EXAM 2 - FRAP, Detergents, and oligosaccharides
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
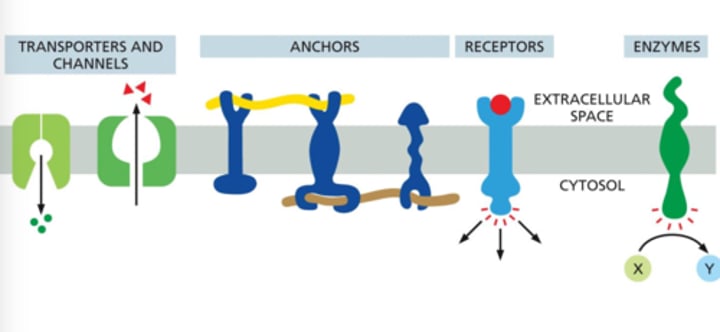
What are the different functions of proteins?
They can act as:
Transporters and channels
Anchors
Receptors
Enzymes
What do transporter proteins and ion channels do?
They allow nutrients into the cell and export metabolic waste
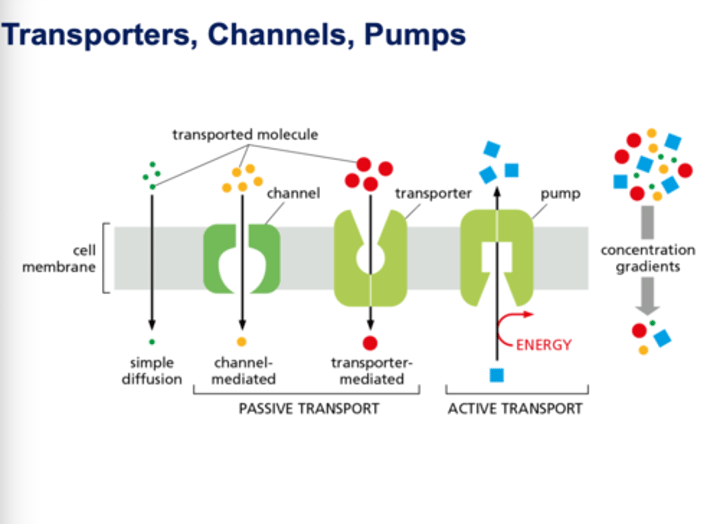
Why can't hydrophilic compounds, like amino acids, pass through the cell membrane by themselves?
The cell membrane is hydrophobic and will not let polar, charged molecules pass through. These molecules need transporter proteins and pumps to go in and out of the cell.
What is the cell cortex?
A meshwork of fibrous anchor proteins. It is found on the inside of the cell, the cytosolic surface.
What molecules make up the cell cortex?
Spectrin dimers, which form elongated filaments
