chemistry 13th edition chapt 1,2,3,7,8
5.0(1)Studied by 12 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:41 PM on 10/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
1
New cards
equilibrium
no observable changes as time goes by
2
New cards
reversible process sign
⇌
3
New cards
scientific method
1. create question
2. background research
3. create hypothesis
4. conduct experiment
5. test hypothesis
6. draw conclusions
7. report results
4
New cards
how to convert farenheit to celsius
(F-32)\*5/9
5
New cards
how to convert celsius to fareheit
9/5\*C+32F
6
New cards
how to convert celsius to kelvin
273\.15+C
7
New cards
dalton’s atomic theory
1. law of conservation of mass
2. reactions can be separated, rearranged, or combined
3. each element’s atom is identical and unique in size, mass, etc.
4. elements are composed of atoms
8
New cards
joseph proust
created law of definite proportions
9
New cards
law of definite proportions
no matter where you find a compound, the elements within it will always have fixed and consistent proportions by mass
10
New cards
law of multiple proportions
two elements can combine in different proportions to create various compounds, and the ratios of their masses in these compounds will be simple whole number ratios
11
New cards
radiation
the emission and transmission of energy through space in waves
12
New cards
JJ Thomson
discovered electrons
13
New cards
charge of an electron
\-1.602\*10^-19 coulombs
14
New cards
who discovered charge of an electron
Robert Milikan
15
New cards
mass of an electron
9\.10\*10^-28
16
New cards
Wilhelm Rontgen
discovered x-rays
17
New cards
Antoine Becquerel
discovered radioactivity
18
New cards
radioactivity
spontaneous emission of particles
19
New cards
plum pudding
equal protons and electrons
20
New cards
proton mass
1\.67\*10^-24
21
New cards
atomic radius number
100pm
22
New cards
molecule
two atoms held by chemical forces
23
New cards
ion
positive or negative charge
24
New cards
allotropes
one of two or more distinct forms of an element
25
New cards
molecular models
ball and stick or space filling
26
New cards
structural formula
shows how elements are bonded in a molecule
27
New cards
binary compounds
two element compounds
28
New cards
ternary compounds
three element compounds
29
New cards
oxoanions
anions of oxoacids
30
New cards
acid
substance that yields hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
31
New cards
oxoacids
acids that contain h,o, and central element
32
New cards
base
substance that yields OH- ions when disolved in water
33
New cards
hydrates
compounds that have a specific number of water molecules attached to them
34
New cards
hydrocarbons
simplest organic compound
35
New cards
functional groups
bonded in a specific way
36
New cards
atomic mass
mass of protons, neutrons, and electrons
37
New cards
F.W. Aston
developed mass spectrometer, discovered isotopes
38
New cards
percent composition formula
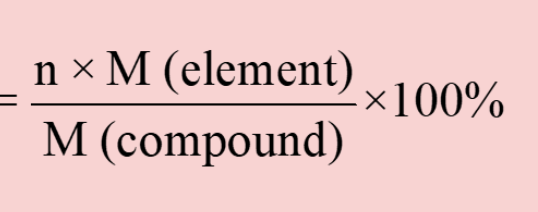
39
New cards
steps to find empirical formula
1. determine grams of element
2. convert grams to moles
3. divide by simplest ratio number if not whole
40
New cards
what do you need to know to calculate molecular formula
approx. molar mass of compound and empirical formula
41
New cards
ratio of molar and empirical mass
molar mass / empirical mass
42
New cards
theoretical yield
actual/percent \* 100%
43
New cards
percent yield
actual/theo \* 100%
44
New cards
quanta
atoms and molecules emit energy only in certain quantities
45
New cards
wave
periodic disturbance that moves through space
46
New cards
speed of wave
*v*=*f*⋅*λ, distance/time*
47
New cards
electromagnetic wave
contains electric and magnetic field
48
New cards
electromagnetic radiation
emission and transmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves
49
New cards
quantum
smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted in form of electromagnetic radiation
50
New cards
relationship formula between energy and frequency in the context of electromagnetic waves
E=hv
51
New cards
photoelectric effect
electrons are ejected from the surface of certain metals exposed to light of a certain frequency
52
