Unit 3 Test
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Investigative journalists who exposed corruption and social injustices. corrupt side of business and public life in 1900s
Law passed because of Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle. an American law that makes it illegal to adulterate or misbrand meat and meat products being sold as food, and ensures that meat and meat products are slaughtered and processed under strictly regulated sanitary conditions.
Theodore Roosevelt’s domestic policy aimed at trust-busting, conservation, and consumer protection. Theodore Roosevelt's domestic program, which reflected his three major goals: conservation of natural resources, corporate law, and consumer protection. These three demands are often referred to as the "three C's" of Roosevelt's Square Deal.
Election of 1912 results
Wilson’s 14 Points PLAN
Signed in 1919 that officially ended World War I, where Germany was forced to accept blame for the war, pay large reparations to the Allied powers, cede territory, and significantly reduce its military capabilities, leading to widespread resentment among the German population that contributed to future conflicts like World War I.
Many in the United States feared recent immigrants and dissidents, particularly those who embraced communist, socialist, or anarchist ideology. This took place in 1919-1920.
significantly contributed to the outbreak of the Spanish-American War by heavily influencing public opinion through sensationalized reporting, which created a strong pro-war sentiment against Spain, ultimately pushing the US government towards military action.
Hearst+Yellow Journalisms causing the Spanish-American War
Roosevelt quarry/belief with HAwaii
IF American lives or business are threatened, the US will get involved in other nations.
EX: Hawaii Takeover with the Marines This policy asserted that the US would intervene in Latin American countries to stabilize them and protect American interests.
Open Door Policy
called for protection of equal privileges for all countries trading with China and for the support of Chinese territorial and administrative integrity (second part did not follow through)
NAACP
Civil rights organization in the United States that works to ensure the rights of African Americans.
Yellow Journalism
A style of sensationalized and exaggerated newspaper reporting that was popular in the late 10th century.
Social Darwinism
A set of ideologies that use Charles Darwin's theory of evolution to justify social, economic, and political views.
suffragist
People who supported extending the right to vote to women in the United States.
Temperance
Social and political movement that advocates for moderation or complete abstinence from alcohol consumption.
prohibition
A nationwide ban on the sale and import of alcoholic beverages that lasted from 1920 to 1933.
expansionism
The practice of increasing a country's size through military conquest or the purchase of colonial territories.
WW1 definition/The Great War
Both referring to the same global conflict that took place from 1914 to 1918, primarily in Europe, where major powers like Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire fought against Great Britian, France, Russia, and later the United Sates.
Militarism
A political ideology where a government prioritizes building and maintaining a strong military force, often with the intention of using it aggressively to expand national interests, sometimes including the glorification of the military and its ideals within society; essentially, placing the military at the forefront of policy and national identity.
Imperialism
The policy of a nation, like the United States, extending its political, economic, and military power over other countries, often through territorial acquisition or gaining significant control over affairs, frequently achieved through the use of force or influence, to expand its own sphere of influene and dominance.
Nationalism (def)
An ideology that emphazises loyalty, devotion, or allegiance to a nation or nation-state and holds that such obligations outweigh other individual or group interests.
Great Migration
The large-scale movement of African Americans from the rural South to urban areas in the North and West between roughly 1910 and 1970.
Espionage Act
A law passed by Congress to criminalize activites that could interfere with the United Sates' war effort during the World War I.
Fourteen Points presented to congress when?
A set of guidelines for world peace that President Woodrow Wilson outlined in a speech to Congress on January 9, 1918.
League of Nations
An international organization that was established after World War I to promote international peace and security.
National Origins Act (1924)
limited the number of immigrants allowed entry into the United States through a national origins quota. The quota provided immigration visas to two percent of the total number of people of each nationality in the United States as of the 1890 national census
Emergency Immigration Act (1921)
Introduced numeral limits on European immigration based on quota system
Volstead Act (1919)
Banned the manufacture and selling of alcohol beverages
Black Tuesday (October 28, 1929)
The collapse of stock prices on wall street. Entered the US into the Great Depression
Leisure and Consumption
time spent having fun and buying products. Rise of consumerism in the 1920s through maginzes and radios ads
New tech in 1920s?
Refrigerators, washing machines, vacuums, radios, airplane travel, Ford T model car
Assembly Line (1920s consumption/product)
Perfected by Ford, it reduced production costs but made jobs repetitive.
What was the Teapot Dome Scandal?
considered one of the greatest scandals in American political history. a political scandal of the early 1920s that involved the administration of Warren G. Harding. The scandal involved bribes paid to Secretary of the Interior Albert B. Fall by oil tycoons Edward Doheny and Harry Sinclair
Election of 1920
Republican Party won because America was tired of the democratic, Wilsons, false promises.
Al Capone
a notorious gangster who prohibited illegal alcohol sales during Prohibiton Movement
21 Amendment
amendment that repealed the 18th amendment and ended prohibition
List of 14 points summarized
No more secret treaties
freedom of seas
removal of economic sorviens
advocating for a significant reduction in military armaments across all nations.
free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims
-13: independence for oppressed minoirty groups
Leaugue of Nations
Debates over the US Ratificationof Treaty of Versilles
Wilson Brought NO republicans, upset the democrats
The Irreconcilables
Led by Henry Cabot Lodge, this group opposed the treaty in any form. They believed that the U.S. should not give up its sovereignty to an international organization.
Reservationists
Led by Lodge, this group wanted to amend the treaty before ratifying it. They worried that the League of Nations could send American troops into war without Senate approval.
Who where the Big Four? (after ww1)
British
US
Italy
France
What The US ended up doing after Treaty was not approved
The United States officially made peace with Germany after World War 1 by signing the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, which was the primary peace treaty that ended the war, although the US did not fully ratify the treaty and notably did not join the League of Nations established within it; instead, the US signed a separate peace treaty with Germany that essentially adopted the terms of Versailles while excluding the League of Nations aspect.
Article X
Clause reassuring league memebers to defend others from external aggression, leading to the US NONMEMBERSHIP
Zimmerman Telegram
Sent to Mexico after Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare. Urged Mexico to join the war on Germnay’s side. US intercepted it and officially declared war BEFORE Mexico could respond/receive telegram.
Queen LiliUokalani
Pro-American business interests had overthrown the Queen when she rejected constitutional limits on her powers. The new government realized that Hawaii was too small and militarily weak to survive in a world of aggressive imperialism, especially on the part of Japan. It was eager for American annexation.
Cuba Rebellion (1895)
Movement of Cuba against spain which had been in control since 1500s.
Election of 1912 and their party running
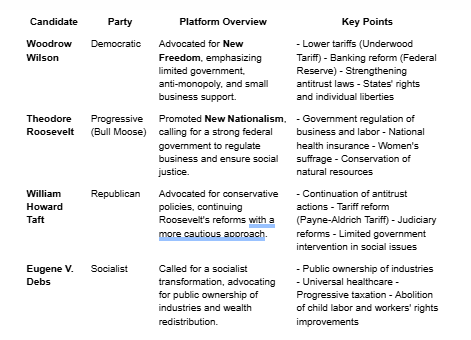

