AS Physics: Waves and Superpositions
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Common Past paper questions
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
By reference to the direction of transfer of energy, state what is meant by longitudinal waves?
Oscillations (of particles) are parallel to (the direction) of energy transfer.
3
New cards
Define frequency of a wave sound.
Frequency is the number of vibrations/oscillations per unit time or the number of wavefronts passing a point per unit time.
4
New cards
A sound wave travels through air. Describe the motion of the air particles relative to the direction of travel of the sound wave.
vibrations/oscillation of the air particles are parallel to the direction of it (the direction of travel of the sound wave).
5
New cards
Describe Doppler Effect.
Observed frequency is different to source frequency when source moves relative to observer.
6
New cards
State what is meant by the frequency of a progressive wave.
The number of oscillations per unit time.
7
New cards
By reference to the direction of the propagation of energy, state what is meant by a longitudinal wave.
vibrations/oscillations (of the particles/wave) are parallel to the direction __**OR**__
in the same direction (of the propagation of energy)
in the same direction (of the propagation of energy)
8
New cards
By reference to the direction of the propagation of energy, state what is meant by a transverse wave.
vibrations/oscillations (of the particles/wave) are perpendicular to the direction (of propagation of energy)
9
New cards
Describe Doppler effect
change/difference in the __observed/apparen__t frequency when the source is moving (relative to the observer).
10
New cards
A progressive wave transfers energy. A stationary wave does not transfer energy. State two other differences between progressive waves and stationary waves.
* __Progressive waves__ - travel through a medium.
* __Stationary waves__ - while stationary waves do not travel.
* __Progressive waves__ all particles have same amplitude.
* __Stationary waves__ - no nodes or antinodes or maximum to minimum/zero amplitude.
* __Progressive waves__ - adjacent particles are not in phase.
* __Stationary waves__ - waves particles are in phase (between adjacent nodes).
* __Stationary waves__ - while stationary waves do not travel.
* __Progressive waves__ all particles have same amplitude.
* __Stationary waves__ - no nodes or antinodes or maximum to minimum/zero amplitude.
* __Progressive waves__ - adjacent particles are not in phase.
* __Stationary waves__ - waves particles are in phase (between adjacent nodes).
11
New cards
What is meant by progressive wave.
energy is moved/transferred/propagated from one place to another (without the bulk movement of the medium).
12
New cards
What is meant by transverse wave.
(particles) oscillate/vibrate at right angles to the direction of travel of the energy/ wavefront.
13
New cards
Define frequency.
number of oscillations per unit time/ number of wavefronts passing a point per unit time.
14
New cards
State what is meant by zero phase difference.
two sound waves of the ==same frequency== that are ==perfectly aligned== have a phase difference of 0 and are said to be “in phase.”
two waves that are in phase add to produce a sound wave with an amplitude equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the two waves.
two waves that are in phase add to produce a sound wave with an amplitude equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the two waves.
15
New cards
Explain what is meant by the following quantities for a wave on the surface of water.
i) displacement
ii) amplitude
iii) frequency
iv) time period
i) displacement
ii) amplitude
iii) frequency
iv) time period
i) __displacement__ - distance from the equilibrium position/ undisturbed position/ midpoint/ rest position
ii) __*amplitude*__ - is the maximum displacement
iii) __frequency__ - is the number of wavefronts/ crests passing on a point per unit time
iv) __time period__ - is the time between adjacent wave fronts
ii) __*amplitude*__ - is the maximum displacement
iii) __frequency__ - is the number of wavefronts/ crests passing on a point per unit time
iv) __time period__ - is the time between adjacent wave fronts
16
New cards
Explain the term **displacement for the wave on the rope**.
the distance the rope/ particles are (above or below) from the equilibrium/ mean/ rest/ undisturbed position (NOT distance moved)
17
New cards
Define for a wave:
i) wavelength λ
ii) frequency *f*
i) wavelength λ
ii) frequency *f*
i) __wavelength__ - minimum distance between two points moving in phase **OR** distance between neighbouring or consecutive peaks or troughs **OR** wavelength is the distance moved by a wavefront in time T or one oscillation/cycle or period (of source)
ii) __frequency__ - number of wavefronts/ (unit) time **OR** number of oscillations per unit time or oscillations/time
ii) __frequency__ - number of wavefronts/ (unit) time **OR** number of oscillations per unit time or oscillations/time
18
New cards
Use your definitions (in flashcard 16) to deduce the relationship between λ, f and speed v of the wave.
