M9.1 angiography/ventriculography
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts, terms, and definitions from the lecture on coronary angiography and ventriculography, aiding in exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What defines concentric and eccentric stenosis?
Concentric stenosis has uniform narrowing,
while eccentric stenosis is irregular and asymmetrical.
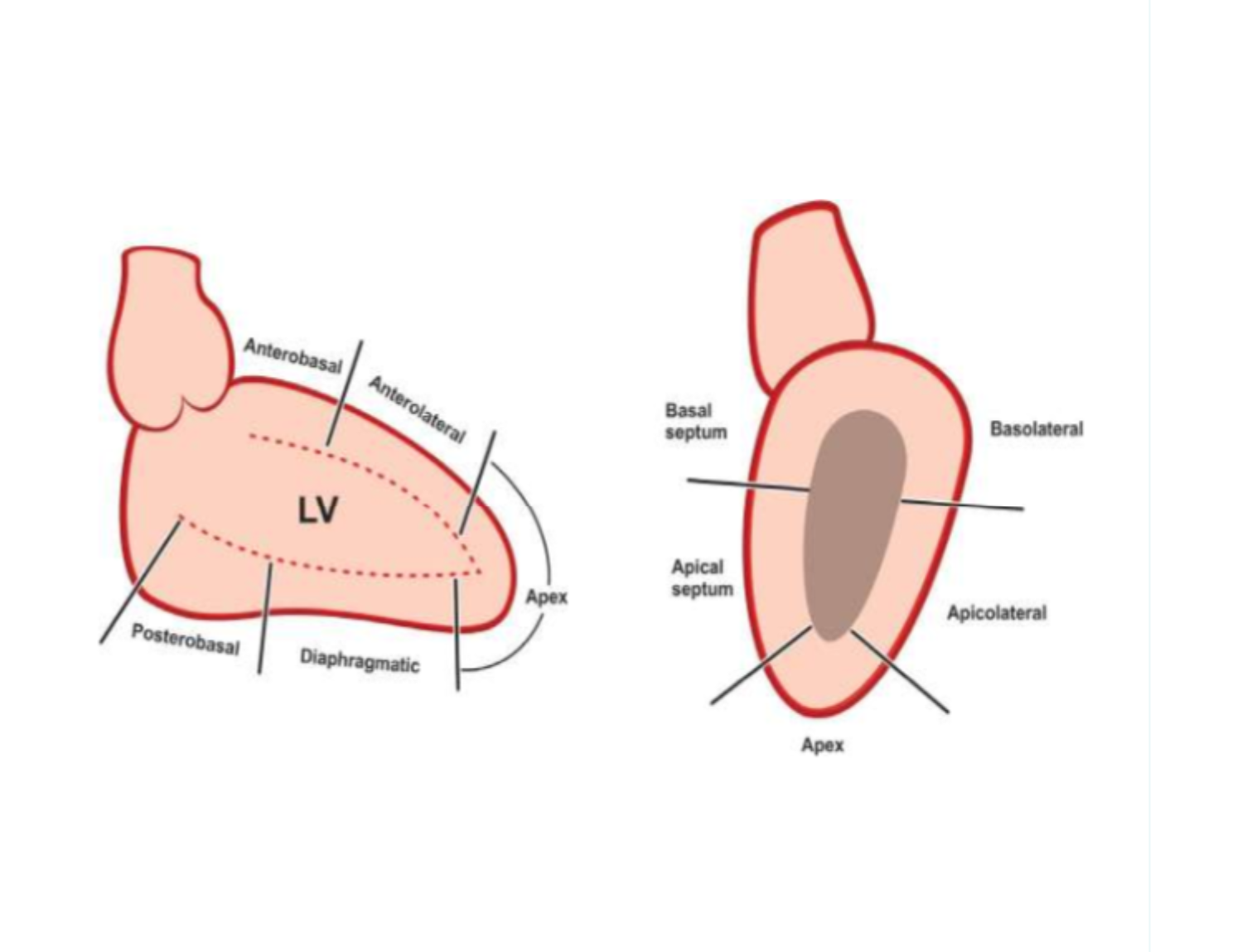
What are the types of ventriculogram kinetic movement dysfunction
x5
Normal,
hypokinesia,
akinesia,
aneurysm,
dyskinesia, and
asynchrony.
What is the advantage of using side holes in angiographic catheters?
3x
They prevent catheter damping
allow additional blood flow from the tip to perfuse the artery.
dissipate ejection pressure
******* catheters have thicker shafts, smaller internal diameters, and tapering tips,
while ****** catheters have larger diameters, non-tapering tips, and reinforced construction.
Diagnostic catheters have thicker shafts, smaller internal diameters, and tapering tips,
while guide catheters have larger diameters, non-tapering tips, and reinforced construction.
What is the definition of hypokinesia observed in a ventriculogram?
Reduced movement of a portion of the heart during contraction.
What is the appearance of akinesia on ventriculogram?
Lack of movement in a region of the heart.
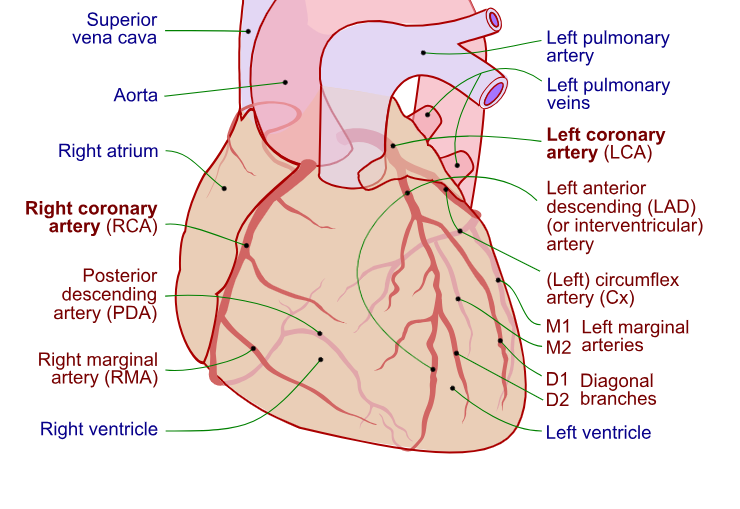
What structures do the diagonal branches supply?
They supply blood to the anterior /anterolateral wall of the left ventricle.
Aortic ***** determines the appropriate curve length required for interaction with the coronary arteries.
Aortic diameter determines the appropriate curve length required for interaction with the coronary arteries.
What does RAO view emphasize in RCA angiographic projections?
The right coronary artery and its branches including PDA and PL branch.
Differentiate between 'flush' and 'selective' catheters.
***** catheters distribute contrast through multiple side holes,
while **** catheters target specific vessels.