Election of 1912: Woodrow Wilson
Election of 1912: Theodore Roosevelt
SPLITS REPUBLICAN VOTE

Election of 1912: William Howard Taft


Election of 1912: Eugene Debs
What was the significance of Upton Sinclars “The Jungle”
Meat inspection Act and Pure Food and Drug act was created under Teddy Roosevelt.
What was the effect of Lincoln Steffens “The SHame of Cities”
City Manger (local and gov), Secret ballots, and Cevil Service exmas where created
What was the effect and significance of Ida A Tarbell “The History of Standard Oil?”
Effect: leads to breakup of standard oil company
significance: example of a bug business harming competition (monopolies vs. small business), establishment of department of commerce and labor (1903)
What was roosevelt forgin policy?
known as “Big Stick Diplomacy,” emphasized using military power and diplomacy to advance U.S. interests. He believed in speaking softly but carrying a big stick (a powerful military), and his actions included:
Panama Canal construction
Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (U.S. intervention in Latin America)
Mediation of the Russo-Japanese War
Great White Fleet showcasing U.S. naval power
Frequent intervention in Latin American countries to maintain stability and prevent European interference
What was Roosevelts dometic policy?
Known as "Square Deal," focused on fairness and reform. It aimed to protect consumers, regulate big business, and conserve natural resources. Key aspects:
Trust-busting (breaking up monopolies)
Labor rights (supporting workers)
Conservation (creating national parks and protecting natural resources)
Consumer protection (regulating food and medicine).
New Nationalism
Herpburn Act
What was Tafts forgien policy?
known as “Dollar Diplomacy,” focused on using U.S. economic power to influence other nations. Key aspects:
Promoted U.S. investment in Latin America and East Asia to secure American interests.
Encouraged American businesses to expand abroad to strengthen economic ties.
Used financial intervention to maintain stability and prevent European influence in the Western Hemisphere.
WHat was Tafts domestic policy?
focused on conservative reform and maintaining stability. Key aspects:
Trust-busting (continued Roosevelt’s efforts to break up monopolies)
Tariff reform (Payne-Aldrich Tariff, though it angered progressives for not lowering tariffs enough)
Strengthening the Interstate Commerce Commission
Support for the 16th Amendment (income tax).
what was Wilsons foreign policy?
ocused on moral diplomacy, promoting democracy and human rights. Key aspects:
Opposed imperialism, favoring support for self-determination.
Intervention in Latin America to maintain stability (e.g., Mexico, Haiti, the Dominican Republic).
Played a key role in founding the League of Nations after WWI.
Wilson’s 14 Points aimed to promote global peace and prevent future wars.
What was Wilsons domestic policy?
focused on New Freedom, aiming to reduce government intervention and promote economic fairness. Key aspects:
Trust-busting (breaking up monopolies)
Tariff reform (Underwood Tariff)
Banking reform (Federal Reserve Act)
Worker protections (Clayton Antitrust Act, Federal Trade Commission).
What was Debs domestic policy?
focused on socialism and the rights of the working class. Key aspects:
Public ownership of major industries (railroads, utilities, etc.)
Universal healthcare and social security
Progressive taxation (higher taxes on the wealthy)
Workers' rights (abolishing child labor, improving labor conditions)
Who was Jane Addams, and what was Hull House?
an American social reformer, activist, and the co-founder of Hull House in Chicago.
Hull House, founded in 1889, was one of the first settlement houses in the U.S., providing social services to immigrants, poor communities, and working-class families.
Hull House offered educational programs, job training, childcare, healthcare, and cultural activities to help improve the lives of disadvantaged individuals, particularly women and children.
Addams is also known for her work in advocating for women's suffrage, labor rights, and peace.
She was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1931 for her work in promoting international peace and social justice