Sanitization
The complete destruction of all microorganisms
Sterilization
Destruction of most pathogens, but not some spores and viruses
Disinfection
How often should you use a biological indicator as a quality control measure
weekly
Sterilization indicator that contains bacterial spores
Biological indicator
What needs to be on a label on an autoclaved pack
Items included in pack, date, initials/name of person
Special tags, tapes, strips, or inserts that confirm if items in an autoclave have been exposed to the correct temperature and steam for the correct time
Sterilization indicators
Chamber pressure in an autoclave should be
15-30lbs
Primary method for sterilizing instruments
autoclave
Temperature must reach what in an autoclave
250-270 degrees F
Proper placement order for multiple PPE
gown, mask/face shields, gloves
Any type of protective gear worn to guard against physical hazards
PPE, personal protective equipment
Type of gloves used when cleaning up that can be decontaminated and reused
utility gloves
Aseptic handwashing should take how long
2 minutes
Common cause of nosocomial infections caused by a resistant Staph bacterium
MRSA, Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Pathogen responsible for healthcare associated infections spread by fecal-oral route, resulting in watery diarrhea, fever
clostridium difficile
What vaccine must be provided free of charge to at risk employees
Hepatitis B virus
Transmission of microorganisms by contact with secretions from the nose, throat, airways and digestive tract
Droplet contact
What is the minimum alchohol content for alchohol based hand sanitizers
60%
Recommended natural nail length should less than
¼ inch
Federal agency responsible for workplace safety
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Administration
Infection caused by a normally beneficial or harmless microorganism
Endogenous infection
Introduction of a pathogen from outside the body
Exogenous infection
Ringworm
Dermatophytes | Contact | Fungal
Thrush/Vaginal yeast
Candida albicans | Bloodborne | Fungal
Pneumocystis
Pneumocystis jirovecii | Airborne | Fungal
Malaria
Plasmodium | Vectorborne | Protozoal
Giardiasis
Giardia intestinalis | Fecal-oral | Protozoal
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasma gondii | Foodborne | Protozoal
Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas vaginalis | Sexually | Protozoal
Pinworms
Enterobius vermicularis | Contact | Parisite
Head lice
Pediculus humanis capitis | Contact | Parisite
Pubic lice
Pthirus pubis | Sexually | Parisite
Scabies
Sarcoptes scabiei | Contact | Parisite
Genital Warts
HPV | Sexually | Viral
Genital Herpes
Herpes simplex virus, type 2 | Sexually | Viral
Cold Sores
Herpes simplex virus, type 1 | Contact | Viral
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis | Fecal-oral | Viral
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis | Bloodborne/Sexually | Viral
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis | Bloodborne | Viral
Common Cold
URI (Upper Respiratory tract Infection) | Droplets | Viral
Chickenpox/Shingles
Varicella-zoster virus | Droplets | Viral
Mononucleosis
Epstein-barr virus | Contact w/ saliva | Viral
Influenza
Influenza Virus | Airborne/Droplets | Viral
Measles
Measles Virus | Airborne/Droplets | Viral
German Measles
Rebulla Virus | Airborne/Droplets | Viral
Mumps
Mumps Virus | Airborne/Droplets | Viral
Whooping Cough
Bordetella perrussis | Airborne | Bacterial
PMC (Pseudomembranous colitis)
Clostridium Difficile | Fecal-oral | Bactieral
Tetanus
Clostrium Tetani | Contact | Bacterial
Diphtheria
Coryne bacterium diphtheria | Contact/Droplets | Bacterial
E.coli Diarrhea
Eschericia Coli | Foodborne | Bacterial
Peptic ulcers
Helicobacter pylori | Fecal/Oral | Bacterial
Gonorrhea
Neisseria Gonorrhea | Sexually | Bacterial
Strep Throat
Streptococcus pyogenes | Droplets | Bacterial
Syphilis
Treponema Pallidum | Sexually | Bacterial
Cholera
Vibriocholerae | Fecal-oral | Bactieral
Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis | Airborne/Droplets | Bacterial
Haemophilus Influenzae type B (HIB)
Hemophilus influenzae | Droplets | Bacterial
Hand sanitizer should be applied to ___ hands.
dry
The most important aseptic procedure for a medical assistant is ___
proper hand hygiene
According to CDC recommendations, what is the minimum length of time a medial assistant should spend scrubbing hands with soap and water when performing hand hygiene
20 seconds
A medical assistant is washing infectious debris off several sharp surgical instruments. What should they do while handling the instruments
Wear utility gloves
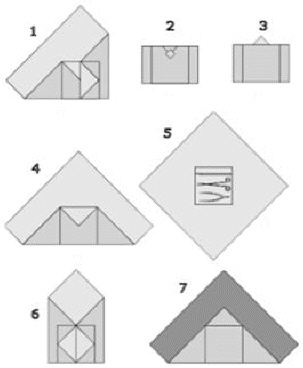
which of the following indicates the correct sequence for wrapping instruments for sterilization
5, 7, 4, 1, 6, 3, 2
Which concentration of bleach solution should a medical assistant use as a disinfectant in a clinical setting
1:10
What is the proper way to wrap hinged instruments
Placed in the open position
Part of the medical assistant’s responsibility is to run the autoclave to sterilize instruments, and once a week the MA should include a biological sterilization indicator with a load as a general quality control measure. Today, she notices that the biological indicator from yesterday’s load is positive. What does a positive result mean
The items in that load are not sterile
Systemic infection
infection that occurs when pathogens enter the blood stream and move thru out the body causing generalized symptoms such as fever vomiting diarrhea, etc
Antisepsis
Prevent of inhibit the growth of pathogens but are not effective against spores and viruses
Ex. Alcohol, betadine
Asepsis
A condition in which no living disease-causing microorganisms are present