Actin filaments
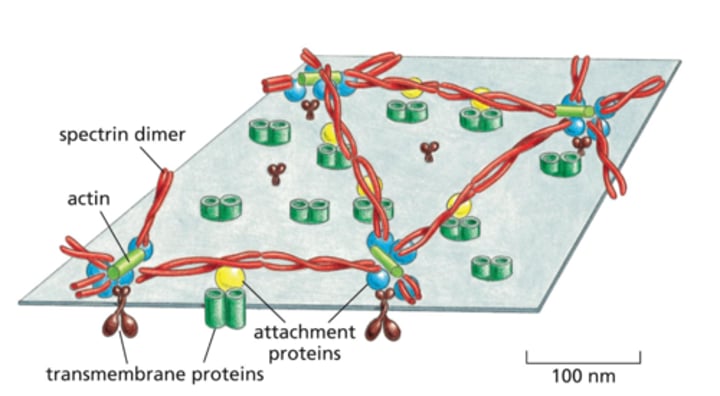
What is the function of the cell cortex?
Maintain cell shape
Provide mechanical stability
Allows cells to move and communicate with the extracellular matrix
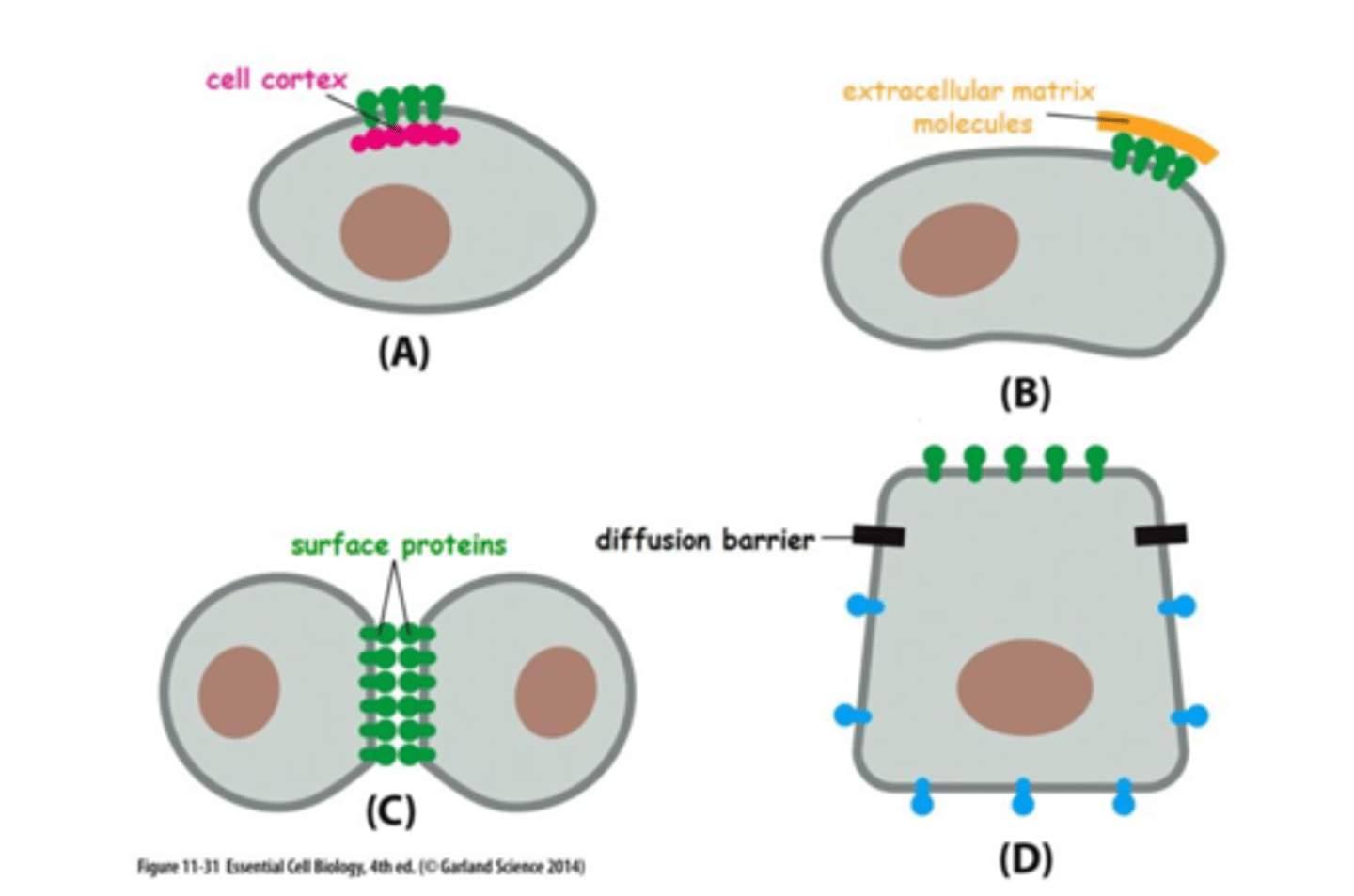
What are the different ways in which the cell can restrict the mobility of plasma membrane proteins?
A. Proteins can be tethered to the cell cortex - the cell does this to fix itself in a specific location
B. Proteins can bind to the extracellular matrix - this cell does this to fix itself in a specific location
C. Proteins can bind to other proteins in neighboring cells - this is done when cells need to be connected with one another
D. The cell can create diffusion barriers (tight junctions) that spatially segregate certain proteins
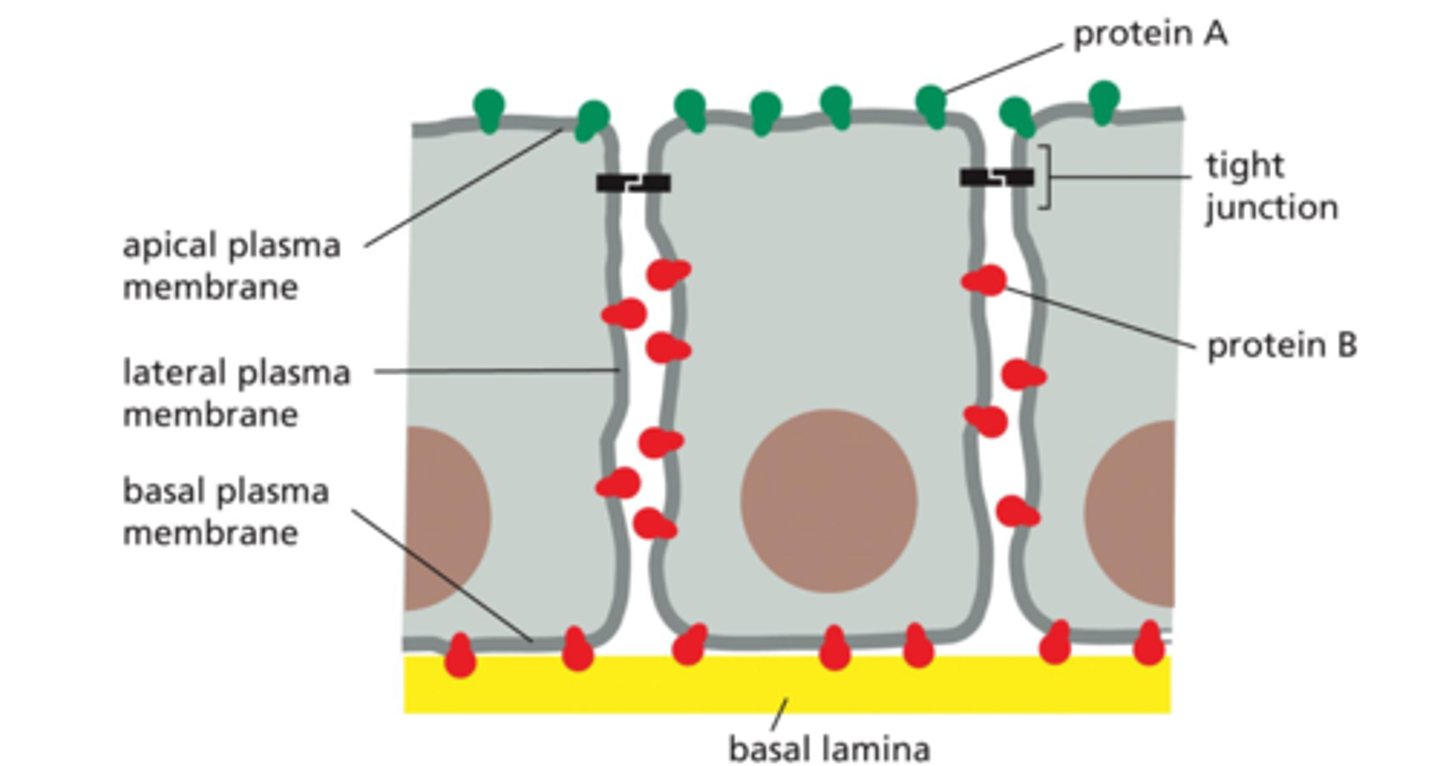
How are diffusion barriers used by epithelial cells that line the gut?