\
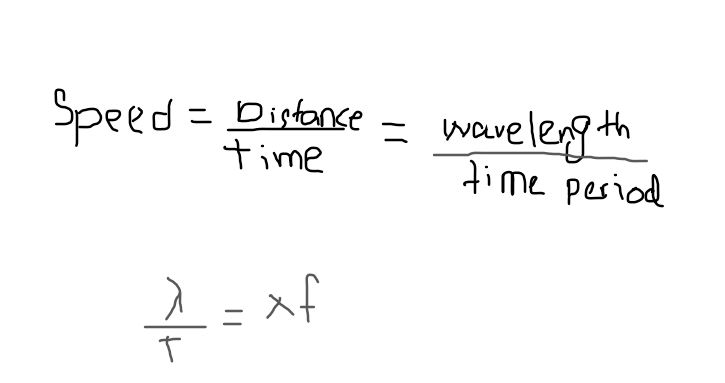
19
New cards
State one property of electromagnetic waves that is not common to other transverse waves.
travel through vacuum/ free space
20
New cards
All the waves in a spectrum can be polarised. Explain the meaning of the term *polarised*.
vibrations are in one direction perpendicular to direction of propagation/ energy transfer
\
A polarised wave oscillates in only one plane (e.g only up and down if vertically polarised), only transverse waves can be polarised. Polarisation provides evidence for the nature of transverse waves because polarisation can only occur if a wave's oscillations are perpendicular to its direction of travel (as they are in transverse waves).
The intensity of a wave is affected by polarisation. As the process of passing through a polarising filter excludes waves of certain orientations, the intensity of the wave after filtering is always less than or equal to its intensity before.
\
A polarised wave oscillates in only one plane (e.g only up and down if vertically polarised), only transverse waves can be polarised. Polarisation provides evidence for the nature of transverse waves because polarisation can only occur if a wave's oscillations are perpendicular to its direction of travel (as they are in transverse waves).
The intensity of a wave is affected by polarisation. As the process of passing through a polarising filter excludes waves of certain orientations, the intensity of the wave after filtering is always less than or equal to its intensity before.
21
New cards
Explain the following terms used to describe stationary waves on a string:
i) node
ii) antinode
i) node
ii) antinode
i) __node__ - zero amplitude/displacement
ii) __antinode__ - maximum amplitude/displacement
ii) __antinode__ - maximum amplitude/displacement
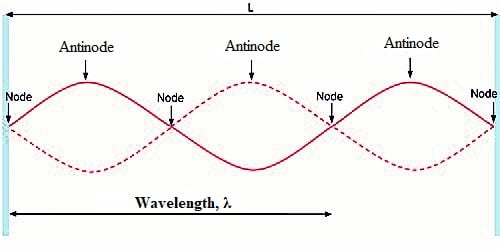
22
New cards
A loudspeaker produces a sound wave of constant frequency. Outline how a cathode ray oscilloscope (c.r.o) can be used to determine this frequency.
connect microphone / (terminals of) loudspeaker to Y-plates of c.r.o. adjust c.r.o. to produce steady wave of 1 (or 2) cycles / wavelengths on screen
measure length of cycle / wavelength and note time-base b
frequency= 1/λb
(assume b is measured as s cm^-1 unless otherwise stated)
(if statement is 'measure T, f= 1/T’ then last two marks are lost)
measure length of cycle / wavelength and note time-base b
frequency= 1/λb
(assume b is measured as s cm^-1 unless otherwise stated)
(if statement is 'measure T, f= 1/T’ then last two marks are lost)
23
New cards
For a progressive wave, state what is meant by its meant by its period.
time for one oscillations/vibrations/cycle **OR** time between a__djacent__ wavefronts (passing the same point) **OR** __shortest__ time between two wavefronts (passing the same point)
24
New cards
State the principle of superposition.
(when two or more) waves meet/overlap (at a point)
(resultant) displacement is sum of the individual displacements
(resultant) displacement is sum of the individual displacements
25
New cards
What is meant by a node of a stationary wave.
particle on stationary wave with zero amplitude.
26
New cards
Difference between nodes vs antinodes.
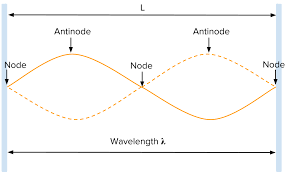
27
New cards
State what is meant by coherent in a wave.
constant phase difference in a wave.
28
New cards