Economics Final Exam
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Adam Smith’s Invisible Hand
The theory that society benefits the most when everyone acts in their best interest by acting voluntarily in the market.
Scarcity
The basic, fundamental problem of economics
Economics
Solving the problem of scarcity
Trade-offs
Sacrificing one benefit to gain another
Markets
Places where buyers and sellers exchange goods and services
Thinking at the margin
Making decisions based on additional costs and benefits
Marginal cost
The cost of producing/consuming one more unit
Marginal benefit
The benefit gained from producing one more unit
Good
Tangible Item that can be purchased
Service
Action done for others that can be purchased
Factors of production
Resources used to make goods
Natural Resources
Land, water, oil
Human Resources
Labor/workers
Capital Resources
Tools, machines
Entrepreneur
Risk-taker who starts a business
Marginal Utility
Extra satisfaction from one more unit
Human Capital
Skills and education
Opportunity Cost
Best alternative given up
Scarcity
Limited resources
Choice
Selecting one choice
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Each additional unit gives less satisfaction
Traditional Economy
Economic system where customs and religion dictate the economy
Command Economy
Economic system where a central government decides the economy
Market Economy
Economic system where the economy is decided by unrestricted competition between businesses (no government).
Mixed Economy
A mix of market and command economy
Specialization
Focusing on one task/product
Division of Labor
Splitting work into tasks
Voluntary Exchange
Trade where both sides benefit
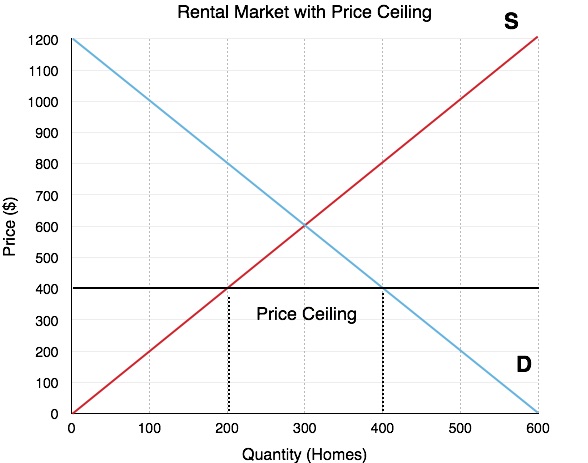
Price Ceiling
A maximum price limit set below equilibrium to keep things affordable.
Price Floor
A minimum price limit set to protect producers.
Equilibrium
Any price where quantity demanded = quantity supplied
Supply
The amount of a good or service that producers are able and willing to sell at all prices.
Demand
The amount of a good or service that people are able and willing to buy at all prices.
Perfect Competition
A large number of firms all produce the same product
Monopolistic Competition
Many producers, similar products
Oligopoly
Few producers, very similar products
Monopoly
One producer, unique product
Absolute Advantage
the ability to produce something more productively than someone else
Comparative Advantage
the ability to produce something with a lower opportunity cost than someone else.
Collusion
A secret agreement between businesses to manipulate the market for their mutual benefit.
Cartel
Formal agreement between competing firms to collude
Negative Externality
An extra cost of production that is not paid for by the producer or consumer (pollution from factory)
Positive Externality
An extra benefit of production that is not paid for by the producer or consumer (view of neighbor’s garden)
Debit Card
a type of payment card that allows consumers to make purchases by directly accessing the funds in their checking accounts
Credit Card
a card that borrowing money that is accompanied by interest and sometimes fees
M1 Money Supply
Liquid assets ready for spending
M2 Money Supply
Savings and time deposits, money that is not easy to access
FDIC Ensured Bank Deposits
insurance to protect your money in the event of a bank failure. Your deposits are automatically insured to at least $250,000
CDs
a savings account that holds a fixed amount of money for a fixed period of time, such as six months, one year, or five years, and in exchange, the issuing bank pays interest.