Epithelial cells form tight junctions with other adjacent epithelial cells to confine proteins involved in the uptake of nutrients to the apical surface of the cell.
Other transport proteins that may may be involved in the export of solutes are confined to the basal and lateral surfaces.
The diffusion barrier made through the tight junctions prevents the two types of proteins from entering each other's domain.
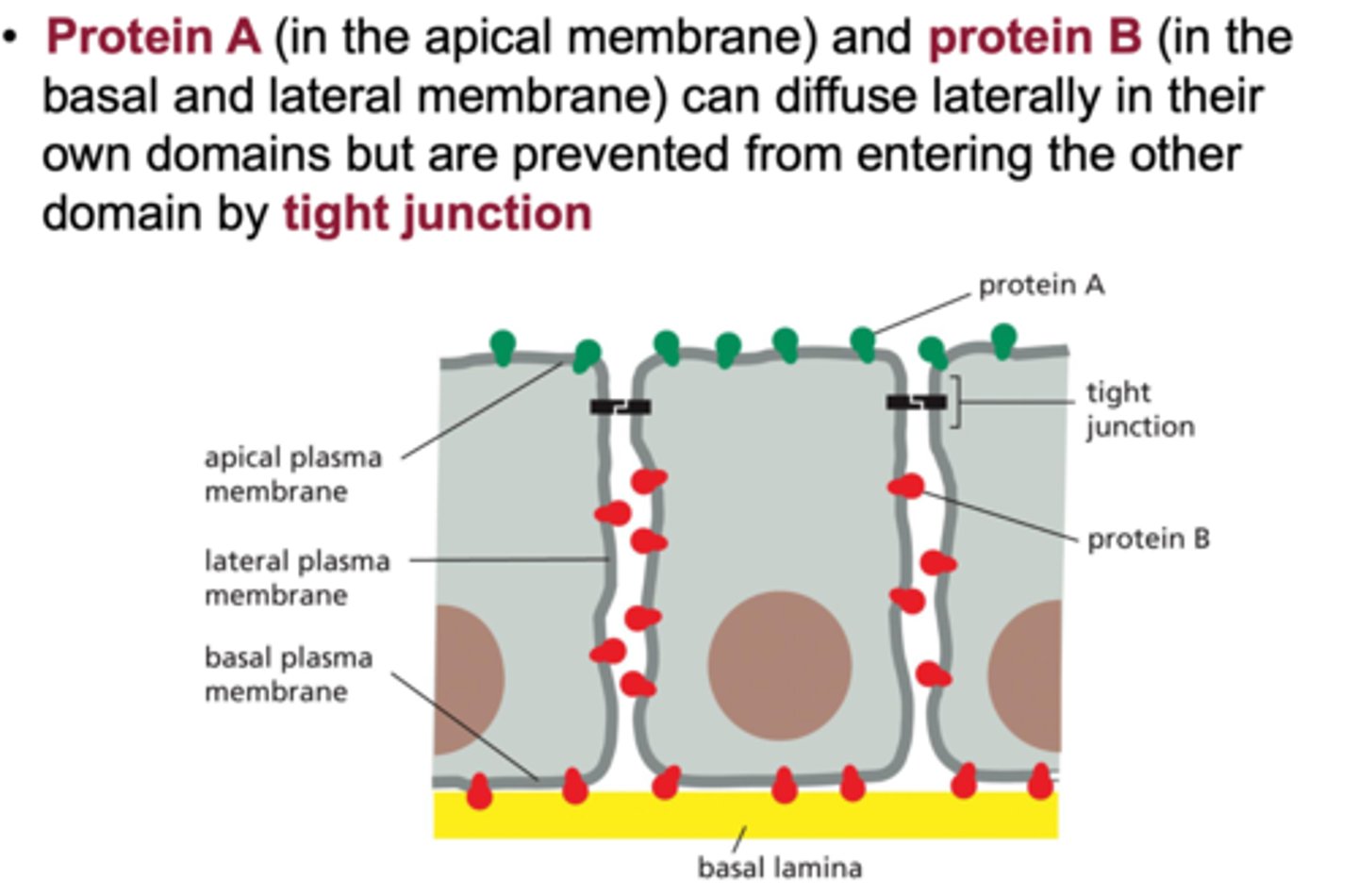
Look at the picture. There is a defect in the epithelial cells of the gut lining which causes nutrients to intermix between the blood and the lumen of the gut. This is preventing the proper uptake and delivery of nutrients to the blood stream.