New cards
photons
particles of light
53
New cards
how are electrons held together
attractive forces that requires light of certain frequency to break them free
54
New cards
relationship between the energy of a photon and kinetic energy
hv=KE + W
w = work function
w = work function
55
New cards
the more intense the light
greater # of electrons emitted
56
New cards
higher frequency of light
greater kinetic energy
57
New cards
particle wave duality
light can be like wave or particles
58
New cards
emission spectra
continous spectra of radiation emitted by substances
59
New cards
line spectra
light emission at specific wavelengths
60
New cards
energy level of electrons in hydrogen
\-Rh(1/n^2)
61
New cards
Rh
2\.18 \* 10^-18J
62
New cards
free electron
electron that is infinitely far from nucleus
63
New cards
ground state
lowest energy state of a system
64
New cards
excited state
higher than ground
65
New cards
Rydberg formula
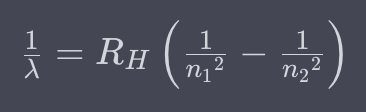
66
New cards
nodes
amplitude is 0
67
New cards
relationship between circumference and wavelength
2πr=hλ
68
New cards
Louis de Broglie
electrons have wavelike properties
69
New cards
De Broglie wavelength equation
h/mv
70
New cards
true or false: wave particles can be observed in submicroscopic and macroscopic
false
71
New cards
heisenburg uncertainty principle
impossible to know mass times volume and position of particle at the same time
72
New cards
schrodinger
created equation that describes behavior and energy of submicroscopic particles
73
New cards
wave function symbol
Ψ
74
New cards
electron density
probability that electron will be in particular region of atom
75
New cards
atomic orbital
wave function of electron
76
New cards
quantum numbers
describe distribution of electrons in hydrogen and other atoms
77
New cards
principal quantum number
integral values
78
New cards
angular momentum quantum number
shape of orbitals (l)
79
New cards
magnetic quantum number
orientation of orbital in space and depends on angular momentum quantum number
80
New cards
electron spin quantum number
value +1/2 or -1/2
81
New cards
electron configuration rules
pauli exclusion principle → two electrons per orbital with opp spin
hunds rule → when filling up the orbitals, place one electron in each orbital of a sublevel before pairing
aufbau principle → when more protons are added, electrons are added to atomic orbitals as well
hunds rule → when filling up the orbitals, place one electron in each orbital of a sublevel before pairing
aufbau principle → when more protons are added, electrons are added to atomic orbitals as well
82
New cards
paramagnetic substance
net unpaired spins attracted by magnet
83
New cards
diamagnetic substance
no net unpaired spins and repel
84
New cards
odd number of electrons useful rule
will always contain one or more unpaired spins
85
New cards
noble gas core
noble gas element that almost replaces element being considered
86
New cards
newlands
law of octaves
87
New cards
isoelectronic
same # of electrons and ground-state electron configuration
88
New cards
effective nuclear charge equation
Zeff = Z - *σ*
89
New cards
expression to remove first electron
3\.94 \* 10^-18J
90
New cards
expression to remove second electron
8\.72 \* 10^-18J
91
New cards
ionic radius
radius of cation or anion
92
New cards
higher the ionization energy
harder to remove electron
93
New cards
electron affinity
negative energy charge that occurs when electron is accepted by an atom in the gaseous state to form an anion
94
New cards
how is electron affinity determined
removing additional electrons from anion
95
New cards
electron affinity trend
increase left and right, decrease up and down
96
New cards
diagonal relationships
simiplarities between pairs of elements in diff groups and periods
97
New cards
charge density
charge of ion/volume
98
New cards
halides
anions derived from halogens
99
New cards
amphoteric
display both acidic and base properties
Explore top notes
Chp 14 Materality: Constructing Social Relationships and Meanings with Things
Updated 1265d ago0.0(0)
Chp 14 Materality: Constructing Social Relationships and Meanings with Things
Updated 1265d ago0.0(0)