Mutual Funds
financial vehicle that pools money from many investors to collectively buy a diversified portfolio of securities (stocks, bonds, etc.) managed by professionals
Stocks
a small piece of ownership in a company that gives you a claim on its earnings and assets
Bonds
a debt security representing a loan made by an investor (lender) to a borrower, usually a corporation or government, for a fixed period
Sole Proprietorships
A business owned by one person
Partnerships
A business owned by 2+ people
Corporations
legally established entity that can enter into contracts, own assets and incur debt, as well as sue and be sued (owned by shareholders)
Franchises
a business model where one company licenses its brand, products, and proven system to another person, allowing them to open and run a similar business
Silent Partner
An investor who has no role in management
Board of Directors
the elected, high-level governing body of an organization, representing shareholders (owners) to oversee management, set strategy, ensure legal compliance, and protect stakeholder value
Unlimited Liablility
business owners are personally responsible for all business debts and obligations
CEO
Chief executive of the company
LLC - Limited Liability Company
a popular business structure that protects owners (called "members") from personal responsibility for business debts
Labor Force
The total number of people who are employed or looking for a job - not including retired, -16, or discouraged workers
Outsourcing
a business strategy where a company hires an external third-party provider to perform tasks, functions, or create goods
Offshoring
the practice of relocating business processes or production to another country
Affirmative Action
a set of policies designed to actively counteract past and present discrimination by creating opportunities in education and employment for historically disadvantaged groups, like women and minorities, ensuring they have fair access to roles and resource
Right-to-work Laws
state-level statutes prohibiting union security agreements, meaning employees in unionized workplaces cannot be forced to join a union or pay dues as a condition of employment
Wage Gap
the persistent difference in average earnings between different demographic groups
Market Failure
when a free market fails to efficiently allocate resources
Externality
Extra costs or benefits of production that are not paid for by the producer or the consumer
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
a U.S. government agency within the Department of Labor that ensures safe and healthy workplaces by setting and enforcing safety standards
US Patent and Trademark Office
is the federal agency under the Department of Commerce and is responsible for granting U.S. patents and registering trademarks.
FTC
a U.S. government agency established to protect consumers and maintain fair competition by preventing deceptive, unfair, and anti-competitive business practices
EPA - environmental protection agency
uses economics to develop cost-effective environmental policies
Eminent Domain
the government's power to seize private property for public use
Public Goods
a product or service that is both non-excludable (people can't be prevented from using it) and non-rivalrous
Upton Sinclair - The Jungle
A book that exposes the appalling working conditions in the meat-packing industry
In-kind benefits
non-cash goods or services provided to individuals, often by governments or employers, to meet specific needs like food, housing, or healthcare, instead of direct money
Cash Transfers
direct payments, often from governments, made to eligible groups of people.
Income Redistribution
the government's process of shifting wealth and income from higher earners to lower earners
Excise Taxes
an indirect tax levied on the production, sale, or consumption of specific goods, services, or activities to reduce purchasing of it
Regressive Tax
Tax takes a larger percentage of income from the poor
Individual Income Taxes
a mandatory financial charge levied by a government on the wages, salaries, investments, and other forms of income earned by individual citizens or households
Corporate Income Taxes
a direct tax levied by federal and state governments on the net profits of corporations, which are separate legal entities from their owners.
Sales Taxes
a consumption tax on the sale of goods and services (varies by state)
Luxury Taxes
a government-imposed surcharge or excise tax levied on goods and services considered non-essential, high-end, or extravagant, rather than necessities
Tax Incidence
determines who ultimately bears the economic burden of a tax
Property Taxes
A tax on real estate collected locally and used to fund services like schools, emergency services, and infrastructure
Payroll Tax
a tax paid on the wages and salaries of employees to finance social insurance programs like Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance
Estate Taxes
a tax on an individual's right to transfer property at their death
Paystub
a pay stub (or pay slip/wage statement) is a document provided by an employer with each paycheck that details an employee's gross earnings, itemized deductions, and final net pay for a specific pay period
W2
United States federal tax document used by employers to report an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck to the IRS and the Social Security Administration (SSA)
Benefits Received
a theory of taxation stating that individuals should pay taxes in proportion to the benefits or services they receive from the government, similar to buying a product
Inflation
the rate at which the general price level of goods and services in an economy rises over time, causing the currency's purchasing power to fall
GDP
the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specific time period
Nominal GDP
the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced in a country within a specific time period, measured at current market prices, without adjusting for inflation or deflation
Real GDP Per Capita
a country's total economic output (Real GDP) adjusted for inflation and divided by its population
Frictional Unemployment
Individuals who are not working because they are “between jobs”
Structural Unemployment
Technological advances have made their jobs unnecessary
Seasonal Unemployment
Job is not needed during that time of year
Cyclical Unemployment
Economy is in decline and their former employers cannot afford to pay them. (unnatural)