You suspect that this intermixing may be due to Protein A not being restricted to the apical surface of the gut epithelial cell.
What technique can you use to track the mobility of Protein A?
You can use Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP). This technique is used to measure the rate of lateral diffusion of membrane proteins.
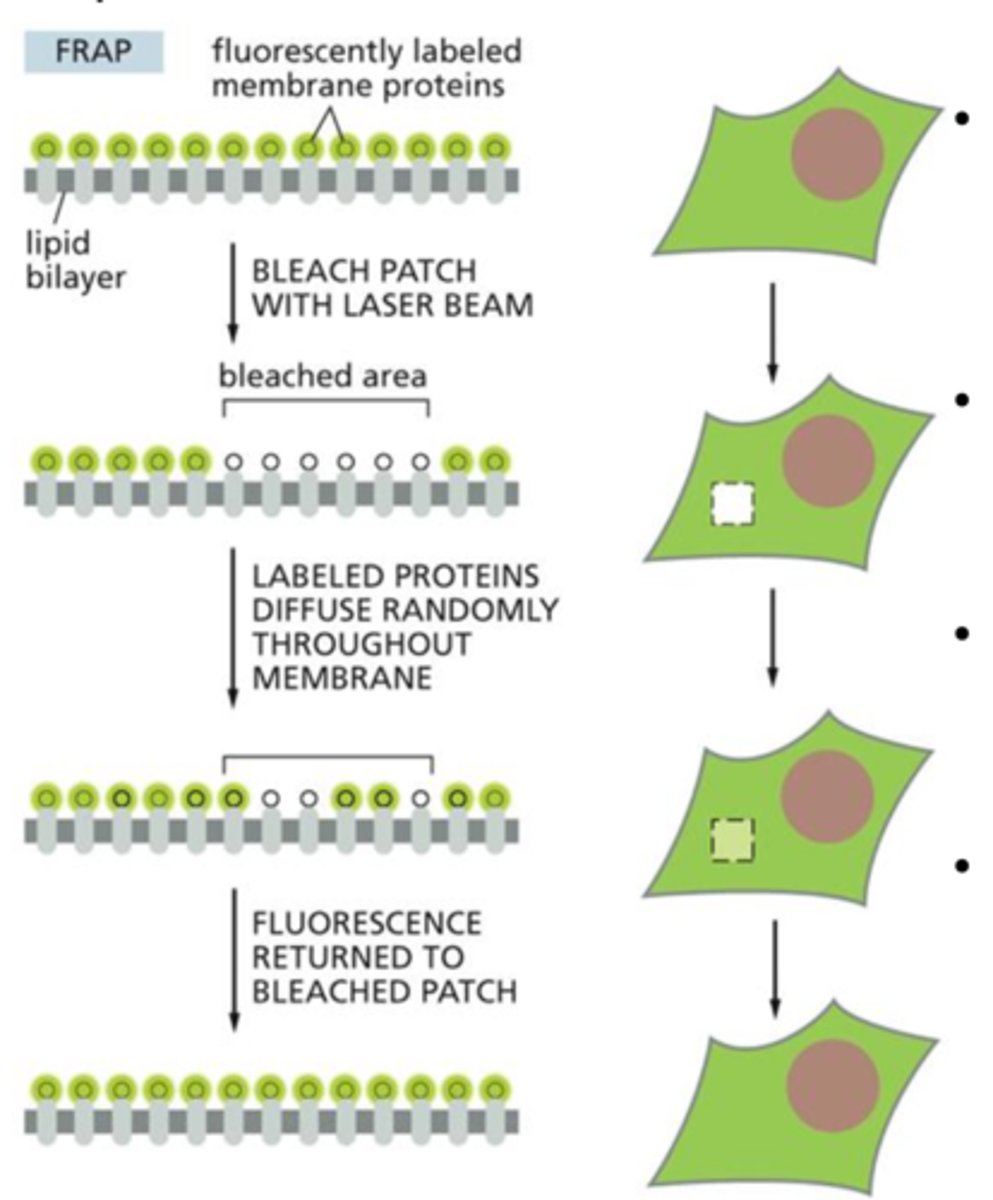
How does FRAP work?
A fluorescent marker is bound to phospholipids that make up a cell membrane.
- This marker is usually green florescent protein (GFP)
Next, a laser is used to bleach a small patch of membrane (stop the patch from fluorescing)
The amount of time it takes for the neighboring, unbleached fluorescent to migrate into the bleached region of the membrane is measured
Look at the picture
Is the graph showing a protein that has high mobility, low mobility, or no mobility?
High mobility
Peak recovery is reached in a relatively short amount of time
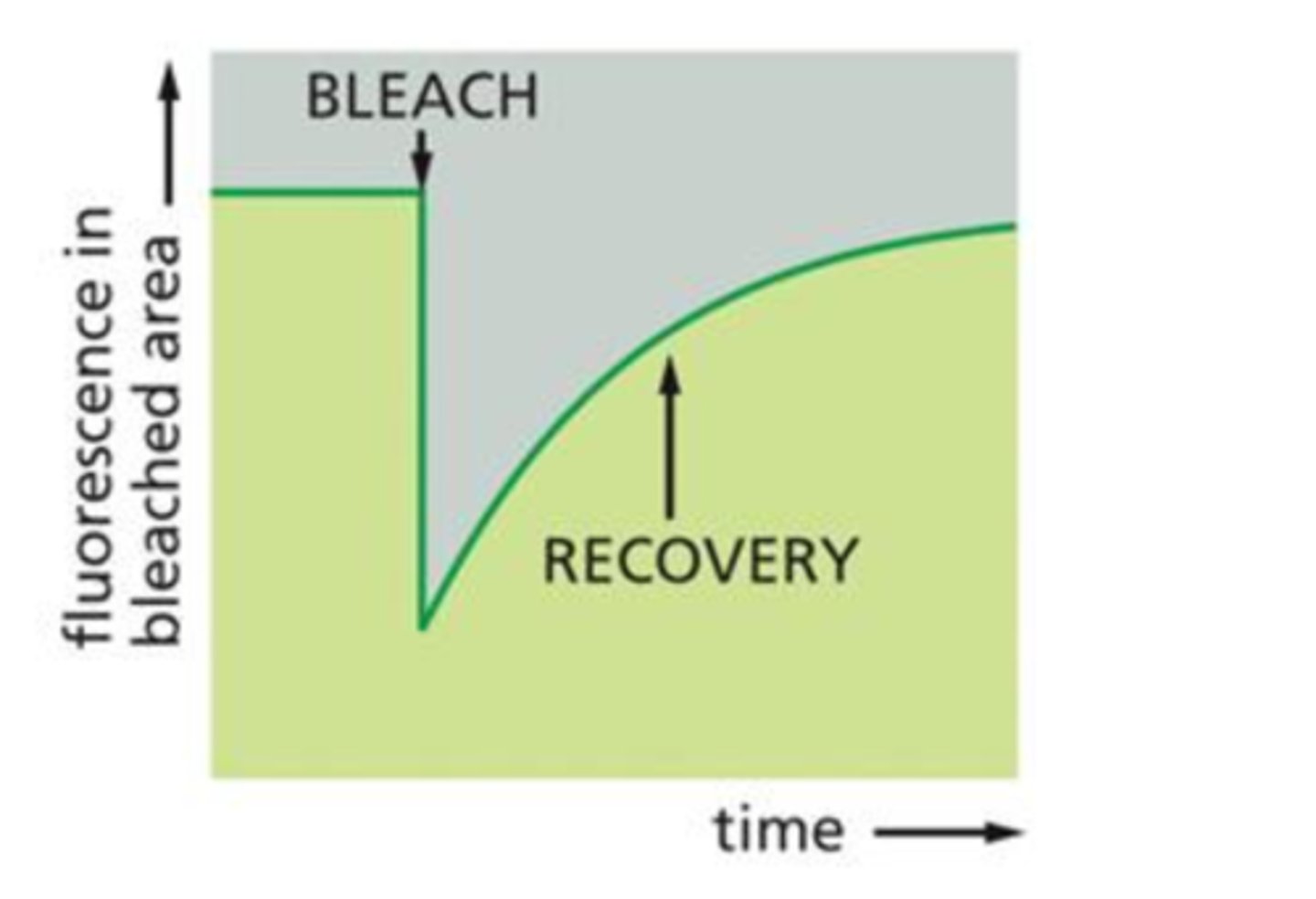
Look at the picture:
Is the graph showing a protein that has high mobility, low mobility, or no mobility?
Low mobility
Peak recovery takes longer to reach
This indicates that the protein has a slower rate of diffusion compared to the previous protein
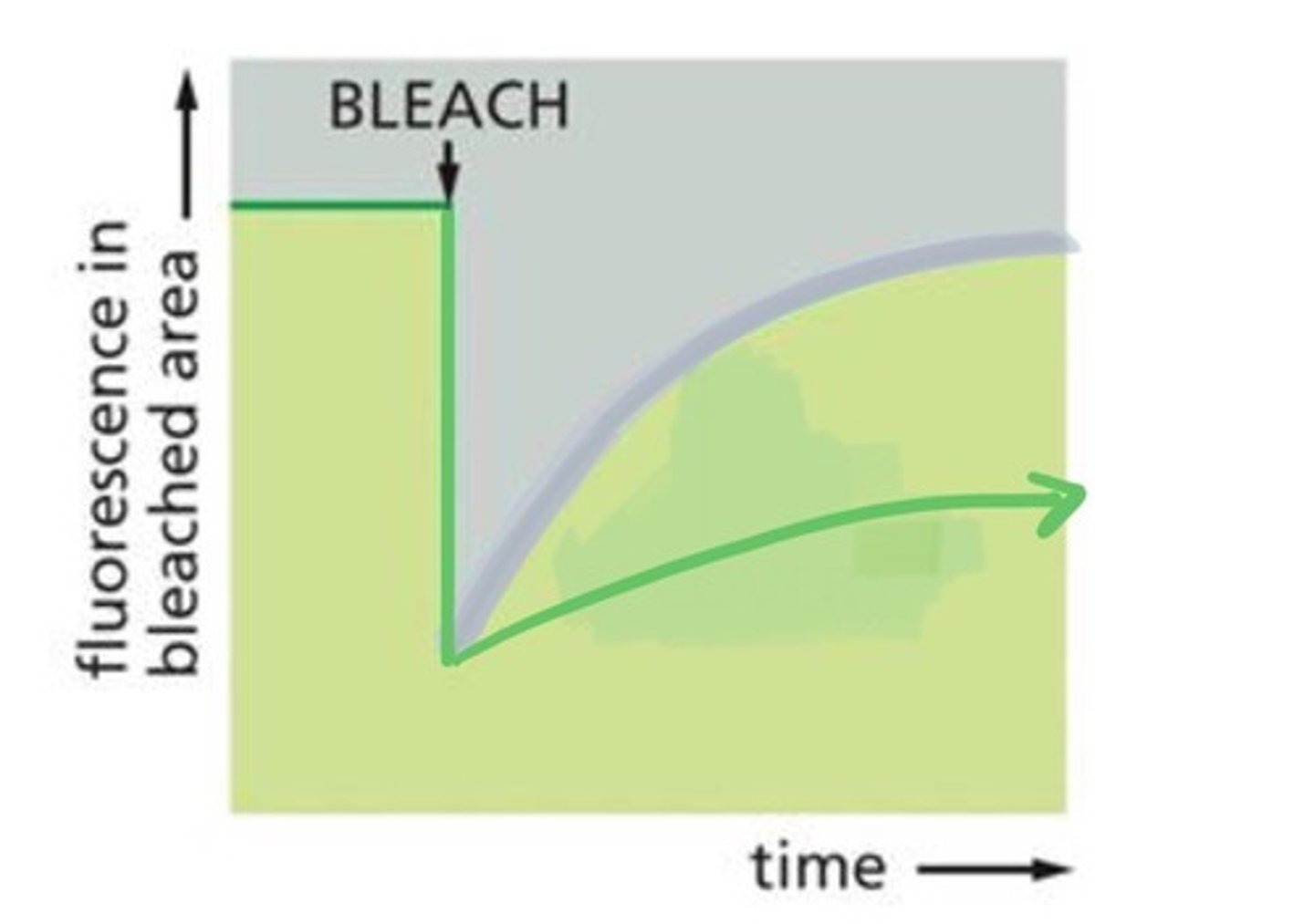
Look at the picture,
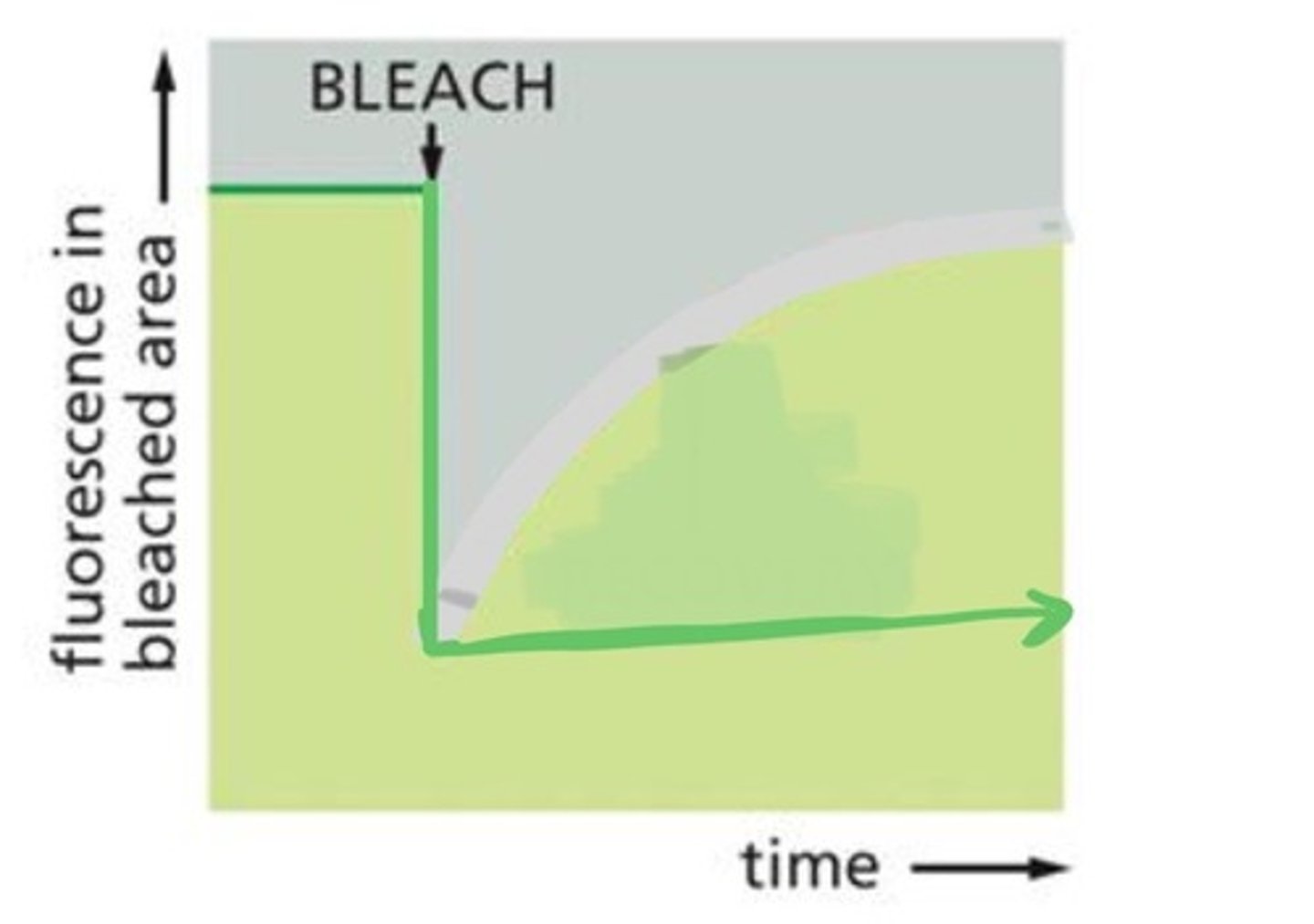
Is the graph showing a protein that has high mobility, low mobility, or no mobility?
No mobility
Protein mobility is restricted
The flat line indicates that the proteins in the membrane have not moved at all
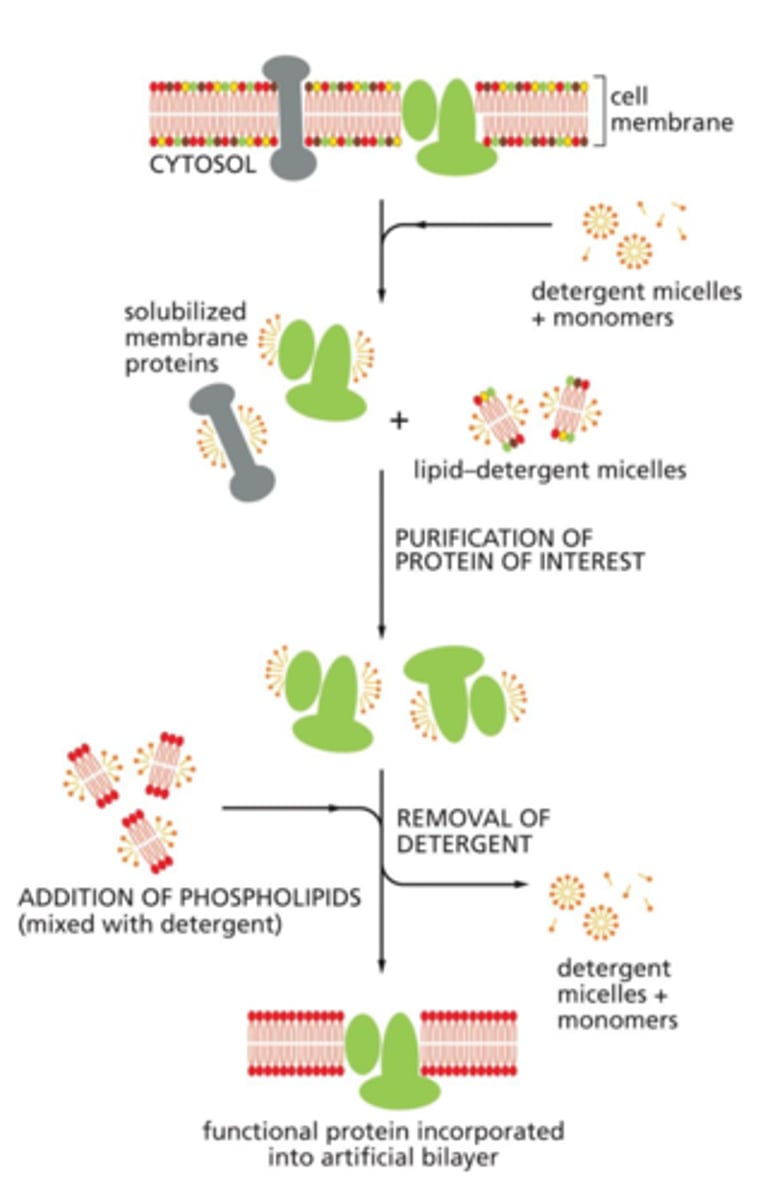
What are detergents?
They are molecules that destroy the lipid bilayer by disrupting hydrophobic associations.
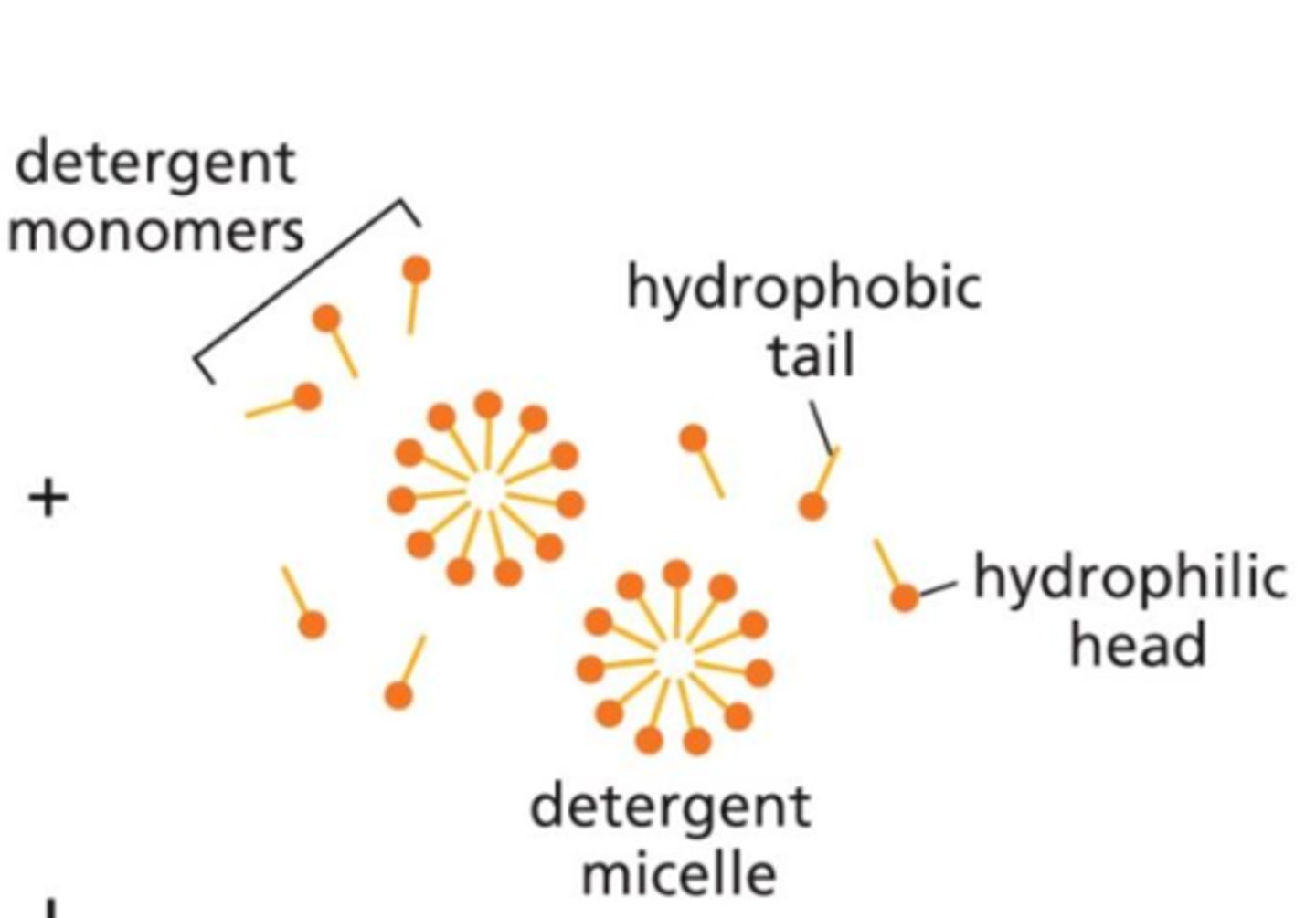
What are some characteristics of detergents?
They are small, amphipathic, and have a single hydrocarbon tail.
Detergents are lipid like molecules and very similar to lipids. What is once major difference between deterrents and lipids?
Detergents have a single hydrocarbon tail where as lipids have two hydrocarbon tails.
Do detergents form a bilayer in aqueous solutions?
No, because they only have a single hydrocarbon tail, they form clusters called micelles in water.

Detergents are amphipathic, why is this important?
This property allows them to enter the membrane, bind to the hydrophobic part of the protein and solubilize it.
Why would you want to solubilize a protein?
Solubilizing proteins allows us to study their specific functions.
The solubilized protein can be reconstituted in an artificial phospholipid vesicle to study its properties.
By isolating a single protein, you can observe its behavior in the absence of molecules that might restrain its movement or activity.
What is the glycocalyx?
An extracellular carbohydrate coating made up of glycolipids and glycoproteins.
What is the function of the glycocalyx?
It gives the cell a slimy surface, allowing the cell to move without sticking to each other (i.e blood cells)
It is involved in the absorption of water
It is also important for cell-cell recognition and adhesion
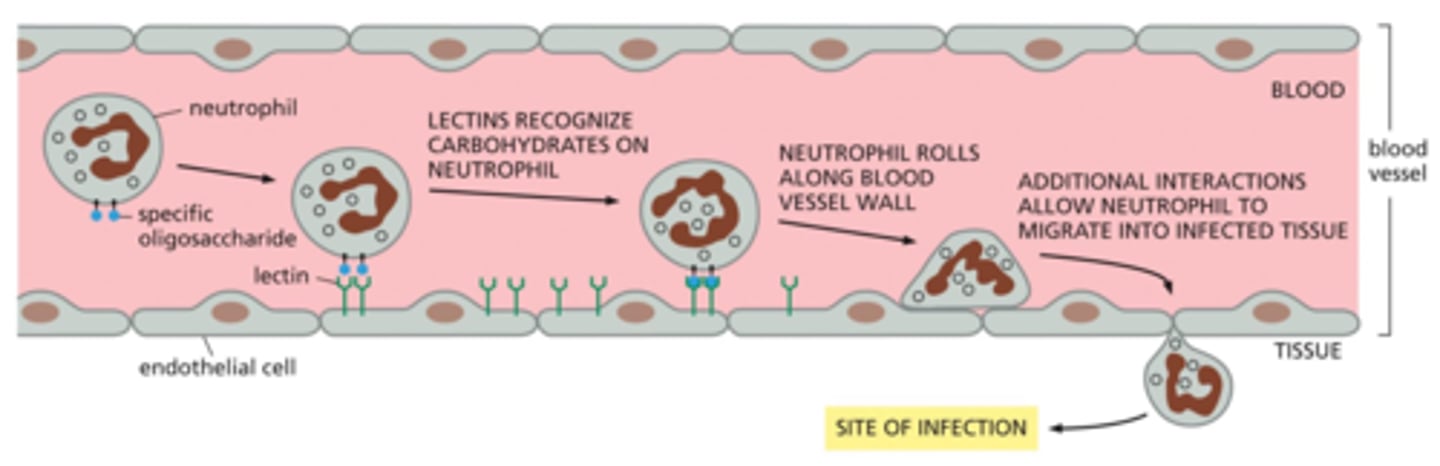
How do oligosaccaharides help with injury repair and our immune response?
Oligosaccharides are a network of glycolipids and glycoproteins found on the surface of neutrophils
Oligosaccharides act as ID tags and are recognized by the lectin proteins of endothelial cells lining the blood vesssels at the site of infection
Once the oligosaccharides bind to the lectins, the neutrophil can migrate to the infected tissue